(3) Seawater Properties and Ocean Circulation Dynamics
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
Solvent
Water effectively dissolves many substances.
Specific Heat
Water requires significant energy to change temperature.
Buoyancy
Water supports marine organisms, aiding their movement.
Polar Molecule
Water has distinct electrical charge regions.
Hydrogen Bonds
Attraction between water molecules keeps it liquid.
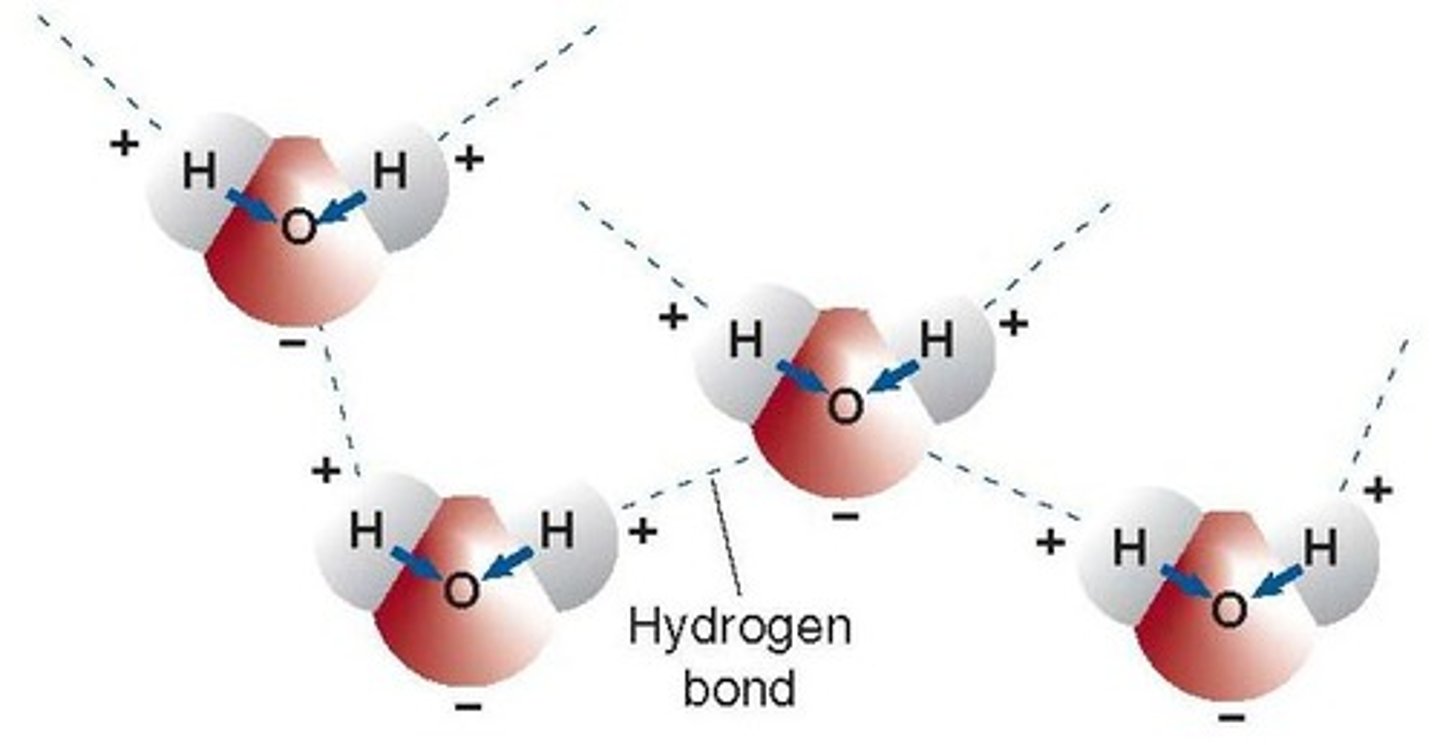
Cohesion
Water molecules stick together, creating high surface tension.
Adhesion
Water's attraction to charged surfaces makes them wet.
