Body Fluids - FFB
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
CSF is the result of ___ of blood/plasma that provides essential support to the brain + spinal cord
Ultrafiltration
CSF - produced in choroid plexuses of the spinal cord + brain where the ____ prevents the passage of most molecules from plasma
Blood Brain Barrier
CSF is continuously flowing through the _____
Arachnoid space
CSF Functions:
Supply nutrients
Remove wastes
Temperature regulation
Physical / mechanical barrier
CSF Tubes - Department + Storage Temp
Tube 1 - Chemistry + Serology - Frozen
Tube 2 - Microbiology - Room Temp
Tube 3 - Hematology - Refrigeration
Tube 4 - Back up + some Microbiology - Room Temp
Traumatic Tap vs Intracranial Hemorrhage

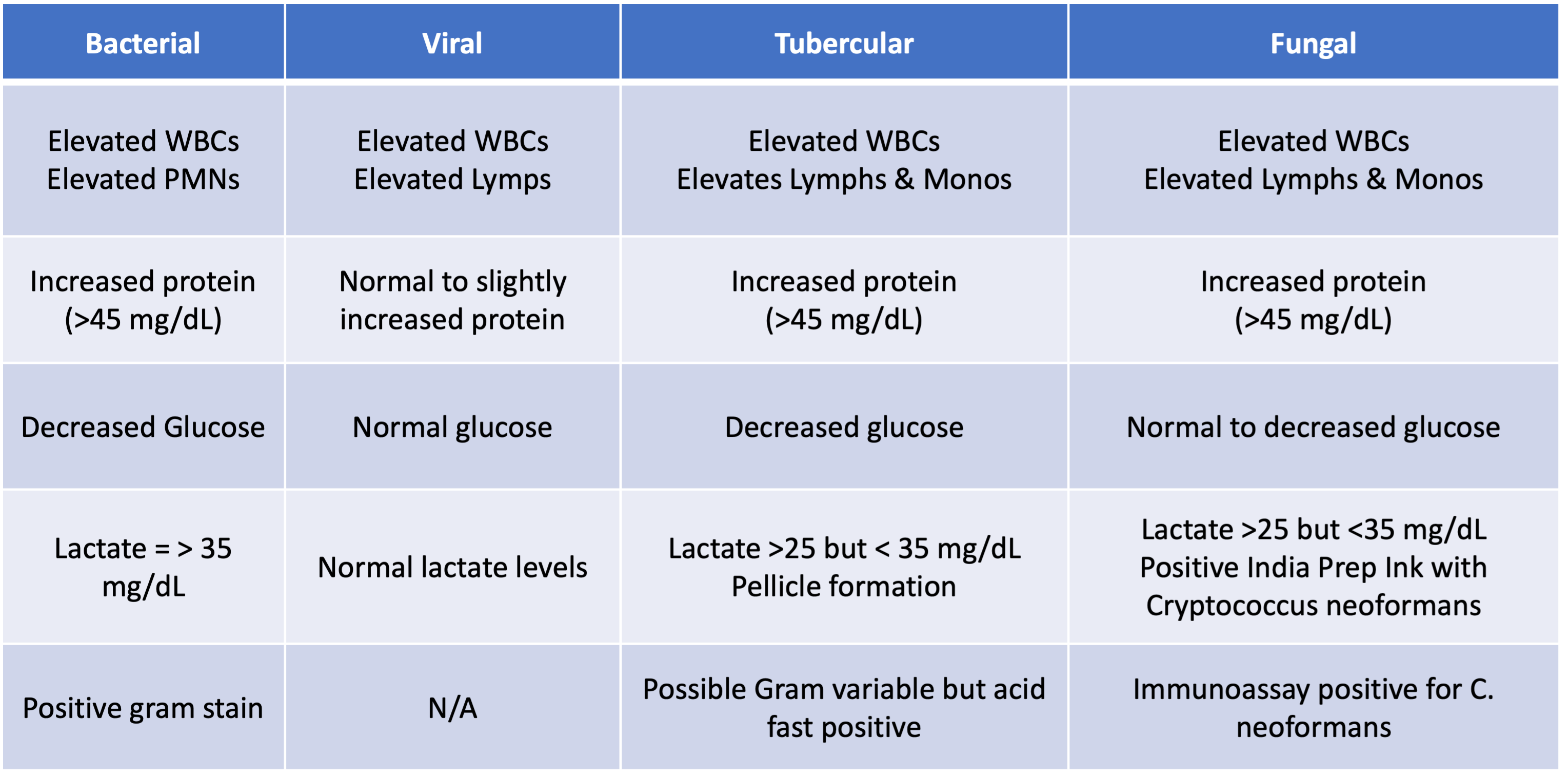
CSF Chemistry - Protein, Glucose, Lactate, Glutamine
Protein - 15-45 mg/dL - Increased in meningitis, hemorrhage, MS - Decreased in CSF leakage
Glucose - 60-70% of blood levels - Decreased in Bacterial, tubercular, or fungal meningitis
Lactate - 10-24 mg/dL - Increased in Meningitis (>35 mg/dL = bacterial, 25-34 mg/dL = fungal or tubercular)
Glutamine - 8-18 mg/dL - Increased in >35 mg/dL = coma, Reye syndrome
Meningitis - Bacterial, Viral, Tubercular, Fungal
CSF Protein - CSF / Serum Albumin Index
CSF albumin (mg/dL) / Serum albumin (g/dL)
>9 represents a compromised BBB
<9 represents an intact BBB
CSF Protein - IgG Index
(CSF IgG / Serum IgG) / (CSF albumin / Serum albumin)
<0.70 - no IgG made within the CNS so it must be coming from elsewhere
>0.70 - indicates IgG is being made from within the CNS ex: multiple sclerosis
Synovial Fluid Crystals
Monosodium urate (MSU) - Gout - Needle-shaped - Birefringence negative → when compensator is parallel to the crystal (slow), the crystal is yellow, when compensator is perpendicular to the crystal (fast) the crystal is blue
Calcium pyrophosphate (CPPD) - Pseudogout - Rhomboid or rods/needles - Birefringence positive → when compensator is parallel to the crystal (slow), the crystal is blue, when compensator is perpendicular to the crystal (fast) the crystal is yellow
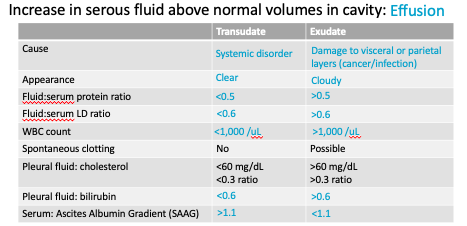
Serous Fluid - Two Membrane Linings
Parietal membrane is the outmost membrane that lines the cavity wall
Visceral membrane is the innermost membrane that directly covers the organs within the cavity
Serous fluid is a plasma ultrafiltrate regulated by ______, _____, + ______
Colloidal pressure (capillary permeability), hydrostatic pressure, oncotic pressure
Effusion - Transudate vs Exudate
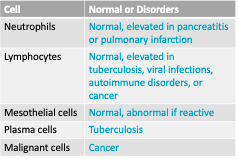
Pleural Fluid (lung) - Cells + Disorders
