Clin Med Disorders of Oropharynx
1/104
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
105 Terms
odontogenic infection
bacterial infections that originate from teeth or supporting structures-may result in local or systemic complications
dental caries
destruction of tooth enamel caused by acid produced by bacteria
gingivitis
inflammation of the gums caused by plaque and tartar buildup, secondary to bacterial infection
periodontitis
chronic inflammatory condition that causes damage to the tissue and bone that support teeth
odontogenic infection clinical presentation
1-2 w of worsening dental pain, facial or neck swelling/pain, fever, malaise, decreased oral intake, odynophagia, trismus, hx of poor hygiene, facial paresthesias, ocular pain, diplopia, dyspnea, sialorrhea, purulent oral secretions
odontogenic infection- physical exam
erythema, edema, induration, tenderness, acute and tender cervical LAD, abscess
odontogenic infection- POCUS
abscess appears anechoic, occasionally loculated mass along bone cortex
odontogenic infection- CT w/ contrast
differentiates cellulitis from abscess
complex abscess formation or spread to deep neck spaces
when POCUS is suboptimal
odontogenic infection- flexible laryngoscopy
impending obstruction or edema necessitating need for urgent airway intervention
dental caries pathogen
strep mutans
dental caries clinical presentation
white spot, rough texture, cavitation, gingival bleeding
dental caries treatment/management
fillings, root canal for pulpitis, preventative care
gingivitis pathogens
strep, fusobacterium, actinomyces, veillonella, treponema
drug-induced gingivitis
phenytoin, CCBs, anticoags, fibrinolytics, OPCs, protease inhibitors, Vit A analogs
gingivitis treatment
good oral hygiene, mechanical debridement, chlorhexidine 0.12% oral rinse, augmentin +/- metronidazole, dietary supplements
