P6: Molecules and matter
1/77
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
78 Terms
States of matter
Solid
Liquid
Gas
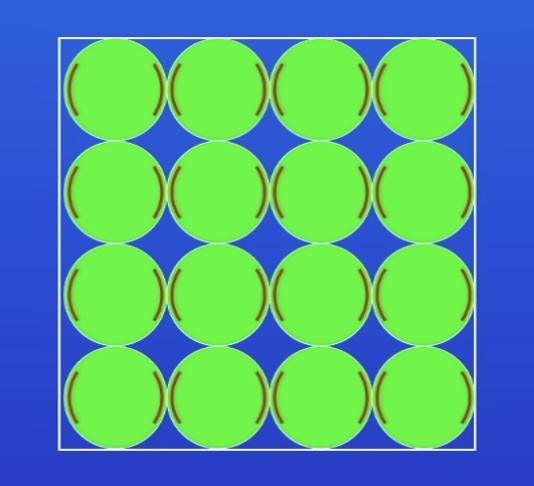
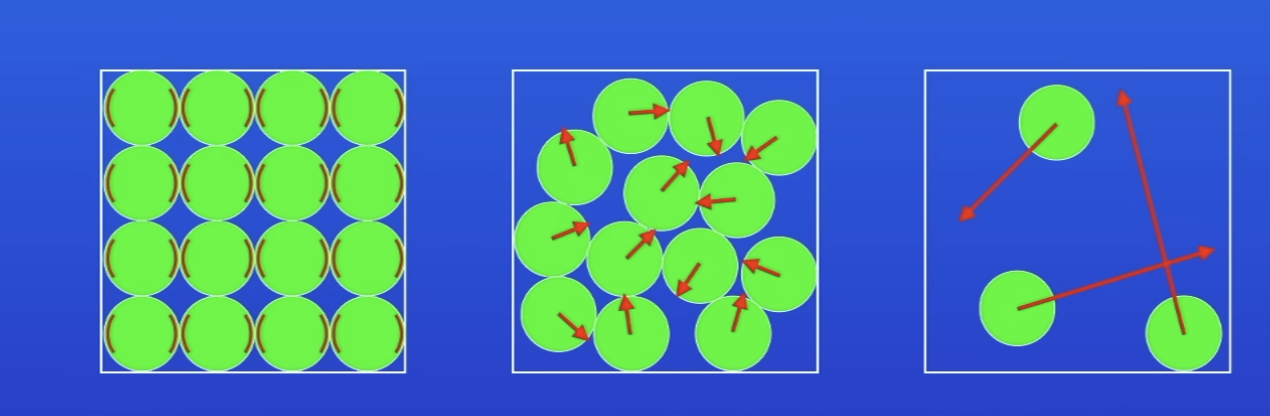
Arrangement of particles in a solid
V close tog
Arranged in regular pattern
Vibrate, but don’t move from place to place
Arrangement of particles in a liquid
Close tog
Not arranged in regular pattern
Move around each other
Arrangement of particles in a gas
V far apart
Not arranged in any pattern
Moving v rapidly
Density
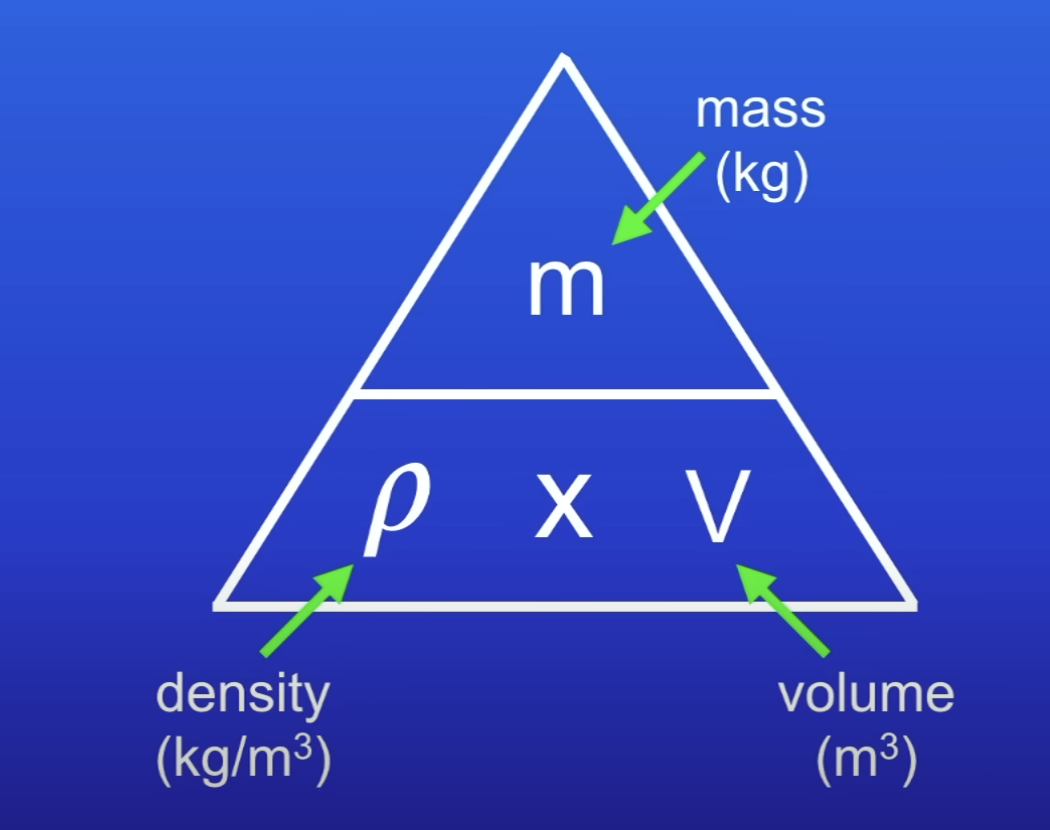
Mass per unit volume of a material
Density equation
Mass / volume
kg / m3
Density of solid, liquid, gas
Solid- v high
Liquid- high
Gas- low
Why do solids have a v high density?
