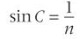Chapter 11: Waves 1
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
What is a progressive wave?
An occilation that travels through matter, transferring energy (butt not matter)
What happens to particles when a waves passes through them
The vibrate but do not move along with the wave
What are the 2 types of progressive waves?
Transverse and Longitudinal
Describe Transverse waves
Ocillations are perpendicular to the transfer of energy (or wave travel) and the waves have peaks and troughs at the maximum and minimum points of displacement
Describe Longitudinal waves
Ocillations are parallel to the direction of energy transfer and have areas of compression where particles are closer together and areas of rarefraction where particles are spread out
Examples of Longitudinal waves
Sound Waves
Ultra Sound
Seismic P Waves
Examples of Transverse waves
Water waves
EM waves
Seismic S waves
Define displacement
The distance from the equilibrium position in a particulat direction
Define amplitude
The maximum displacement from the origin
Define wavelength
The minimum distance between two adjacent points on a wave ocillating in phase
Define period
The time taken for a full oscillation of one wavelength to pass a given point
Define frequency
The number of complete oscillations passing a given point per second
What is wavespeed
The distance travelled by a wave per unit time
What is the wave equation
The equation that relates the frequency, wavelength and wavespeed A
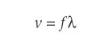
What is the relationship between time period and frequency and how can they be related in an equation
frequency and time period are reciprocals of eachother
and they are linked by the equation:
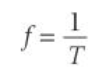
What is a wave profile
A graph showing the displacement of the particles in the wave against the distance along the wave
What are the uses of wave profiles
used to determine the wavelength and amplitude of both types of wave
What is phase difference
the difference in displacement of particles along a wave (measured in radians or degrees)
What is it known as when two particles oscillate in ‘step with each other‘
aka in phase with each other and the phase diff will be a multiple of 2π ( both particles reach their maximum positive/ negative displacement at the same time)
What is the equation of phase difference
Where x = the distance separated by the two points
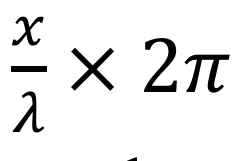
What does it mean when particles are in antiphase
When they are oscillating with a phase diff of π or equivalent
How can you find the frequency of a wave
using an oscilloscope, it is fed a signal (which is received using a mic). The timebase is set on the x-axis and amplitude on the y. The time taken for one full oscillation is measured then that is used to find the freq
What is a timebase
the time interval represented by one horizontal square on an oscilloscope screen
What can happen to all progressive waves
can all be reflected, refracted and diffracted
Where does reflection occur
When a wave changes direction at a boundary between two media AND remaining in the original medium e.g light off a mirror (angle of incidence = angle of reflection) and the wavelength and frequency remain the same
What is the law of reflection
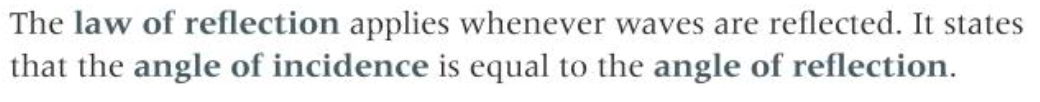
Where does refraction occur
When a wave changes direction as it changes speed whilst it enters a new medium. In the new medium the freq remains the same but the wavespeed changes resulting in a changed wavelength (There will be partial reflection at the boundary of the two media)
What and where does diffraction occur
It is the spreading out of a wave front as it passes through a gap. The wavelength and freq are not changed
What are the conditions under which max diffraction occurs
When the gap the waves passes through is the same size as the wavelength of the incident wave
What is polarisation
When the oscillation of a wave is restricted to one plane only - and when this is the case for a wave it is ‘plane polarised‘
What type of wave can be polarised and why can the other type not be
Transverse waves can be polarised as their oscillations occur in many planes at 90* to energy transfer but longitudinal waves cannot as the direction of energy transfer is in one plane already
What wave properties can you demonstrate using a ripple tank
Refraction using areas of shallow and deep water
Diffraction using a slit
How to demonstrate the polarisation of visible light
Using polarising filters, both are placed on top of eachother in the same orientation and one is slowly rotated by 90* the light intensity will decrease to a minimum as no planes of light can pass through BOTH of the filters
What is the intensity of a progressive wave defined as
The radiant power passing through a surface per unit area
What is the equation for Intensity
Where
I = Intensity in Watts per square metre
P = Radiant power
A = Cross sectional area of the surface
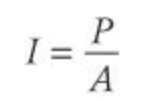
From the equation for intensity, what kind of relationship does the intensity have from the distance from the source
Inverse square relationship
What is the surface area of a sphere
4πr2
State the relationship between Intensity and amplitude
Intensity (Proportional to) Amplitude²
What kind of waves are EM waves
Transverse, they consist of magnetic and electric fields which oscillate at right angles to each other and can travel through vacuums and all EM waves travel at the same speed
What is the wavelength range for each of the types of EM waves
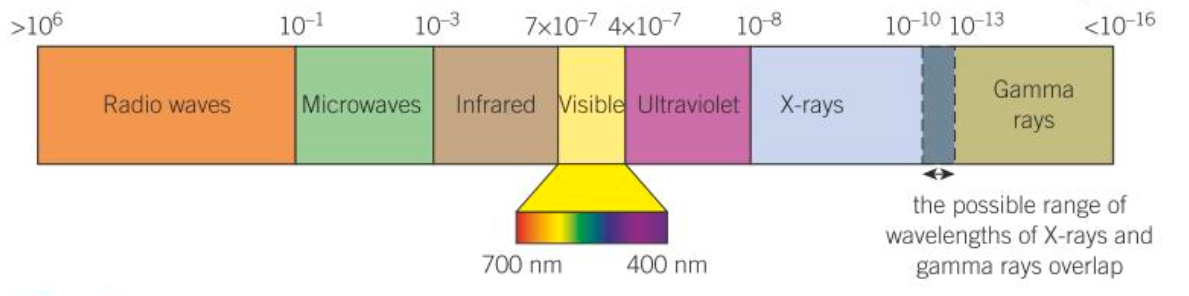
What is special about X-rays and Gamma rays compared to the other EM waves
X-rays and Gamma rays overlap in wavelength ranges and are not classified by wavelength but y their origin (X-rays come from fast moving electrons) (Gamma come from unstable atomic nuclei)
What are the properties of EM waves
Can be reflected, refracted and diffracted and can be plane polarised as they are transverse
What is the speed at which EM waves travel in a vacuum
3.0 × 10^8 ms
What is the refractive index
The angle at which the light refracts depending on a property of the material
How is the refractive index of a material calculated
Where
n = refractive index
c = speed of light in a vacuum
v = speed of light through the material
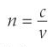
The greater the refractive index….
The more the ray bends towards the normal when changing medium
What is the equation for calculating the angle of refraction
where k is a constant and theata is the angle made with the incident ray and the normal
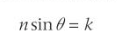
What is Total Internal Reflection and when does it happen
Occurs when light strikes the boundary at a large angle to the normal which results in all the light being reflecting into the original medium due to it being reflected internally
What are the 2 conditions for TIR to occur
The light must be travelling through a medium with a higher refractive index than the medium it strikes
The angle at which the light strikes the boundary must be above the critical angle
What is the relationship between the critical angle and the refractive index
The greater the refractive index. the lower the critical angle