if drug induced- stop/change offended med
periodontitis
progression of gingivitis, shift to gram - bacteria
periodontitis clinical presentation
gingival inflammation with bleeding, loss of gingival attachment, painless
periodontitis diagnostic workup
dental eval with periapical, bitewing, and/or panoramic xrays
treatment for severe periodontitis
amoxicillin or augmentin + metronidazole x14 days
PCN allergy: cephalosporin + metronidazole
or azithro, clarithro, or doxy if unable to take cephalosporin
mechanical debridgement
treatment for nonsevere periodontitis
topical abx formulation- 2% minocycline hcl microspheres, 10% doxy hyclate ER liquid, 0.5% clarithro gel, or chlorhexidine periodontal chips
scaling and root planing
cellulitis treatment
augmentin- 1st choice
pcn allergy- clindamycin
dental extraction of necrotic tooth
abscess treatment
needle aspiration, I&D, temp drain placement, culture
tooth extraction
abx- ampicillin-sulbactam (preferred), Pen G + metronidazole
PCN allergy- 2nd/3rd gen cephalosporin, levofloxacin, doxy, meropenem
IV therapy until improvement then change to oral
Ludwig angina
life-threatening cellulitis of the soft tissue of the floor of the mouth and neck
rapidly progressive and may lead to airway obstruction
Ludwig angina cause
dental infection in 2nd/3rd molars sublingual, submental, and submandibular compartments.
polymicrobial + and - (staph, strep, peptostrep, fusobacterium, bacteroides, actinomyces)
Ludwig angina risk fx
diabetes, oral malignancy, poor oral hygiene, dental caries, recent dental tx, malnutrition, alcoholism, immunocompromised
Ludwig angina S&S
recent dental pain, mouth pain, fever, fatigue, chills, weakness, trismus
tripod position, drooling, dysphagia, "hot potato voice", tongue swelling, bull neck, firm & swollen floor of mouth, restricted tongue mobility, restricted mouth opening