Particles packed close tog → lot of mass per unit vol
Why do liquids have a high density?
Particles close tog → lot of mass per unit vol
Why do gases have a low density?
Particles v far apart → small mass per unit vol
What is unusual about polystyrene and why?
Solid, but has low density
Full of air spaces → small mass for vol
When will objects float in a liquid?
If object has density less than density of liquid
How to measure density of a solid object or liquid?
Measure its mass
Measure its vol
Use density equation
What type of change is changes of state?
Physical changes
Why are changes of state physical changes, not chemical?
Material recovers its original properties if the change is reversed
+ no new substances produced
When do substances change state?
Put in / remove energy
Heat / cool
Law of conservation of mass for change of state
When substances change state mass is conserved
Changes of state
Melt- S→L
Freeze- L→S
Boil- L→G
Evaporate- L→G
Condense- G→L
Sublimate- S→G
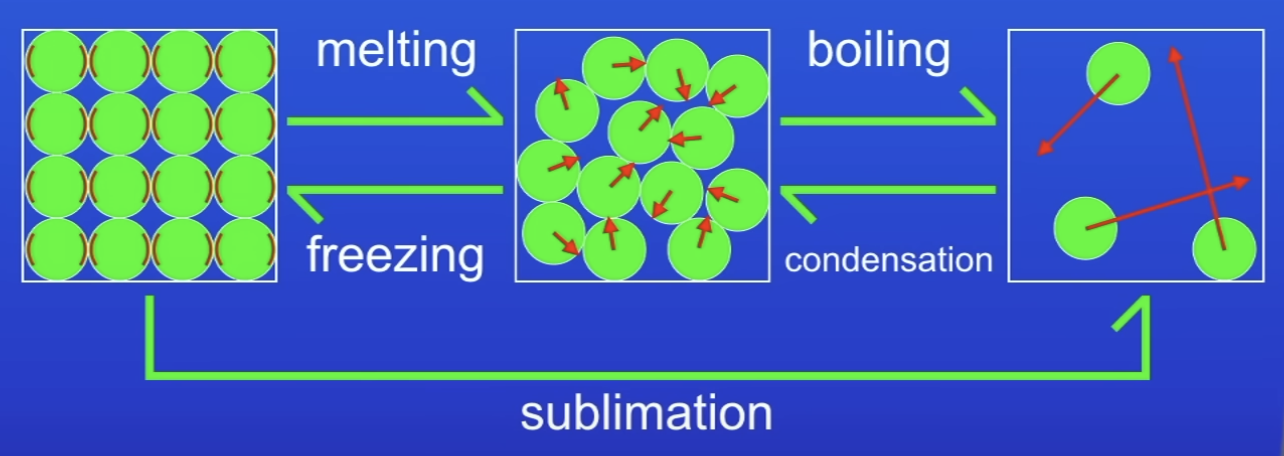
In which state do particles have most energy?
Gas
How do you know all particles have kinetic energy?
