molecular bio exam 4 ch.10
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
what are restriction enzymes?
they cleave DNA at specific nucleotide sequences. different bacterial species produce different restriction enzymes
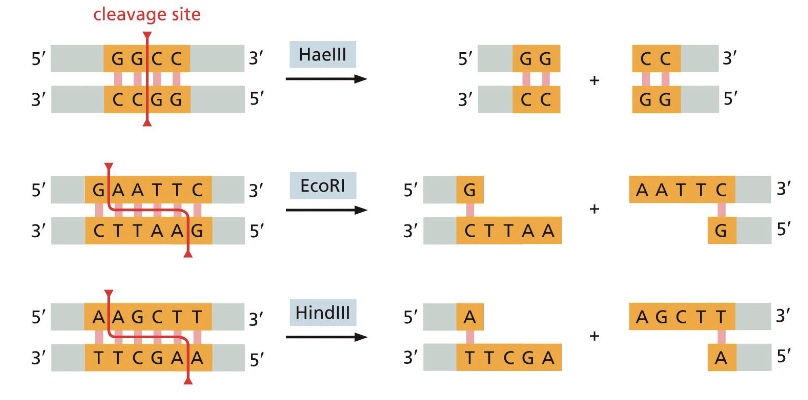
what sequences do restriction enzymes target?
short sequences of 4-8 nucleotides, sites of cleavage will occur by chance

label the following:
negative electrode
positive electrode
smallest and largest band
where is the propidium iodine added
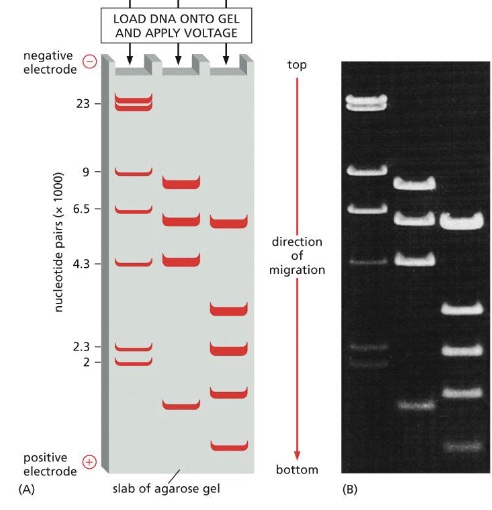
how does gel electrophoresis work?
a mixture of DNA fragments is loaded at one end
a voltage is applied
after several hours the DNA fragments become separated according to size
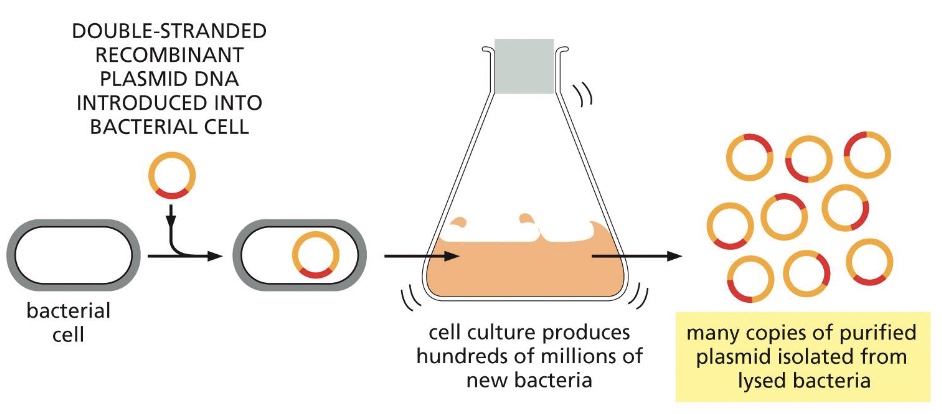
what is transformation?
process by which cells take up exogenous DNA molecules from their surroundings and express genes present on that DNA. It requires competent bacteria
how do you introduce plasmid into bacteria to be amplified?
