USPS Final
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
marbury v madison
scotus has right to judicial review - can strike down laws that they deem unconstitutional (MADE(ison) laws that the supreme court doesn’t like have to be thrown into the mar (sea))
district court
1st level of federal court, they hear trials
circuit court of appeals
2nd level of federal court, each court gets assigned to one of 13 circuits
SCOTUS
3rd level of federal courts, they choose which cases they want to take on
judiciary act of 1925
SCOTUS has the choice to decide which cases they take on, can also choose to take on specific parts of cases (scotus can JUDge which cases they want to ACT on)
senate judiciary committee
when someone nominated for senate, they appear in front of committee and are questioned
legal model
justices will make decisions based on these rational tenets: originalism (og meaning), precedent/doctrinalism (development of constitution over time), textualism (what does the text say exactly), and structuralism (how does this fit into other parts of constitution)
downsian voting
comparing expected utility/happiness for incumbent party A to expected utility of challenging party (B) - (if you’re DOWN about A, then see if B is any better)
median voter theorem
under certain circumstances (single peaked preferences, ideology = unidimensional, only goal is to win, candidates can change their positions freely) then the candidates’ positions will converge to this median voter line and then voters will choose one of the two
retrospective voting
retrospective voting = voting based on the PAST performance of the incumbent party (retrospective —> looking back to the past)
valence issues
these are certain things that the average voter is assumed to care about: economic prosperity, peace, less corruption, and freedom from disease (people VALUE the VALence issUEs)
political business cycles
question of whether or not the government sets up the economy to better every four years (CYCLES of having good economy - starts out bad then ends good)
question wording effect
exactly how you word a political question can affect the answer, especially for those who aren’t as politically in tune (they’ll search the question for clues on how to form an opinion)
receive, accept, sample method
method in which you take the info you RECEIVE, choose what to ACCEPT and store in your brain, then draw from the SAMPLE of info when you’re asked a political question
federalist 10
representative democracy is preferable to direct democracy, large republics viable because they prevent any one faction from dominating (anti creation of these faction political parties)
duvergers law
if you have a political system in which a plurality of votes determines the winner, then there will tend to only be two parties (nothing DIVERGES and you have just the two parties)
parties in the first party system
federalist - hamilton, adam’s, john marshall, supported stronger national government, against the war of 1812, skeptical of slavery VS democratic republicans - jefferson, madison, monroe, wanted weaker national government, more states’ rights and supportive of slavery
parties in the second party system
Whigs - Abraham Lincoln, Henry Clay, William Henry Harrison, stronger national government (wanted to see economic growth), supported stronger for cities business and industrial development, mixed views on slavery VS democrats - andrew jackson, martin van buren, james polk, weaker national government, more states’ rights and mostly supportive of slavery
party realignment
when the groups of people who give disproportionate support to to these major parties start to change
activists in the 19th century
frederick douglass, lucretia mott, susan b anthony, sojourner truth
seneca falls convention
this was the beginning of the women’s suffrage movement, occurred as a result of women being banned from sitting at the world anti slavery convention
National Woman Suffrage Association
