2. Inorganic Chem
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
know the colours formed in flame tests for these cations:
• Li+ is
• Na+ is
• K+ is
• Ca2+ is
• Cu2+ is
red
yellow
lilace
orange-red
blue-green
insoluble: carbonates EXCEPT
group 1 and ammonium compounds
insoluble: hydroxides EXCEPT
group 1 hydroxides, calcium hydroxide (slightly soluble)
solubles
common group 1 and ammonium compounds
nitrates
common chlorides (except barium and lead II)
common sulfates (except barium, calcium, lead II)
test for anions: halogens (precipitates formed) and why is it acidified
Cl–, Br– and I– using acidified (nitric acid) silver nitrate solution
white
cream
yellow
acidified: prevents unreacted hydroxide ions reacting with the silver ions
what is used to test for SO4²-
HCl first, then barium chloride solution
acid reacts with any carbonate ions present
white precipitate
test for cations: Cu2+, Fe2+ and Fe3+
by using sodium hydroxide solution:
blue precipitate
green precipitate
brown precipitate
test for anion: CO₃²⁻
Carbonates react with dilute acids to create carbon dioxide.
This gas can be bubbled through limewater, if the limewater goes cloudy, the gas is CO2
test for anion: (NH₄⁺)
Add a few drops of sodium hydroxide (NaOH) solution to the sample containing ammonium ions.
Heat the mixture gently.
smell/ damp red litmus paper → turn blue
ammonium ion charge
1+
carbonate ion charge
2-
sulfate ion charge
2-
nitrate ion charge
1-
sulfide ion charge
2-
silver ion charge
1+
name: H₂SO₄
sulphuric acid
aluminium ion charge
3+
what donor is an acid
proton (H⁺ ions)
what acceptor is a base
proton
define alkali
Specific type of base that is soluble in water
oxidising agent
causes oxidation
gain electrons
is reduced
oxidation number decreases
reducing agent
donates electrons to another element/ion - reduces the other species
oxidised
barrier methods
protective layer that prevents moisture and oxygen from reaching the iron
paint
oil
galvanising
ZINC only
sacrificial protection
more reactive metal to protect iron from rusting (eg magnesium, zinc)
4 most abundant gases in dry air
78% nitrogen, 21% oxygen, 0.9% argon and 0.037% carbon dioxide -
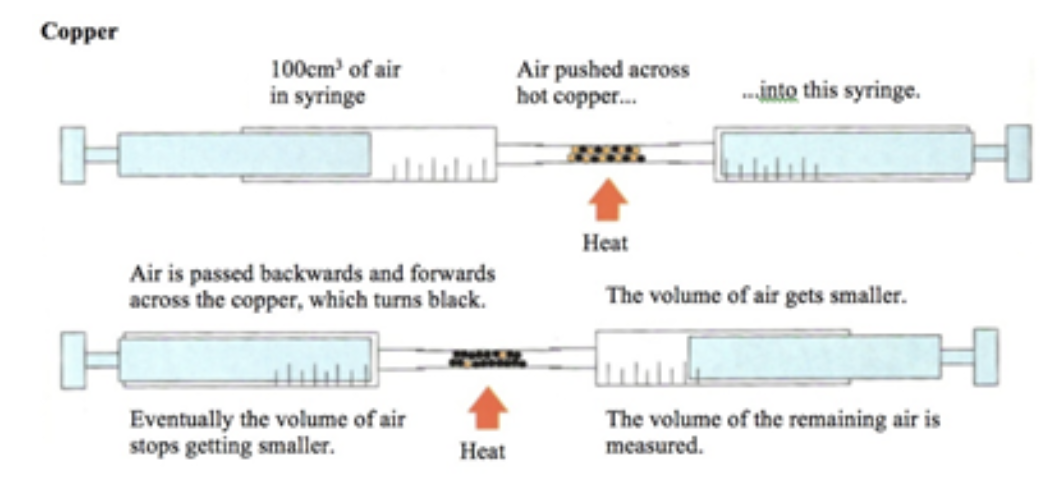
% volume of oxygen using metal
oxygen in air is used up, volume of air decreases about 20% - copper is in excess
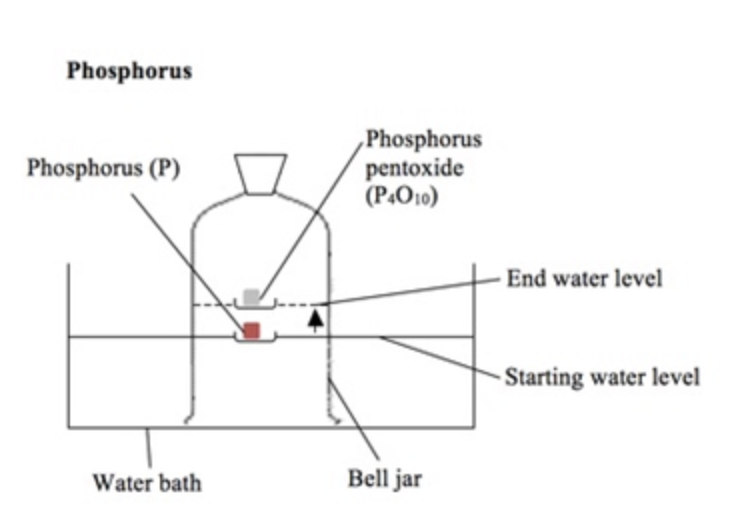
% volume of oxygen using non-metal (eg phosphorus)
The phosphorus is lit with a hot wire.
