Module 6 phenols + benzene
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
what is the molecular formula benzene
C₆H₆
what is the bond angle and shape of carbons in benzene
120°C
trigonal planar
what type of molecule is benzene ?
Cyclic
what is the general formula of benzene
CₙHₙ
what forms the delocalised π ring in benzene
the fourth e⁻ is delocalised
the lone e⁻ in the p-orbital overlap to form a delocalised ring of electrons
what are the two structures/ models of benzene
Kekule model
the delocalised model
which experimental data proves that kekule model is incorrect
C-C bonds are the same length / in kekules bonds would have different lengths and strengths because of the C=c bonds
Benzene is unreactive and doesn't undergo addition reactions readily
∆H Hydrogenation is about 152 kjmol⁻1 less then expected
why is benzene unreactive?
due to the delocalised ring of π 6 electrons in 6 p-orbitals
hard to break the π ring
another name for kekule structure
triene
how do we know benzene doesn't contain C=C
Bromine water doesn't react with benzene
no visible change
what is the bonding in benzene
Carbons have 3 covalent bonds
spare lone electron in the p-orbital overlap to form delocalised π ring
What are arenes/aromatic compounds?
molecules containing a benzene ring
how to name benzene
when benzene is the main functional group ( C₆H₆) --> the suffix is benzene
when benzene isn't main functional group, the molecule is named as a phenyl group - prefix
the suffix comes from other molecule
naming benzene ( image)
Give functional group lowest number
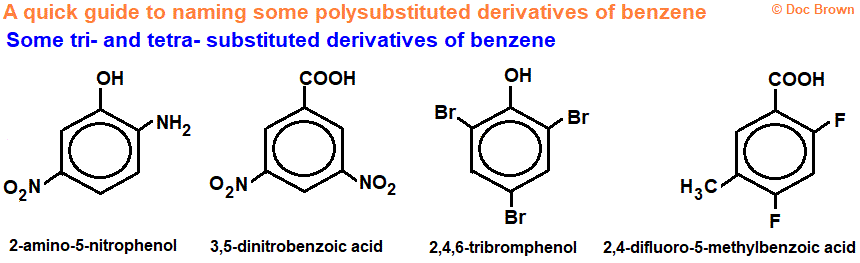
what is a phenyl group molecule formula
C₆H₅
similarities between kekule and delocalised structure of benzene
both have p-orbitals overlapping sideways
π bond above and below plane of carbon atoms
Phenol image
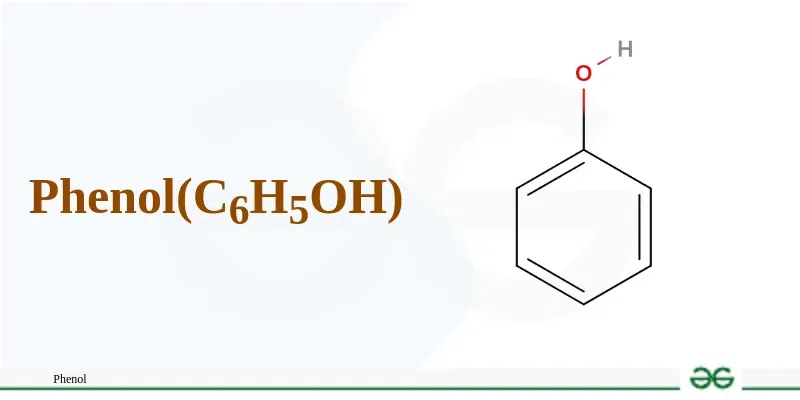
molecular formula of Phenol
C₆H₅OH
what are the reactions benzene undergoes
Nitration
Halogenation
Acylation
Alkylation
what is the only type of reaction benzene undergoes
Electrophilic substitution