These transformed bacteria are then suspended in a nutrient rich broth and allowed to proliferate to subsequently isolate the plasmid DNA from million of bacteria
what is hybridization?
experimental technique in which two complementary nucleic acid strands come together and form hydrogen bonds to produce a double strand. This technique is to detect specific nucleotide sequences in either DNA or RNA
what does dideoxy sequencing (Sanger sequencing) require?
Primer (only one!!)
Normal dNTPs
DNA polymerase
Special chain-terminating nucleotides, ddNTPs
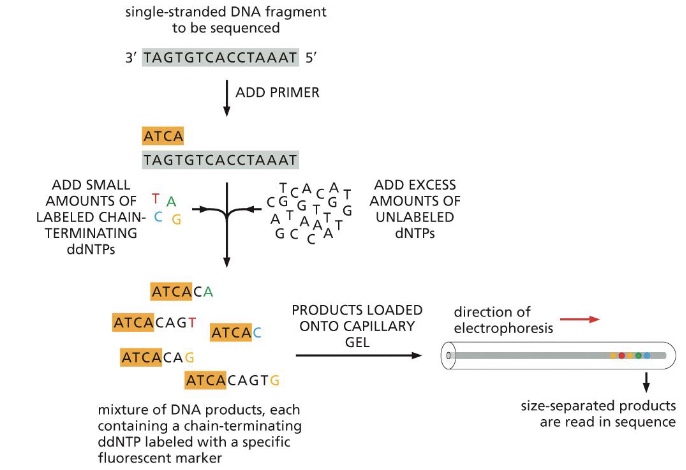
what is dideoxy sequencing (Sanger sequencing)?
Standard method of DNA sequencing
- Produce a collection of different DNA copies that terminate at every position in the original DNA sequence
- The product is run through a capillary gel
- Detector records fluorescence
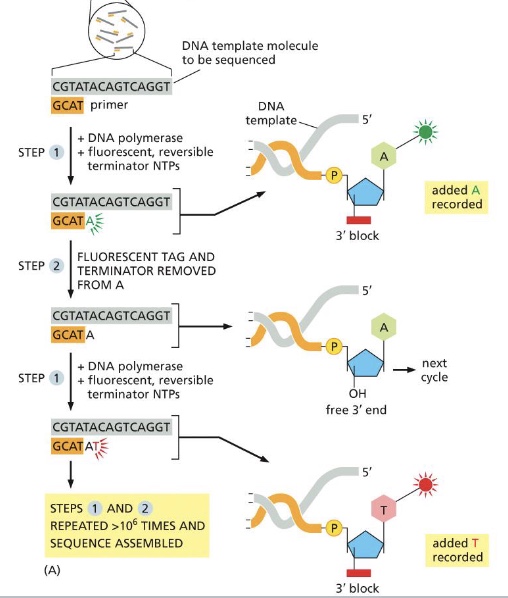
what is illumina sequencing?
is based on the basic principles of automated dideoxy sequencing. A genome or other large DNA sample of interest is broken into millions of short fragments. these fragments are attached to a glass surface and amplified by PCR
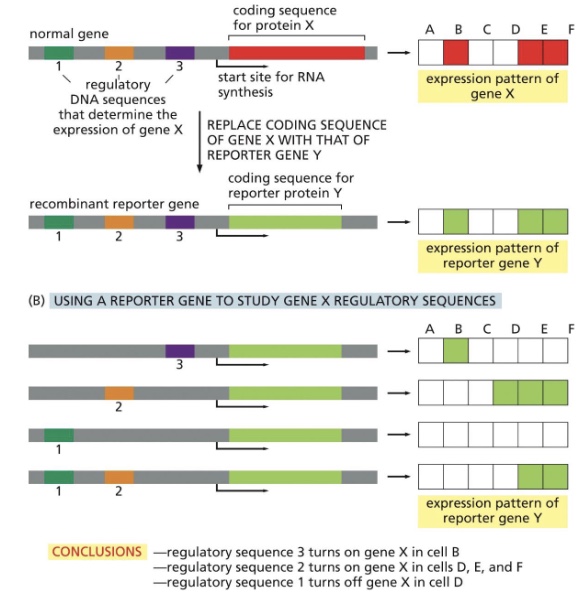
what is a reporter gene?
gene encoding a protein whose activity is easy to monitor experimentally (fluorescence of enzymatic activity). It is used to study the expression pattern of a target gene or the location of its protein product
what are examples of loss of function studies?