It reacts with the oxygen in the air and causes the water level in the bell jar to rise by about 20%.
presence of water using anhydrous copper(II) sulfate
Anhydrous copper(II) sulfate is white; water = blue
phenophtalein
colorless in acidic solutions
pink in basic solutions
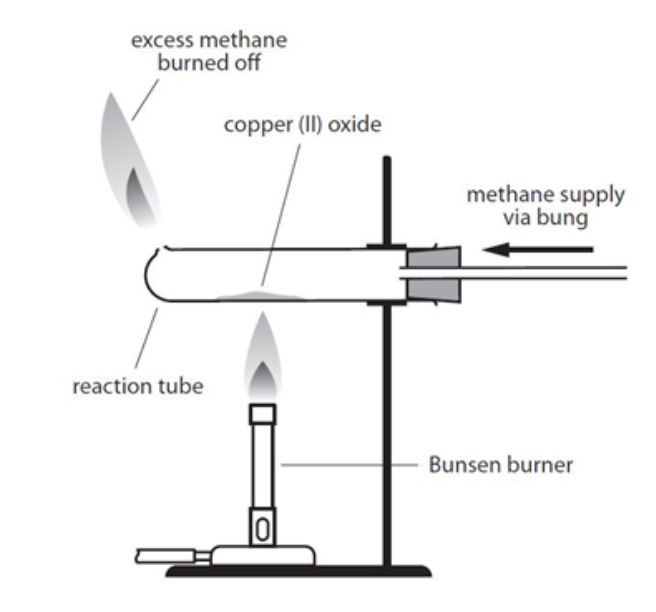
method of metal oxide by REDUCTION
heated with gas tap (methane)
light excess gas escaping tube hole
light bunsen under tube; moving it side to side
solid: black → rusty brown/ copper
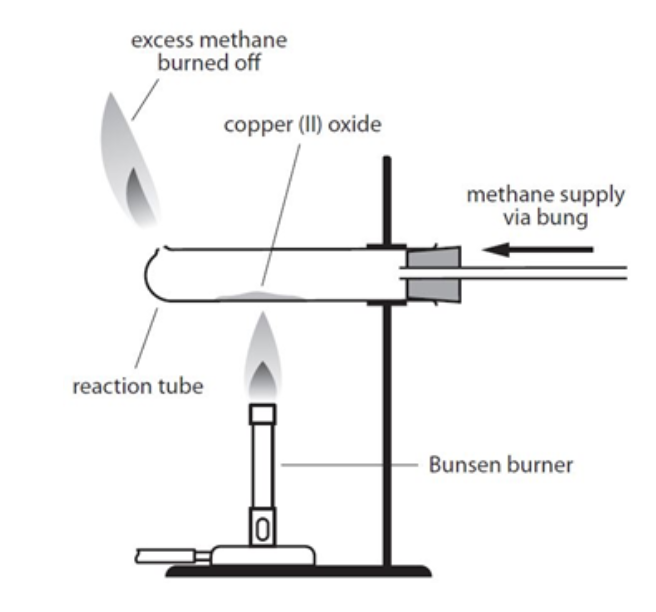
METHANE GAS PASSED OVER SOLID WHILE COOLING
prevent solid getting oxidised back to copper oxide
why is the methane set alight (bright yellow-green)
flammable; prevent accumulation of gas, reducing fire risks
% element in a compound
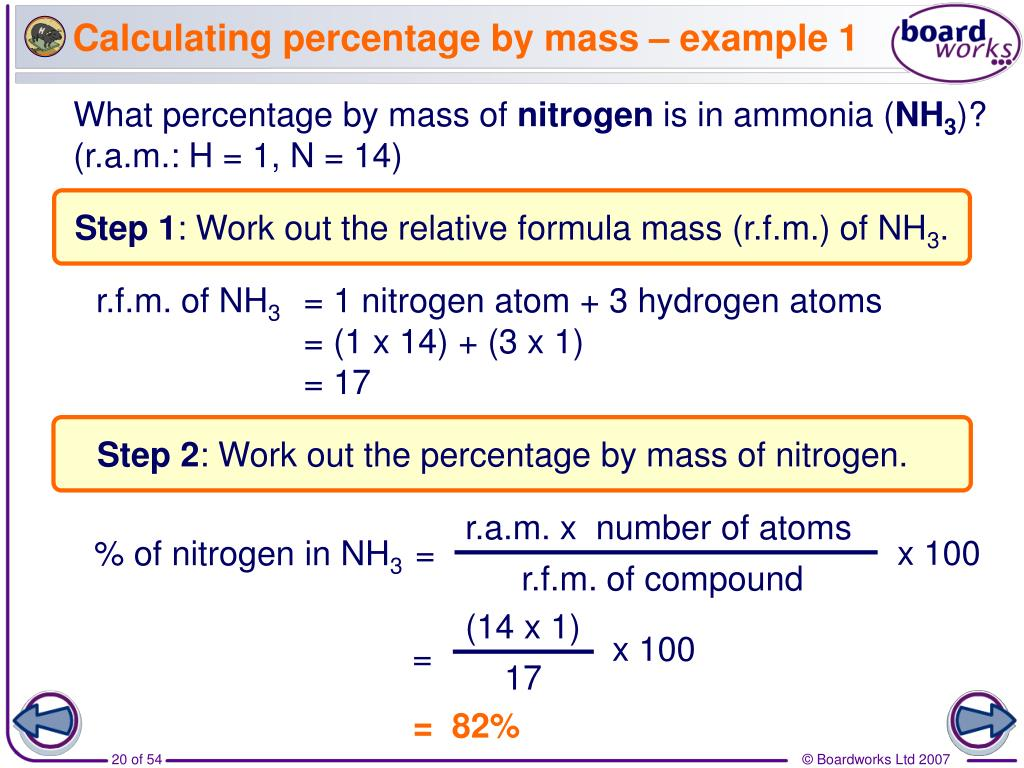
group 1 melting and boling point trend + why?
melting and boiling points decrease as you go down; number of electron shells increase, atomic radii gets bigger, attraction between nuclei and valence electrons decrease; bonds are weaker, less energy needed to break them
group 7 boiling points trend
boiling points increase as you go down
intermolecular forces get stronger
electron shells increase
more energy needed to break IMFs