APEX IV anesthetics & Franco PP
1/237
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
238 Terms
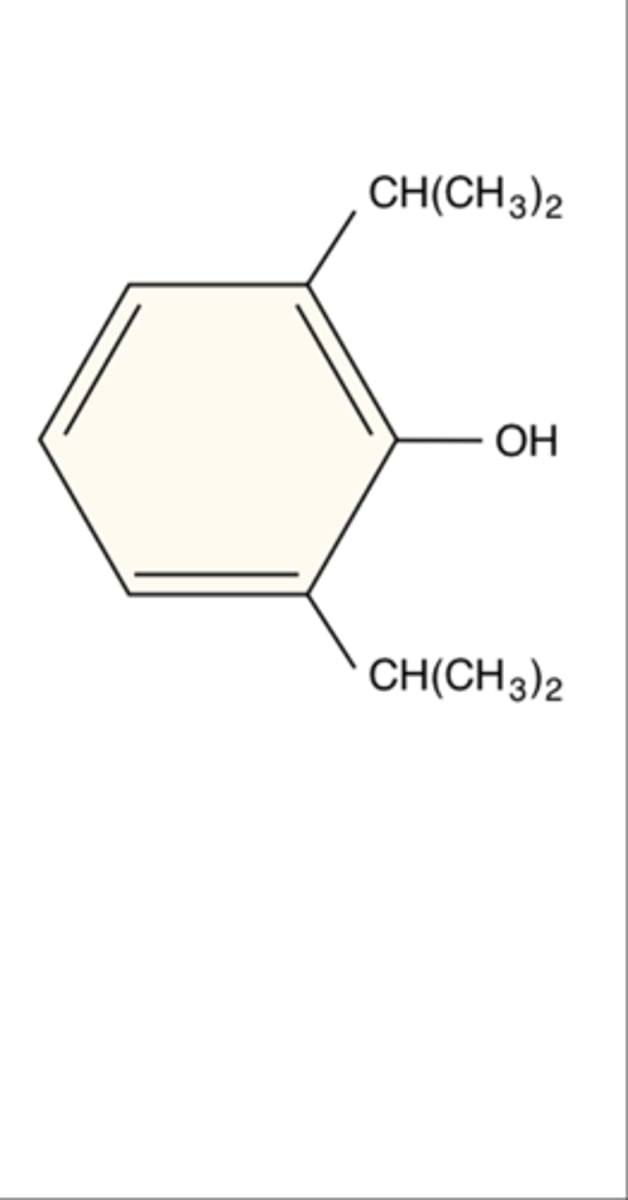
Chemical name of propofol
2,6-diisopropylphenol
GABA (4)
Inhibitory
most abundant inhibitie receptor
distributed throughout cns
almost all GA enhance GABA
NMDA (2)
Blockage
Found pre, post, and extrasynaptically
Glycine and VG Na+ channels (4)
glycine locatlizes near cell body
inhibitory role- imobility
no ketamine activity
propofol + Na channel contributes to antiepileptic activity
Class of propofol
Isopropylphenol
Propofol formulation
1% solution in lipid emulsion of 10% soybean oil, 2.25% glycerol, and 1.2% purified egg lecithin
Long chain of triglycerides
prop pH and pKa
pH= 4.5-6.4
pKa=11
Diprivan pH and pKa
pH= 7-8.5
pKa=11
Preservative in Diprivan
Disodium edetate
Preservative in generic propofol
Sodium metabisulfite
MOA of propofol
Direct GABA-A agonist which increases chloride conductance and causes neuronal hyper polarization
Dose of propofol induction and infusion
1.5-2.5mg/kg IV for induction
25-200mcg/kg/min infusion
Onset of propofol
30-60 seconds
Duration of propofol
5-10 minutes
Propofol clearance/ metabolisjm
Liver (P450 blood flow dependent) and extra hepatic- lungs
Active metabolite of propofol
None
Brain concentration of propofol peaks at...
