Management (Robbins & Coulter) - Chapter 4
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
Parochialism
Viewing the world solely through your own perspectives,leading to an inability to regonize differences between people
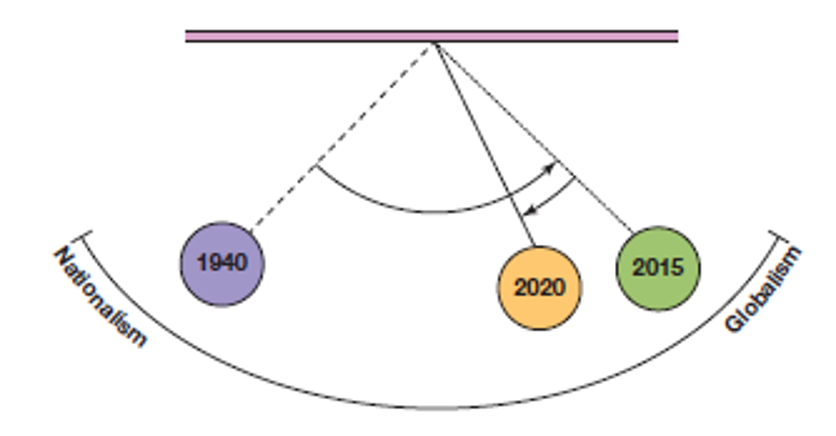
Nationalism vs. Globalism Pendulum
←goes back to nationalism as politics change
globalism still exists→
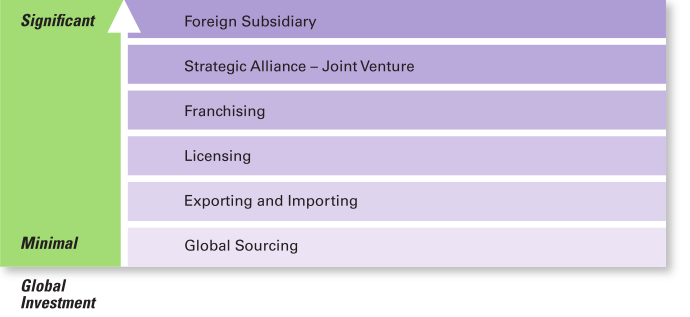
How Organizations Go Global
as you go up you have less control
global sourcing has the least level of investment and the most control
foreign subsidiary has the highest level of investment and the least control
How to apply cultural guidelines?
At a simplistic level it means, “When in Rome, do as the Romans do”
However, Hofstede and the GLOBE studies will help you alert managers to potential problems that might emerge due to cultural differences
What Americans are Like
Americans are very informal.
Americans are direct.
Americans are competitive.
Americans are achievers.
Americans are independent and individualistic.
Americans value personal space.
Americans dislike silence.
Americans value punctuality.
Americans value cleanliness.
Political/Legal Environmet
U.S. managers are accustomed to a stable legal and political system
Managers must stay informed of the specific laws in countries where they do business
Some countries have risky political climates(some countries have virtually meaningless contracts that will lead to never-ending court)
Globalization will continue despite its critics because
The infrastructure is already in place for global trade.
The evidence shows globalization is NOT the cause of unemployment—technology is the culprit.
Managers need to develop requisite skills to be a global manager
Different Types of International Organizations
Multinational corporation (MNC)
Multidomestic corporation
Global company
Transnational or borderless organization
North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA)
an agreement among the Mexican, Canadian, and U.S. governments in which barriers to trade have been eliminated
Replaced by USMCA (July 2020)
British vote to Exit E U (2016)
also known as Brexit. The vote was in response to nationalist feelings in the UK
Donald Trump elected U S president (2016)
elected on an America First campaign due to distrust of career politicians
Trans-Pacific Partnership (2016)
TPP was a trade agreement among Pacific rim countries that fell apart for lack of support
USMCA (2018)
President Trump’s renegotiated version of NAFTA
Regional Trading Alliances
• Global competition and the global economy are shaped by regional trading agreements, including:
– European Union (EU)
– North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA)
The European Union
a union of 28 democratic European nations created as a unified economic and trade entity with the euro as a single common currency
World Trade Organization (WTO)
•global organization of 161 countries that deals with the rules of trade among nations
Essentially replaced G A T T
International Monetary Fund (IMF)
An organization of 188 countries that promotes international monetary cooperation and provides advice, loans, and technical assistance
World Bank Group
a group of very closely associated institutions that provides financial and technical assistance to developing countries
GATT
a 1948 agreement between countries to reduce or eliminate trade barriers
Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD)
an international economic organization that helps its 34 member countries achieve sustainable economic growth and employment
Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN)
a trading alliance of 10 Southeast Asian nations
Global Milestones
World Economic Forum (1974) is a Swiss non-profit foundation that brings world leaders together each year to discuss factors of common interest
Margaret Thatcher elected Prime Minister of U K (1979). She was very pro free trade.
