The Human Eye
1/125
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
126 Terms
What are the three overlapping functions performed by the nervous system?
Sensory Input
Integration
Motor output
What does sensory input involve?
Light-detecting cells i.e. rods and cones of the retina in the eyes
What is Sensory Input?
Conduction of signals from sensory receptors to integration centre
Sensory Input is the conduction of signals from … to integration centre
sensory receptors
Sensory Input is the conduction of signals from sensory receptors to …
integration centre
What is Integration?
Process by which the information from the environmental stimulation of the sensory receptors is interpreted
What is information interpreted during integration then associated with?
With appropriate responses of the body
Where is integration carried out and what is it carried out by?
In the central nervous system (CNS) by the brain and spinal cord [in vertebrates]
What is Motor Output?
Conduction of signals from the Integration Centre, the CNS to the effectors, muscles or gland cells which actually carry out the body's response to stimulus
What is the integration centre in motor output?
CNS
What is the effector in motor output?
muscle cells or gland cells
From receptor to effector, how is information transmitted from one neurone to another?
a combination of electrical signals (nerve impulse) and chemicals (neurotransmitters)
What does the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) do?
Communicate motor and sensory signals between the central nervous system and the rest of the body
Each eyeball lies in a socket in the skull called the …
orbit
The eyeball is attached to the eye socket by?
Six rectus muscles
What do the six rectus muscles do?
Enable the eyeball to rotate slightly within the socket

1
iris
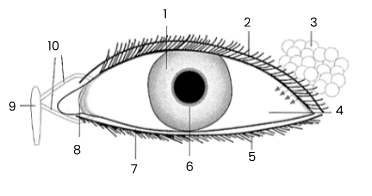
2
upper eyelid
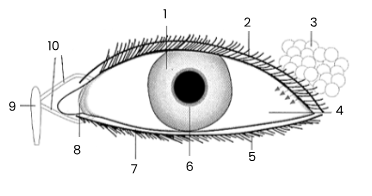
3
tear gland
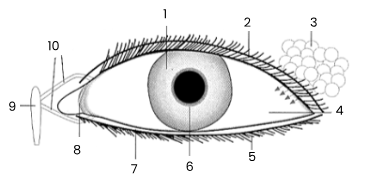
4
sclerotic coat/sclera covered by conjunctiva
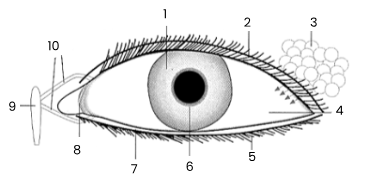
5
eye lashes
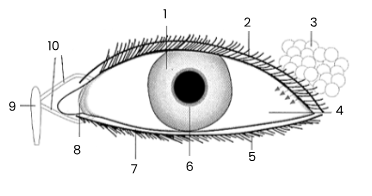
6
pupil
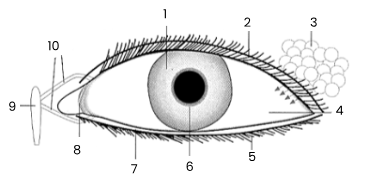
7
lower eyelid
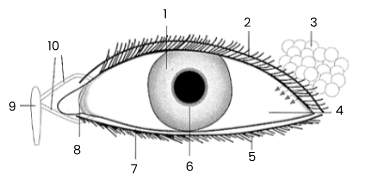
8
remains of third eyelid (nicitating membrane)
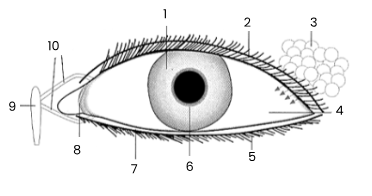
9
tear sac empties into nasal cavity

10
tear ducts
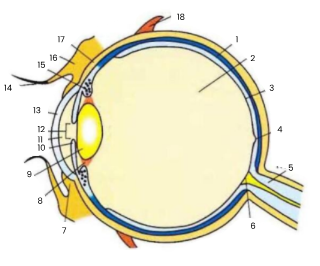
1
choroid
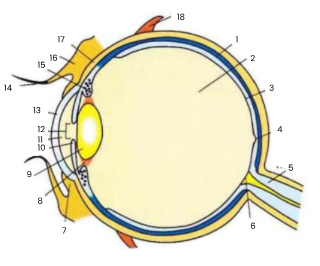
2
vitreous humour
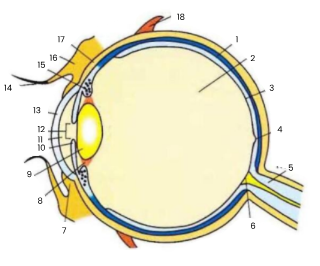
3
retina
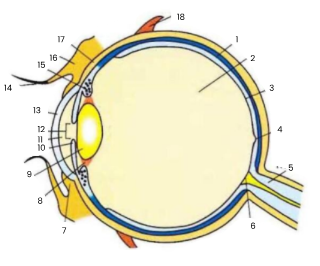
4
fovea
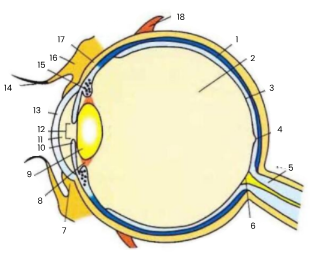
5
optic nerve
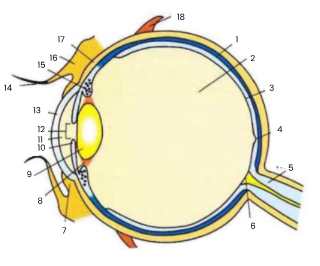
6
blind spot
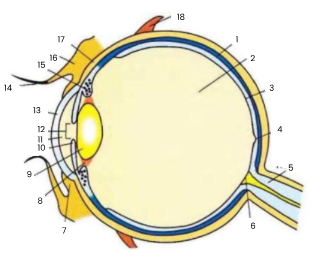
7
conjunctiva
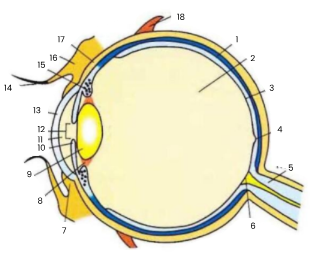
8
suspensory ligament
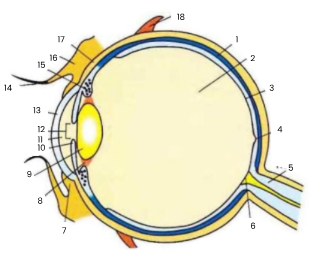
9
lens
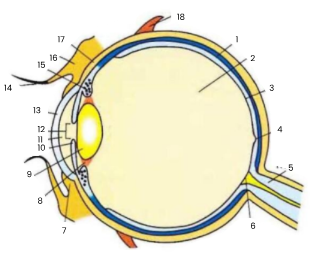
10
iris
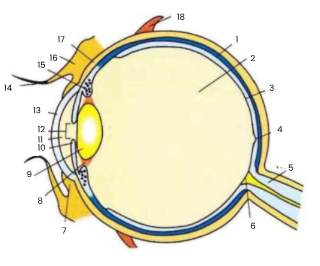
11
aqueous humour
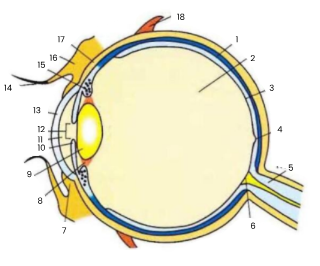
12
pupil
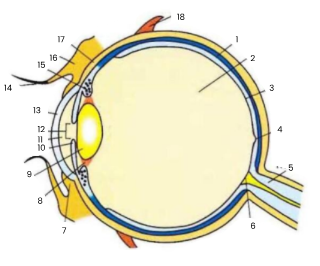
13
cornea
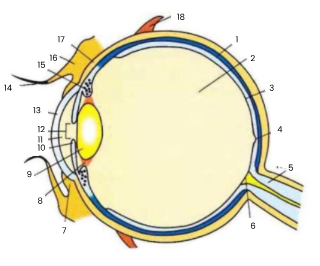
14
eyelash
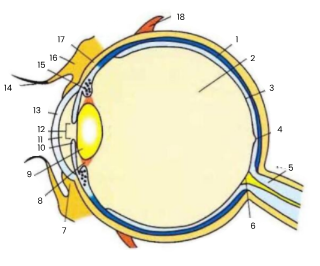
15
ciliary body
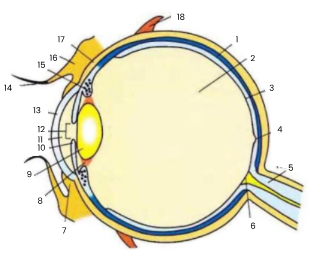
16
eyelid
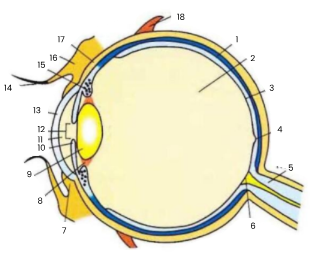
17
sclera
What type of membrane is the conjunctiva?