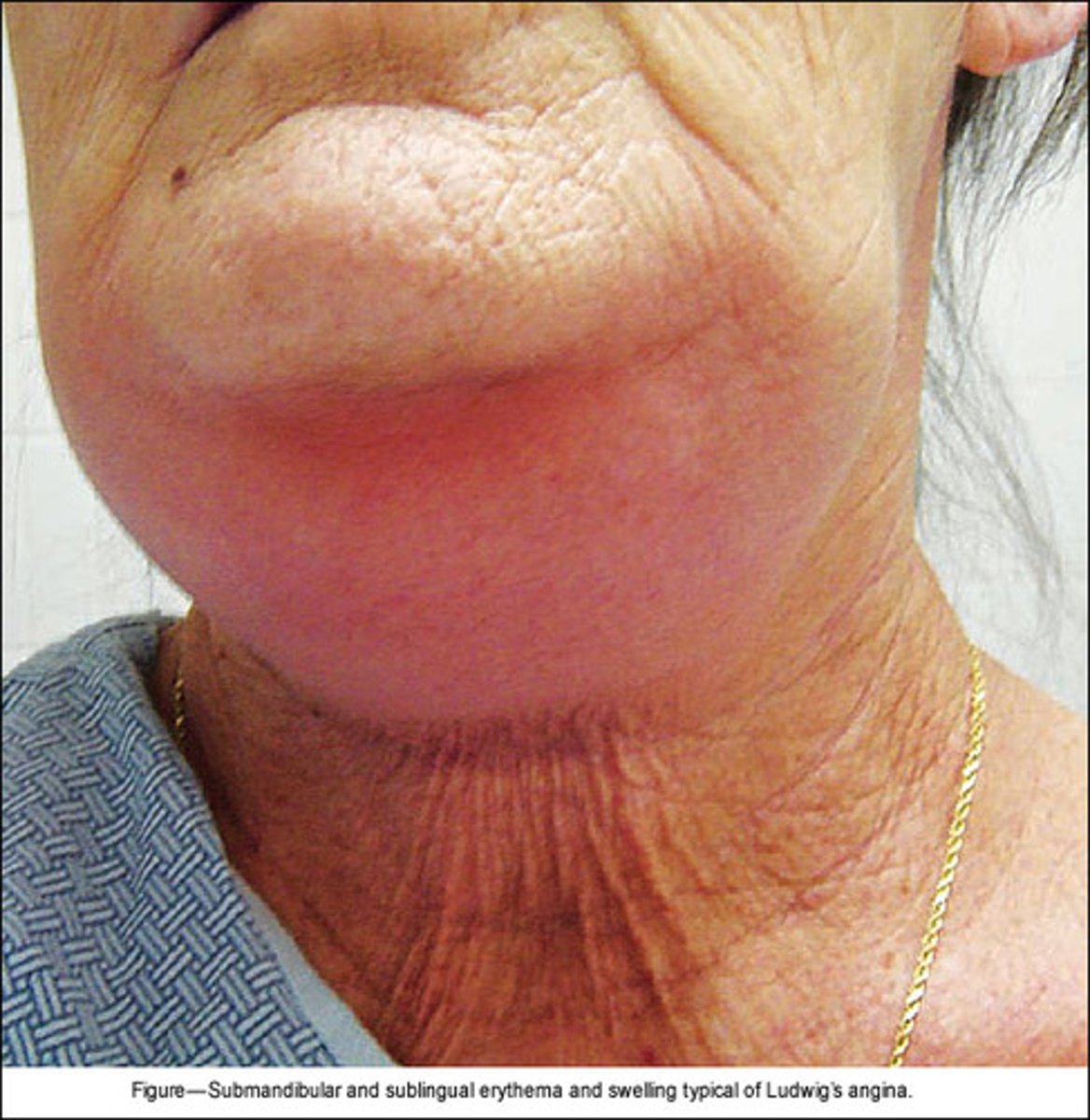
Ludwig angina diagnosis
clinical diagnosis, neck CT with contrast
Ludwig angina treatment
secure airway (flexible nasotracheal intubation preferred)
broad spectrum IV antibiotics- ampicillin-sulbactam or clindamycin
IV corticosteroids and nebulized epi
surgical drainage
aphthous ulcers
canker sores/ulcerative stomatitis
painful, round/oval, shallow sore that develops on the inside of the mouth
very common
aphthous ulcer subtypes
minor (1cm, heal in 10-14 days)
major (>1cm, may be disabling)
herpetiform
aphthous ulcer cause
unknown - possible link to herpes virus 6
triggered by stress, trauma, nutritional deficiences
aphthous ulcer S&S
single or multiple well-circumscribed, annular lesion
yellow-gray centers with red halos on buccal or labial mucosa
painful
spares hard palate and gingiva (differs from HSV)
aphthous ulcers treatment
usually resolve on their own
avoid irritants, topical steroid paste (triamcinolone 0.1% paste), oral steroid (prednisone), H2 blocker (cimetidine), "magic mouthwash"
HIV patients- thalidomide
magic mouthwash
contains anesthetic, antihistamine, antacid
may contain antibiotic, antifungal, steroid
herpes stomatitis
contagious viral infection of the mouth caused by HSV-1
spread from direct contact, droplets, lesions
children 6mo-5yrs MC affected
herpes stomatitis S&S
fever, sore throat, malaise, anorexia, pharyngeal erythema and edema
painful vesicular/ulcerative lesions on gingiva, palate, buccal, and labia mucosa that appear flat, yellowish, 2-5mm
heal within 2-3 weeks w/o scarring

herpes stomatitis treatment
topical acyclovir cream or oral acyclovir suspension
oral must start w/in 72hrs of onset
herpes labialis
cold sores
