Coasts
1/211
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
212 Terms
What are coasts
Where sea and water interact. Influenced by terrestrial processes(erosion, deposition), human factors(pollution and settlements) ,marine processes(tidal and waves) and atmospheric factors(climate and storms)
What’s fetch
Distance of open water which a wave has passed
What are main type of waves
Constructive and destructive
What are types of erosion
Hydraulic action, abrasion, attrition and corrosion
What are types of sub aerial processes
Mass movement and weathering
What are types of transportation
Saltation, traction, suspension and solution
What’s attrition
Materials carried by waves so they bump into each other and become smoother and smaller
What’s hydraulic action
Water forced into cracks of coastline so air expands in rocks causing minor explosion
What’s corrosion
Acid in salt water slowly dissolves rocks on coast like limestone and chalk
What’s abrasion
Coast is worn down by material carried by waves which through rocks against coast at high velocity
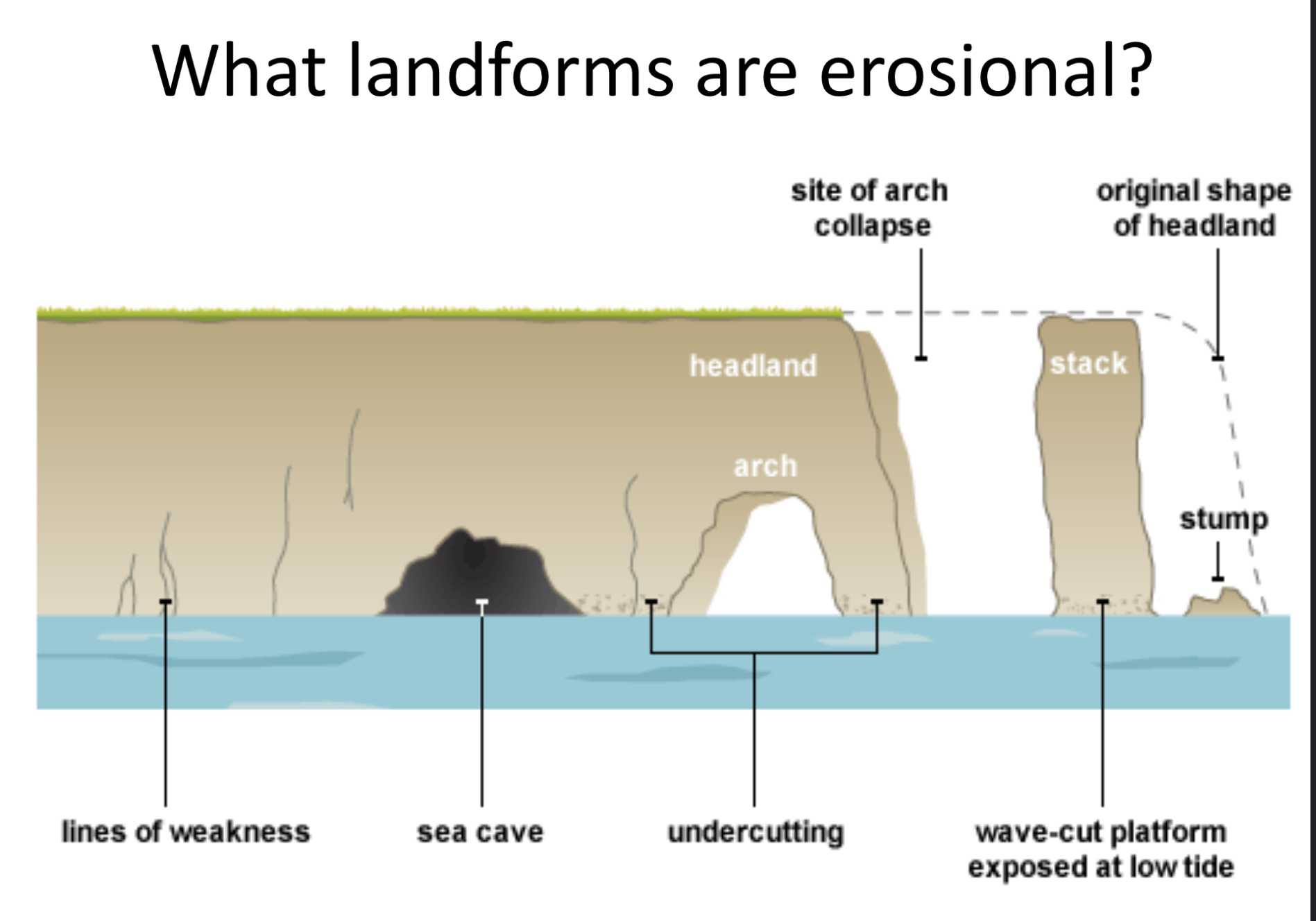
What landforms are erosion all
Cave, headland , arch, stack and stump
What landforms are depositional
Beach, tombolo, barrier spit, lagoon, bay barrier, wave cut platform, wave built terrace
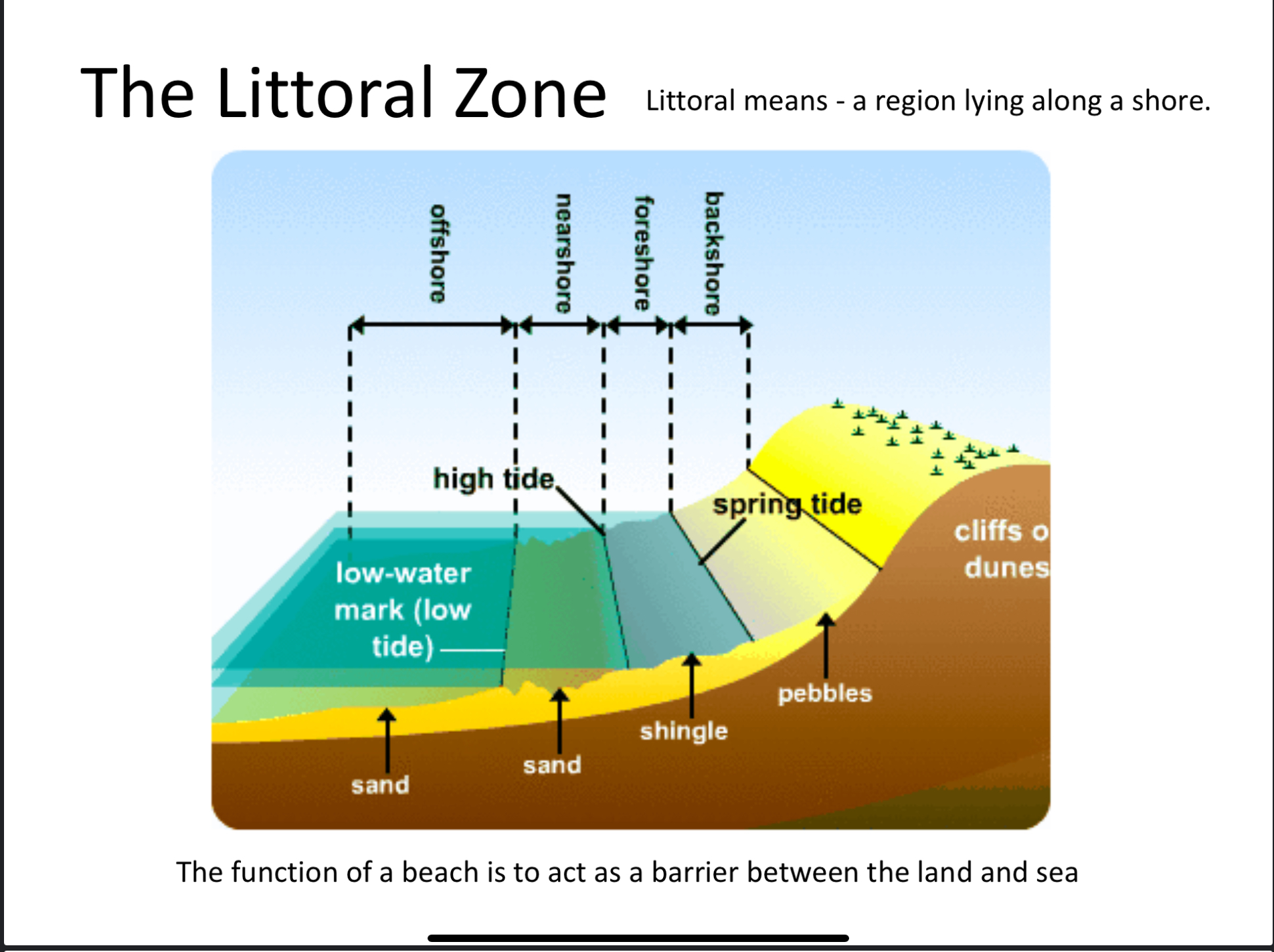
What’s the littoral zone
Area of the coast that can be affected by wave action
What’s the function of a beach
Acts as a barrier between land and sea
Back shore in a littoral zone
Not affected by wave action but can be in storm events.
