Lab 11: Peripheral Nervous System Overview
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
Cranial Nerves
12 pairs of nerves that primarily originate in the brainstem, except Olfactory and Optic.
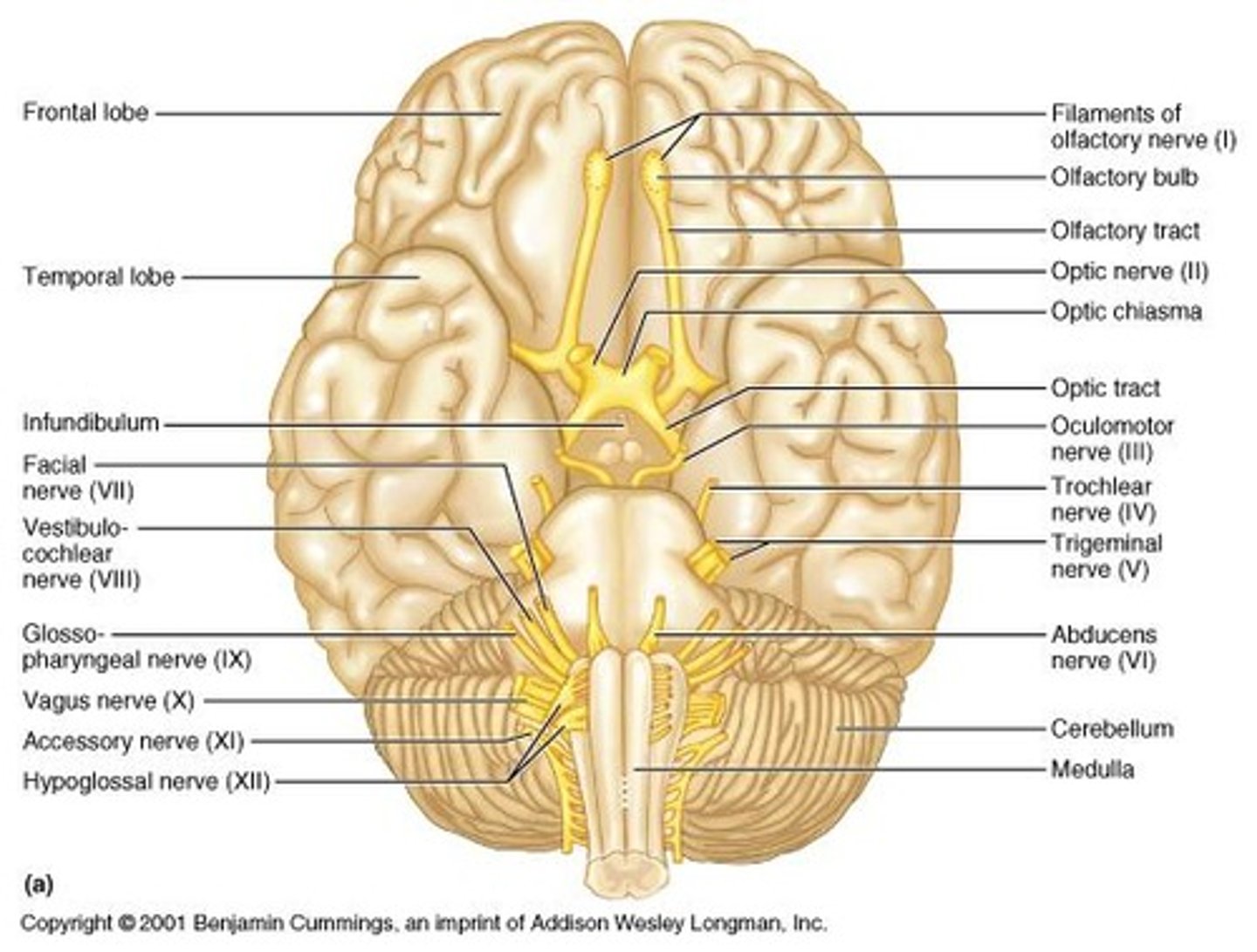
Olfactory Nerve (I)
Sensory nerve responsible for the sense of smell; exits from the olfactory fossa in the cribriform plate.
Optic Nerve (II)
Sensory nerve responsible for vision and visual field; exits from the optic foramen.