Ronald Reagan elected U S President (1980). Joined Thatcher as a pro free trade advocate
Fall of the Soviet Union (1991). Created 9 member states
Global Trade Mechanisms
•World Trade Organization (W T O)
•International Monetary Fund (I M F)
•World Bank Group
•General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (G A T T)
•Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (O E C D)
Ethnocentric attitude
view that home country has best work practices (also self-referencing criteria or SRC)
Polycentric attitude
view that managers in the host country know the best approaches
Geocentric attitude
A world oriented view that focuses on using the best approaches and people from around the globe
Transnational or borderness organization
An MNC in which artificial geographical barrieres are eliminated. Uses the best work practices regardless where there from.
Structures and techniquies organizations use as they go international?
1. Global sourcing
2. Exporting
3. Importing
4. Licensing
5. Franchising
6. Global strategic alliance
7. Joint venture
8. Foreign subsidiary
Global sourcing
Purchasing materials or labor from around the world wherever it is cheapest
reshoring→ don’t want all of it gone, some brought back to home country
near-shoring→ some brought to a nearby shore to keep it close(especially since the pandemic)
Exporting
Making products domestically and selling them abroad
Importing
Acquiring products made abroad and selling them domestically
Licensing
An organization gives another organization the right to make or sell its products using its technology or product specifications
allowing a third party a license to sell products
risk of property being stolen
Franchising
An organization gives another organization the right to use its name and operating methods
particularly restaurants
Strategic alliance
A partnership between an organization and foreign company partner(s) in which both share resources and knowledge in developing new products or building production facilities
Joint venture
A specific type of strategic alliance in which the partners agree to form a separate, independent organization for some business purpose
may be 2 or more companies
Foreign subsidiary
Directly investing in a foreign country by setting up a separate and independent production facility or office
requires the most amount of investment
you work by yourself
Free market economy
An economic system in which resources are primary owned and controlled by the private sector
Planned economy
An economic system in which economic decisions are planned by a central government
Ex: India
National culture
The values and attitudes shared by individuals from a specific country that shape their behavior and beliefs about what is important
Economies of Scale
Thinking global act local
Not necessary to know the language in other countries, but useful
Global Leadership and Organizational Behavior Effectiveness (GLOBE)
Power distance
Uncertainty avoidance
Assertiveness
Humane orientation
Future orientation
Institutional collectivism
Gender differentiation
In-group collectivism
Performance orientation
Cultural intelligence
Cultural awareness and sensitivity skills.
Global mind set
Attributes that allow a leader to be effective in cross-cultural environments
Globalization
A process by which organizations develop influence or operations in other countries
nationalism
patriotic ideals and policies that glorify a country’s values
Law of comparative advantage
The economic proposition that a country should produce goods or services for which it has the lowest opportunity cost
Global company
An MNC that centralizes management and other decisions in the home country. It makes it's business in the place they come from or was raised.
What was the first monetary order that would govern financial relations between countries and explain its significance
The Bretton Woods conference - It was an agreement between the US, Canada, Western Europe, Australia, and Japan to establish the rules for commercial and financial relations. It shaped global trade by opening the door to ongoing agreements, institutions, and events like the IMF, GATT, and OECD and paved the way for future trade development.
The "Win-Win argument" (for globalization) was based on what?
The law of comparative advantage
Essentially says a ‘rising tide floats all boats.’
Globalization benefits all trading partners.
Downsides to globalization:
1. Wage stagnation
2. Labor shipped to other countries
3. Inflow of immigrants
4. Increasing economic inequality
5. Undermines middle class
Advantages of globalization
1. Boosts economy
2. Increases wages
3. Provides lower cost goods to consumers
What is the reason for unemployment?
Technology (need more skilled workers)
National culture is shaped by:
Societys social traditions; Political and economical philosophy; and legal system
Hofstede's five dimensions of national culture
1. Power distance
2. Uncertainty avoidance
3. Future orientation (short/long term)
4. Institutional Collectivism (Individualistic/Collectivistic)
5. Humane orientation (achievement/nurturing)
Nine GLOBE dimensions
1. Power distance
2. Uncertainty avoidance
3. Future orientation (short/long term)
4. Institutional Collectivism (Individualistic/Collectivistic)
5. Humane orientation (achievement/nurturing)
6. Assertiveness
7. Gender differentiation
8. In-group collectivism
9. Performance orientation
Challenges of doing business globally?
1. The openness of globalization and cultural differences
2. Managing global workforce (need cultural intelligence and global mindset)
Globalization Highlights
After W W I nations became more protectionist
After W W I I the trend toward globalization started
Numerous agreements, institutions, and events pushed for globalization