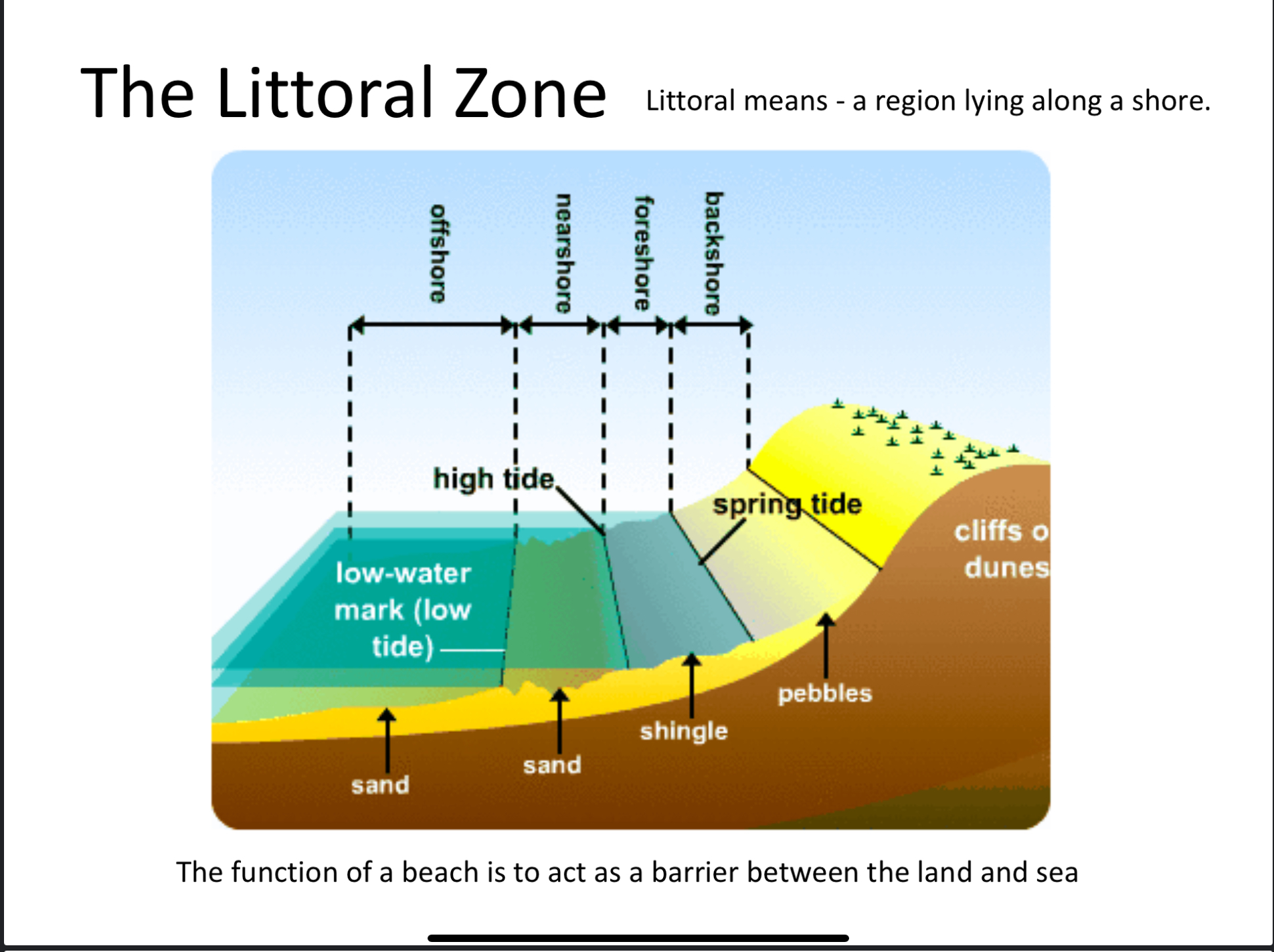
Fore shore in littoral zone
Intertidal area between high and low tide
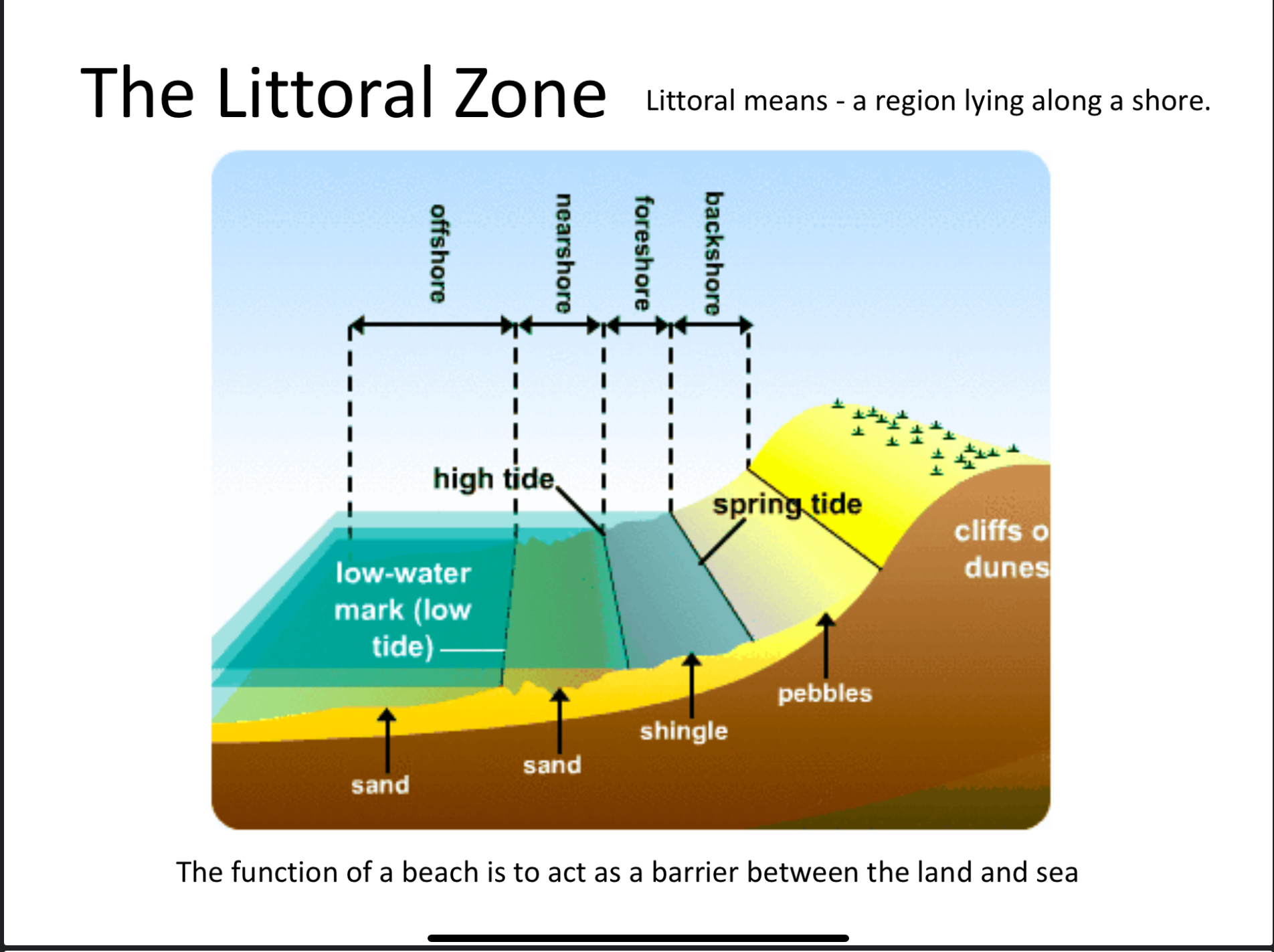
Nearshore in littoral zone
Breaker zone because friction between seabed and waves causes them to break
Offshore in littoral zone
area outside of wave action
What are storm beaches
Highest berm left by storm waves during spring tides(highest due to gravitational pull of moon and sun). Sediment is thrown up by the large waves and remainS. More common in shingle beaches affected by destructive beaches.
What are the long term factors that affect coasts
Geology like rocky type and structure. Coasts can be classified as rocky, sand or estuarine as well as concordant or discordant.
Sea level changes due to global warming or tectonic activity as plates move up and down during earthquakes. Eustatic and isostatic changes in sea levels leading to submergent or emergent landforms
What are rocky coasts
more resistant geology so steeper cliffs. High energy environment so has more erosion
What are coastal plain landscapes
Low relief land that slopes towards the sea. Can be sandy or estuarine coastlines. Form due to coastal accretion as it’s a low energy environment so more deposition occurs than erosion. Has dunes as well as wetlands and salt marshes due to poor drainage.
What’s the role of dunes
To stabilise coasts and reduce erosion
How do short term factors affect coasts
High or low tides. Destructive or constructive waves, storm events. This causes coasts to retreat or advance depending on rates of deposition and erosion. Can create low or high energy environments
How are estuarine coasts formed
Formed at the mouth and made of and and silt
What are berms
