SPID 3.2 - Persuasion And Marketing
1/30
Earn XP
Description and Tags
30 question-and-answer flashcards covering definitions, dual-process models, source–message–audience factors, power and cognition matching studies, brand perception, anthropomorphism, and resistance to persuasion.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
What is persuasion in the context of attitude and behaviour?
A deliberate attempt to change attitudes, beliefs, or behaviours through direct messages that the receiver internalises.
Name the three components of the tripartite model of attitude.
Affect (positive/negative evaluation), Behaviour (readiness to act), and Cognition (collection of thoughts).
How do implicit attitudes differ from explicit attitudes in measurement?
Implicit attitudes are gauged by indirect, automatic, implicit measures whose purpose is not obvious; explicit attitudes are measured by direct, deliberate, explicit self-reports.
looks at measurement, processing and mental construct
What laboratory reasons are there for the attitude-to-behaviour gap?
not clear which component of the model is important in a sitch
Not clear which attitude is driving behaviour in a sitch
Behave toward one attitude one attitude object could be controlled by attitude toward another
What is the heuristic systematic model (chaiken)?
Theories proposing that persuasive messages are processed either heuristically (using simple cues) or systematically (through effortful evaluation of arguments).
What is heuristic processing?
argument quality not important
Less demanding cognitively
Relies on simple rules eg majority rules
The default
What is systematic processing?
argument quality is more important
Effortful scrutiny of all relevant info
Eg are the arguments logically coherent
One has motivation to be accurate, one has cognitive capacity for effortful processing and one tends by personality to clear explanations
When does heuristic processing dominate according to Chaiken's Heuristic–Systematic Model?
When people lack motivation, cognitive capacity, or a dispositional need for thorough explanation.
Why is attitude change from systematic processing more enduring?
Because the recipient scrutinises and integrates the arguments, grounding the new attitude and making it harder to alter.
How do motivation and distraction interact with argument strength in persuasion?
High motivation and low distraction lead to systematic processing where strong arguments persuade more; low motivation or high distraction favour heuristic processing where argument strength matters less.
What three broad categories of factors affect persuasion?
Source
message
audience
Give three source factors that influence persuasiveness.
Expertise, trustworthiness, likeability (also status or shared group membership).
Give two message factors that influence persuasiveness.
One- versus two-sided arguments and emotional versus cognitive appeal
Give two audience factors that influence persuasiveness.
Intelligence level and need for cognition
According to Dubois, Rucker & Galinsky (2016), how does power matching between source and audience affect persuasion?
Messages are most persuasive when they share characteristics with the audience (in terms of power)
measured power with baseline, low and high power condition
Either communicator (source) or audience
Measured audience attitudes, coding of argument as competent and warm
results showed in high power condition, high power communicator was most persuasive and same for low
How do high-power communicators tend to frame their arguments?
Less depedent on others
More agentic
Focus on competence
What kind of arguments do low-power communicators use, and who finds them most persuasive?
more dependent on others
More communal
Focused on warmth
How did Maio and Esses study matching message and audience in terms of need for cognition/affect?
Need for affect scales from -3 to +3 and rated things eg. Like to dwell on my emotions
Need for cognition scale from 1-5 and rated things eg i enjoy a task that involves coming up with new solutions to problem
How did haddock study need for congiton/affect in the lemphur study?
Message orientation being either affect or cognition oriented about lemphurs
Measures attitudes towards lemphurs
Affect message = induce positive emotions in reader
Cognition message = positive factual information
cognition messages worked best for high cognition, low affect and vice versa
How do people typically process expert messages when they are NOT motivated?
They rely on source expertise as a heuristic and pay little attention to argument quality.
However more likely to attend closely to expert’s argument and process systematically when interested
When motivated how do we process expertise arguments?
systematically process expert message more than non-experts
Seem to confirm existing attitudes
What is proattitudinal v counterattitudinal in the context of expertise?