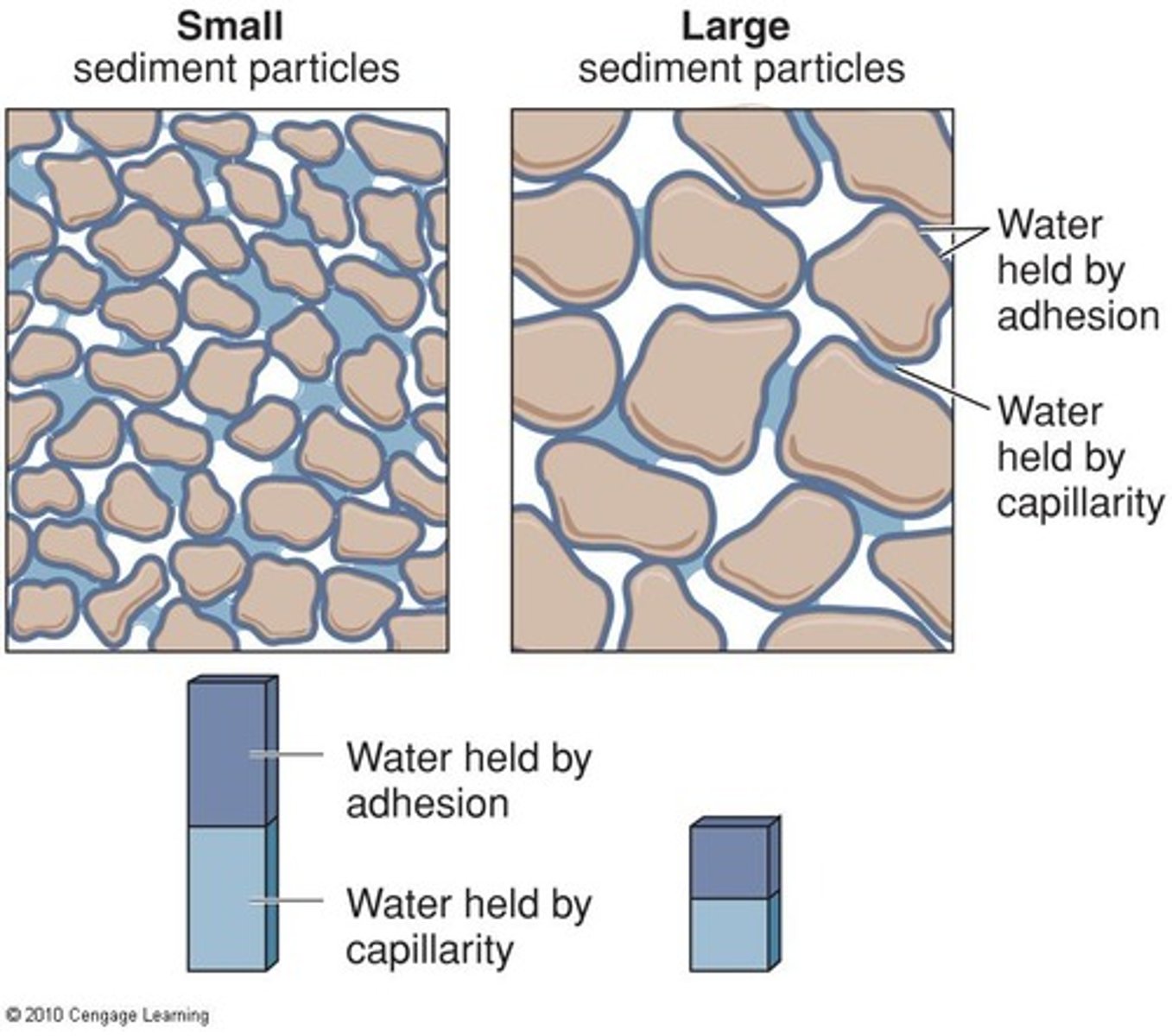
Capillary Action
Water rises in narrow spaces due to adhesion.
Heat Capacity
Ocean stores large amounts of heat energy.
Salinity
Concentration of salts in seawater, approx. 3.5%.