Formed as sand or shingle slowly move up the beach by successive incoming tides. Common in shingle beaches
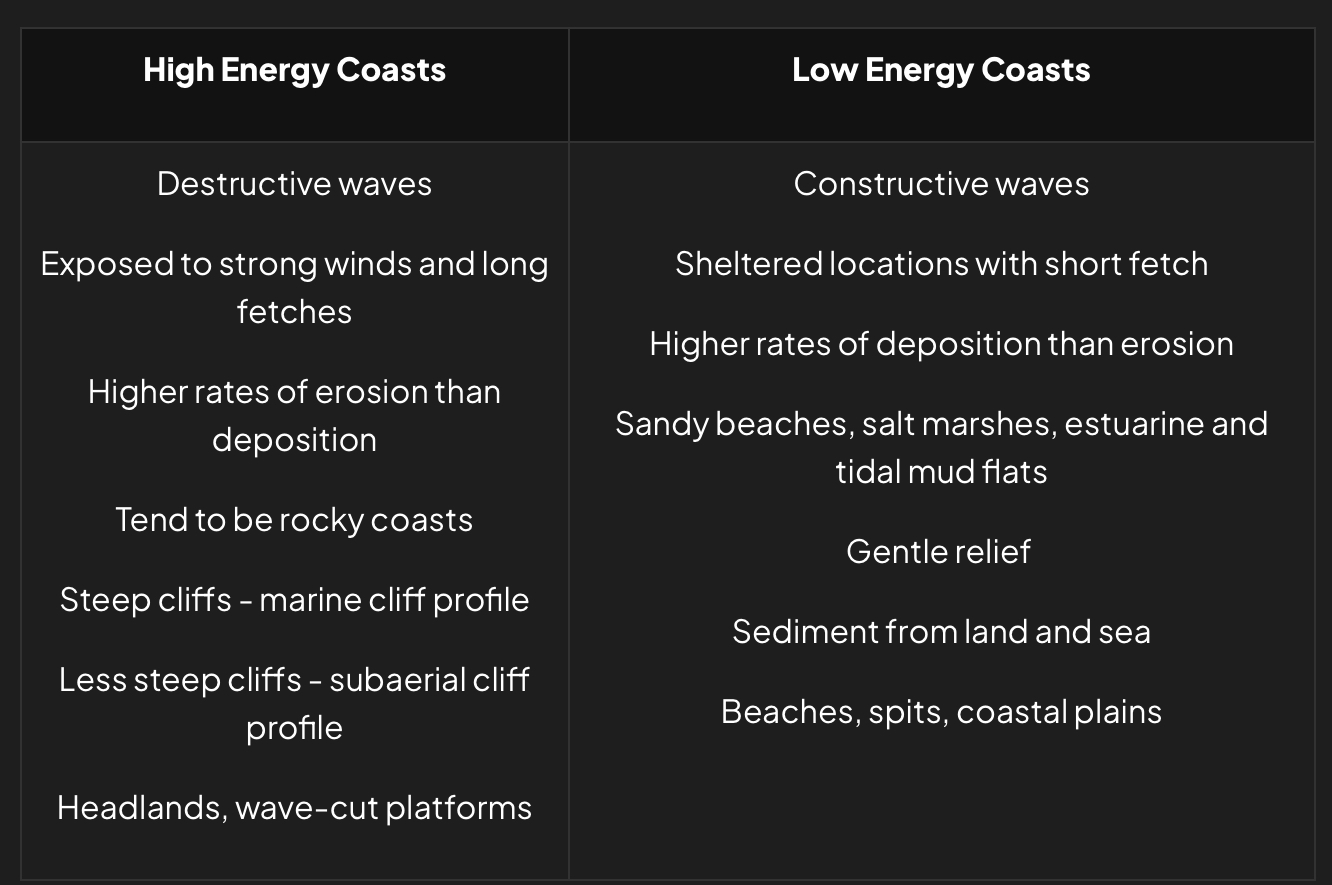
What’s difference between high energy coasts and low energy coasts
What are cusps and how are they formed
Semi circular shapes along a beach formed when outgoing rip current and incoming waves set up nearly circular water movements.
What’s wave refraction
Bending of waves caused by reductions energy. As waves approach they’re refracted so energy is concentrated around bays and can cause coves . Energy decreases as water depth increases.
Classic sediment
Comes from weathering of rock and varies from very small clay particles to sand pebbles and boulders.
Biogenic sediment
Skeletons and sediments of marine organisms
Non cohesive sediment
Larger particles moved grain by grain like sand
Cohesive sediment
Small clay and mud particles bond together
How does sediment move around the UK coast
In sediment cells also known as littoral cells
What’s the difference between weathering and erosion
Erosion- breakdown and movement of rock by water or wind
Weathering is the breakdown in situ of rock( mechanical, chemical and biological
What is mechanical weathering
Or crystallisation . Sea water forced into cracks of rocks by waves. Water evaporates leaving salt behind and so salt crystals grow fracturing rock further and causing it to break down
What’s chemical weathering
Rain is slightly acidic which reacts with weak minerals causing rocks to dissolve and decay limestone and chalk
What’s biological weathering
Vegetation roots grows into cracks of rock and split the rock apart
What’s rock fall
Sudden form of mass movement. Rock fall occurs when fragments of rock weathered from cliff face fall under gravity and collect at base
