Cell Growth, Division, and Differentiation Processes
1/156
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
157 Terms
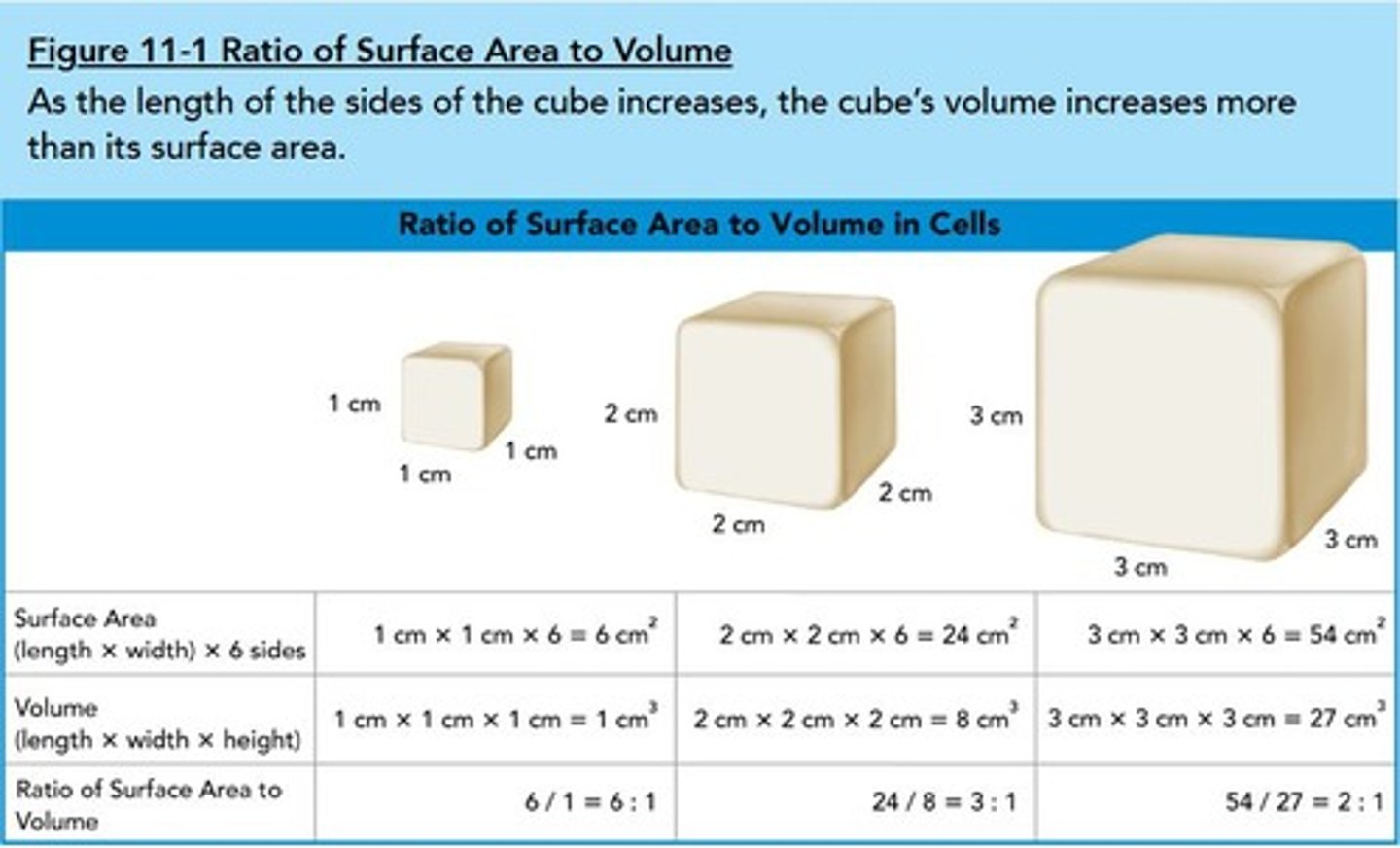
Cell Size Efficiency
Larger cells are less efficient in transport.