Practical Salinity Units
Salinity expressed based on conductivity measurements.
Dissolved Organic Matter
Organic substances passing through a 0.22 µm filter.
Particulate Organic Matter
Organic matter retained on a 0.22 µm filter.
Oxygen-Minimum Zone
Layer with low oxygen below sunlit waters.
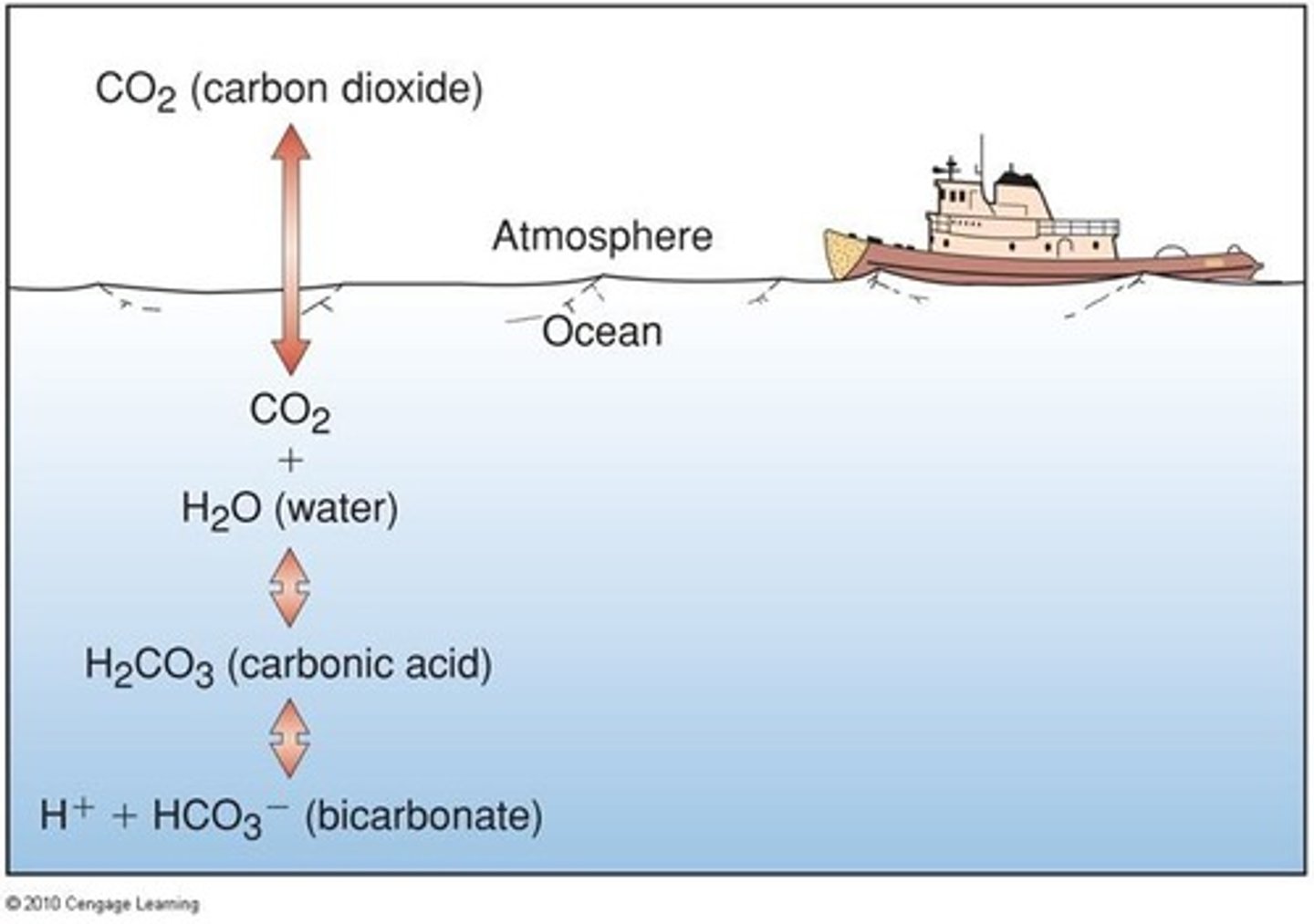
Inorganic Carbon Forms
Includes CO2, bicarbonate, and carbonate ions.