What’s rotational slumping
Mass movement- bottom of cliff is eroded by waves so slope is steeper and cliff slides downards in rotation. Caused by saturation of rain making it heavier and lubricating it
What’s lithology
Physical properties of a rock such as its resistance to erosion.
Hard rock like granite are resistant to weathering and erosion so erodes at 1mm per year
Soft rock like limestone are more susceptible to erosion and weathering so erodes 2.5mm
What are concordant coastlines
Layers of rocks parallel to coast e.g Lulworth cove. Hard rock like limestone acts as a barrier for soft rock like clay so erosion is slow but if there’s a fault marine processes take place exposing soft rock. Eroding of soft rock occurs until another band of hard rock is reached, this creates a circular shadow in coastline called a COVE
What’s discordant coastline
Layers of rock are perpendicular to coast e.g Swanage bay
Different types of rocks exposed to marine processes at same time but soft rock will erode faster. Differential erosion creates headlands where rock is more resistant and bays where it’s less resistant. Waves refract and energy is focused on ends of headlands creating caves arch stack and stumps with wave cut notches and platforms
What are examples of concordant coastlines
Dalmatian and haff coastlines as well as lulworth cove in Dorset UK
Formation of Dalmatian coast
Concordant coastline Found in Croatia. Formed by tectonic activity and sea level rise. Tectonic activity created anticlines which are upward folds in rock strata and sync lines that are downward folds on rock strata. Sea level rise in devensian glacial period flooded synclines so anticlines only emerge out of water. Resulted in islands running parallel to coast.