Surface Area
Determines nutrient intake and waste removal rate.
Cell Volume
Affects oxygen usage and waste production.
Surface Area to Volume Ratio
Critical for efficient cellular function.
Information Overload
Occurs when DNA cannot meet cellular demands.
Cell Division
Process where a cell replicates DNA and splits.
Asexual Reproduction
Genetically identical offspring from one parent.
Binary Fission
Single parent produces identical offspring.

Budding
Offspring grows off parent cell.
Vegetative Propagation
Budding process in plants.
Sexual Reproduction
Fusion of reproductive cells from two parents.
Chromosomes
DNA bundles that organize genetic material.
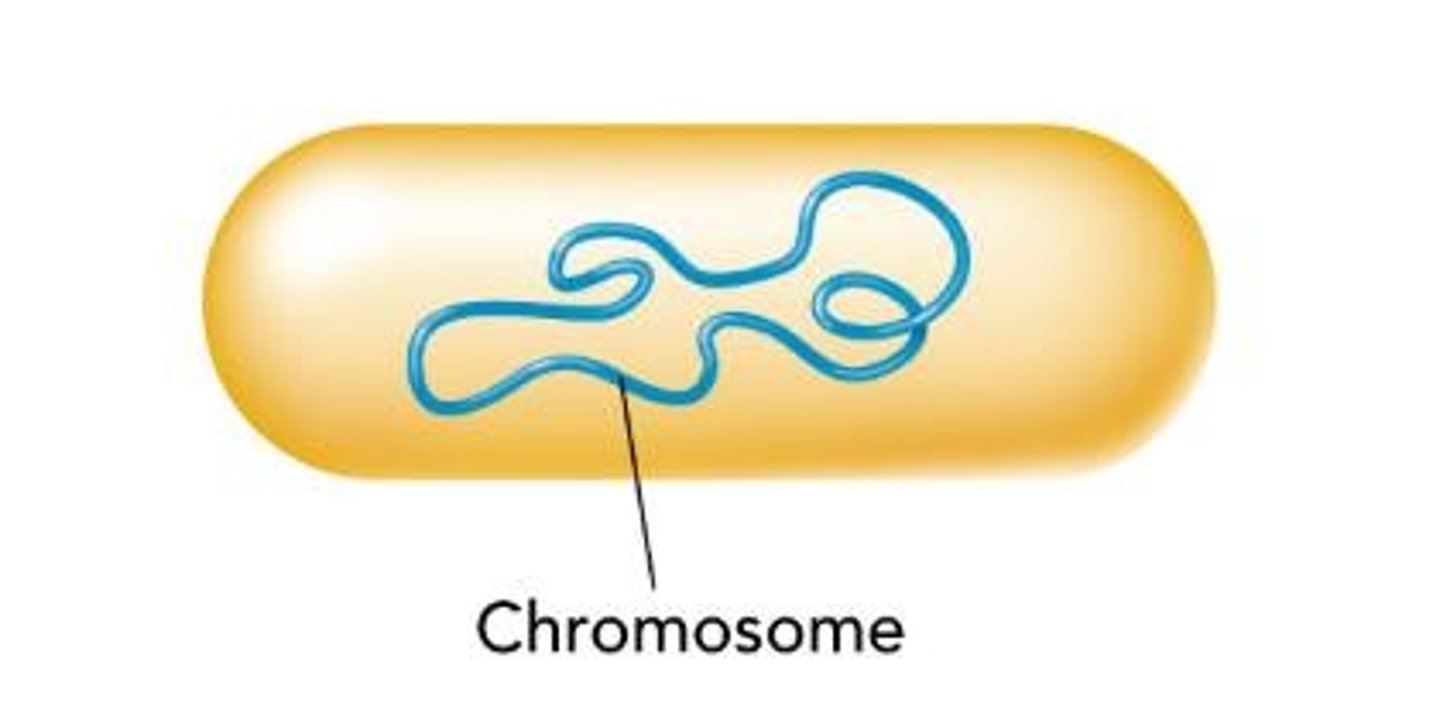
Prokaryotic DNA
Single circular chromosome in cytoplasm.