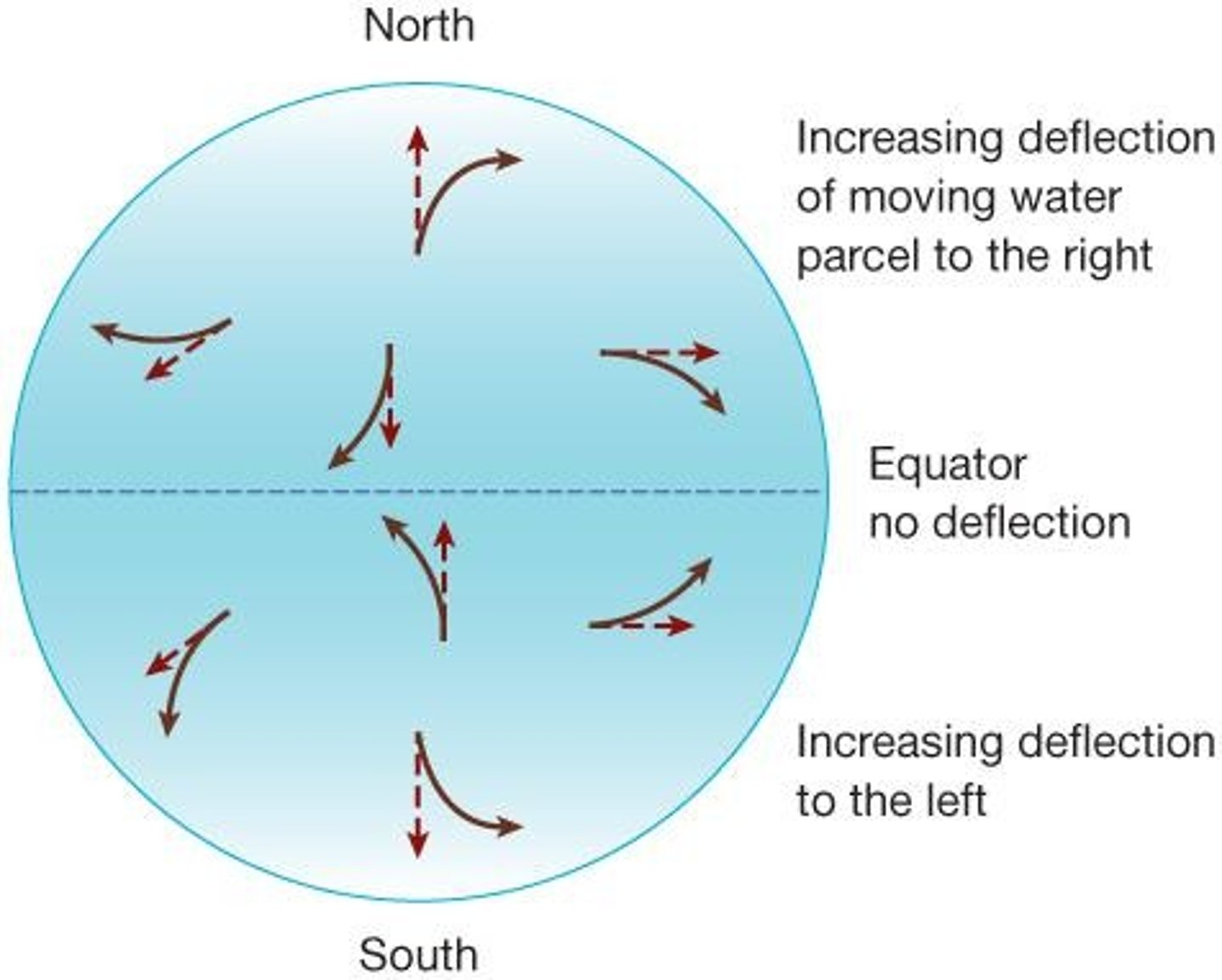
Coriolis Effect
Deflection of winds due to Earth's rotation.