Formation of Haff coast
Created by deposition of unconsolidated material. Melted ice sheets deposited thick layers of gravel on tundra plains. As sea levels rose constructive waves pushed sediment landwards. Sand or gravel ridges formed across bays and river mouth trapping river water behind them creating lagoons. Formed along Baltic coastline
Micro features
Rock formation and tectonics leads to anomalies forming within rocks, creating areas of weaknesses leading to more rapid erosion and weathering, like joints folding and faults
What are joints
Micro feature- vertical cracks caused by tectonic movement and contraction
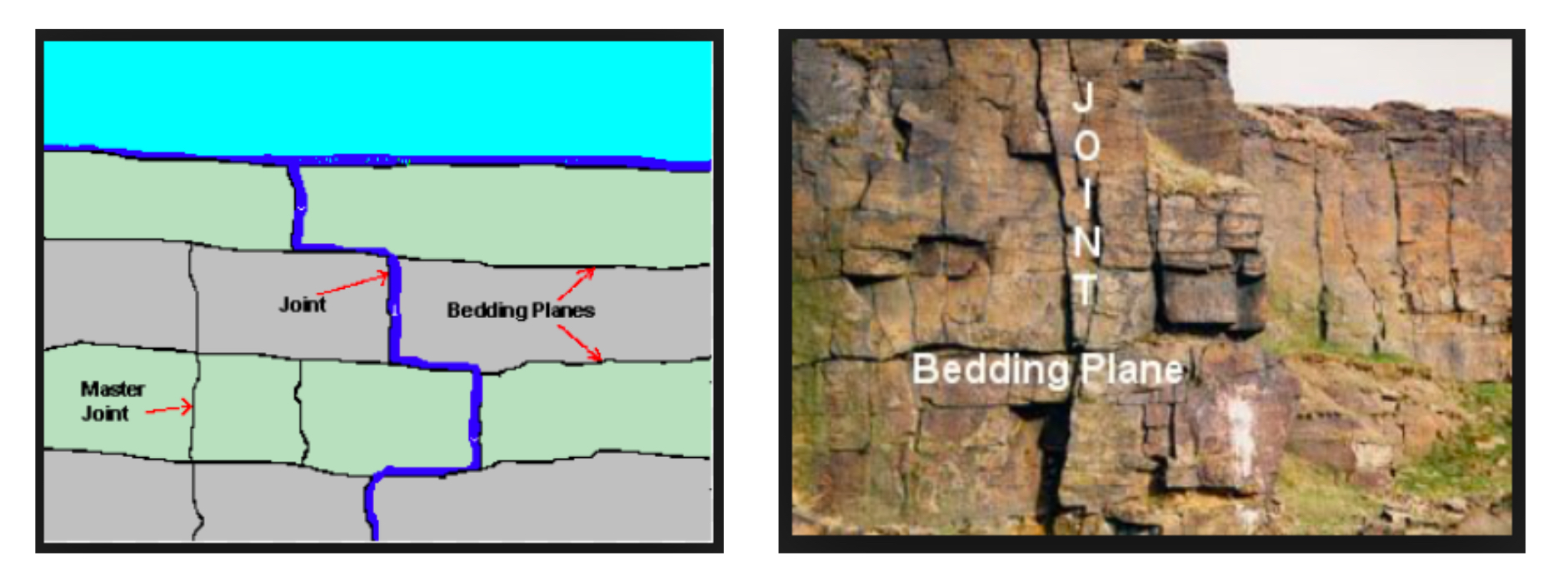
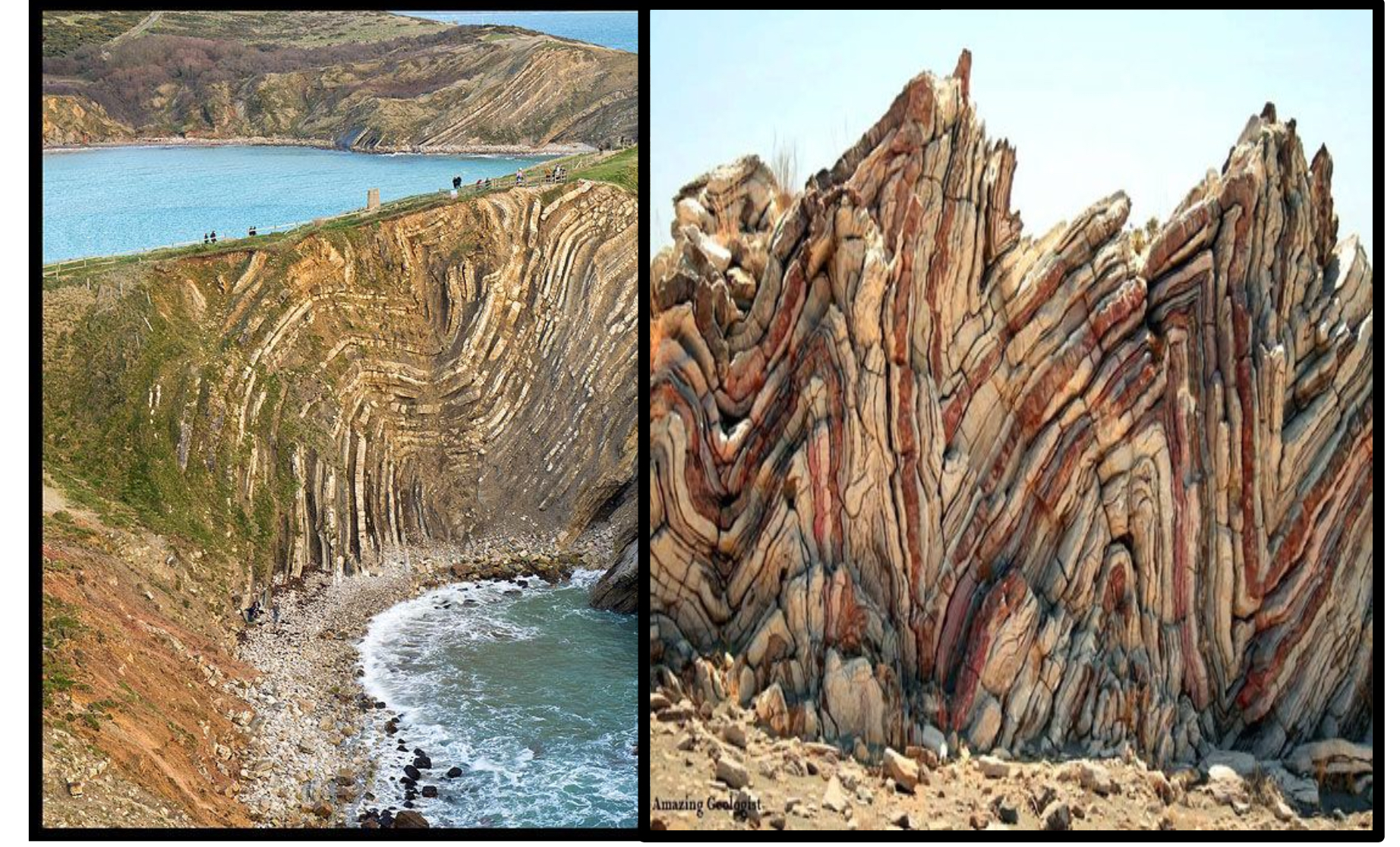
What are folding
Micro feature- rocks under pressure due to tectonic movement and becomes folded without breaking

What are faults
Micro feature -pressure fractures rocks and is very sudden and causes earthquakes.
What effect does micro features have on coastal topography ( arrangement of an area)
Affects weathering and erosion rates and thus cliff profiles
What are cliff profiles
The angle and height of the cliff face including any features and is dependent on lithology.
What are three types of cliff profiles?
Uniform horizontal layers of rocks
Rocks dip gently seaward with near vertical joins
Rocks dip inland so steep stable cliff
What is coastal recession
It is the rate of recession which is the speed at which the coastline is moving inward. Mainly caused by lithology.
What are igneous rocks?
Slowest erosion rate with 0.1cm a year.
Crystalline structure interlocking so more resistant.
Fewer joints.
E.g granite basalt, dole rite