Particles in:
S: vibrate
L: move around each other
G: move v rapidly
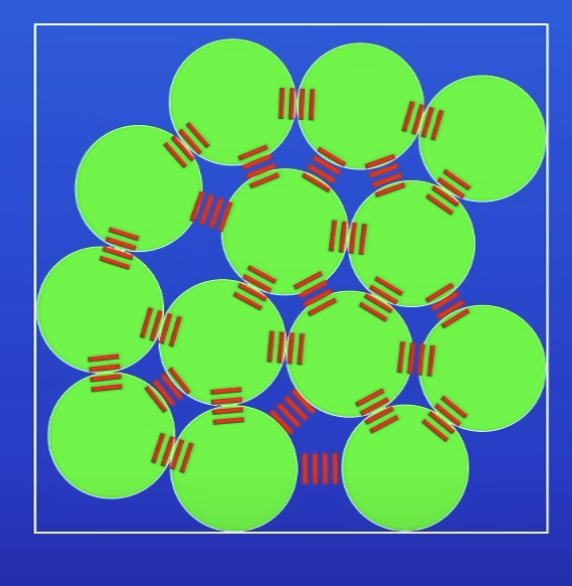
How are particles held tog?
Intermolecular forces
How are molecules held tog?
Chemical bonds
How do you know particles have potential energy?
They have:
IF or chemical bonds betw them
Internal energy
Energy is stored in a system by the particles (atoms and molecules) that make up the system
What makes up internal energy?
Total kinetic + potential energy of all the particles that make up a system
What happens to IE if you heat a substance?
Increase IE
What happens to IE if you cool a substance?
Decrease IE
Explain changes to state in terms of increasing IE
Heat solid, increase IE
At MP, solid melts into liquid
Heat liquid, increase IE
At BP, liquid boils to gas
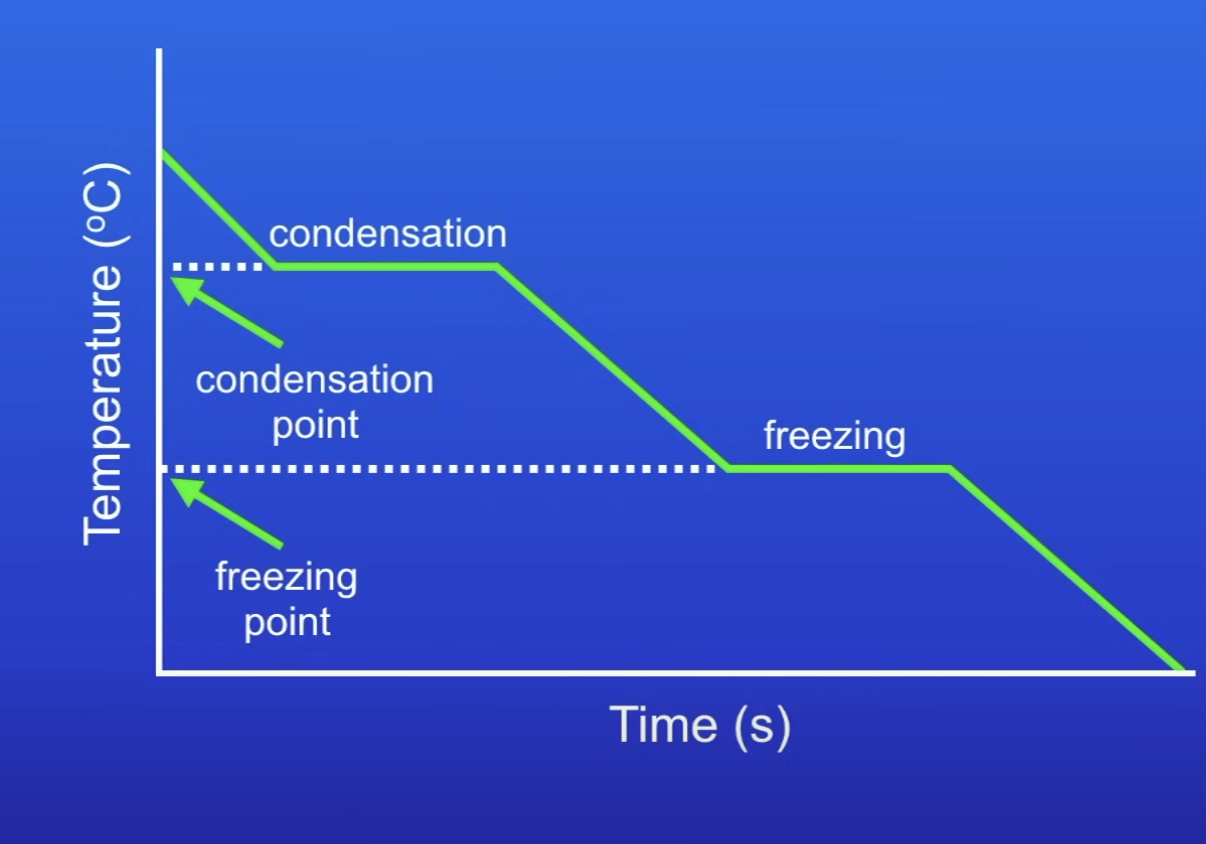
Explain changes to state in terms of decreasing IE
Cool gas, reduce IE
At BP, gas condenses to liquid
Cool liquid, reduce IE
At MP, liquid freezes to solid
Sublimation
When solid turns directly to a gas
Evaporation
When liquid turns to gas, but only on the surface of the liquid
Why does evaporation only occur on the surface of the liquid?