1 minute
-Blood concentration declines over time.
-There is a rapid distribution from the blood to the vessel rich group. Then from the VRG to the muscle and fat.
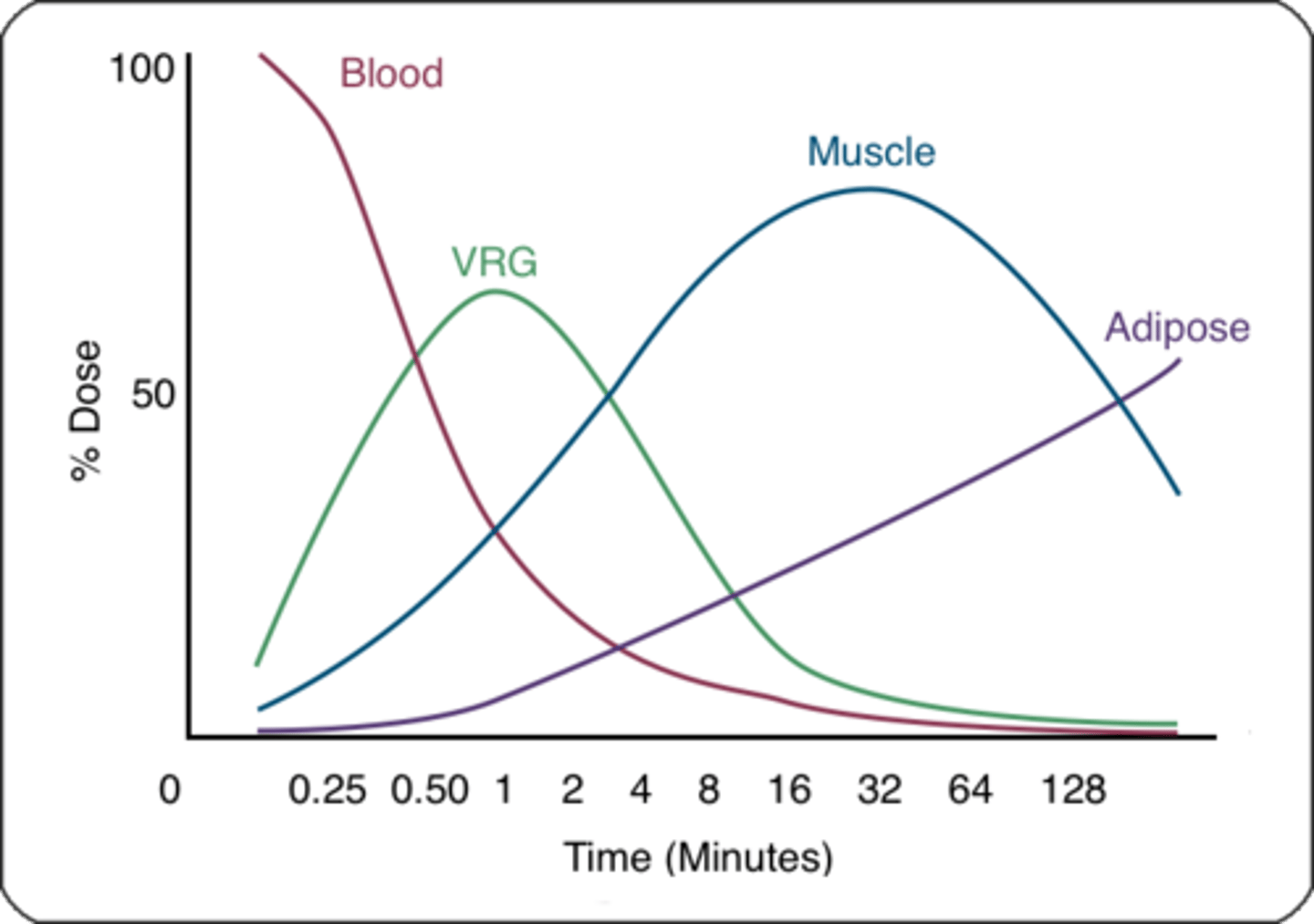
Awakening from propofol is due to...