grouped vesicles w/erythematous base caused by secondary recurrent HSV-1
usually reoccur at the same site, mucocutaneous junction of lip MC
may follow stress, illness, sun exposure
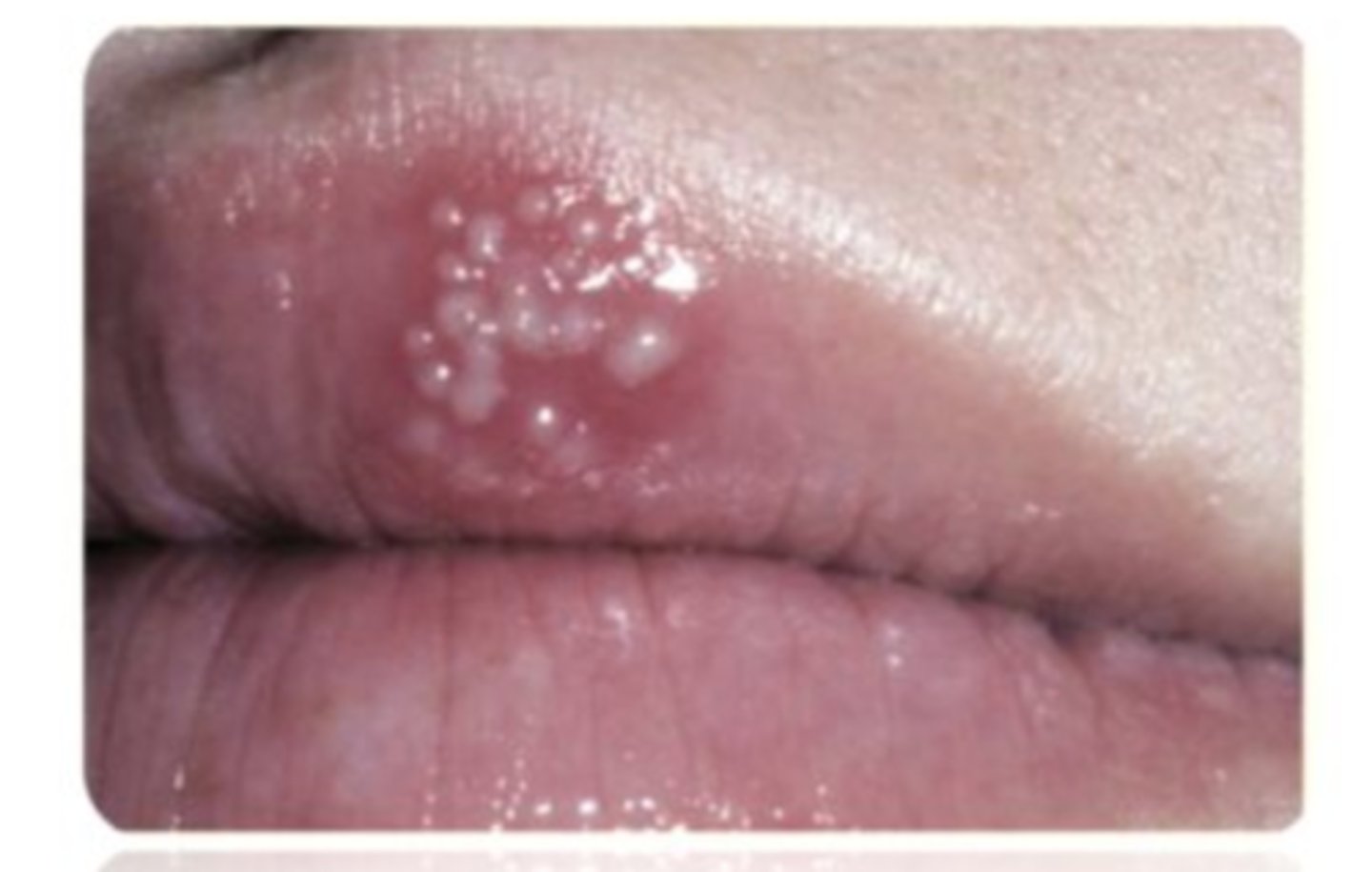
herpes labialis treatment
valacyclovir 2000mg PO q12hr x1 day, acyclovir 200mg PO 5xday for 7-10 days ~within 24-48hr onset
suppressive therapy for frequent outbreaks- valacyclovir 500mg (1g if >10 outbreaks/year)
lysine
sunscreen
oral candidiasis
overgrowth on candida from oral flora
thrush
oral candidiasis risk factors
denture use, poor oral hygiene, dry mouth, DM, anemia, chemo, inhaled corticosteroids, abx use, immunocompromised, nursing babies
pseudomembranous oral candidiasis S&S
asymptomatic
if symptomatic- burning, bleeding, altered taste perception
white curd-like plaques that can be rubbed off leaving erythematous or bleeding base
tongue, labial and buccal mucosa, gingiva, palate, oropharynx
angular chelitis
painful, erythematous, fissured patches of commissures of the mouth; usually bilateral
usually candida overgrowth, can also be caused by s. aureus or strep
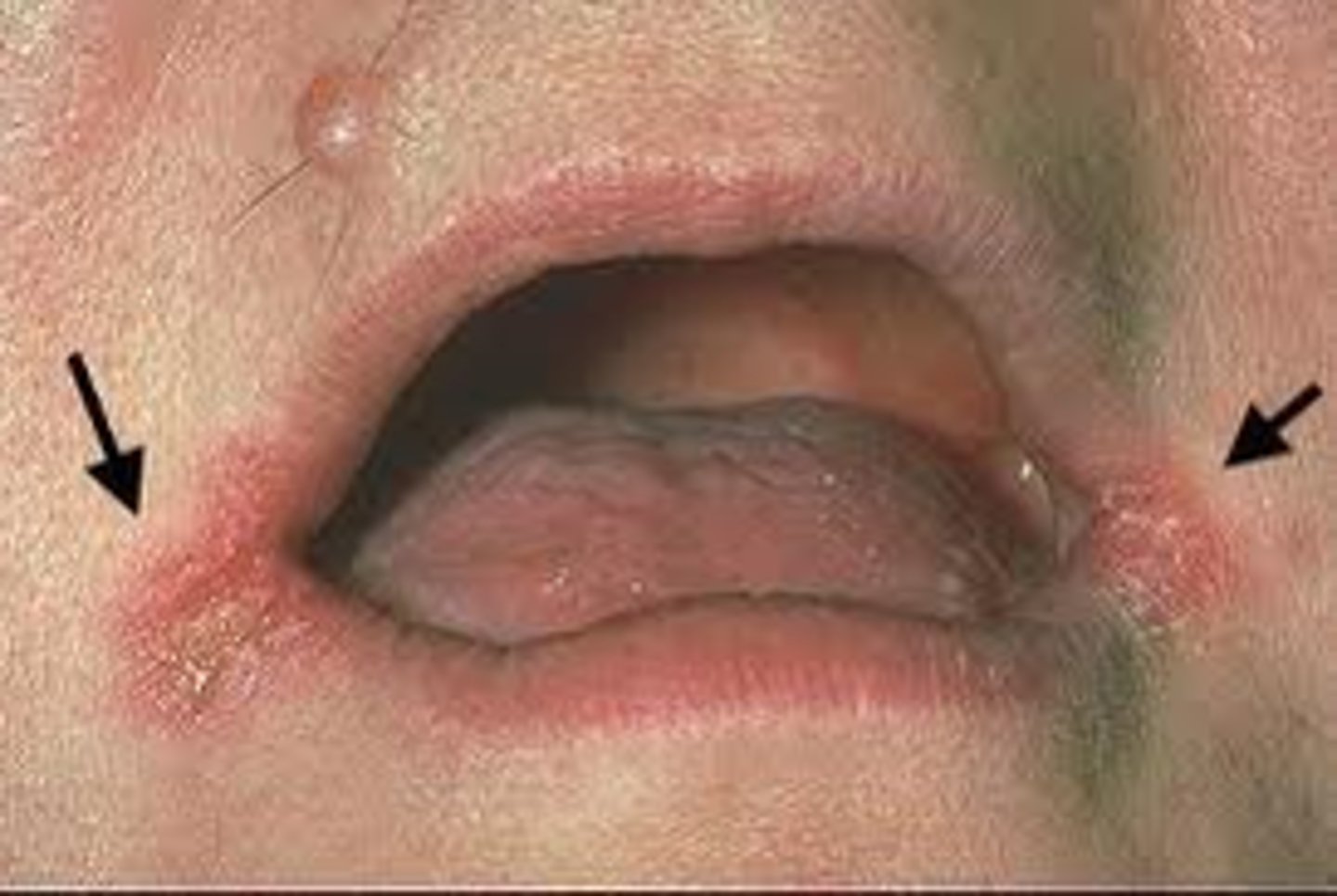
angular chelitis treatment
nystatin suspension 100,000 units/ml - 5mL PO four times a day
clotrimazole lozenge
fluconazole (avoid in 1st trimester of pregnancy)
2% miconazole cream for breastfeeding mothers
angular chelitis pt education
keep mouth angles dry, clean dentures with chlorhexidine, boil pacifiers and bottle nipples, rinse mouth after using inhaled corticosteroids
deep neck infection
local extension of infections in tonsils, pharynx, parotid glands, cervical lymph nodes, or odontogenic structures. Affects neck cervical spaces
life threatening
polymicrobial
deep neck infection S&S
may appear toxic
fever, neck pain, respiratory distress, neck swelling, dysphagia, dysphonia, trismus