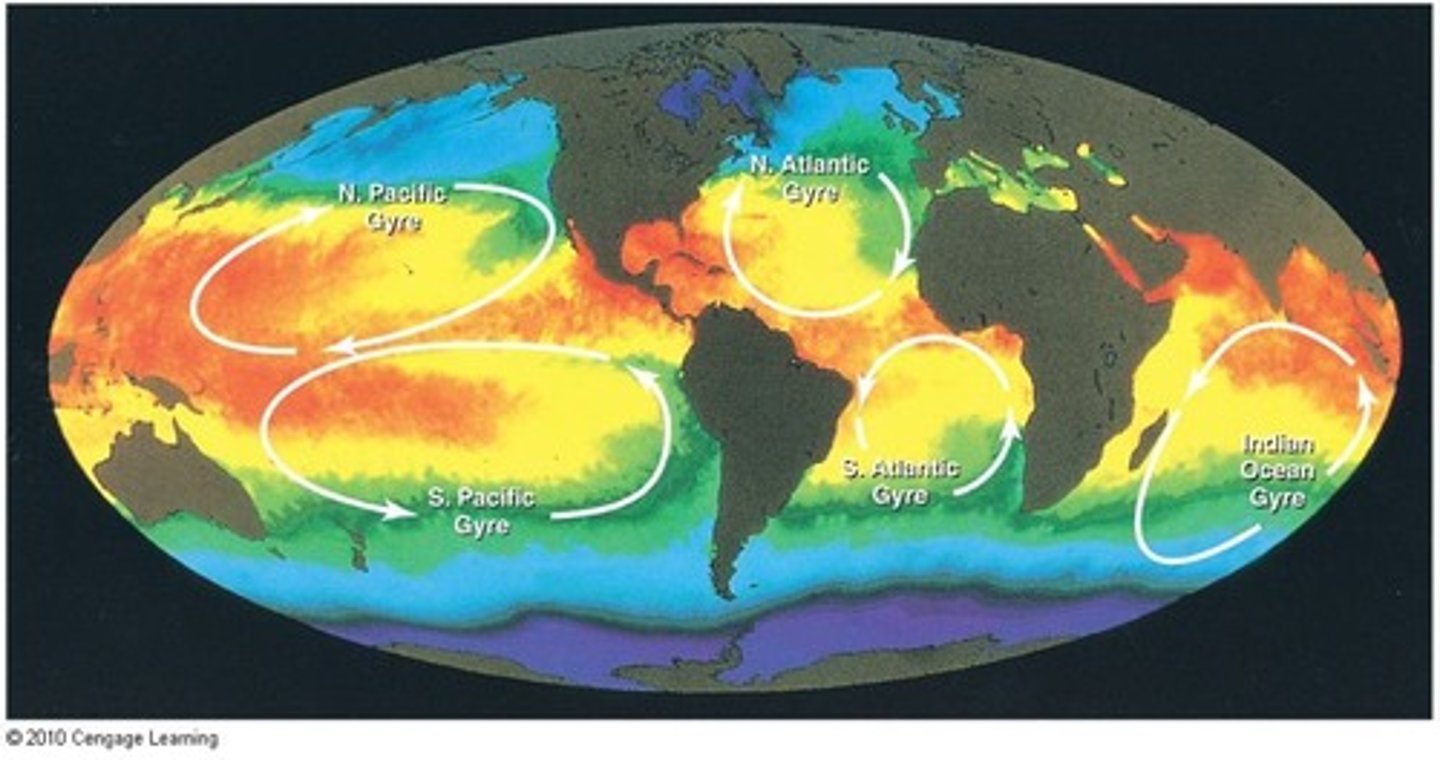
Gyres
Circular ocean currents formed by wind and Coriolis.
Western-Boundary Currents
Fast currents moving warm water poleward.
Eastern-Boundary Currents
Slow currents transporting cold water equatorward.
Thermocline
Layer with rapid temperature change with depth.