redistribution out of the brain
WHy is prop favorable to contamination
EDTA
Pro of prop
rapid onset and recovery
Cons of prop (4)
narrow TI
HD/resp depressin
pain on injection
Prop infusion syndrome
Cardiovascular effects of propofol
Decreased BP (d/t decreased SNS tone and vasodilation),
Decreased SVR
Decreased venous tone, preload, and myocardial contractility
Respiratory effects of propofol
-Shifts CO2 response curve down and to the right (less sensitive to CO2) leads to respiratory depression/apnea
-Inhibits hypoxic ventilatory drive
CNS effects of propofol
-Rapid and pleasant LOC/emergence
-Dose dependent anxiolysis, sedation, and amnesia
- Decreased CMRO2, CBF, ICP, and intraocular pressure and CPP- autoregulation is maintained
-Can produce burst suppression/ Anticonvulsant properties, but myoclonus may occur (rare cases of seizures)
-NO analgesia
Why may urine be green with a propofol infusion?
Phenol excretion
Why may urine be cloudy with a propofol infusion?
Increased uric acid excretion (not suggestive of renal impairment or infection)
How does propofol have antioxidant properties?
It has free radical scavenging properties
Most people with an egg allergy are allergic to...
the albumin in egg whites
Is propofol safe to administer to patients with egg, soy and peanut allergies?
YES!
-Exception: patients allergic to lecithin in egg yokes (very rare) should not be administered propofol
An increased long chain triglyceride load impairs ___ and ___ which causes the muscle and cardiac cells to be starved of oxygen and leads to ___
-oxidative phosphorylation and fatty acid metabolism
-propofol infusion syndrome.
Risk factors for propofol infusion syndrome (8)
>4mg/kg/hr (>67mcg/kg/min)
Infusion >48 hours
Inadequate oxygen delivery
Sepsis
Continuous catecholamine infusions
High dose steroids
Significant cerebral injury
-More common in adults and elderly critically ill patients because prolonged propofol use with children is discouraged by the FDA
Clinical presentation of propofol infusion syndrome
-Acute refractory bradycardia L/T asystole, plus at least one of the following:
Metabolic acidosis (base deficit >10),
rhabdo,
enlarged/fatty liver,
renal failure
HLD
lipemia (cloudy plasma or blood) (early)
Treatment of propofol infusion syndrome (7)
Discontinue propofol,
maximize gas exchange,
cardiac pacing,
PDEIs,
glucagon,
ECMO,
renal replacement therapy
How does prop decrease BP
Decrease SNS, vasodilation, dec SVR, dec Venous return, and decrease myocardial contractility
Before removing propofol, the vial and rubber stopper must be cleansed with...
70% isopropyl alcohol
Propofol in a syringe/ open vial- must be discarded within...
6 hours
A propofol infusion and tubing from a vial must be discarded within...
12 hours
Prop pharmacokinetics (4)
Rapid metabolized in liver (elderly require less and children require more)
Accumulation with infusion elimination half life is 1-2 hours
reversibly binds to erythrocytes and plasma protein
highly lipid soluble
Which formulation of propofol should be avoided in asthmatics and infants? why?