what is the overall equation for the nitration of Benzene
C₆H₆ + HNO₃ → C₆H₅NO₂ + H₂O
catalyst in the nitration of benzene
Concentrated H₂SO₄
why is the catalyst in nitration of benzene the catalyst
H₂SO₄ is reformed during the reaction
effects of using higher temperatures in the nitration of benzene
Forms Poly nitro benzenes instead of mono
how to form nitro benzene
React benzene with Nitric acid ( HNO₃)
what are the 3 steps in electrophilic substitution reactions
Step 1 —> forming the electrophile
Step 2 —> electrophile attack ( Mechanism)
Step 3 —> reforming the catalysts
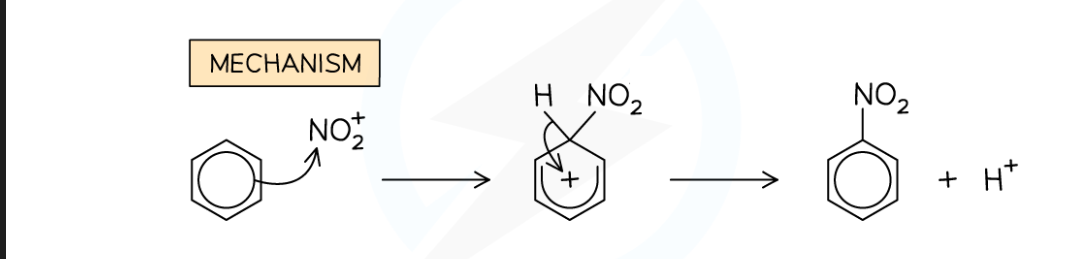
equation for forming the nitronium ion
HNO₃ + H₂SO → NO₂⁺ + HSO₄⁻ + H₂O
Electrophilic substitution ( Nitration) mechanism
Equation to reform the catalyst in the nitration of benzene
HSO₄ + H⁺ → H₂SO₄
H⁺ comes from the mechanism
what is the nitration of benzene
benzene + Nitric acid
general equation for the Halogenation of benzene
C₆H₆ + X₂ → C₆H₅X + HX
X= Cl / Br
what are the catalysts for the halogenation of benzene
Halogen carriers
what are the halogen carriers
aluminum chloride (AlCl₃)
Iron bromide (FeBr₃)
what is the electrophile in the Nitration of benzene
NO₂⁺
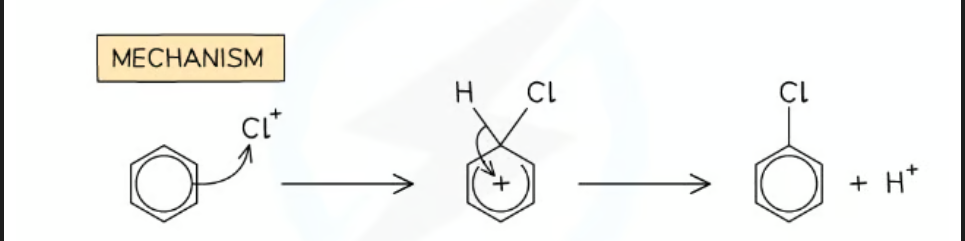
what is the electrophile in the halogenation of benzene
Cl⁺/Br⁺
equations for making the electrophile in the halogenation of Benzene
AlCl₃ + Cl₂ → AlCl₄⁻ + Cl⁺
how is the electrophile formed in the halogenation of benzene
Halogen carrier reacts with the halogen forming a halogen carrier ( 4 halogens ) anion and a halogen cation
Electrophilic substitution ( Halogenation) mechanism
Equations to reform catalyst halogenation of benzene
AlCl₄⁻ + H⁺ → AlCl₃ + HCL
Why do we use halogen carriers for Benzene and not alkenes
Benzene has a delocalised π bond ring makes it too stable
Alkenes has a localised π bond which is less stable
what is always carbon - 1 in a phenol
Carbon attached to Hydroxyl group
what is the suffix of all phenols
phenol
What is the PH of phenols
slightly acidic
word equation for Phenol + sodium hydroxide
Phenol + sodium hydroxide —> sodium phenoxide + water