Halocline
Layer with rapid salinity change with depth.
Pycnocline
Layer with rapid density change with depth.
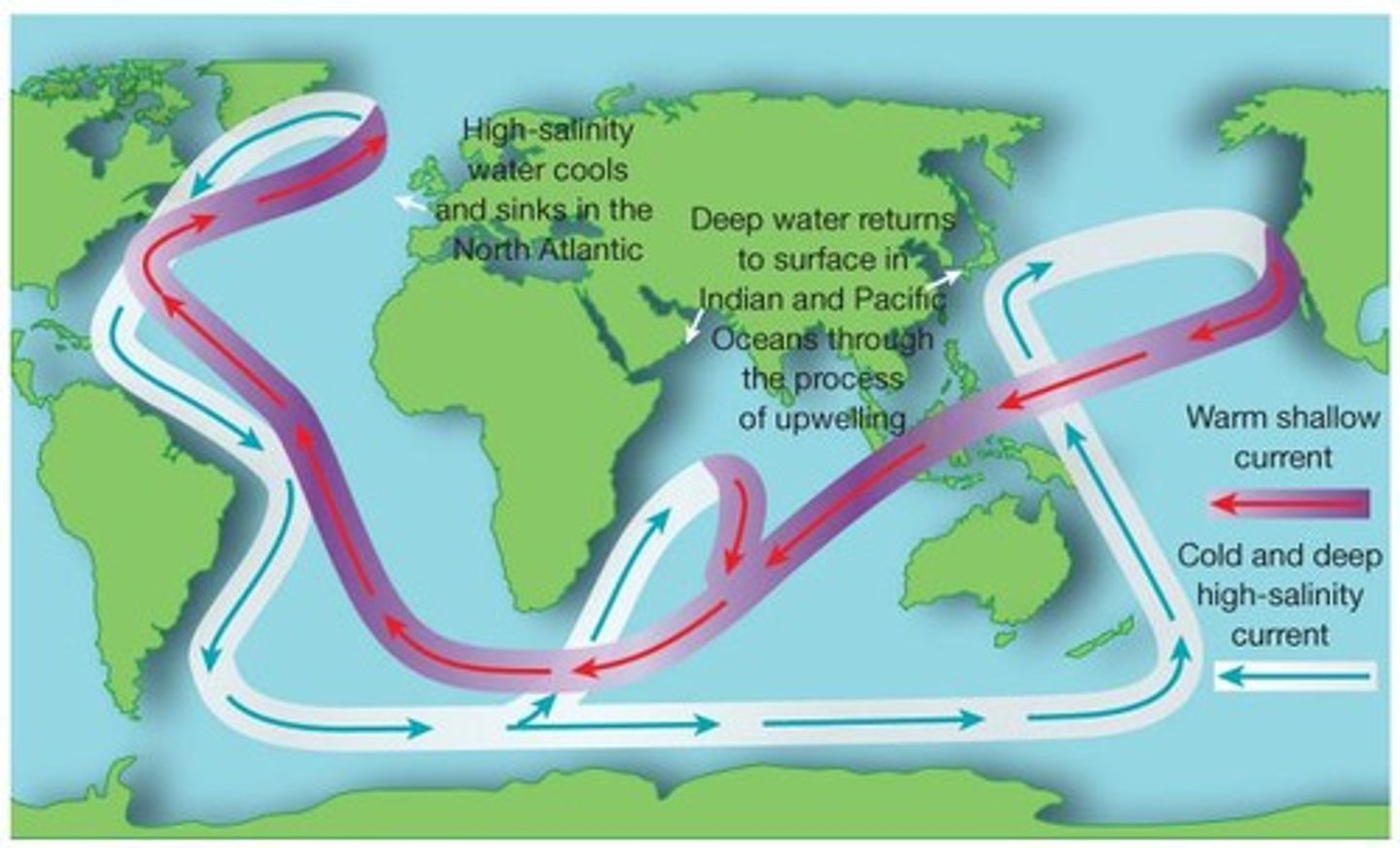
Thermohaline Circulation
Global water movement driven by temperature and salinity.