Generic - the preservative metabisulfite is bronchial irritant and can precipitate bronchospasm. Benzyl alcohol should be avoided in infants
(Diprivan is ok to use because it contains disodium ethylenediamine tetraacetic acid (EDTA) as the preservative) and doesn’t cause bronchoconstriction
Dose of propofol to reduce itching from spinal opioids and cholestasis
10mg IV
Dose of propofol to treat PONV
10-20mg IV or an infusion of 10mcg/kg/min
How to decrease propofol pain on injection
-Inject into a larger, more proximal vein
-Lidocaine
-Give opioid prior to propofol
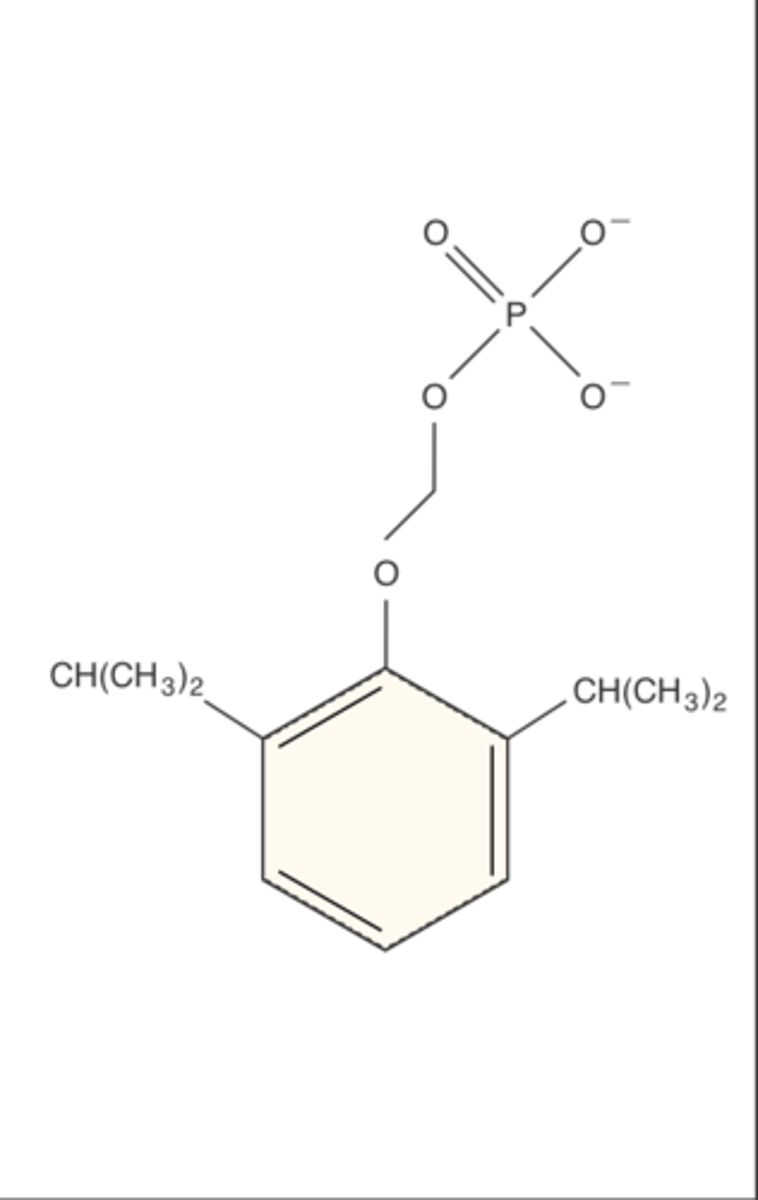
Chemical name of fospropofol and class
Chemical name:Phosphono-O-methyl 2,6 diisopropylphenol
Class: Isopropylphenol
delete
delete
Formulation of fospropofol and benefits
Aqueous solution
-no pain/ burning on injection but causes burning vag/anal
-no preservative but doesnt support microbial growth the same way lipid emulsions do
MOA of fospropofol
Prodrug metabolized to propofol by the enzyme alkaline phosphatase present in vascular endothelium and liver
Thus, slower onset of action and longer duration.