divisions of cervical fascia
superficial- SQ neck tissue and platysma that envelops head and neck
deep- divided into superficial, middle, and deep layers
deep cervical fascia- superficial layer
submaxillary and parotid glands, trapezius, SCM, strap muscles
odontogenic and submandibular infections
deep cervical fascia- middle layer
pharynx, larynx, trachea, upper esophagus, thyroid, parathyroid glands
pharyngeal, tonsillar, laryngeal, and odontogenic (2nd/3rd molars) infection
deep cervical fascia- deep layer
"danger space"
covers vertebral column and muscles of the spine, continuity with the mediastinum
upper aerodigestive infections, retropharyngeal, vertebral, and prevertebral abscesses due to IV drug use
pharyngitis
inflammation of the mucus membranes of the oropharynx
MC in children <5yo
pharyngitis causes
viral (MC)
can also be bacterial, candida, environmental allergies, chemical exposures
acute viral pharyngitis
sore throat + other URI symptoms (cough, rhinorrhea, conjunctivitis, headache, rash)
treat with supportive therapy
acute streptococcal pharyngitis (GAS)
strep throat
caused by strep pyogenes (group A beta-hemolytic strep- GABHS)
accounts for 1 in 4 children w/acute pharyngitis
strep throat S&S
acute onset without signs of viral URI
sore throat, ear pain, temp >100.4, scarlatiniform rash, pharyngeal erythema, palatal petechiae, uvulitis, tonsillar exudates, cervical adenopathy
strep throat workup
RADT, throat culture (gold standard), modified centor scor
modified centor score
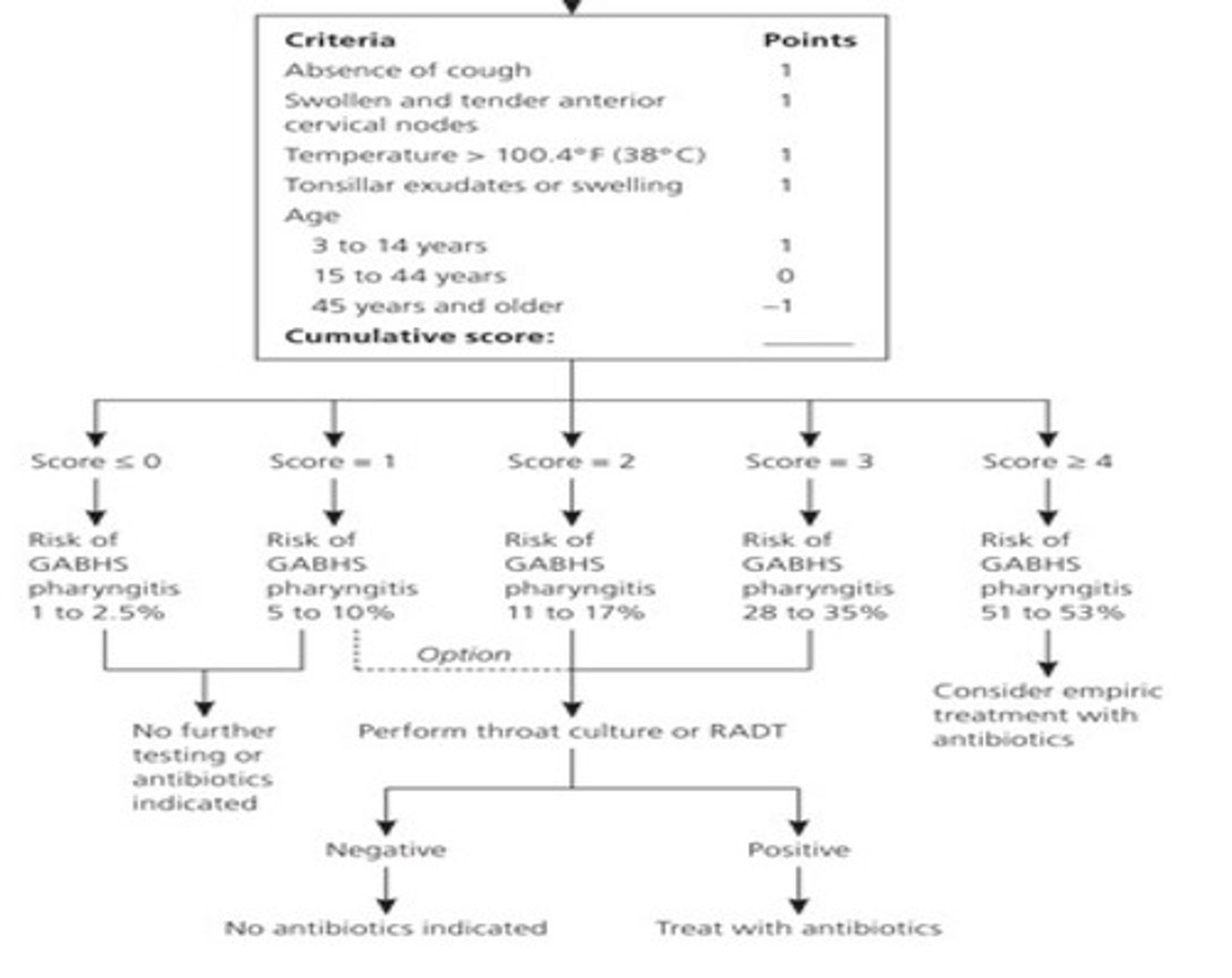
strep throat treatment
PCN V PO, PCN G IM (pcn is treatment of choice) or amoxicillin
PCN allergy: cephalosporins, macrolides, clindamycin
complications of untreated GABHS
scarlet fever, acute rheumatic fever, post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis
chronic carriers of GABHS
persistent presence w/o active infection
little risk for complications or transmission
indications for tonsillectomy in children
>/= 7 GAS infections in a year, >/= 5 episodes annually x2 years, >/=3 episodes annually x3 years
hx of peritonsillar abscess or multiple throat infections with multiple drug allergies
obstructed sleep-disordered breathing
parent education for children s/p tonsillectomy
manage pain w/NSAIDs or acetaminophen
pain will improve after 3-5 days and recur when scabs fall off around day 7
peritonsillar abscess
pocket of infection in peritonsillar space
complication of bacterial pharyngeal/tonsillar infection
peritonsillar abscess S&S
typically unilateral, severe sore throat, odynophagia, "hot potato voice"
unilateral swelling of soft palate, tonsil is medially displaced, uvula shifted to opposite side
peritonsillar abscess treatment
referral to ENT for needle aspiration and I&D
laryngitis
inflammation of the larynx
laryngitis etiology
URI, overuse, GERD, irritants
chronic laryngitis- consider GERD, vocal nodules, polyps
laryngitis clinical presentation
hoarseness, loss of voice, sore throat
not contagious unless due to URI
laryngitis treatment
rest voice, humidified air, home remedies, treat underlying cause
ENT referral for laryngoscopy if no resolution
epiglottitis
inflammation of the epiglottis and nearby structures caused by h. flu type B
rare
medical emergency
epiglottitis risk factors
3x more common in adults, men>women, middle aged, high BMI, DM, pneumonia, Sjogren syndorme, epiglottic cyst
epiglottitis symptoms
sudden onset of fever, dysphagia, drooling, sore throat, thick-muffled voice, stridor
epiglottitis physical exam findings
tripoding, retractions, labored breathing, cyanosis may be present, significant pain w/external palpation of larynx