RNA interference (RNAi)
CRISPR knockout
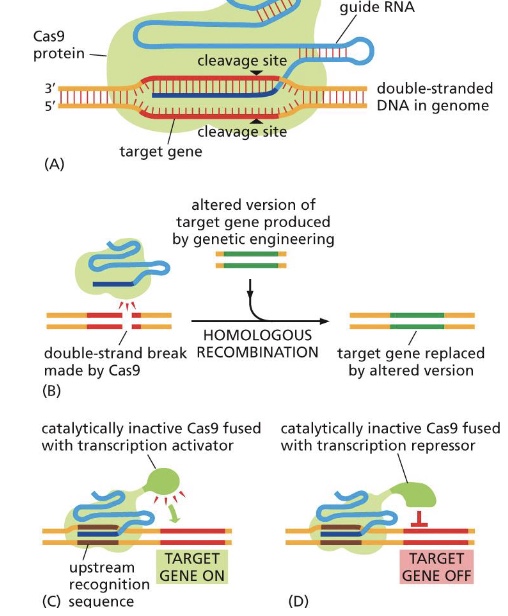
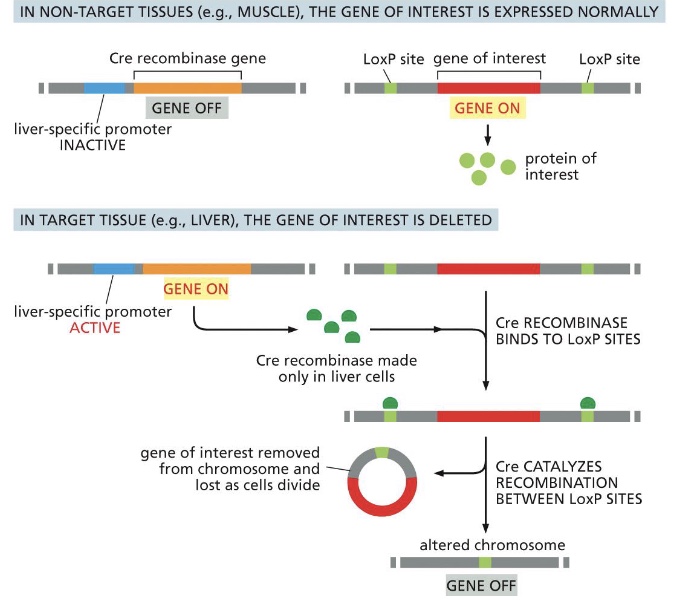
what is a conditional knockout?
a gene can be selectively disabled in a particular target tissue
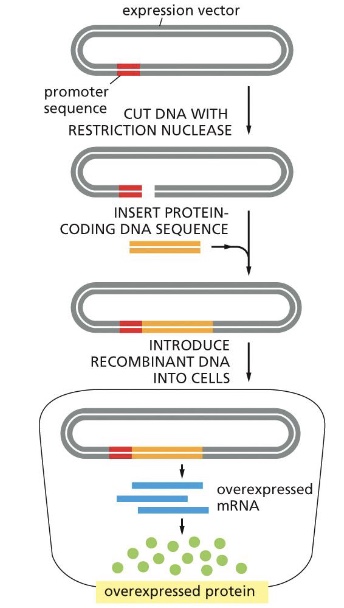
how can rare proteins be made in large amounts?
Large amounts of a protein can be produced from a protein-coding DNA sequence inserted into an expression vector (=expression plasmid) and introduced into cells. This technology is now used to make large amounts of many medically useful proteins, including hormones such as insulin or viral proteins for vaccines. Also for structural studies