Eukaryotic DNA
Multiple chromosomes tightly bound to histones.
Histones
Proteins that package and order DNA.
Chromatin
Complex of DNA and proteins in eukaryotes.
Cell Membrane
Barrier for nutrient and waste exchange.
Cell Growth Limitations
Cells must divide to maintain efficiency.
Nucleotide
Building blocks of DNA storing genetic information.
Daughter Cells
Result of cell division, more efficient.
Cellular Transport
Movement of materials across cell membrane.
Cellular Efficiency
Dependent on size and surface area.
Cellular Demands
Increased as cell size increases.
Nucleosome
DNA wrapped around 8 histones forming a bead-like structure.
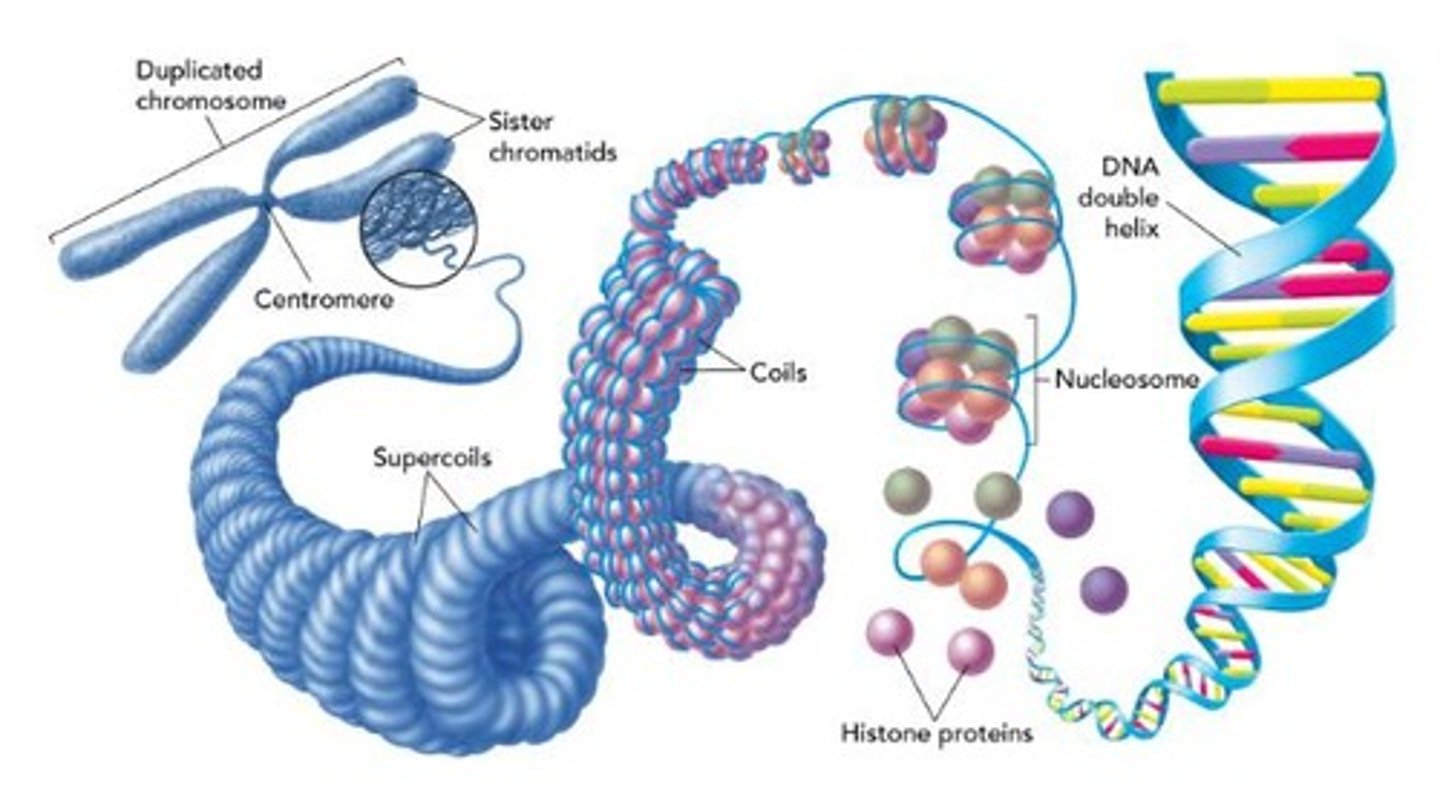
Chromosome
Duplicated DNA structure visible during cell division.