Amniotic Fluid Functions:
Provide protection + cushion to the fetus
Allow for fetal movement
Relegate temperatures
Allow for fetal lung maturity/development
Durine the first trimester, amniotic fluid is similar to _____ + during development, amniotic fluid becomes more like ____
Maternal Plasma
Urine
Amniotic fluid volume ____ due to ____
Increases
Fetal urine
Creatinine usage for amniotic fluid
May be used to determine gestational age of fetus (<36 weeks = 1.5-2.0 mg/dL, >36 weeks = >2.0 mg/dL)
May be used to differentiate maternal fluid from amniotic fluid (amniotic fluid = <3.5 mg/dL + UREA <30 mg/dL, Urine = 10 mg/dL + UREA up to 300 mg/dL)
Amniotic Fluid Testing
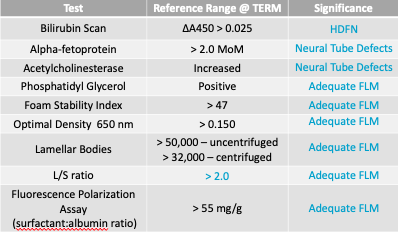
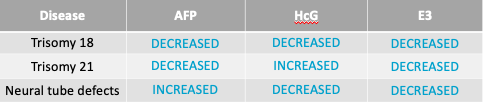
Triple Marker Screening (Amniotic Fluid)
Liley Graph (Amniotic Fluid)
Zone I - slight bilirubin increase w/ mild effect on fetus; no intervention
Zone II - moderate hemolysis + careful monitoring for worsening conditions, but no intervention; higher probability of early/induced labor + exchange transfusion upon delivery
Zone III - severe hemolysis + high bilirubin levels are affecting fetal health; Reflex to FLM testing, intervention is required through induction of labor or intra-uterine exchange transfusions
Vaginal Fluid Used in Clinical Laboratory Testing to Diagnose:
Infections
Pregnancy Complications
Forensic/crime Investigations
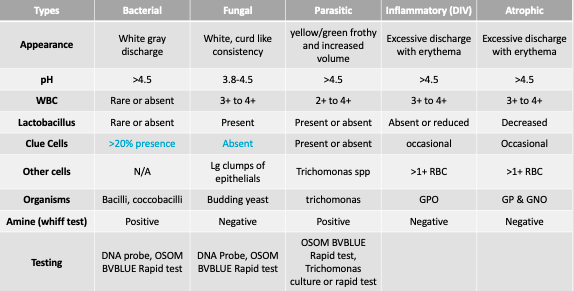
Normal Flora of Vaginal Fluid
Lactobacillus + squamous epithelium
Vaginal Fluid Cells - Clue cells, Parabasal, Basal
Clue cells - pathogenic = seen in bacterial infections, squamous cell coated in bacteria
Parabasal - desquamative inflammation vaginitis (DIV)
Basal - not normally seen in vaginal fluid + indicate altered vaginal flora like DIV
Trichomoniasis
STI due to parasitic protozoan
Green to yellow frothy discharge
Candidiasis
Yeast infection
White “curd-like” discharge
KOH prep + gram stain will reveal yeast + possible hyphae elements
Desquamative Inflammatory Vaginitis (DIV)
Beta hemolytic Streptococcus (Group A/B) or Atrophic vaginitis from decreased estrogen
High WBCs, RBCs, parabasla, + basal cells w/ little to no normal flora
Atrophic Vaginitis
Postmenopausal syndrome causing the thinning of vaginal mucosal lining due to decreased estrogen levels
pH >4.5 w/ negative amine test + change normal flora
Vaginal Infections Compared
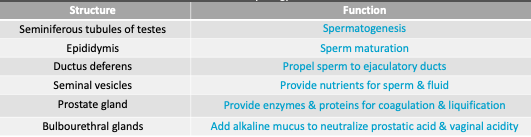
Seminal Fluid - Physiology
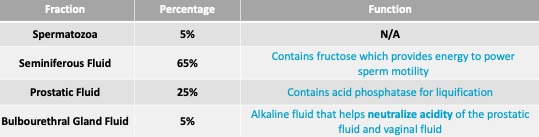
Seminal Fluid - Fractions
Seminal Fluid 2 Portions
First/early portion contains: spermatozoa, low first portion = decreased sperm count