Oculomotor Nerve (III)
Motor nerve that controls eye muscles and pupil; exits from the superior orbital fissure.
Trochlear Nerve (IV)
Motor nerve responsible for one eye muscle (superior oblique); exits from the superior orbital fissure.
Trigeminal Nerve (V)
Sensory and motor nerve; the largest cranial nerve.
Ophthalmic Branch (V1)
Sensory branch of the Trigeminal nerve responsible for sensation in the forehead, around the eyes, and cornea; exits from the superior orbital fissure.
Maxillary Branch (V2)
Sensory branch of the Trigeminal nerve responsible for sensation in teeth, gums, and skin over the maxilla; exits from the foramen rotundum.
Mandibular Branch (V3)
Sensory and motor branch of the Trigeminal nerve responsible for sensation in the teeth of the lower jaw and tongue, and mastication; exits from the foramen ovale.
Abducens Nerve (VI)
Motor nerve responsible for eye muscle (lateral rectus); exits from the superior orbital fissure.
Facial Nerve (VII)
Sensory and motor nerve; responsible for taste in the anterior part of the tongue and facial expression; exits from the internal auditory meatus and stylomastoid foramen.
Vestibulocochlear Nerve (VIII)
Sensory nerve responsible for hearing and balance; exits from the internal auditory meatus.
Glossopharyngeal Nerve (IX)
Sensory and motor nerve responsible for taste in the posterior part of the tongue and pharyngeal muscles; exits from the jugular foramen.
Vagus Nerve (X)
Sensory and motor nerve responsible for thoracic and abdominal viscera; provides parasympathetic innervation to abdominal organs; exits from the jugular foramen.
Spinal Accessory Nerve (XI)
Motor nerve responsible for sternocleidomastoid and trapezius muscles; exits from the jugular foramen.