Cell Cycle
Process of cell growth, preparation, and division.
Prokaryotic Cell Cycle
Growth, DNA replication, and division in prokaryotes.
Binary Fission
Asexual reproduction creating two identical cells.
Eukaryotic Cell Cycle
Four stages: G1, S, G2, and M.
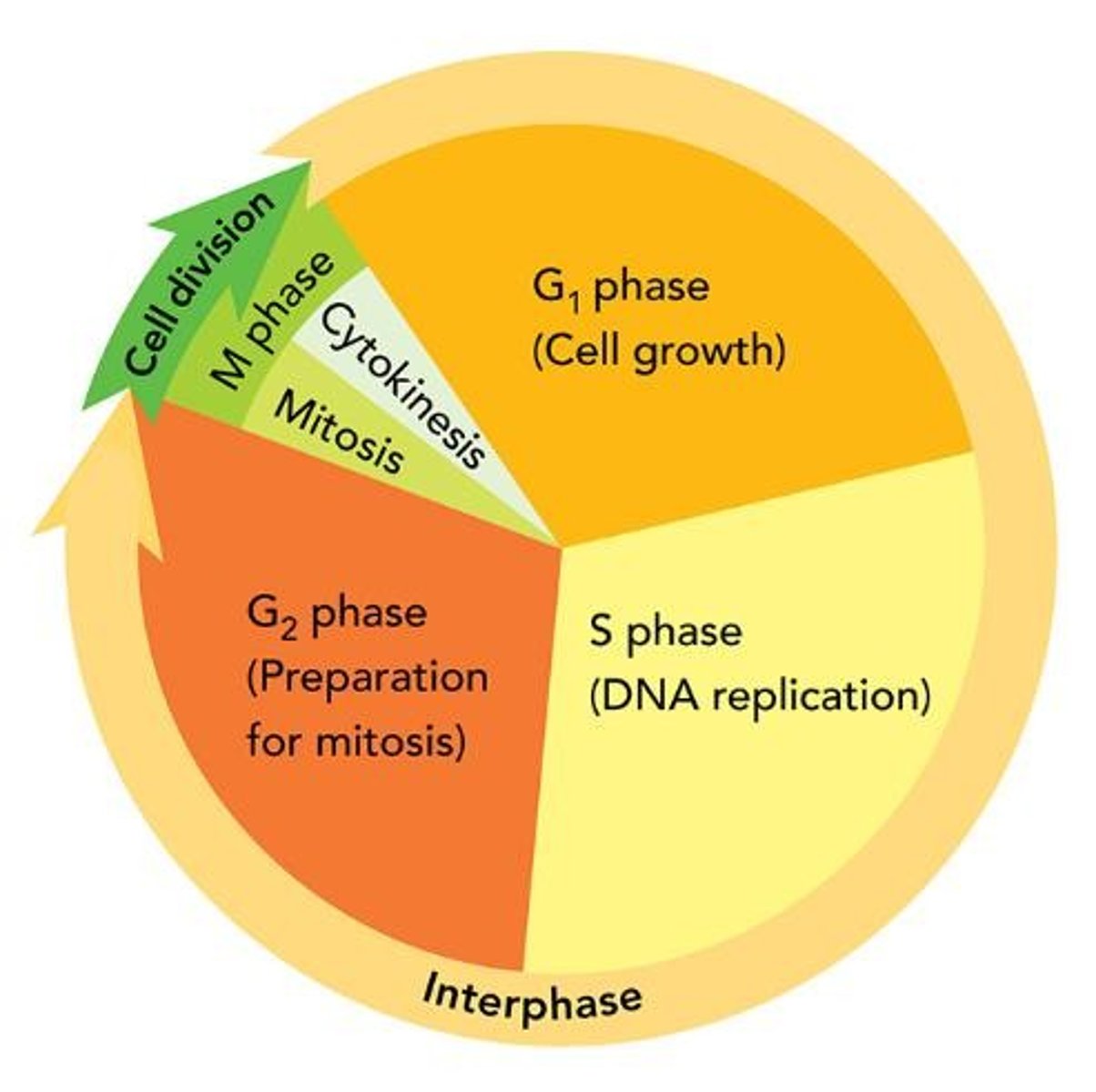
Interphase
Growth period between cell divisions in eukaryotes.
G1 Phase
Cell growth and synthesis of proteins and organelles.
S Phase
DNA synthesis and chromosome replication occurs.
G2 Phase
Preparation for cell division, organelles produced.
M Phase
Cell division producing two daughter cells.
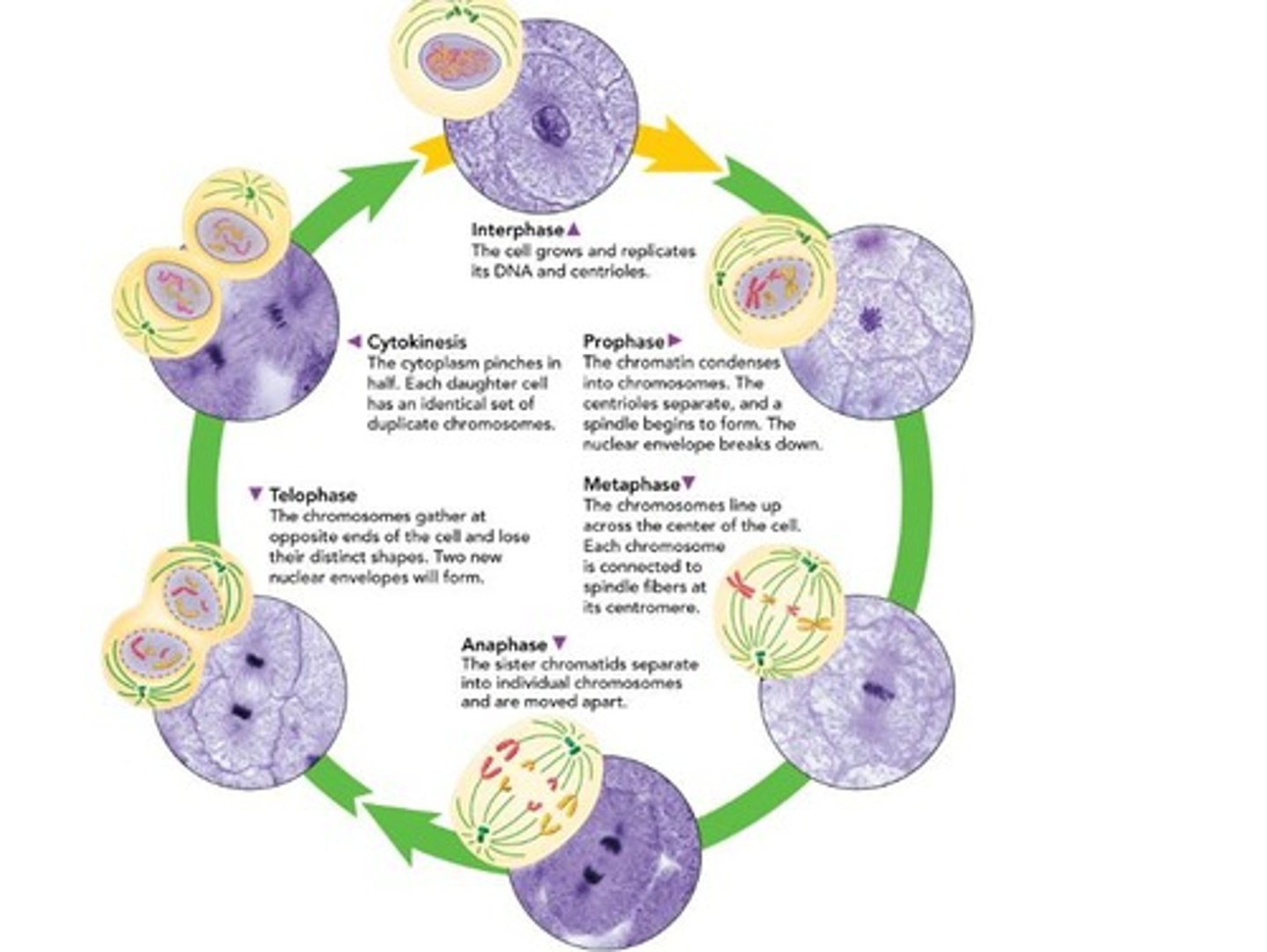
Mitosis
Division of the cell nucleus into two nuclei.