Dose of fospropofol
Initial bolus: 6.5mg/kg IV
Repeat bolus: 1.6mg/kg not more than q4min
Onset of fospropofol
5-13 minutes
Duration of fospropofol
15-45 minutes
Metabolism of fospropofol yields...
propofol, formaldehyde, and phosphate
-Formaldehyde is metabolized in the liver to formate and excreted in the urine

Active metabolite of Fospropofol
propofol is active metabolite;
Fosopropofol is prodrug (inactive—> active)
Clearance of fospropofol
-Same as propofol
(CYP450 enzymes in liver and lungs)
Side effects of fospropofol
Genital and anal burning
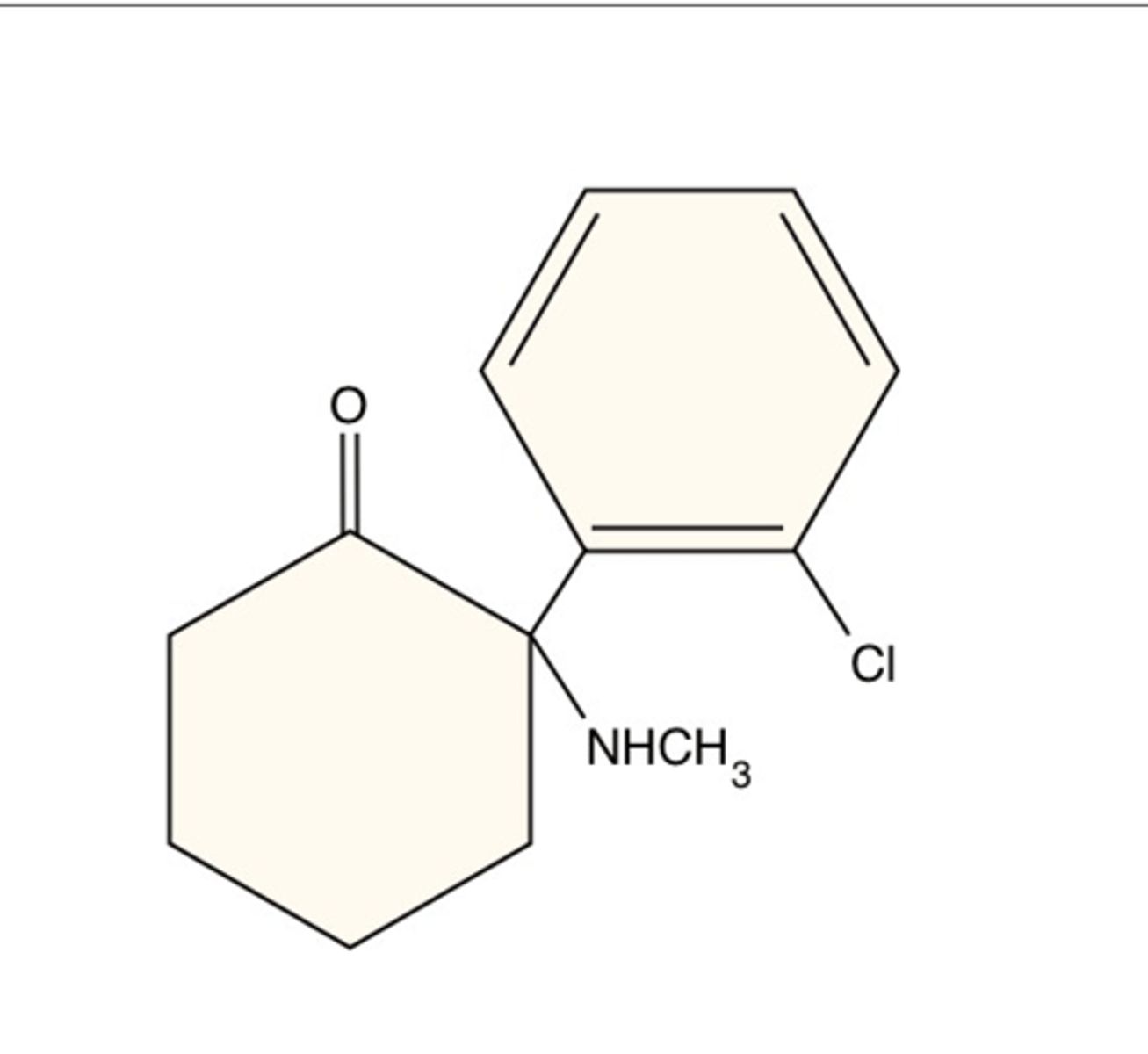
Chemical name of ketamine
2(o-Chlorophenyl)-2(methylamino) cyclohexanone hydrochloride
-Has a ketone group and amine group
Class of ketamine
Arylcyclohexylamine
Phencyclidine derivative producing “dissociative anesthesia”
¡Induction + analgesia
¡Resembles catatonic state
¡Does not require lipid emulsion and produces profound analgesia at subanesthetic doses
ketamine use
¡Intense analgesia and prompt induction of anesthesia
¡Somatic > visceral pain
¡Blocks central sensitization and wind-up in dorsal horn of SC
¡Also prevents opioid-induced hyperalgesia
¡Increased secretions - consider Robinul
¡No pain with injection
¡Not a respiratory depressant
Formulation of ketamine
Aqueous solution, available as 1, 5, or 10%
Racemic mixture
pKa 7.5
not significantly protein bound
MOA of ketamine
-NMDA antagonist (antagonizes glutamate)
-Secondary receptors target: opioid, MAO, serotonin, NE, muscarinic, sodium channels
-PCP derivative- Dissociates the thalamus (sensory) from the limbic system (awareness)
Dose of ketamine
IV induction:
IV maintenance:
Low dose infusion:
Analgesia:
IM:
PO:
