halide ions
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
how does oxidising ability of halide ions change down the group?
attraction between outer e- and nucleus decreases down group as ions get bigger
so oxidising ability decreases
give the eqns for halides reacting w/ concentrated sulfuric acid:
NaX + H2SO4 → NaHSO4 + HX
give the further reaction for some halides reducing sulfuric acid:
2HX + H2SO4 → X2 + SO2 + 2H2O
give the overall eqn for halides reacting w/ concentrated sulfuric acid and reducing it further:
2NaX + 3H2SO4 → 2NaHSO4 + X2 + SO2 + 2H2O
give the half eqns for some halides reducing sulfuric acid:
2X- → X2 + 2e-
H2SO4 + 2H+ +2e- → SO2 + 2H2O
name and explain the observations for the reactions of NaF and NaCl w/ H2SO4:
HF and HCl are not strong enough reducing agents to reduce the H2SO4 further
not a redox reaction - oxidation states of halogens and sulfur remain the same
observation: misty white fumes of HF / HCl
name and explain the observations for the reaction of NaBr w/ H2SO4:
HBr is a strong enough reducing agent to reduce H2SO4 further
second eqn = redox: Br oxidised (from -1 to 0) and S reduced from (+6 to +4)
observations: misty fumes of HBr, red-brown vapour Br2, choking fumes of SO2
what are the overall and ionic eqns for the overall reaction of sodium bromide w/ sulfuric acid, w/ the sulfuric acid being further reduced?
ionic: 2Br− + 3SO42- + 6H+ → 2HSO4- + Br2 + SO2 + 2H2O
overall: 2NaBr + 3H2SO4 → 2NaHSO4 + Br2 + SO2 + 2H2O
give and explain the eqns for NaI reacting w/ sulfuric acid:
NaI(s) + H2SO4 (l) → NaHSO4 (s) + HI(g)
HI can reduce H2SO4 further: 2HI(aq) + H2SO4 (l) → I2 (s) + SO2 (g) + 2H2O(l)
HI is a very strong reducing agent and can reduce the SO2 again to S and H2S: 6HI(g) + H2SO4(l) → 3I2(s) + S(s) + 4H2O(l)
6HI(g) + SO2(g)→ H2S(g) + 3I2(s) + 2H2O (l)
give and explain the observations for NaI reacting w/ sulfuric acid:
misty white fumes (HI)
purple vapour (I2)
yellow solid formed (S)
rotten egg smell (H2S)
black solid formed (I2)
choking fumes (SO2)
give the overall and overall ionic eqns for NaI reacting w/ H2SO4 and the observations:
overall: 8NaI + 9H2SO4 → 4I2 + 8NaHSO4 + H2S + 4H2O
ionic: 8I− + SO42- + 10H+ → 4I2 + H2S + 4H2O
observations: purple vapour released, black solid formed and a rotten egg smell
how can we test for halide ions in aqueous solution?
add 10 drops of substance you are testing to a clean, dry test tube
add approx 5 drops of dilute nitric acid and shake
add 10 drops silver nitrate solution and record observations
add dilute then concentrated ammonia and record further observations
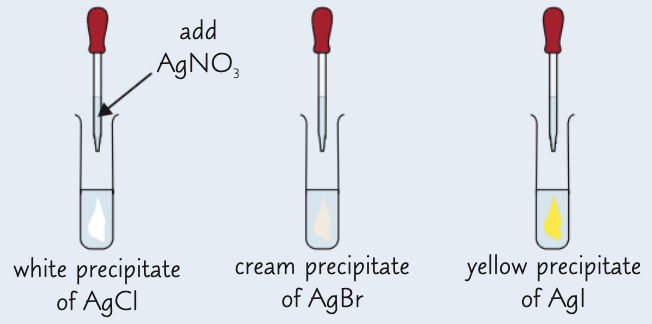
give the general eqn for the reaction of halide ions w/ silver nitrate:
Ag+ (aq) + X- (aq) → AgX (s)
give the results of the silver nitrate test:
AgCl - white ppt
AgBr - cream ppt
AgI - yellow ppt
give the results for the silver halide ppts dissolving in ammonia:
AgCl - dissolves in dilute ammonia to form a colourless solution
AgBr - dissolves in concentrated ammonia to form a colourless solution
AgI - does not dissolve