Cytokinesis
Division of the cytoplasm following mitosis.
Prophase
First mitosis phase, longest duration.
Metaphase
Chromosomes align at the cell's equatorial plane.
Anaphase
Sister chromatids separate and move apart.
Telophase
Nuclear membranes reform around separated chromosomes.
Supercoiled Chromatin
Highly condensed DNA structure during cell division.
DNA Replication
Process of copying DNA before cell division.
Cell Growth
Increase in cell size and metabolic activity.
Chromatin
Uncoiled DNA in the nucleus during interphase.
Organelles
Cell structures performing specific functions.
Prophase
Chromosomes condense and spindle forms.
Chromatids
Duplicated chromosomes appear as two thick strands.
Centromere
Point where sister chromatids are attached.
Spindle
Microtubule system aiding chromosome separation.
Centrosome
Region where spindle fibers originate.
Centrioles
Paired structures that help organize spindles.
Metaphase
Chromosomes align at the cell's center.
Telophase
Chromosomes spread into chromatin; nuclear envelope reforms.
Cytokinesis
Division of cytoplasm forming two separate cells.
Animal Cytokinesis
Cell membrane pinches inward to separate cells.
Plant Cytokinesis
Cell plate forms between divided nuclei.
Cell Plate
Structure developing into membranes in plant cells.
G0 Phase
Cell cycle phase not preparing for division.