Proattitudinal = when people agree with us we trust expert arguments heuristically but structinise non-expedients to identify weaknesses
Counterattitudinal = when people disagree with is we ignore non-exports but scrutinise experts to better counter them
How is expertise persuasiveness studied?
attitude pre-assessment where people are sorted into pro-attitudinal and counter-attitudinal conditions
Source manipulation of expert and non-expert
Argument manipulation of strong and weak
Attitude post-assessment of argument
Pro-attitudinal = expert increases argument view
Counter-attitudinal arguments= expert decrease agreement view
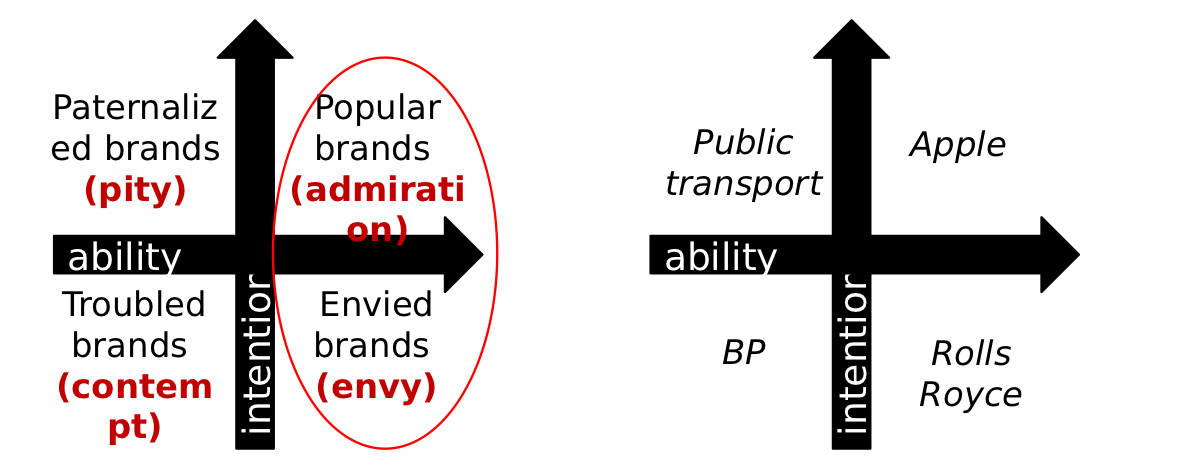
What two dimensions define the Brands as Intentional Agents Framework (BIAF)?
Perceived intentions (warmth) and perceived ability (competence) of the brand.
How does the BIAF framework work?
Paternalists (pity) eg public transport, popular (Admiration) eg apple, troubled (contempt) eg BP and envied eg rolls Royce
How do strong brand relationships work according to Alvarez and fournier?
loyalty beyond habit
Reflect self concept
Existent to negative info
Betrayal when they fall short
Relay on anthropomorphism
Eg apple, Chanel and BBC
What is anthropomorphism in marketing?
Attributing human characteristics to brands or products so they are perceived as social agents
Used in product design so products have human features to have a positive effect on impressions
How id anthropomorphism in brands studied by Kwak?
learned about anthropomorphised/not product
Non anthropomorphised = image is machine like and uses “it is”
Anthropomorphised = image looks human and uses “I am”
Social beliefs of entity theorists or incremental theorists
Entity = behaviour consistent over time and characterise a person based on a single act
Incremental = believe that behaviour changes with context and is no stable
When a bran is more human, entity holds mistakes against it and incremental not
Extra conditions of brands denying, apologising or compensating
What were Kwak’s results?
Entity = high post attitudes for compensation generally, highest for non-anthro post compensation and lowest for anthro pre/apology. Higher for non-anthro generally
Incremental = more stable for anthro and non-anthro, highest for anthro post/compensation and lowest for anthro post/denial
What are audience residence strategies for persuasion according to fransen?
avoidance = physical, mechanical and cognitive
Contesting = content, source, tactics
Empowering = attitude bolstering, social validation, self assertion
What are resistance neutralising tactics to persuasion according to fransen?
Against avoidance = forced exposure, branded content, viral marketing
Against contesting = two sided advertising, cognitive depletion, distraction, safety cues
Against empowering = self affirmation, freedom