Only particles on the surface have enough energy to turn into a gas
How does heating affect the energy stored within the system?
Changes energy stored by increasing the energy of the particles that make up the system
What does heating a substance do?
Raises temp of the system
Produces a change of state
Specific heat capacity
Amt of energy needed to raise the temp of 1kg of the substance by 1°C
Specific heat capacity equation
∆ E = m c ∆ θ
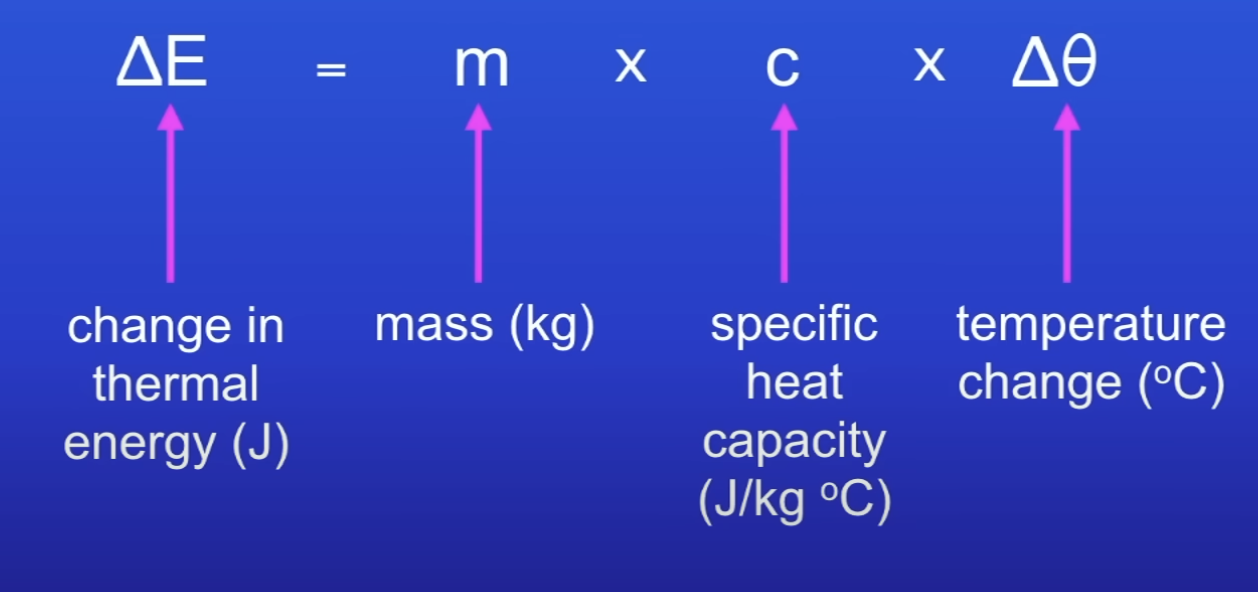
If the temp of the system increases, what does the increase in temp depend on?
Mass of substance heated
Type of material
The energy input to the system
What is the internal energy of a substance due to?
KE- due to particles movement
PE- due to forces betw particles + bonds betw atoms in molecules
During a change of state, why does is there a horizontal line?