IV induction: 1-2 mg/kg
IV maintenance: 1-3 mg/min
Low dose infusion: 1-3 mcg/kg/min (opioid sparing effect)
Analgesia: 0.1-0.5 mg/kg
IM: 4-8 mg/kg
PO: 10 mg/kg
Onset of ketamine
IV/IM/PO
30-60 seconds IV
2-4 minutes IM
Variable PO
Duration of ketamine
10-20 minutes
Up to 60-90 minutes for return to full orientation
Ketamine clearance
Liver (CYP450) via demethylation
Chronic use will induce the enzymes leads to rapid escalation in tolerance
elimination half life= 2-3 hours
Active metabolite of ketamine
Norketamine - 1/3 to 1/5 the potency of ketamine, relies on renal excretion
CV effects of ketamine
-Increased SNS tone (good for hemodynamic instability, bad if severe CAD),
increases myocardial O2 requirements
Increases CO, HR, SVR, and PVR (caution RV failure)
-Subhypnotic doses usually do not activate the SNS (<0.5 mg/kg)
-Myocardial depressant in patients with depleted catecholamines (sepsis) or sympathectomy
Respiratory effects of ketamine
-Bronchodilation
-Maintains respiratory drive (possible brief apnea after induction)
-Does not shift the CO2 curve
-Maintains intact upper airway muscle tone/airway reflexes—> still rx aspiration
-Increases oral/pulmonary secretions (glycopyrolate helps)
CNS effects of ketamine
Increased CMRO2, CBF, ICP, intraocular pressure, — rapid delivery to brain
¡Peak [plasma] around 1 minutes IV and 5 minutes IM
-Nystagmus or blepharospasm (caution with ocular surgery that requires a still eye)
-Emergence delirium
¡Avoid in patients with acute intermittent porphyria
Ketamine effect on eeg
¡Increases cortical amplitude of SSEP’s
¡Auditory and VEP’s are decreased
¡Does not alter seizure threshold
How does emergence delirium present?