created by Stanton and Anthony, believed that white women should have the right to vote over black men (it’s the NATIONAL association so only “true” members of the nation should have rights)
American Women Suffrage Movement
Lucy Stone and Julia Ward Howe created movement, focused solely on the right to vote to try and attract as many supporters as possible (ALL AMERICANS encapsulated)
national individual based civic organizations
orgs that don’t have local chapters
lone wolves (Hanrie Han)
these are staff/volunteers who do everything on their own, “one person doing too many things”
mobilizers (Han)
people who donate to the cause to maintain their membership, little involvement, gain these people through marketing/individual outreach/functional outreach
organizers (Han)
they branch out and building what the org is trying to accomplish, others bring in others who bring in others
regional community orgs
multiple communities that band together to try and get change on a bigger level
indexing
news will cover different sides of a story and different opinions based on the proportion that politicians are talking about it
game schema
focuses on political conflict (how this will affect the country, the people, etc) rather than talking about the actual policies and what they detail
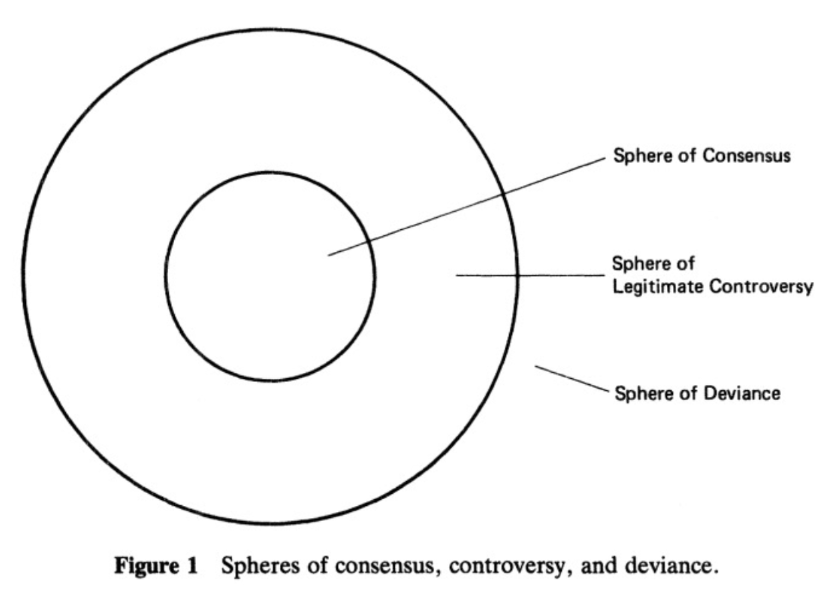
sphere of consensus
the press decides when there is this sphere of consensus - essentially something that is seen as legitimate fact
agenda setting
the media doesn’t change what you think but it changes the topics you think are most important
priming
when the media doesn’t change what you think, but rather what you think about - make diff choices based on what issues you think are salient
framing
same event but diff parts of it are covered in the media which could have an effect on how you think about it
presidential public funding system
largely defunct but not unconstitutional - used to be that presidential nominees accepting the public funding for their campaigns with a cap (if accepted the gov would match donation up to cap), but not used anymore bc they can make more money by actually accepting donations
1971/74 FECA
limit to how much you can donate, PAC rules, presidential funding system, federal election committee, limits on candidate spending (struck down), ban on corporate campaign spending
buckley v valeo
this removed the FECA restriction on the amount of money a candidate can spend (buck the spending limits)
indep expenditures
advocating for a candidate without coordinating with that candidate or campaign org (doing it all yourself)
citizens united v fec
ruled that indep expenditures should be allowed not just for indivs, but for any organization as well (the citizens are united in their support for the org that supports the campaign)
super pacs
independent expenditure only pacs
pacs
political action committees, have to disclose their spending
dark money
creating certain orgs that don’t have to disclose campaign spending bc they aren’t created by FECA (LLC - private companies and non-profits)
traceability
policy has visible outcomes that are directly linked to the gov
thermostatic preferences
preferences that move against the policy change (if room too hot, thermostat makes it colder
midterm backlash
long term trend of president losing seats in the house during midterm elections
juan linz criticisms of presidential systems
conflict between president and legislature, fixed terms mean that president doesn’t need to care about being a good president, fixed terms also mean that it’s hard to remove pres from position of power, winner take all reduces representation, president is in this strange role as head of gov and symbol of country (if you oppose pres you oppose the symbol of the country)
competitive authoritarianism
elections are held, but despite holding these elections, the other rules of democracy are frequently broken - need to gatekeep
gatekeeping
mainstream parties isolate and defeat extremist forces, root out extremist