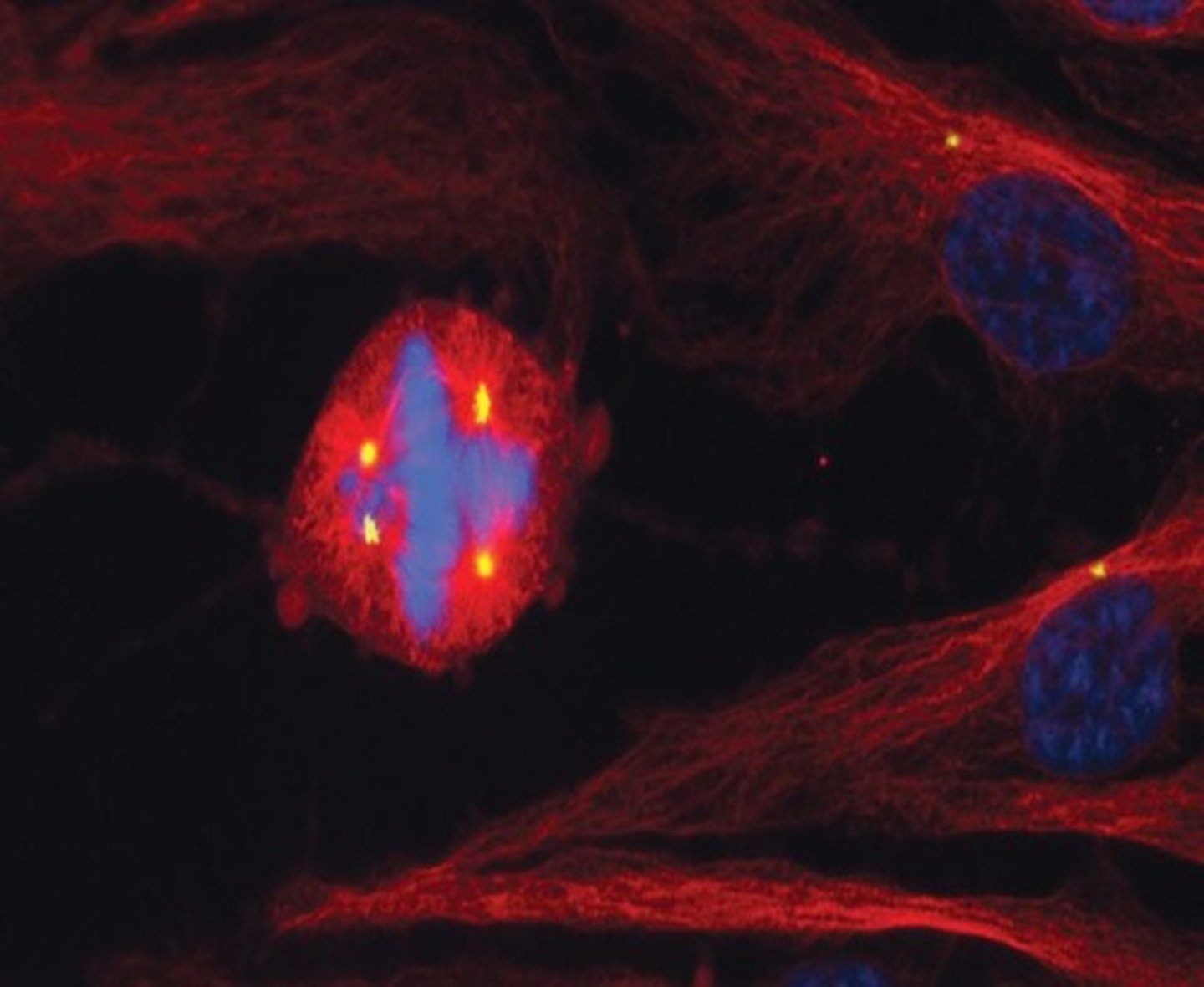
Cancer Cell Division
Divides with four spindle poles instead of two.
Cell Cycle Regulation
Controls prevent excessive cell growth and division.
Contact Inhibition
Cells stop dividing upon contact with others.
Microtubules
Filaments that disassemble during anaphase movement.
Nuclear Envelope
Membrane surrounding the nucleus re-forms in telophase.
Nucleolus
Structure that becomes visible in daughter nuclei.
Sister Chromatids
Identical copies of a chromosome connected at centromere.
M Phase
Phase of the cell cycle involving mitosis and cytokinesis.
Cell Cycle
Sequence of events in cell division and growth.
Regulatory Proteins
Proteins controlling the cell cycle phases.
Internal Regulatory Proteins
Proteins responding to events inside the cell.
External Regulatory Proteins
Proteins responding to external cell events.