What are metamorphic- foliated rocks
Slow erosion rate with 0.1-3cm a year.
Causes folation when crystals rearrange and line up facing the same direction
Often folded and fractured creating faults.
E,g Slate, shale, Schist
What are metamorphic-non foliated rocks
Slow erosion rate with 0.1-3cm . Metamorphism causes grains to recrystallise into a very solid interlocking network. These rocks are resistant and again folding and faulting makes them less resistant than igneous rocks
What are sedimentary rocks
Fast erosion rates with 5-10cm a year. Most are clastic(made up of broken pieces of older rocks). Younger rocks weaker than older because they haven’t been compressed long enough so more reactive . Bedding planes and joints make them even more vulnerable to recession e.g. sandstone, limestone, clay
Types of lithology- unconsolidated material
Sediment has been cemented to make solid rock(lithification)
Types of lithology- pore water pressure
Internal force within cliffs exerted by groundwater within them(in interstitial gaps). Pores affect how permeable a rock is
What does periglacial mean
Periglacial areas are next to glaciers. If still cold they have permafrost making cliffs resistant. If ice has retreated the me,ted water will wash unsourced material on land
What’s continuous permafrost
Coldest region. 1500m depth, no melting of surface layer. E.g Siberia
What’s discontinuous permafrost
Surface layer melt in summer which is the active layer so lots of water is released. Slightly warmer region like in north Canada. 20-30m deep.
what’s sporadic permafrost
0 degrees. Isolated spot. Cold and minimal thawing.