Energy put in weakens / breaks FoA betw particles
IE of system increases
NOT changing temp
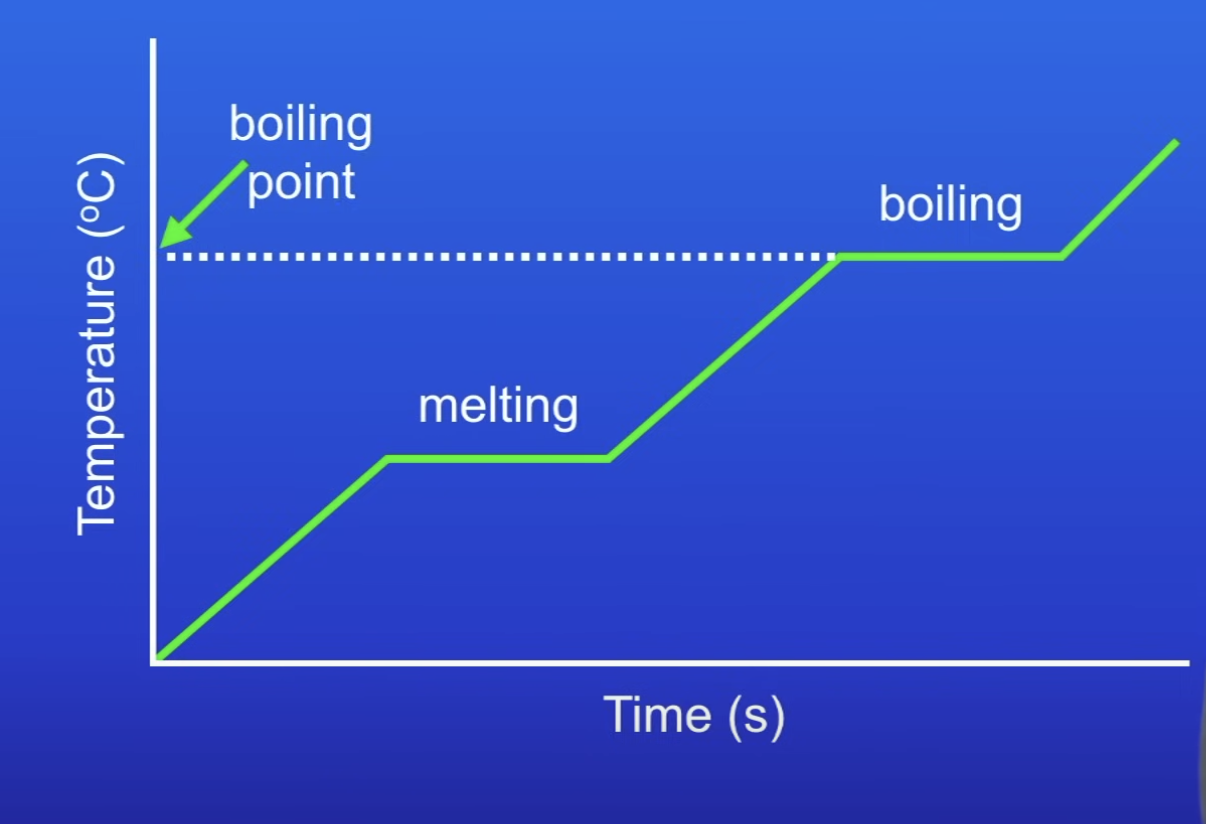
Heating graph
Cooling graph
On a heating graph, what happens when you heat a substance?
Increase temp, as we r increasing energy of particles
Boiling vs evaporation
B: occurs thru out a liquid at BP
L: occurs only on surface of liquid, below BP
Latent heat
Energy needed for a substance to change state
Increasing the temp of a substance…
Increases its IE
What varies betw SLG?
Strength of FoA
What affects the MP + BP of a substance?
Impurities
What happens when a change of state occurs?
The energy supplied changes the energy stored (internal energy) but not the temp
What happens to temp during a change of state?
Stops increasing
Stays constant
Why is temp constant during a change of state?
Energy put in weakens / breaks FoA betw particles
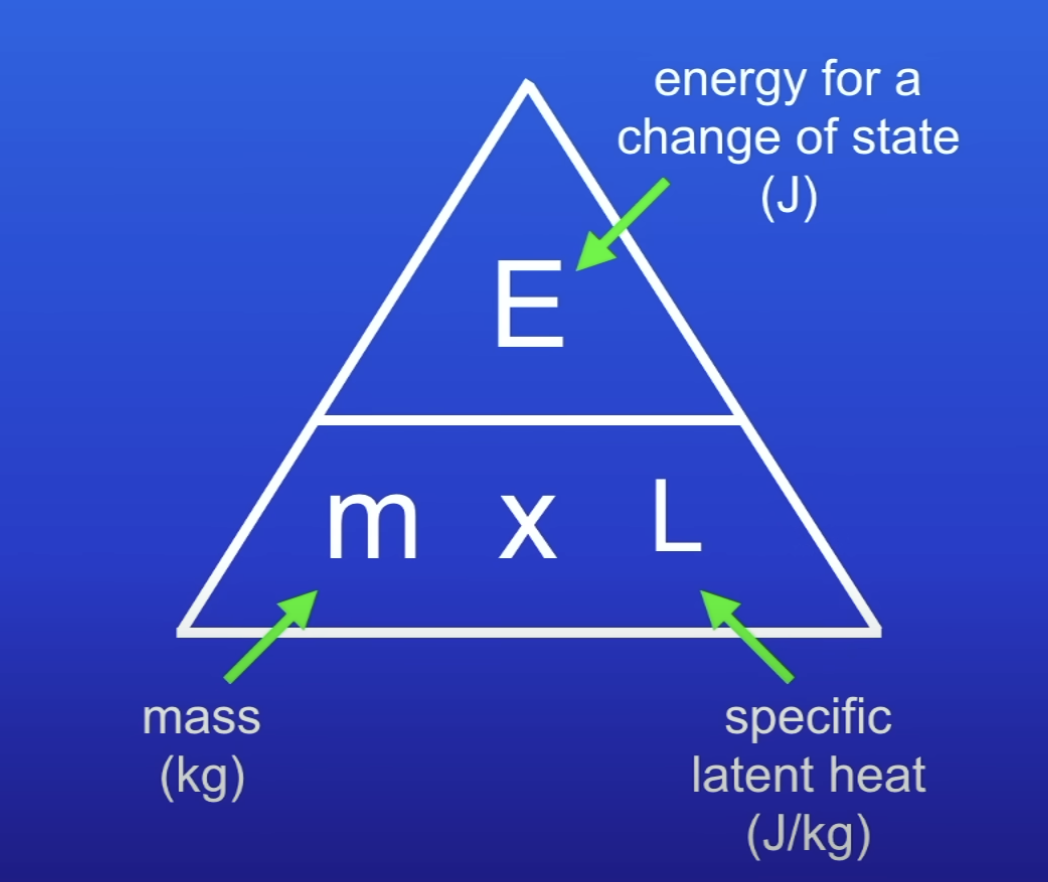
Specific latent heat
Amt of energy needed to change the state of 1kg of the substance with no change in temp
Specific latent heat of fusion