do not attempt an oral eval with direct visualization -can exacerbate
epiglottitis management
ICU admit, examination using nasal fiberoptic endoscope, thumb sign on xray, emergency airway/trach tray on standby
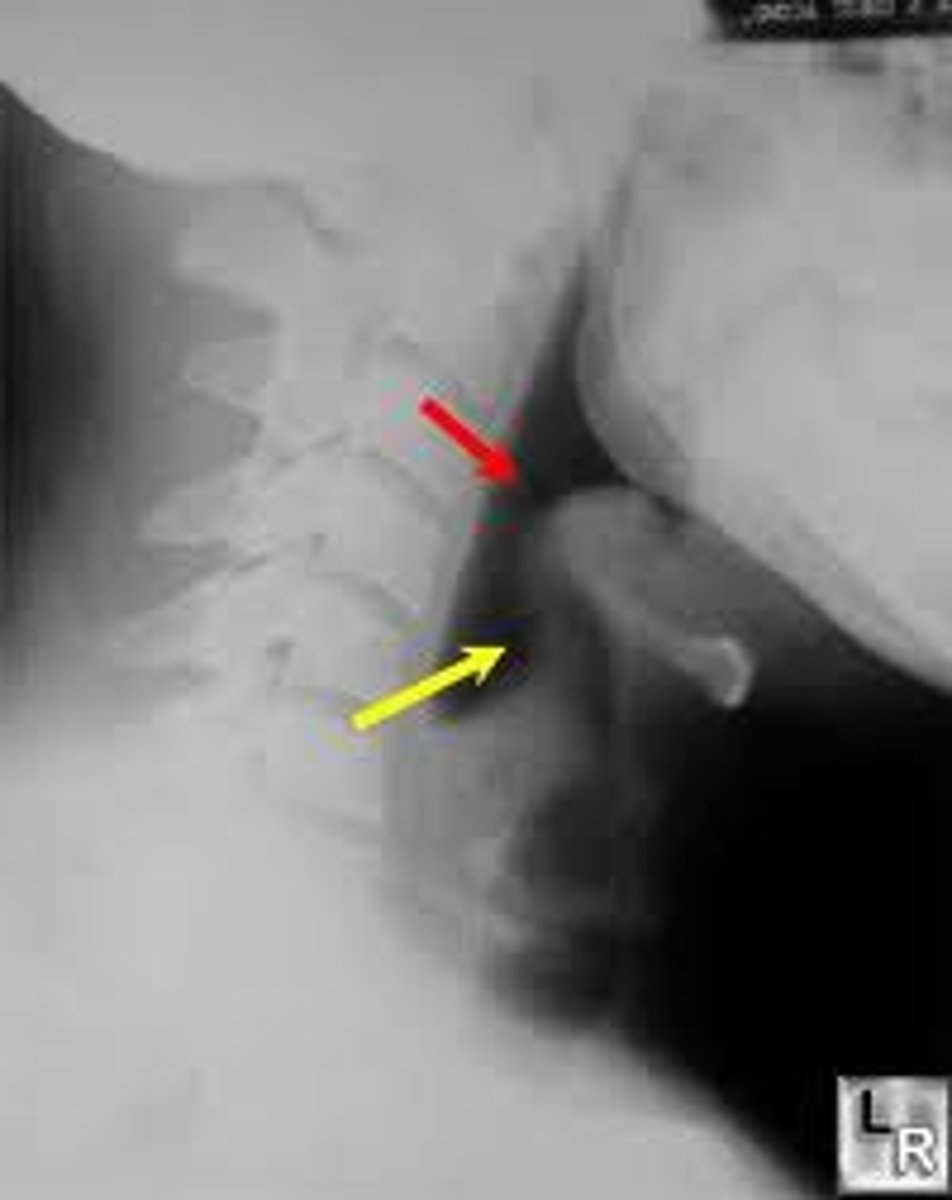
epiglottitis treatment
IV cefotaxamine 2g q 6h or ceftriaxone 1-2g/day
IV corticosteroids (debated)
close observation
acute bacterial sialadenitis
bacterial infection of the salivary gland, MC in parotid
S aureus MC
occurs w/stasis of salivary flow from dehydration or decreased oral intake
acute bacterial sialadenitis risk factors
DM, hypothyroidism, renal failure, Sjogren's syndrome, anticholinergic meds, stones or duct strictures
acute bacterial sialadenitis S&S
acute onset of pain and swelling of the affected gland
induration, edema and extreme localized tenderness, unilateral
diagnosis of acute bacterial sialadenitis
massage gland to express purulent drainage and culture
CT scan
acute bacterial sialadenitis treatment
warm compress, increased oral intake, sialagogues (lemon drops), gland massage
severe cases- IV nafcillin 1g
less severe cases- oral augmentin 875mg
resolution 2-3 weeks
I&D if abscess formation
acute non-suppurative sialadenitis
inflammation of the salivary glands not secondary to bacterial infection
MC cause is Mumps
85% cases are 15yo and younger
acute non-suppurative sialadenitis S&S
local pain, edema, otalgia, trismus, commonly bilateral
acute non-suppurative sialadenitis diagnosis and treatment
viral serology
supportive treatment
vaccine has reduced incidence by 99%
chronic sialadenitis
repeat episodes of pain and inflammation, MC in parotid gland
caused by decreased salivary flow or stasis from stone, stricture, scar tissue, tumor compression
chronic sialadenitis presentation and diagnosis
less severe than acute