¡visual, auditory, proprioceptive, and confusional illusions- Nightmares and hallucinations
Risk factors for emergence delirium with ketamine
Age >15, female, dose >2mg/kg, history of personality disorder
Most effective way to prevent emergence delirium with ketamine
Benzos - Midazolam is better than diazepam
Ketamine brings a risk of nightmares and hallucinations for up to...
24 hours- ranges from 5-30%
Ketamine and analgesia
-Provides analgesia and opioid-sparing effects (only induction agent that does this)
-Relieves somatic > visceral pain
-Blocks central sensitization and wind-up in the dorsal horn of the spinal cord
-Prevents opioid-induced hyperalgesia after remifentanil infusion
-Analgesic properties make it good for burn and chronic pain patients (subhypnotic doses are being used to treat severe depression)
Chronic ketamine use may cause...
ulcerative cystitis
DEXTROMETHORPHAN MOA
¡NMDA antagonist common in OTC cough suppressants
¡Equal potency to codeine as antitussive, but lacks analgesic or physical dependence problems
dextromethorphan SE
¡Excessive intake – HTN, tachycardia, somnolence, agitation, slurred speech, ataxia, diaphoresis, skeletal muscle rigidity, seizures, coma, and decreased core body temperature.
¡Psychoactive effects create abuse potential
True or False: Patients with a history of acute intermittent porphyria should NOT be administered ketamine.
True
Ketamine protein binding compared to other induction agents
Smallest amount of plasma protein binding (12%)
Induction agent with highest amount of protein binding
Propofol (98%)
-Diazepam 98%
-Midazolam 94%
-Dexmedetomidine 94%
-Lorazepam 90%
-Etomidate 75%
-Ketamine 12%
Chemical name of etomidate (Amidate)
R-1 methyl-1 a-methylbenzyl imidazole 5-carboxylate
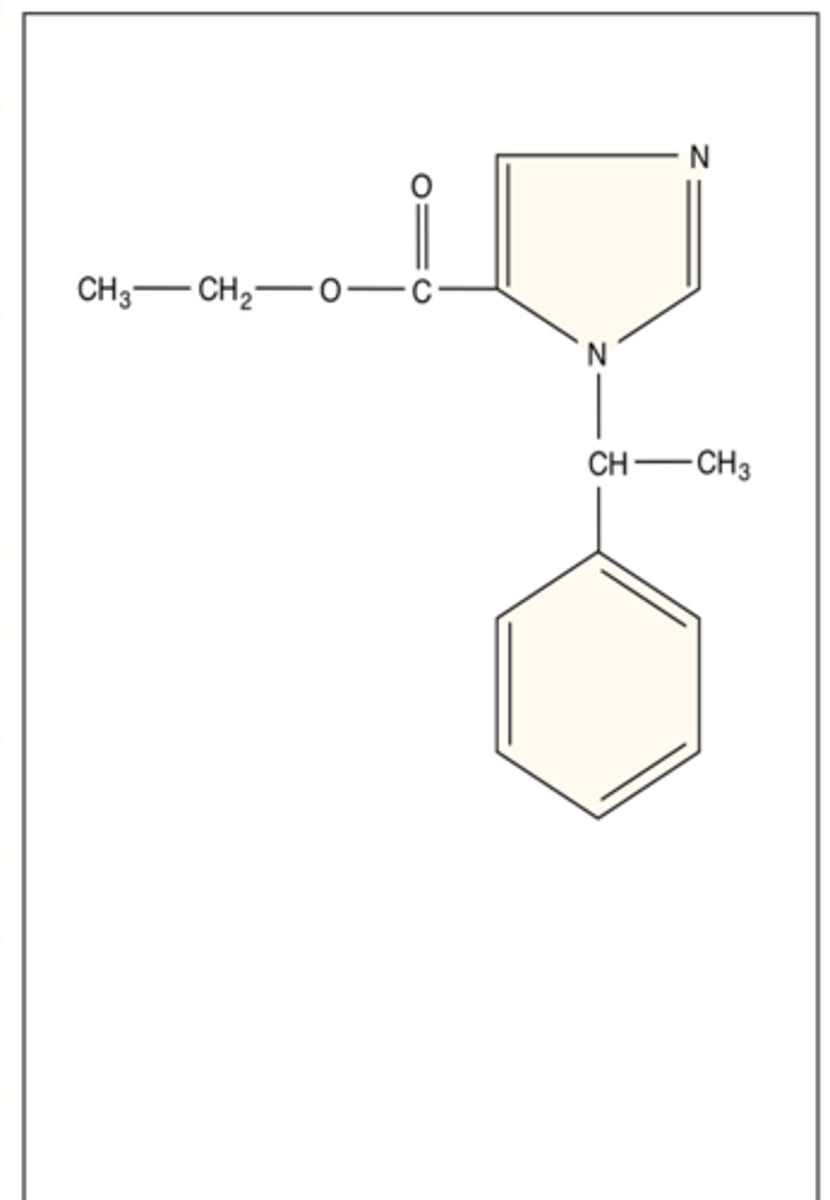
Class of etomidate
what happens when in acidic pH and physiologic pH
Imidazole
Has carboxylated imidazole containing Water-soluble (acidic pH) ad lipid-soluble (physiologic pH)
-Acidic pH --> imidazole ring opens --> increased water solubility
-Physiologic pH --> imidazole ring closes --> increased lipid solubility
ETOMIDATE - Pharmacokinetics (3)
Large VOD – peaks around 1 minute