What are coastal vegetation
They act as stabilisers and roots bind sediments together.
What are submerged plants and surface level plants
Submerged plants are protective layers against moving water. Surface level plants are plants protecting sediment from erosion of wind. They are protected by sand dunes,salt marshes, coral reefs, mangroves.
Plant adaptation- halophytes
Salt tolerant e.g mangroves grown in water
Plant adaptation- xerophytes
Drought tolerant- salt water is drying and sand doesn’t retain water. E.g marram grass
Plant adaptation- Psammophytes
Grown in wind blown sand, tolerates dry salty conditions and being buried e.g sea holly
Key concepts for plant communities
Plant succession-changing structure of a plant community over time as bare sediment is colonised . Each step in change is called a serial change
Zonation- how ecosystems change spatially away from the shoreline
Pioneer species- first hardy species to colonise areas of exposed sediment
Climax communities- final stage of succession with greatest biodiversity.e.g woodlands in uk
What are sand dunes and where are they found
Sand mounds formed by wind blowing wind over each other
What are salt marshes
Low energy environment. Tides and rivers bringing sediment in and out and as small particles are deposited they stick together. These sediments are then colonised by algae ,pioneer species .
What are waves
Friction between wind and water. Energy from wind transferred to water
What factors impact size of wave
Wind strength, fetch, water depth, time of wind blowing
Wave period
Time taken for two crests to pass a given point
What’s the wavelength
It’s the product of waves velocity and period
How are waves formed
At sea waves move in circular motion ,energy moves not water,
When water is deep, there’s very little motion
When the sea gets shallow, wavelength shorten and friction slows base of wave but the top moves faster
The water now moves in elliptical motion
This makes the water move to shore so wave breaks
Difference between constructive and destructive waves
Why do constructive waves encourage deposition
Long wavelengths and low frequency which prevents erosion as no sediment is taken into sea.Lack of a breaker component so waves spill and move up a beach to deposit materials. Weak backswash and suppressed wave gradient means no sediment is carried into sea
Why do destructive waves encourage erosion
Short wavelength and high frequency leads to erosion of sediment in sea because there’s more water to transport. Has a breaker so plunges at beach when a height is reached so they don’t travel up a beach.
What’s the seasonal variation of beaches
In winter, with rough weather, sand is stored offshore
In summer with calmer weather sand is stored at the beach
How are wave cut notches and wave cut platforms formed
Waves break at foot of cliff so eroding it, creating a wave cut notch. The rock above notch becomes unstable and collapses. Attrition and transportation removes rock debris.The cliff retreats leaving behind a wave cut platform
How are arches formed
2 caves next to each other on headland join as erosion widens the base.
How are stacks and stumps formed
Arches collapse leaving isolated pillars of rocks which are eroded further into stumps
How are caves formed
Joints faults eroded by hydraulic action and abrasion. Blowhole made when overlapping rock is collapsed and cave opens at ground level.
Define beach morphology
Profile of the beach(steep/shallow slope) concerned with the movement of sediment caused by wave action
What’s the beach morphology of summer and winter beaches FINISH WITH PPT
Summer: low energy constructive waves, steep beach angle, large particles at back of beach. Berm ridges
Two types of deposition
Flocculations- smallest sediment like clay stick together so they become heavy enough to sink. Last to sink
Gravity setting- heaviest largest sediments deposited first
What are the impacts of seasonal change on beach morphology
Creates summer or winter profiles due to variations of wave activity.
Sediment is dragged offshore by destructive waves in winter and returned by constructive waves in summer. Summer as steeper slopes than winter.
Define beach profiles and what are they dependent on?
Landscape of beach both and below water. Describes distribution, shape, size, type of sediment deposited. They are dependent on distance from shoreline
what’s the significance of distance from the shoreline in beach profiles
Fine shingle particles along drift aligned beaches are carried away by LSD so becomes rounded as they move
Where are coastal deposition found at and what causes them
Occurs in low energy environments so have reduced effects of waves ,tides and currents.
They are caused by waves losing energy as they slow down so dropping sediment
How does erosion and deposition occur with waves
Moves sediment up and down the beach in the direction of wind(LSD)
How does erosion and deposition occur with tides
Determines where erosion takes place
How does erosion and deposition occur with rip currents s
Takes sediment from offshore to nearshore
How does erosion and deposition occur with other currents
Takes sediment from offshore to onshore or vice versa
Define Longshore drift and the factors affecting it
Movement of material along a coast by waves which approach at an angle to the shore but recede directly away from it. Factors: geology, rivers, tides, simonant wint, prevailing wind(most common wind), shape of coastline- refraction, man made obstacles(sea defenses)
How does the greatest rate of LSD occur
When waves approach coast at 30 degrees angle.
How does swans and backswash work in LSD
Awash carries material up beach in direction of wind and backswash carries sediment back to the sea at right angles