Pre Ib Chem Final Vocab
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/52
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
1
New cards
Group
Collums going left to right
2
New cards
Period
Rows going top to bottom
3
New cards
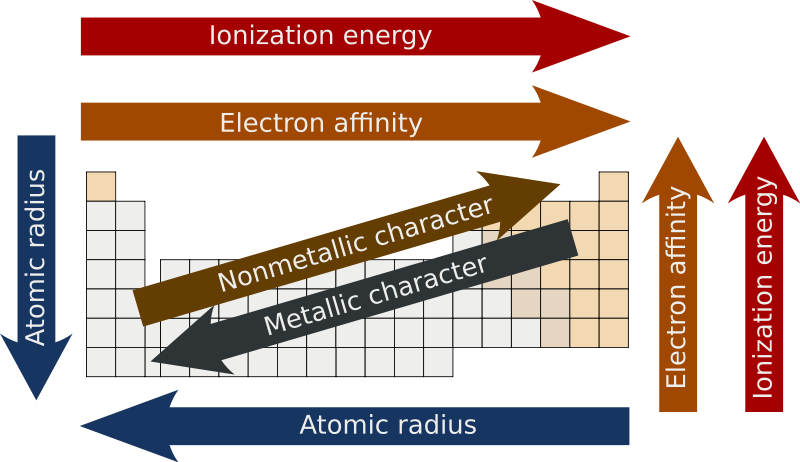
\
Periodic Trends
4
New cards
Atomic radius
The radius of an atom; increases going top to bottom on the Periodic table
5
New cards
Ionization energy
measure of the difficulty in removing an electron from an atom or ion
6
New cards
Neutron
Neutral; found in the nucleus of atoms
7
New cards
Proton
Positive; Found in the nucleus of atoms
8
New cards
Electron
Negative; Found orbiting the nucleus of atoms
9
New cards
Valence Electron
Electrons on the outer most ring of atoms
10
New cards
Alpha Decay
nuclear decay process where an unstable nucleus changes to another element by shooting out a particle composed of two protons and two neutrons (similar to that of a helium particle)
11
New cards
Beta Decay
Decay in which a Proton is converted into a neutron, releasing an electron and changing and element
12
New cards
Gamma Decay
emission of electromagnetic radiation of an extremely high frequency i.e. very high energy, giving out excess energy in order to stabilize the unstable nucleus
13
New cards
Electromagnetic Spectrum
the range of frequencies of electromagnetic radiation and their respective wavelengths and photon energies
14
New cards
Wavelength
distance between waves of energy
15
New cards
Frequency
number of waves which occur over a period of time
16
New cards
Electron configuration
distribution of electrons of an atom
17
New cards
Orbital
location of an electron around an atom
18
New cards
Molecular Geometry
three-dimensional arrangement of the atoms that constitute a molecule
19
New cards
Isotope
An atom which has equal protons but differing neutrons
20
New cards
Reactivity
The ability of an element to interact with other elements
21
New cards
Dipole/Polar
Points at which a molecule has differing electronegativity
22
New cards
Non-polar
Compound which does not differ in electronegativity
23
New cards
Polarity/Partial Charge
separation of electric charge in a molecule
24
New cards
Ionic Bonds
chemical bond formed when one atom gives up one or more electrons to another atom
25
New cards
Electronegativity
the tendency for an atom of a given chemical element to attract shared electrons when forming a chemical bond
26
New cards
Transfer electrons
Electrons which relocate to another atom
27
New cards
Polyatomic Ion
ion which despite having multiple atoms, behaves as a single unit.
28
New cards
Cation
positively charged ion
29
New cards
Anion
negatively charged ion
30
New cards
Covalent Bond
sharing of electron pairs between atoms
31
New cards
Lewis Dot Structures
Visual form of drawing chemicals using letters and dots
32
New cards
Noble Gas
Elements on the right side of the Periodic table; unreactive and 8 Valence electrons
33
New cards
Structural Formula
Drawn images to depict a chemical formula visually
34
New cards
Octet Rule
the rule which states Bonded atoms tend to have 8 Valence electrons, that of a noble gas.
35
New cards
Lone Pair Electrons
pair of Valence electrons which aren't used to form a bond between atoms
36
New cards
Bonded Pair Electrons
2 electrons which reside in the same orbital
37
New cards
Unpaired Electrons
electrons which aren't paired, orbit alone
38
New cards
Single Bond
chemical bond involving 2 Valence electrons
39
New cards
Double Bond
chemical bind involving 4 Valence electrons
40
New cards
Triple Bond
chemical bond involving 6 Valence electrons rather than 2 or 4, having three bonds
41
New cards
HONC 1234
rule which states that Hydrogen has 1 bond, oxygen 2, nitrogen 3, and carbon 4.
42
New cards
Combustion
reaction resulting in Fuel + O2 → CO2 + H2O.
43
New cards
Combination
process in which chemicals combine to form a single product
44
New cards
Decomposition
process in which chemicals break down into smaller components
45
New cards
Double displacement
chemical process involving the exchange of bonds between two reacting chemical species
46
New cards
Single displacement
chemical reaction in which one element is replaced by another in a compound
47
New cards
Chemical equation
equation involving chemicals
48
New cards
Reactant
substance that takes part in and undergoes change during a reaction.
49
New cards
Product
The stuff created in a reaction
50
New cards
Mole
Unit of measurement used to describe having 6.02x10^23 of a substance
51
New cards
Avogadro's Number
6\.02x10^23 (mole)
52
New cards
Molar Mass
the mass in grams of one mole of a substance
53
New cards
Dimensional Analysis
a method used to convert one unit to a different unit