Second/later portion: most of the semen volume is present, low second portion = higher sperm count
Seminal Fluid - Collection
Following sexual abstinence of at least 2 days but no more than 7 days
Two abnormal samples (of 3) is considered significant
Sterile container, kept at room temp, + delivered to lab within 1 hour
Gastric acid is one of the main secretions of the stomach, produced by the ______
Parietal cells
Excess gastric acid (HCL) production is seen in gastrulas like:
Zollinger-Ellison syndrome
Reasons for Performing Gastric Analysis Include:
Detect gastrin secreting tumors (Zollinger-Ellison syndrome)
Detect recurrent peptic ulcer disease
Evaluating hyperacidity
Evaluating effectiveness of surgery to reduce acid output
Diagnosis of achlorhydria
Detect delayed gastric emptying
Diagnosis of upper GI hemorrhage
Sweat Test
Measures amount of salt chemicals (sodium + chloride) in sweat via pilocarpine iontophoresis
Helps diagnose Cystic Fibrosis
>60 = positive
40-60 = borderline
<40 = negative
Cystic Fibrosis
Genetic disorder that affects mucus membranes of the lungs, pancreas, + other organs as a chronic disease
Caused by mutation to CFTR gene, creating dysfunction CFTR protein (CFTRdelta508) + thus a loss of chloride channel functionality
Secretory Diarrhea
Increased secretion of water from external forces/circumstances, overriding the excess water reabsorption of the large intestine
Osmotic Diarrhea
Caused by poor absorption where excess solutes in the intestinal lumen draw water into the intestines due to incomplete food breakdown
Maldigestion - impaired food digestion
Malabsorption - impaired nutrient absorption
Altered Motility Diarrhea - Rapid gastric Emptying (RGE)
Hypermotile stomach + shortened gastric emptying + is associated w/ early dumping syndrome (EDS)
Fecal Fluid Testing - Fecal Leukocyte Testing
For neutrophils, indicative of invasive bacteria
Fecal Fluid Testing - Muscle Fiber Testing
Identifying undigested fibers useful to diagnose pancreatic insufficiency or cystic fibrosis
Undigested fibers have striations running vertically + horizontally
Fecal Fluid Testing - Fat Testing
Stool w/ steatorrhea can be screened for the presence of excess fecal fats
Indicates pancreatic insufficiency or small bowel disease
Associated w/ osmotic diarrhea (maldigestion + malabsorption)
3 day sample collection to quantify
Fecal Fluid Testing - Occult Blood Test
Detect “hidden” blood within fecal matter
Associated w/ colorectal cancer
Fecal Fluid Testing - APT Test
Determine if bloody stool is due to fetal bleed (HbF) or swallowing of maternal blood during birth (HbA)