Amt of energy needed to change 1kg of substance from solid to liquid with no change in temp
Specific latent heat of vaporisation
Amt of energy needed to change 1kg of substance from liquid to vapour with no change in temp
Energy for a change of state equation
E = m L
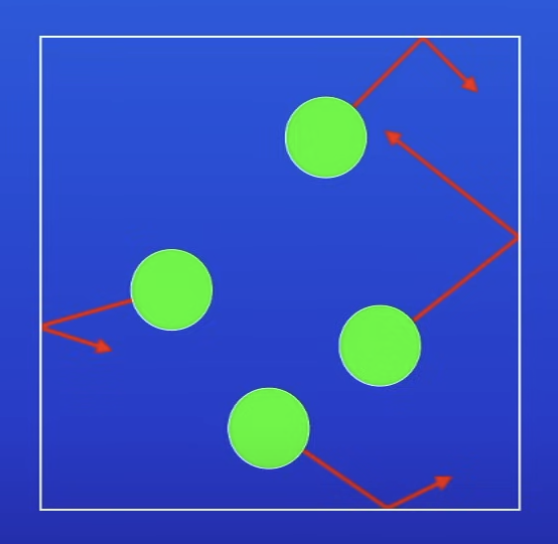
Particles in a gas are in?
Constant random motion
v far apart
What is the pressure of a gas caused by?
Particles colliding w the walls of the container that the gas is held in
How to increase the pressure of a gas?
Increase the:
No. of collisions per second
Energy of each collision
What does increasing the no. of collisions per s + energy of each collision do in a gas?
Increase temp
How to change pressure exerted by a gas?
Change temp of gas
Temperature of a gas
Average KE of particles
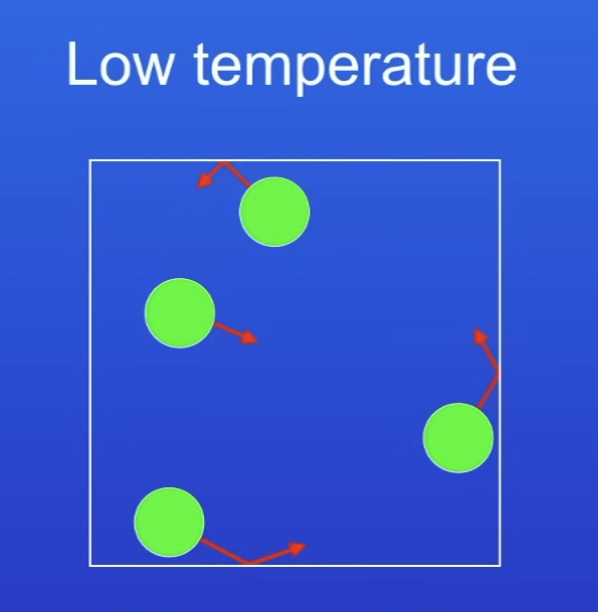
Pressure of gases at low temp + why?
Low pressure
Low temp → particles have lower KE
So fewer collisions per s
+ lower energy collisions
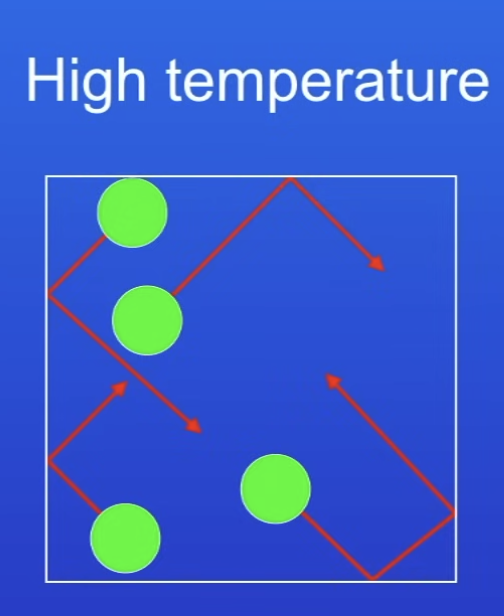
Pressure of gases at high temp + why?