CT scan to identify underlying cause
chronic sialadenitis treatment
treat underlying cause
if no cause found, treat with sialagogues, hydration, massage, NSAIDs
excision can be effective
sialolithiasis
formation of stone in the duct system, usually in submandibular gland (Wharton's duct)
sialolithiasis clinical presentation
postprandial salivary pain and swelling, may have hx of recurrent acute sialadenitis
sialolithiasis diagnosis
bimanual palpation along course of Wharton's duct may reveal stone
CT showing large radio-opaque stone
sialolithiasis treatment
sx removal of stone, lithotripsy, gland excision
oral leukoplakia
persistent, adherent white plaque of the oral mucosa that cannot be rubbed off; results from a disturbance of surface epithelium
most are idiopathic, 2-6% are early SCC
increases risk of esophageal SCC
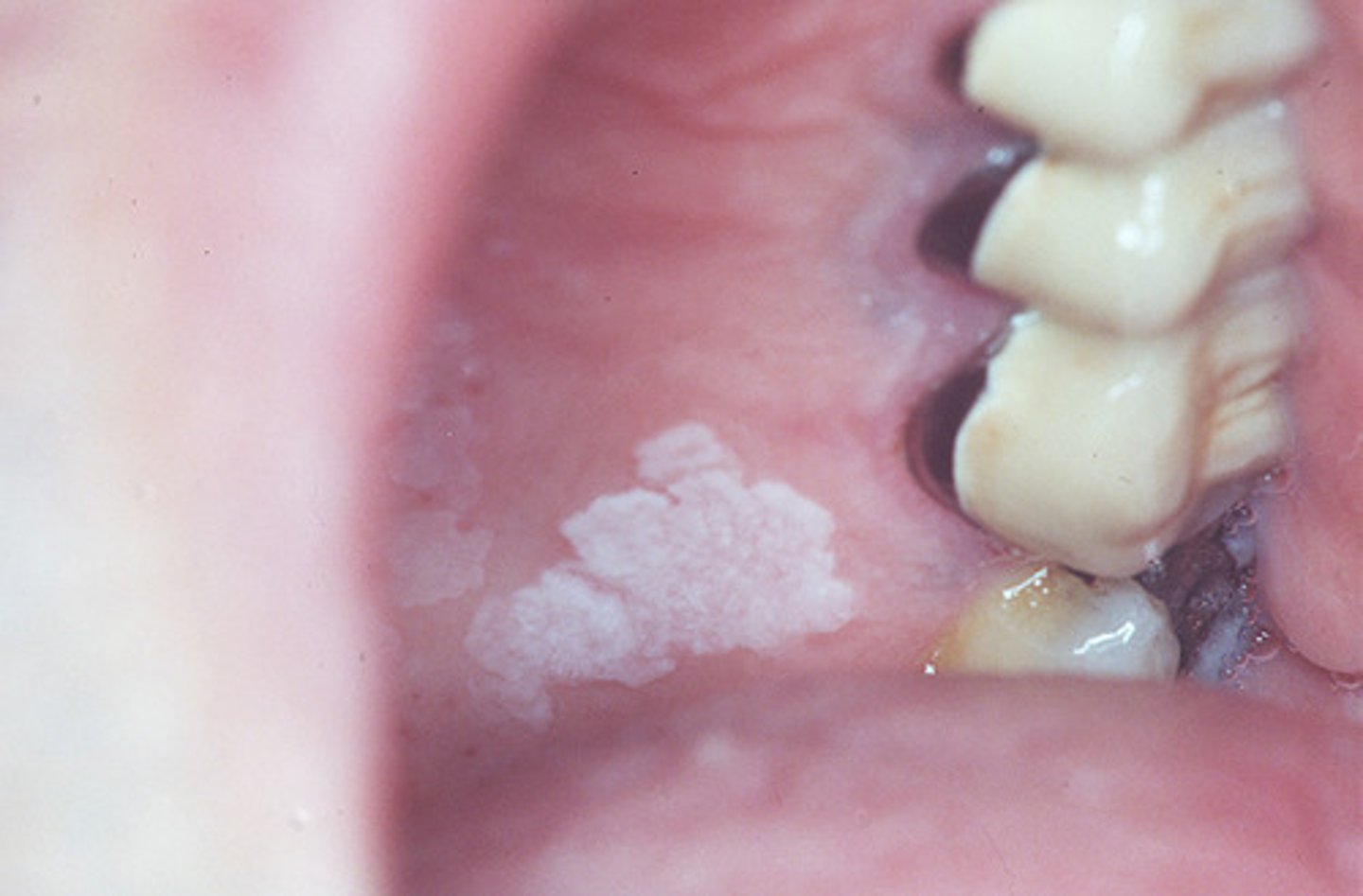
oral leukoplakia risk factors
chewing tobacco, smoking, excessive alcohol, poorly-fitting dentures, trauma to cheeks
oral leukoplakia diagnosis
ENT eval with biopsy
must rule out other causes (fungal, neoplasm)
oral leukoplakia treatment
discontinue tobacco/alcohol, avoid triggers, close f/u on small lesions, sx excision, cryotherapy ablation or CO2 laser ablation
oropharyngeal trauma
wounds to hard and soft palate, tonsils, and posterior pharyngeal walls
commonly involves a young child falling with an object in the mouth
complications of oropharyngeal trauma
ICA injury- compresses ICA against lateral process of cervical vertebra causing intimal tear
deep neck space infection
GSW or air bag deployment with object in mouth may have
penetrating neck injuries
if you see focal neuro changes with oropharyngeal trauma think:
ICA injury
symptoms of deep neck infection 24hr after oropharyngeal trauma
fever, neck pain, torticollis, drooling