Unit 1: Biochemistry -#8 The Cell Membrane
1/4
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
5 Terms
The Cell Membrane
Separates the living cell from nonliving surrounding
Selectively Permeable - Controls which substances can cross the membrane, allows some substances to cross more easily than others
Keep nutrients in and waste products out
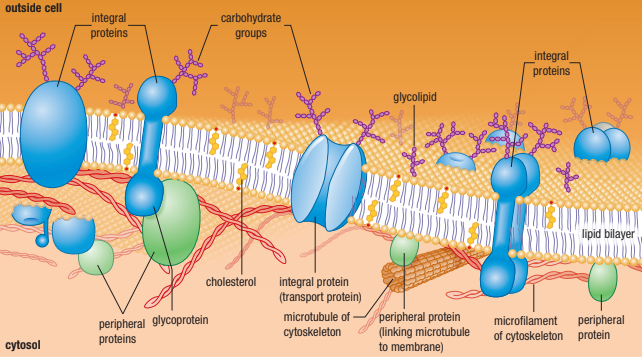
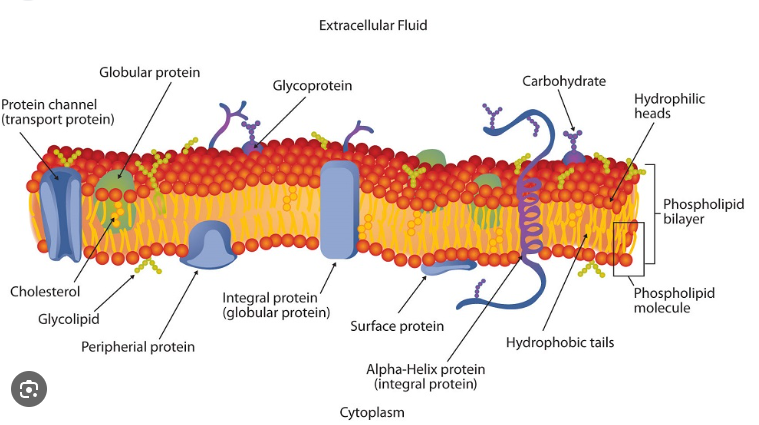
The Fluid Mosiac Model
Membranes are not rigid, with molecules locked in place
Instead molecules are in constant motion (Fluid Part)
Membrane consists of a fluid phospholipid bilayer - proteins embedded into it float freely
There are many types of proteins, lipids and carbohydrates embedded in the membrane (Mosiac Part)
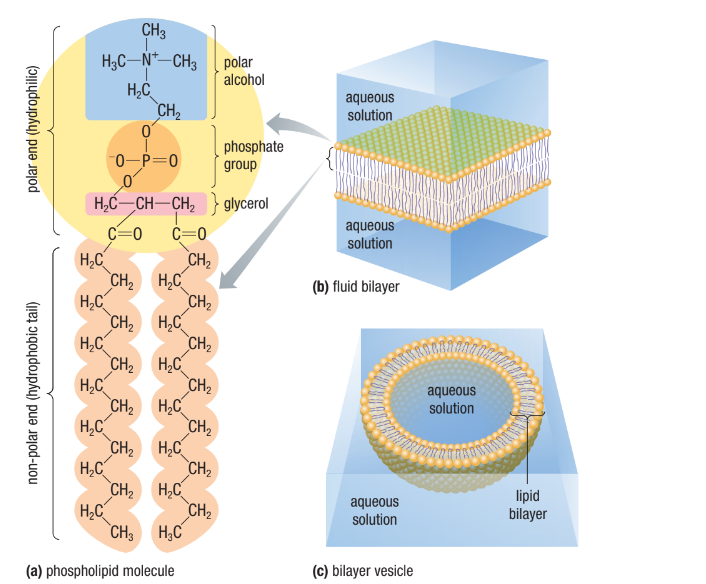
Phospholipids
Phosphate Group Head (Hydrophilic Polar Head)
2 Fatty Acid Tails (Hydrophobic Non-Polar Tails)
Forms a lipid bilayer in aqueous (watery environments) that is two lipid molecules thick
No water inside the lipid bilayer itself - water is present outside and inside the cell
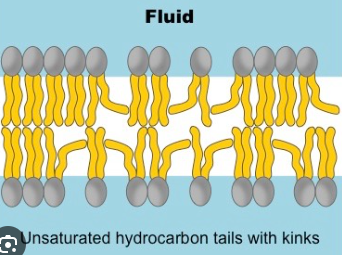
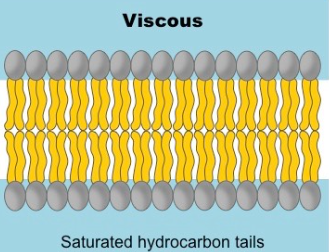
Fluidity - Saturated Fatty Acids
Saturated hydrocarbons - each carbon is bound to the maximum number of hydrogen atoms
Single bounds cause the membrane to form a semi solid gel due to linear arrangement
Have a straight shape - lipids are able to pack together more tightly
Fluidity - Unsaturated Fatty Acids
Double bonds in an unsaturated fatty acid bend its structure - lipid molecules are less straight and more loosely packed
Double bonds keep membrane fluid (less viscous)