High pressure
High temp → particles have higher KE
So more collisions per s
+ higher energy collisions
Relation between the temp of a gas + its pressure at constant volume
Increasing temp → increases pressure, bc”
Increase temp → particles have more KE
→ more collisions per s
+ higher energy collisions
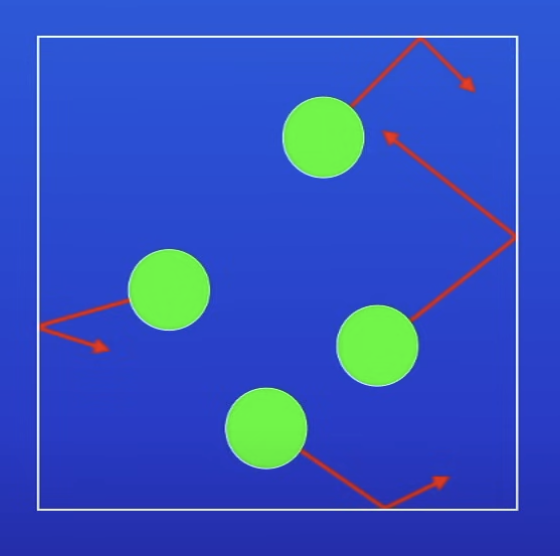
What do particle collisions cause?
A force that acts at right angles to the walls of the gas container → causes gas pressure
How does this force that acts at right angles to the walls of the container cause gas pressure?
When the force acts over an area of the contained
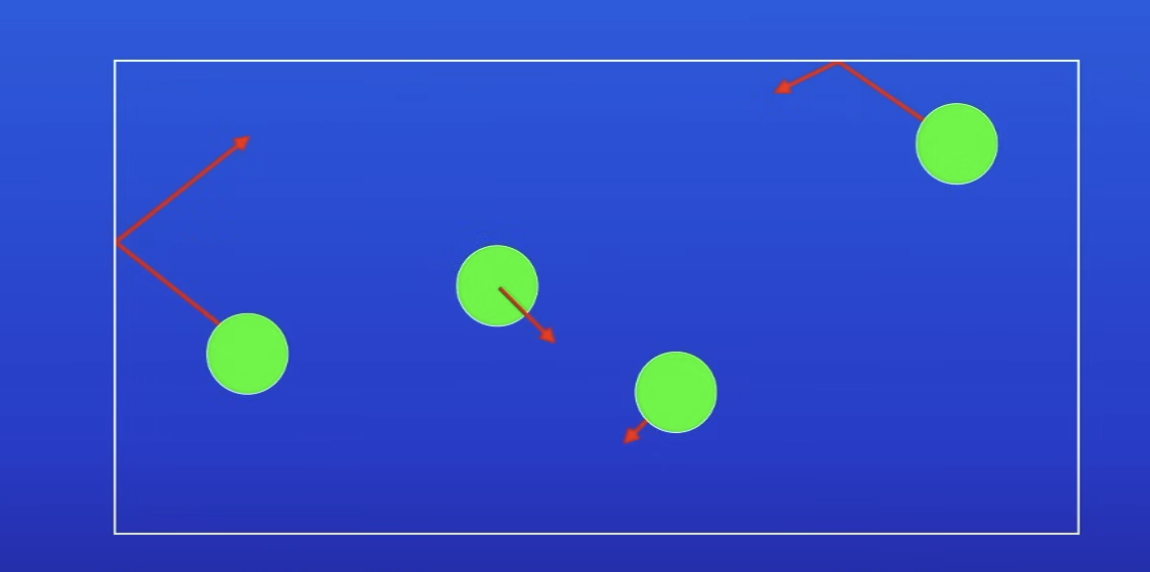

What does increasing vol of a container (temp constant) do to gas pressure?
Decrease pressure
Why does increasing vol cause a decrease in gas pressure?
Increased space betw particles
So particles travel much further b4 colliding w walls of the container
So less no. of collisions per s betw particles + walls of the container
Relationship of pressure of gas to volume?
Pressure of a gas inversely proportional to volume
What does it mean if pressure of a gas is inversely proportional to volume?