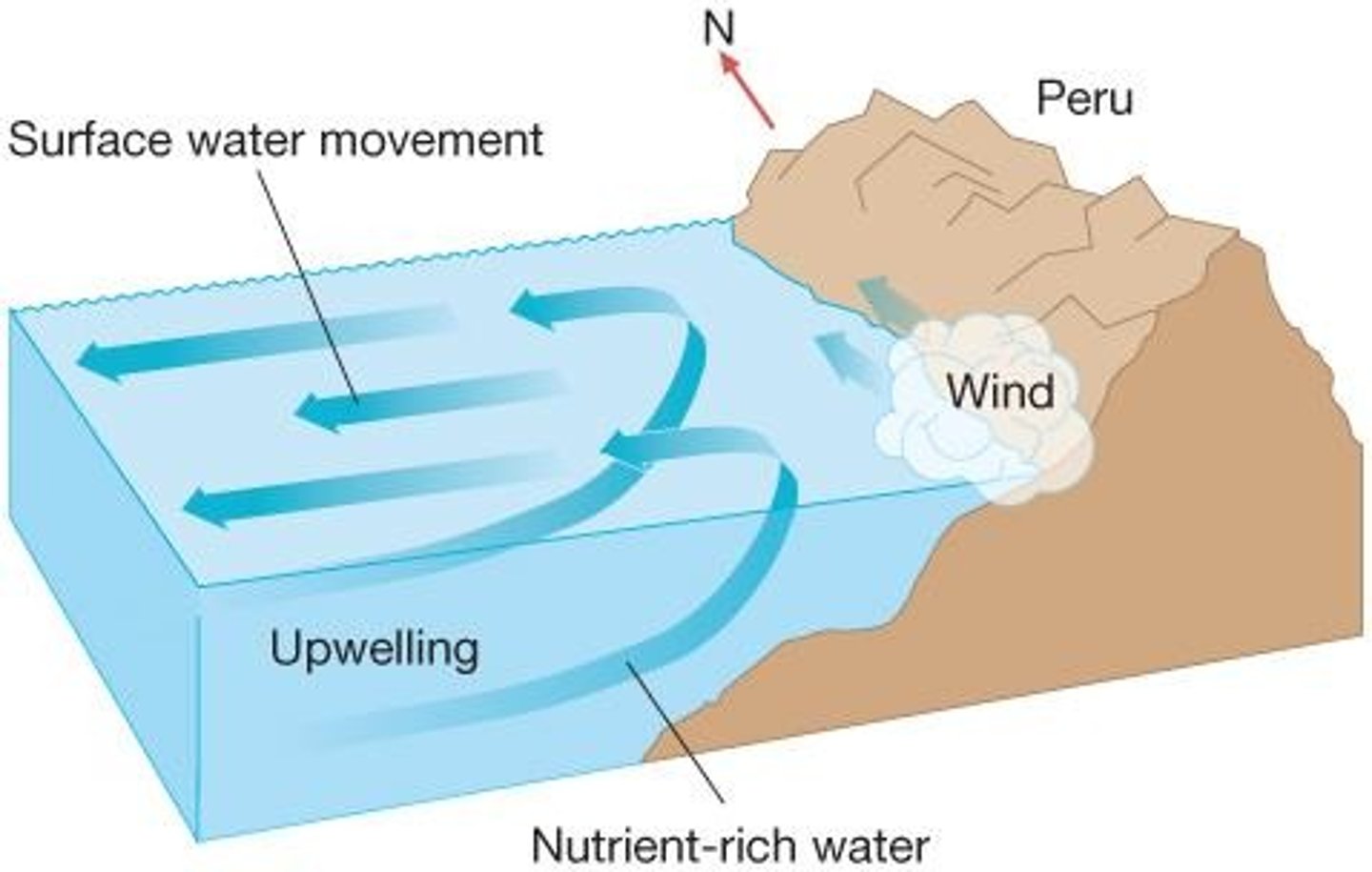
Coastal Upwelling
Nutrient-rich water rises to replace surface water.