displayed equation for phenol + sodium hydroxide
dont show ionic bond C⁺ attracts to anion
why dont phenols react with Na₂CO₃
sodium carbonate isn’t a strong enough base
Cant remove the H⁺ from the O₂ atom
what are electron donating groups ( EDG)
increase the electron density of Carbon 2,4,6
makes them more susceptible to electrophilic attacks
Examples of EDG
NH₂ ( amino group)
OH ( Hydroxyl group)
Why are phenols more susceptible to electrophiles then benzene
Higher electron density
due to the lone electron pair in the p orbital of the Oxygen atom overlaps with the delocalised π ring
what is Electron withdrawing group ( EWG)
Decrease electron density from the ring
re directs the electrophile to carbon 5,3
example of a EWG and features
NO₂
no orbitals that can overlap with the delocalised ring
electronegative
why do phenols react with Br₂ when benzene doesn't
higher electron density
what are the Friedel-Crafts reactiosn
Acylation
Alkylation
what are the conditions for Friedel-Crafts reactions
Heat under reflux
Halogen carrier catalyst
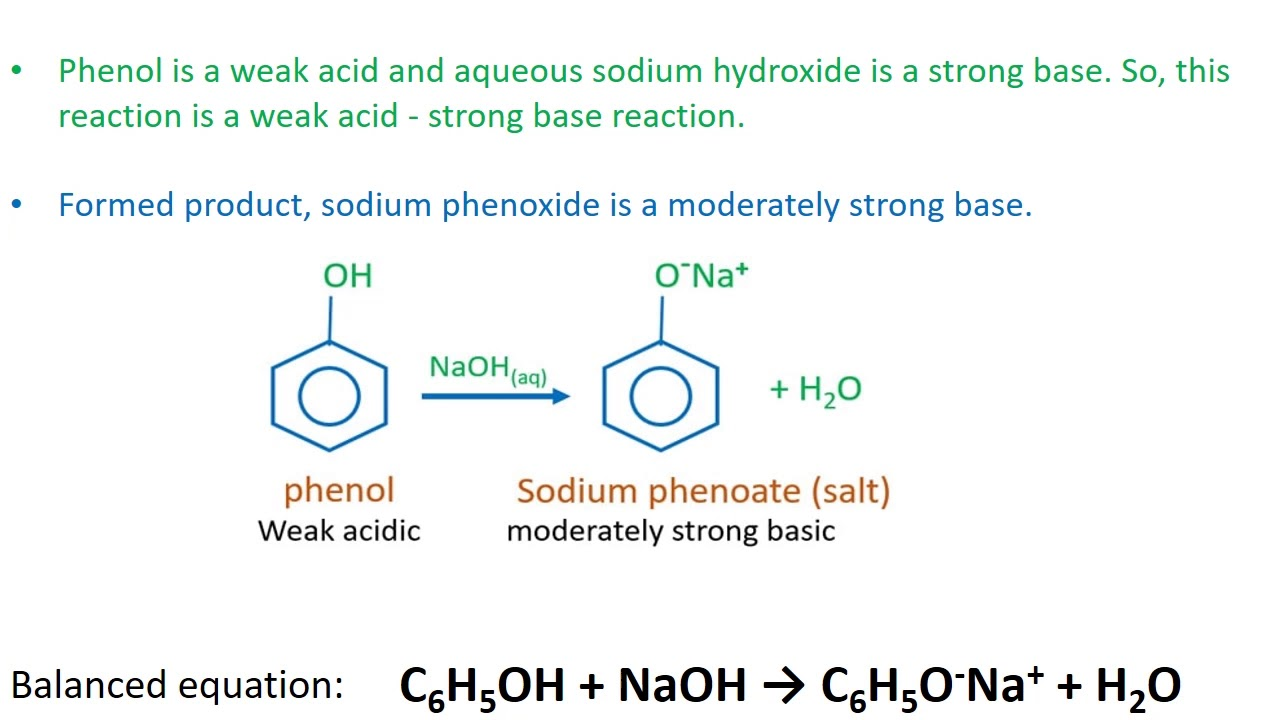
acyl group ( image)
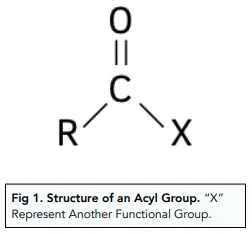
Acyl group + Benzene =
Phenyl ketone + HCL
Products of Acylation of benzene
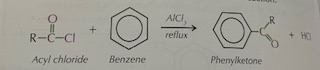
Role of halogen carrier in Friedel-Crafts reactions
Halogen carrier strengths the electrophile ( making a carbocation) → increases polarity
Generating electrophile in Acylation equation
R-COCL + AlCl₃ → RC⁺O + AlCl₄⁻
what type of electrophile is acyl chloride
Weak electrophile
Acylation of benzene mechanism ( Image)
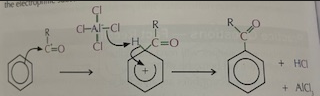
effects of halogen carrier in Friedel Crafts
generates Carbocation
Removes and steals halogen from alky/ Acyl
General equation for Alkylation reaction
R - X + Benzene → Phenyl alkane + HX
Forming the electrophiles in Alkylation equation
R-X + AlCl₃ → R⁺ + AlCl₄⁻
Friedel crafts mechanism explanation
Carbocation accepts lone pair e⁻ from the benzene
makes benzene partial and positive
Halogen anion Cl breaks to join hydrogen to HCl
Forms phenyl ketone