Growth Factors
Proteins stimulating cell growth and division.
Cyclin
Protein regulating the cell cycle timing.
Mitosis-Promoting Factor (MPF)
Complex triggering mitosis via cyclin and enzyme.
G1 Checkpoint
Ensures cell growth and organelle replication.
G2 Checkpoint
Confirms successful DNA replication before mitosis.
Metaphase Checkpoint
Verifies chromosome attachment to spindle apparatus.
Apoptosis
Programmed cell death for tissue development.
Chromatin
Complex of DNA and proteins in cells.
Spindle Fibers
Structures aiding chromosome separation during mitosis.
Anaphase
Phase where chromosomes separate during mitosis.
Embryonic Development
Process of growth and formation of embryos.
Wound Healing
Repair process following injury to tissues.
Cell Division
Process where a parent cell divides into daughter cells.
Checkpoint Mechanism
System ensuring proper cell cycle progression.
Excessive Cell Growth
Uncontrolled proliferation leading to tissue disruption.
Nutrient Level
Availability of essential substances for cell function.
DNA Damage
Alterations in DNA structure affecting cell function.
Cell Cycle Phases
Stages including G1, S, G2, and M phases.
Neighboring Cells
Cells adjacent to others, influencing growth regulation.
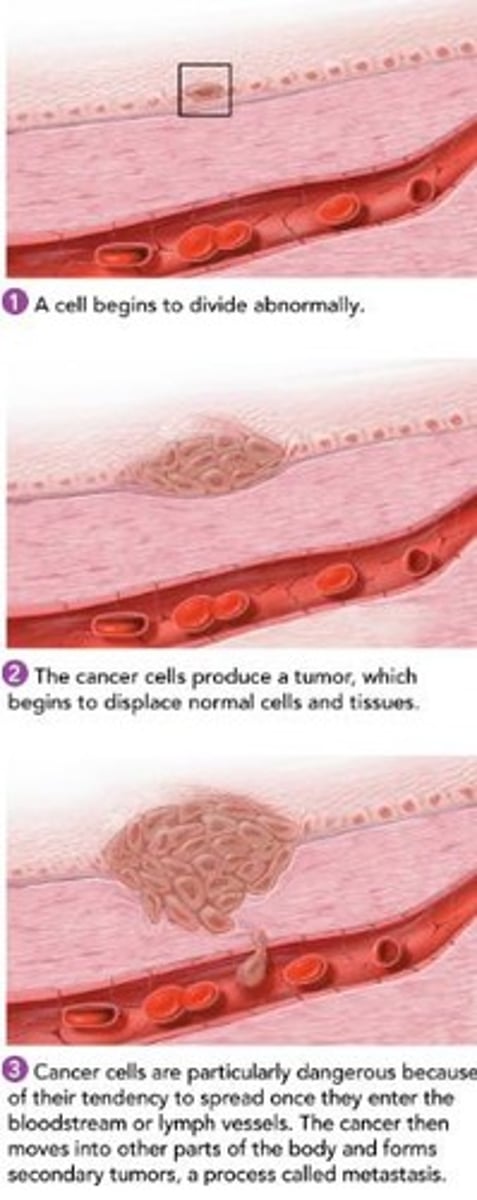
Cancer
Disorder of uncontrolled cell growth.
Tumor
Mass of cells formed by cancer.
Benign Tumor
Noncancerous tumor that doesn't spread.
Malignant Tumor
Cancerous tumor that invades healthy tissue.
Metastasis
Spread of cancer to other body parts.
p53 Gene
Checkpoint protein gene regulating cell cycle.
Cell Cycle
Sequence of events in cell division.
Chemotherapy
Use of chemicals to treat cancer.
Radiation Therapy
Treatment using high-energy radiation beams.
Secondary Tumors
New tumors formed from metastasized cancer.
Cell Growth Regulation
Control mechanisms for normal cell division.