Thin transparent membrane
Mucous membrane
What is the conjunctiva continuous with?
skin of eyelids
What does the conjunctiva protect and from what?
protects cornea at front of eyeball against friction
What does the conjunctiva cover?
Covers sclera (white of eye) in front
Which part of the eye is a mucous membrane that secretes mucus and keeps the eyeball moist?
conjunctiva
What part of the eye forms a small bulge in front of the eye?
cornea
What is the cornea?
anterior end of sclera
Where does most refraction of light occur?
cornea
The cornea is the … portion of the sclera, allowing light to pass through it to reach the retina
transparent
The cornea is the transparent portion of the sclera, allowing light to pass through it to reach the …
retina
Where does the cornea refract light into?
pupil
What make up the wall of the eye?
Sclera
Choroid
Retina
What is the sclera?
Tough white outer layer of eyeball
What does the sclera do?
Protects eyeball against mechanical injury
What does the choroid contain?
blood vessels that supply the retina with oxygen and nutrients
Which part of the eye contains blood vessels that supply the retina with oxygen and nutrients?
choroid
What colour is the choroid?
Pigmented black
Why is the choroid pigmented black?
prevent internal reflection of light
What is the retina?
innermost layer of the eyeball that contains photoreceptors (rods and cones)
Which part of the eye contains photoreceptors?
retina
What do photoreceptors do?
detect stimuli
What are cones concerned with?
color vision in bright light
What are rods concerned with?
vision in dim light
What does the optic nerve do?
transmits nerve impulses (information) from photoreceptors to the brain
The iris is part of the …
choroid
The iris is the anterior end of the …
choroid
Which two parts of the eye are part of the wall of the eye and which part?
cornea = anterior end of sclera
iris = anterior end of choroid
What is the function of the iris?
controls the size of the pupil → controls amount of light entering eye
Which part of the eye controls the pupil size/how much light enters the eye?
Iris
What does the iris contain to control the size of the pupil?
two involuntary muscles: circular and radial muscles
Circular and radial muscles are an … action
involuntary
What do the circular and radial muscles control?
Size of pupil
What does the iris contain?
Pigment that gives the eye its colour
What is the pupil?
Hole in the centre of the iris that allows light to enter the eye
What is the function of the pupil?
Allow light to enter the eye
What is the function of the lens?
Focuses light rays onto retina by changing shape
Why are the lens elastic?
change thickness and shape to refract light onto retina
What type of structure do the lens have?
Transparent, biconvex, elastic
What is the function of the suspensory ligaments?
holds lens in position by attaching lens to ciliary body
How do the suspensory ligaments hold the lens in position?
By attaching lens to ciliary body
What does the ciliary body contain?
Muscles which control the curvature of the lens
What is the function of the ciliary body?
Control lens curvature and supports lens
What is the function of the vitreous humour?
supports lens
refracts light rays and keeps eyeball firm
The vitreous humour helps refract light onto the …
retina
What type of substance is the vitreous humour?
transparent, jelly-like
What type of substance is the aqueous humour?
transparent and watery fluid
What is the function of the aqueous humour?
refracts light and keeps eyeball firm
maintains shape of the anterior chamber of eyeball
Which part of the eye maintains shape of the anterior chamber of eyeball?
aqueous humour
Which parts of the eye are capable of refracting light?
cornea (into pupil)
lens (onto retina)
vitreous humour (onto retina)
Which part of the eye is used for protection?
conjunctiva (cornea at front against friction)
sclera (outer layer against mechanical injury)
vitreous humour (keeps eyeball firm)
aqueous humour (keeps eyeball firm)
What is the conjunctiva lubricated by?
Tears secreted by the lachrymal or tear gland
Where are the lachrymal or tear gland located?
outer corner of the upper eyelid
Where do tears flow out from?
Between eyelids and exposed part of the eyeball
Approximately how many rod cells and cone cells does the retina contain?
about 125 million rod cells and 6 million cone cells
How many types of photoreceptors (light-sensitive cells) are there?
Two types: rods and cones
What are rods and cones named after?
Their shapes
What is the fovea also known as?
yellow spot