Hypoglossal Nerve (XII)
Motor nerve responsible for tongue and throat muscles; exits from the hypoglossal canal.
Spinal Nerves
31 pairs of nerves that arise from rootlets sprouting from the spinal cord, with both sensory and motor functions.
Dorsal Roots
Roots of spinal nerves that carry sensory information.
Ventral Roots
Roots of spinal nerves that carry motor information.
Dorsal Rami
Branches of spinal nerves that innervate deep muscles of the dorsal trunk and skin near the midline of the back.
Ventral Rami
Branches of spinal nerves that form intercostal nerves in the thoracic region and nerve plexuses elsewhere.
Cervical Plexus
Formed from C1-C4; most nerves are sensory to the neck region, with the phrenic nerve innervating the diaphragm.
Brachial Plexus
Formed from C5-T1; consists of three major trunks, six divisions, and three cords.
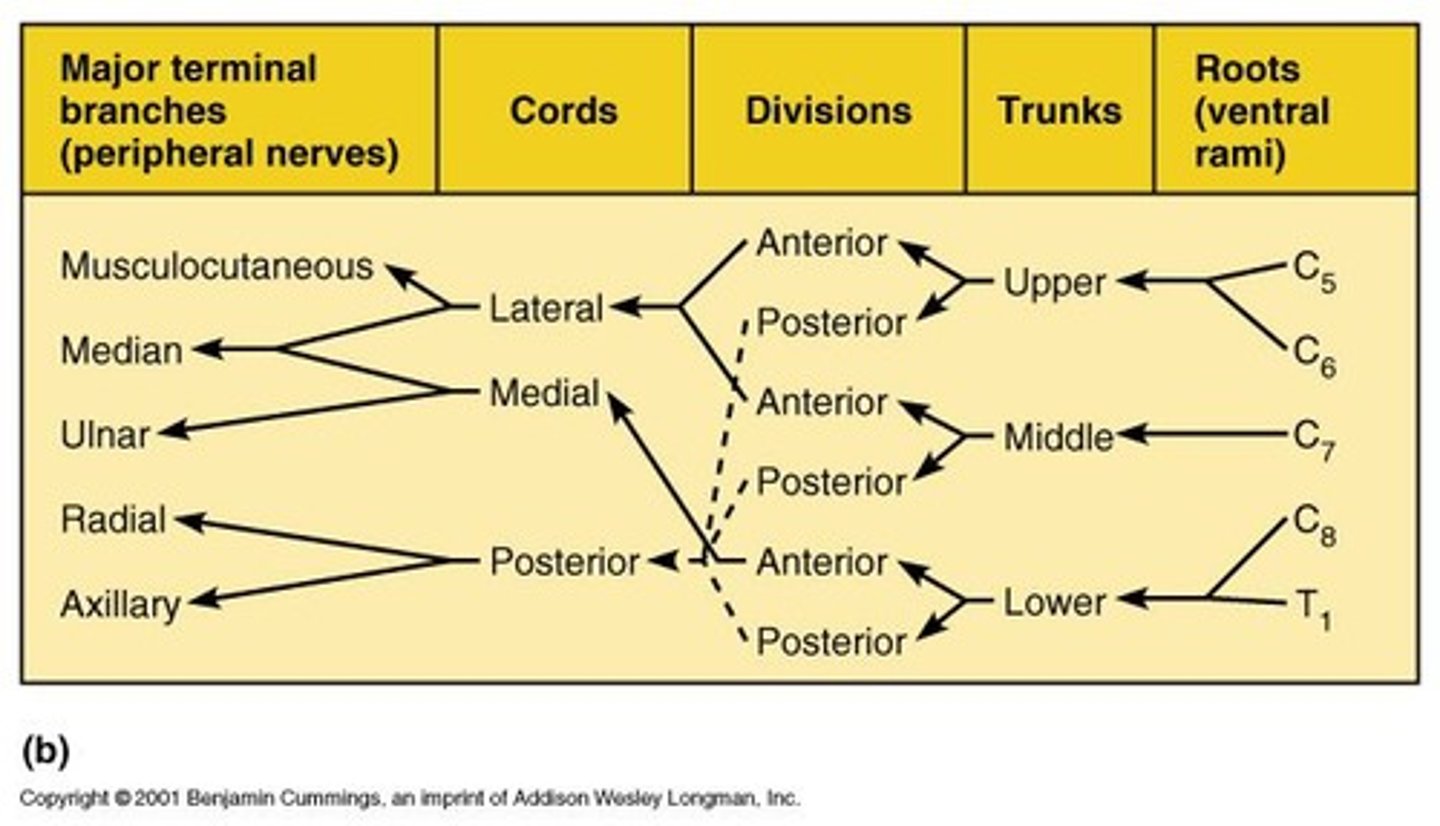
Axillary Nerve
Motor - deltoid and teres minor muscles; Sensory - skin around deltoid and upper arm.
Radial Nerve
Motor - extensors of arm and forearm; Sensory - dorsum of hand, forearm; Common clinical - wrist drop due to crutches.
Musculocutaneous Nerve
Motor - anterior arm muscles; Sensory - lateral forearm.
Ulnar Nerve
Motor - 2 forearm flexors, many intrinsic hand muscles; Sensory - ulnar side of arm and hand; Commonly referred to as the funny bone.
Median Nerve
Motor - innervates all but 2 of the flexors of the forearm and muscles near the thumb; Sensory - skin on radial side of palm; Clinical - carpal tunnel syndrome.
Thoracic Nerves (2-12)
No plexus; Motor to intercostal muscles; Sensory - skin of overlying area; Nerves run from spinal cord out through costal grooves in ribs.
