biology final
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/60
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
1
New cards
which fat is solid at room temperature?
saturated fat
2
New cards
which fat is liquid at room temperature?
unsaturated fat
3
New cards
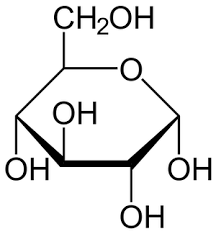
carbohydrates
monomer: monosaccharides
elements: carbon, hydrogen, oxygen
subunit: C6H12O6
bonds: covalent
example: glucose, fructose
elements: carbon, hydrogen, oxygen
subunit: C6H12O6
bonds: covalent
example: glucose, fructose
4
New cards
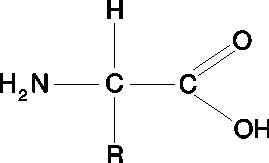
proteins
monomer: amino acids
elements: carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen
subunits: primary, secondary, tertiary, quaternary
bonds: covalent, hydrogen
example: meat, cheese, beans
elements: carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen
subunits: primary, secondary, tertiary, quaternary
bonds: covalent, hydrogen
example: meat, cheese, beans
5
New cards
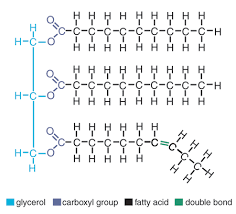
lipids
monomer: glycerol/fatty acids
elements: carbon, hydrogen, oxygen
subunits: unsaturated, saturated
bonds: covalent
example: oil, earwax, butter
elements: carbon, hydrogen, oxygen
subunits: unsaturated, saturated
bonds: covalent
example: oil, earwax, butter
6
New cards
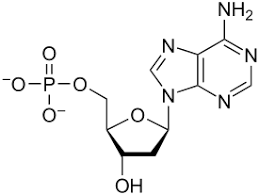
nucleic acids
monomer: nucleotides
elements: carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorus
subunits: DNA, RNA
bonds: covalent, hydrogen
example: adenine, thymine, cytosine, guanine
elements: carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorus
subunits: DNA, RNA
bonds: covalent, hydrogen
example: adenine, thymine, cytosine, guanine
7
New cards
enzyme effectiveness is affected by temperature, pH, and enzyme concentration
true
8
New cards
enzymes can be reused at the end of a reaction
true
9
New cards
enzymes are made to fit certain substrates
true
10
New cards
enzymes help chemical reactions by lowering the activation energy of the reaction
true
11
New cards
covalent bonds
a chemical bond that involves the sharing of electron pairs between atoms
12
New cards
qualitative data
gathers information that is not in numerical form quant
13
New cards
quantitative data
information that can be measured and written down with numbers
14
New cards
what are the 3 parts of cell theory?
1. all living organisms are composed of one or more cells
2. cells are the basic unit of life
3. cells arise from pre-existing cells
15
New cards
cell membrane
protect the cell from its surroundings; made of phospholipid bilayer and contains channels(made of protein) that help move substances across the membrane
16
New cards
diffusion
the movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration
17
New cards
hypertonic environment
a solution where the concentration of solutes is greater than inside the cell, and water is less concentrated than the inside of the cell
18
New cards
hypotonic environment
a solution where the concentration of solutes is less than inside the cell, and water is more concentrated than the inside of the cell
19
New cards
isotonic environment
a solution where the concentration of solutes is the same as the inside of the cell, and water is equally concentrated inside and outside of the cell
20
New cards
osmosis
the diffusion of water when solutes are unable to pass through a semipermeable membrane
21
New cards
active transport
the movement of ions or molecules across a cell membrane from a region of low concentration to a region of already high concentration, assisted by enzymes and requiring energy
22
New cards
how does a sodium-potassium pump work?
sodium-potassium pump exchanges 3 Na+ ions for 2k+ ions against their concentration gradients by using one ATP for energy
23
New cards
endocytosis
a form of bulk active transport, in which the cell surrounds an object using its cell membrane and engulfs it so it can consume it to obtain nourishment/fight infection
24
New cards
phagocytosis
“eating” larger particles
25
New cards
pinocytosis
“drinking” smaller particles
26
New cards
photosynthesis formula
6H2O+6CO2+energy-->C6H12O6+6O2
27
New cards
aerobic respiration formula
C6H12O6+6O2-->6H2O+6CO2+energy
28
New cards
photosynthesis reactants
water and carbon dioxide
29
New cards
photosynthesis products
sugar and oxygen
30
New cards
aerobic respiration reactants
sugar and oxygen
31
New cards
aerobic respiration products
water and carbon dioxide
32
New cards
what are the 3 major steps of aerobic respiration?
* glycolysis(2 ATP)
* krebs cycle(2 ATP)
* electron transport chain(34 ATP)
* krebs cycle(2 ATP)
* electron transport chain(34 ATP)
33
New cards
in photosynthesis, what are the light-dependent reactions for?
light energy strikes chlorophyll and splits H2O to release O2 to generate ATP
34
New cards
in photosynthesis, what are the light-independent reactions for?
uses ATP from photosynthesis to synthesize C6H12O6 from CO2
35
New cards
exocytosis
a process where the contents of a cell vacuole are released to the exterior through fusion of the vacuole membrane within the cell membrane
36
New cards
what are the special properties of water?
high polarity, adhesion, cohesion, lower density as a solid, high specific heat, capillary action
37
New cards
monomers
small molecules that can join together in a repeating pattern to form complex molecules(polymers)
38
New cards
catalyst
substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction by lowering the activation energy
39
New cards
enzyme
a substance which acts as a catalyst to bring on a chemical reaction
40
New cards
denaturation
when the structure of a protein changes in result of excessive acid or temperature; can be temporary or permanent
41
New cards
golgi apparatus
factory where proteins from ER are further processed and sorted for transport to their destinations
42
New cards
lysosomes
rid cells of waste products
43
New cards
mitochondria
generates most of the chemical energy needed to power the cell’s biochemical reactions
44
New cards
chloroplast
converts light energy into relatively stable chemical energy via photosynthesis
45
New cards
where does respiration take place?
in the mitochondria
46
New cards
what compound do living things use to store energy?
adenosine triphosphate (ATP)
47
New cards
equilibrium
a state in which opposing forces or actions are balanced so that one is not stronger or greater than the other
48
New cards
facilitated diffusion
diffusion of large and/or polar particles through protein channel or carrier protein
49
New cards
crenation
animal cell shrivels when placed in hypertonic solution
50
New cards
turgor pressure
force within plant cell that pushes the plasma membrane against the cell wall
51
New cards
lysis
animal cells burst when exposed to hypotonic solution
52
New cards
protein pump
transmembrane proteins that are involved in the active transport of ions against the gradient of concentration across membranes
53
New cards
ionic bond
type of bond where 1 atom transfers electron to another; opposites attract
54
New cards
induced fit
Substrate-specific changes by the active site to make a reaction happen
55
New cards
classification
(least to most specific) domain, kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus, species; dear king phillip come over for good soup
56
New cards
characteristics of life
respond to stimuli, grow and change, evolution, reproduction, complex chemistry, homeostasis, cellular structure, use of energy(metabolism), genetic information
57
New cards
ALL life has:
cells, membranes, cytoplasm, DNA, ribosomes
58
New cards
cytoplasm
a medium for chemical reaction
59
New cards
ribosomes
the site of protein synthesis
60
New cards
nucleus
the repository of genetic information; the cell's control center
61
New cards
endoplasmic reticulum (ER)
protein synthesis, transport, and folding, lipid and steroid synthesis, carbohydrate metabolism and calcium storage