Highly protein bound
Redistribution and rapid metabolism by hydrolysis
Formulation of etomidate
2 forms:
-35% propylene glycol (venous irritation and injection pain)
-Lipid emulsion (less venous irritation and injection pain)
MOA of etomidate
GABA-A agonist
Dose of etomidate
0.2-0.4 mg/kg IV
Onset of etomidate
30-60 seconds
Duration of etomidate
5-15 minutes
Clearance of etomidate
Hepatic P450 enzymes and plasma esterases
-Rapid awakening d/t redistribution, NOT metabolism
Active metabolite of etomidate
None
CV effects of etomidate
-Hemodynamic stability with minimal changes HR, SV and CO
-Decreased SVR with small decrease BP
-Does not block SNS response to laryngoscopy (opioid or esmolol will help)
Respiratory effects of etomidate
Mild respiratory depression
CNS effects of etomidate
-Decreased CMRO2, CBF (cerebral vasoconstriction), and ICP
-CPP stable
-No analgesia
-May increase risk of seizure activity in susceptible patients
Which anesthetic agent increases mortaility in the patient with addisonian crisis?
A. Etomidate
Propofol
Dexmed
Midazolam
A. Etomidate
Pro of etomidate
hemodynamic stability
Con of etomidate
does not block effects of laryngoscopy
Key SE of etomidate
Myoclonus
PONV (more than any induction agent
Suppression of adrenal function for up to 24 hours (avoid in sepsis and acute adrenal failure
Acute intermittent porphyria
Myoclonus
Involuntary skeletal muscle contractions, dystonia, or tremor (not a seizure)
Mechanism of myoclonus
Unclear; Likely an imbalance between excitatory and inhibitory pathways in the thalamocortical tract
Etomidate and seizure activity
-No history of seizures
-History of seizures
-No history of seizure: etomidate does not increase the risk of seizure
-History of seizures: etomidate can increase epileptiform (seizure like) activity and possibly increase the risk of seizures (useful for mapping seizure foci)
Cortisol and aldosterone synthesis are dependent on which enzyme? Where is this located?
11-beta-hydroxylase
Possibly also 17-alpha-hydroxylase
Located in the adrenal cortex
How does etomidate cause adrenocortical suppression?
Inhibits 11-beta-hydroxylase and 17-alpha-hydroxylase
(this is why not cont infusion in ICU)