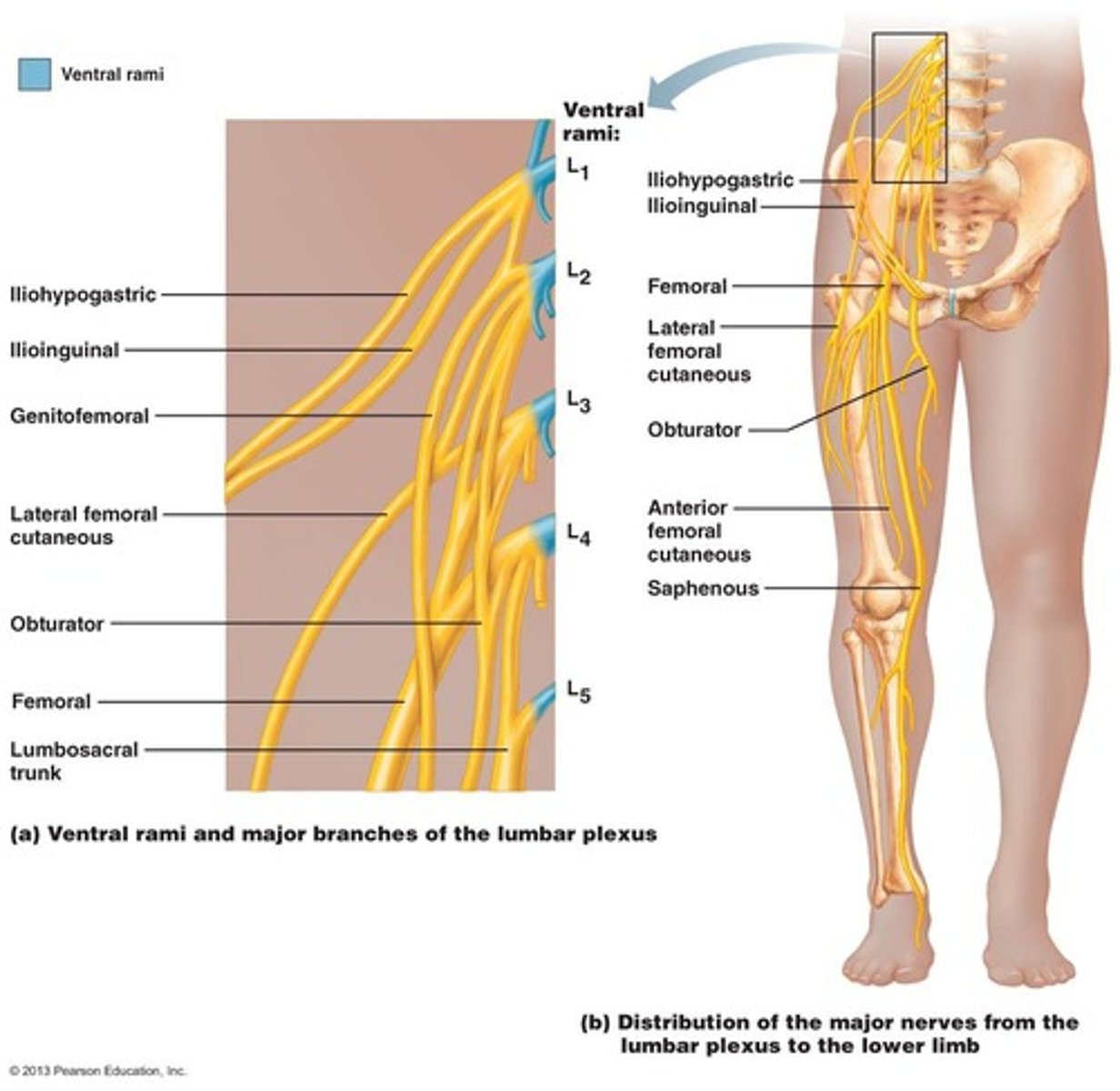
Lumbar Plexus
L1-L5; Branches mainly go to the anterior of the lower limb.
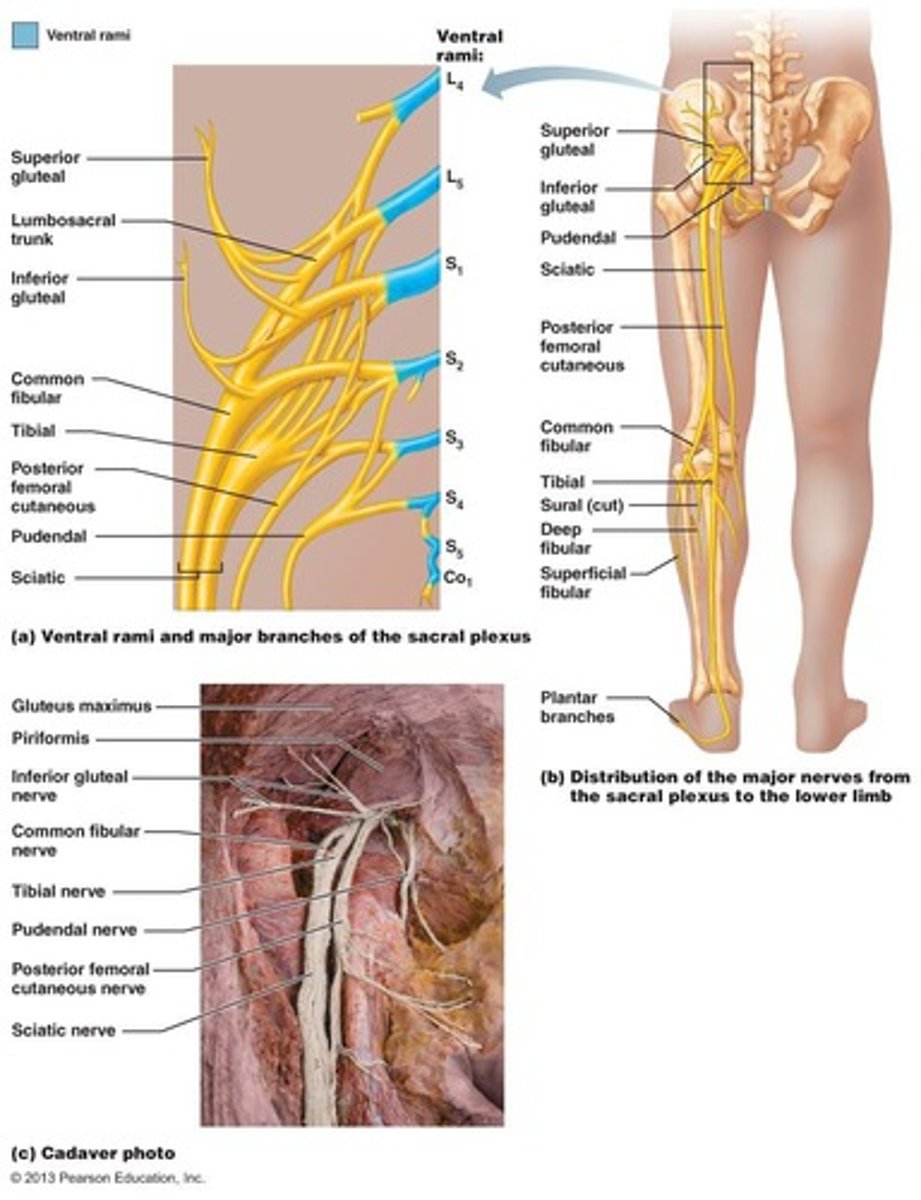
Sacral Plexus
L5-S4; Branches mainly go to the posterior of the lower limb.
Obturator Nerve
Motor - supplies the muscles that adduct the thigh; Sensory - Skin of medial thigh.
Femoral Nerve
Motor - iliopsoas, quads, sartorius; Sensory - anterior of upper leg and to the top of the foot as the saphenous nerve.
Sciatic Nerve
Tibial and common peroneal nerves bound together (L5 - S4); Runs down back of leg and splits just above the popliteal fossa into the Tibial and Fibular nerves.
Tibial Portion of Sciatic Nerve
Motor - posterior thigh (hamstrings) and lower leg (plantarflexors) muscles; Sensory - much of the posterior thigh and lower leg and sole of foot as the Sural nerve.
Peroneal/Fibular Portion of Sciatic Nerve
Motor - runs laterally around head of fibula and innervates the fibularis muscles and dorsiflexors of the lower leg; Sensory - lateral lower leg and dorsum of foot mainly as the superficial fibular nerve.
Reflex Arc
Most reflex arcs involve 3 neurons; some only require 2 and function without an association neuron.
Hypoflexia
Malnutrition, neuronal lesions, aging.
Hyperflexia
Usually seen with increased muscle tone due to damage to the motor cortex.
Scaling Reflex Responses
++++: Very brisk, hyperactive; +++: More brisk than average; ++: Normal response; +: Somewhat diminished; 0: No response, usually pathological.
Stretch Reflexes
Involves muscle groups and specific spinal nerves.
Plantar Reflex
Normal response is toe curling in adults; Damage can lead to Babinski's sign, which is dorsiflexion of the toes.
Babinski's Sign
Normal in babies; indicates damage in adults when there is dorsiflexion of the toes
Pupillary Reflex
Controlled by cranial nerve; pupil constricts when light is shone on it.
On
Occassion
Our
Trusty
Truck
Acts
Funny
Very
Good
Vehicle
Any
How
Olfactory
Optic
Oculomotor
Trochlear
Trigeminal
Abducens
Facial
Vestibulocochlear
Glossopharyngeal
Vagus
Accessory
Hypoglossal