Vol increases → pressure decreases
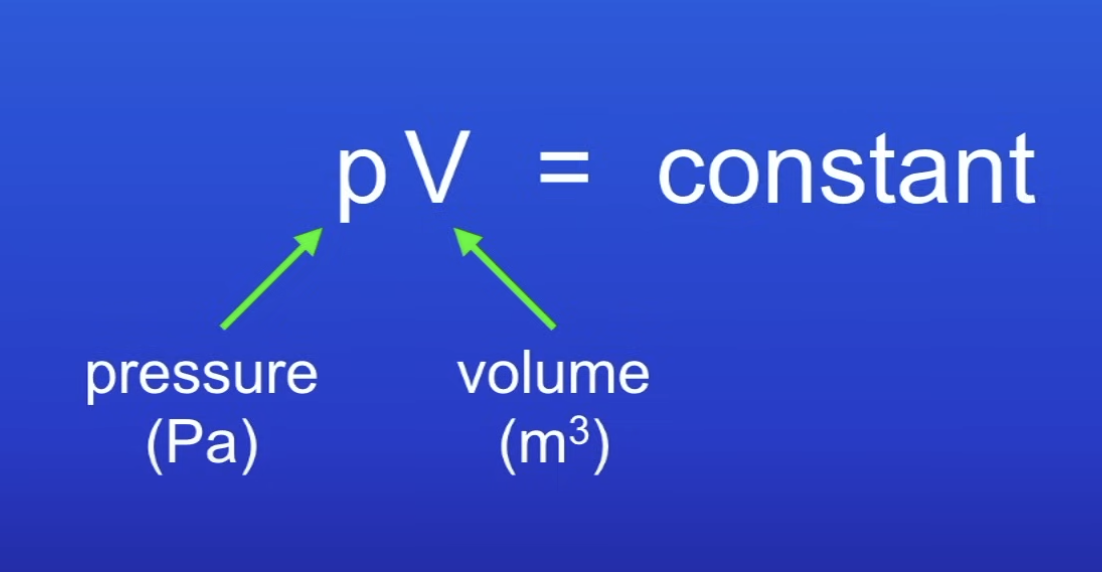
For a fixed mass of gas held at a constant temp:
pressure × volume = constant
p1V1=p2V2
What do pressure changes cause?
A gas to be compressed / expanded
What does pressure produce?
A net force at right angles to the wall of the gas container (or any surface)
Work
Transfer of energy by a force
What does doing work on an enclosed gas do?
Increases the internal energy of the gas
What does increases IE of a gas by doing work on it cause + why?
Increase in temp of the gas
Bc KE of gas particles increased
+ temp= avg KE of particles
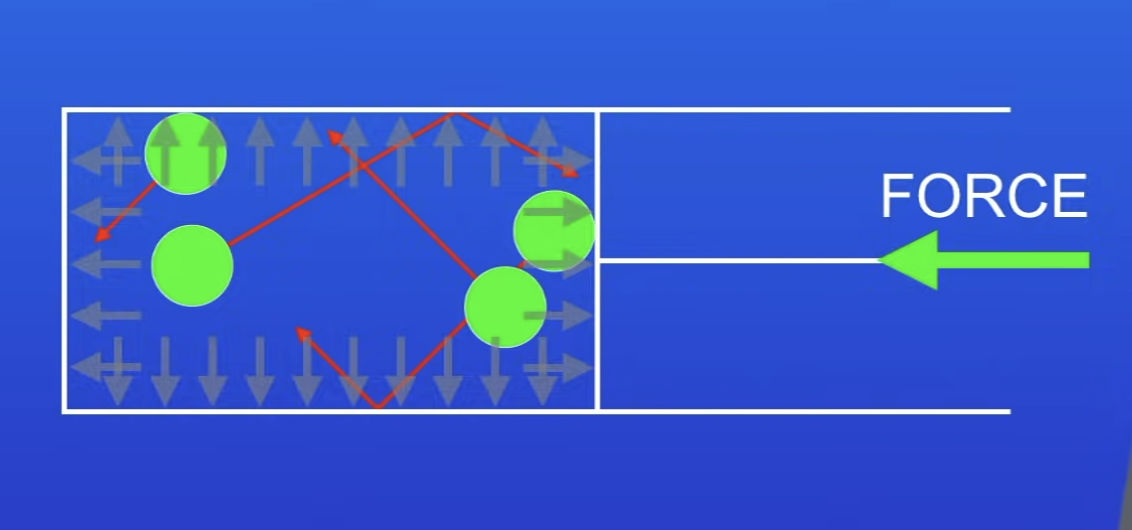
To compress a gas, what must be done?
Work
Why does compressing a gas increase its IE?
Carried out work
Applied a force to the gas
So ET to gas particles
Why do bicycle pumps get warm when inflating a tyre?
Work done on the gas → we increase its IE