Dental Anatomy Exam 1
1/116
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
117 Terms
What is the maxillary arch?
Upper arch
What is the mandibular arch?
lower arch
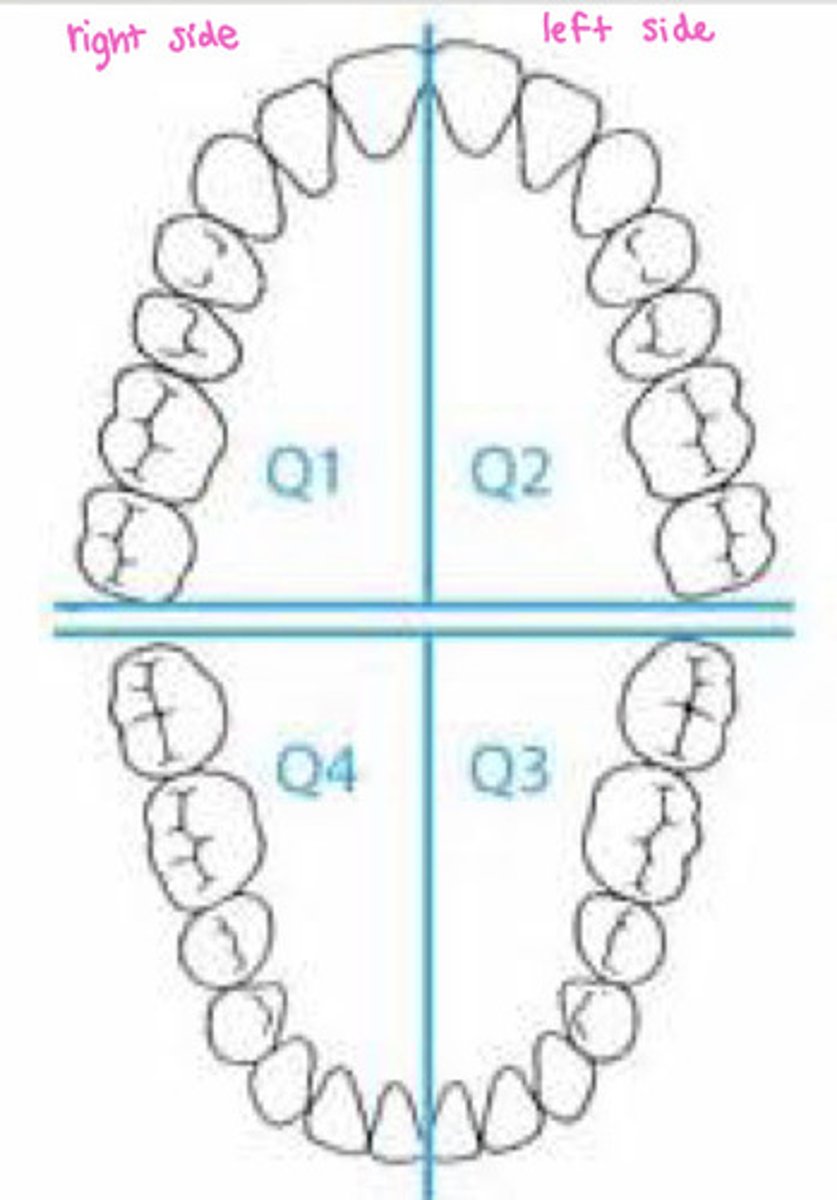
What are quadrants?
right upper quadrant, left upper quadrant, right lower quadrant, left lower quadrant
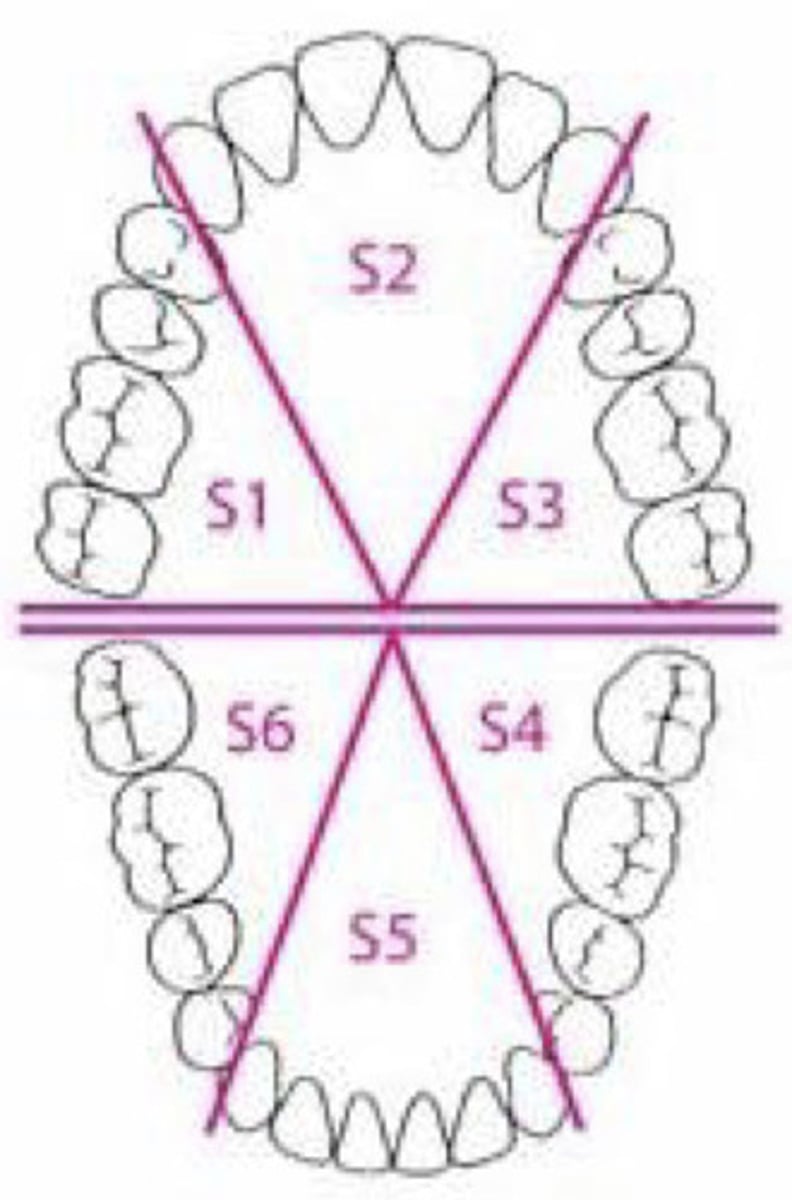
What are sextants?
maxillary right posterior, maxillary anterior, maxillary left posterior, mandibular right posterior, mandibular anterior, mandibular left posterior
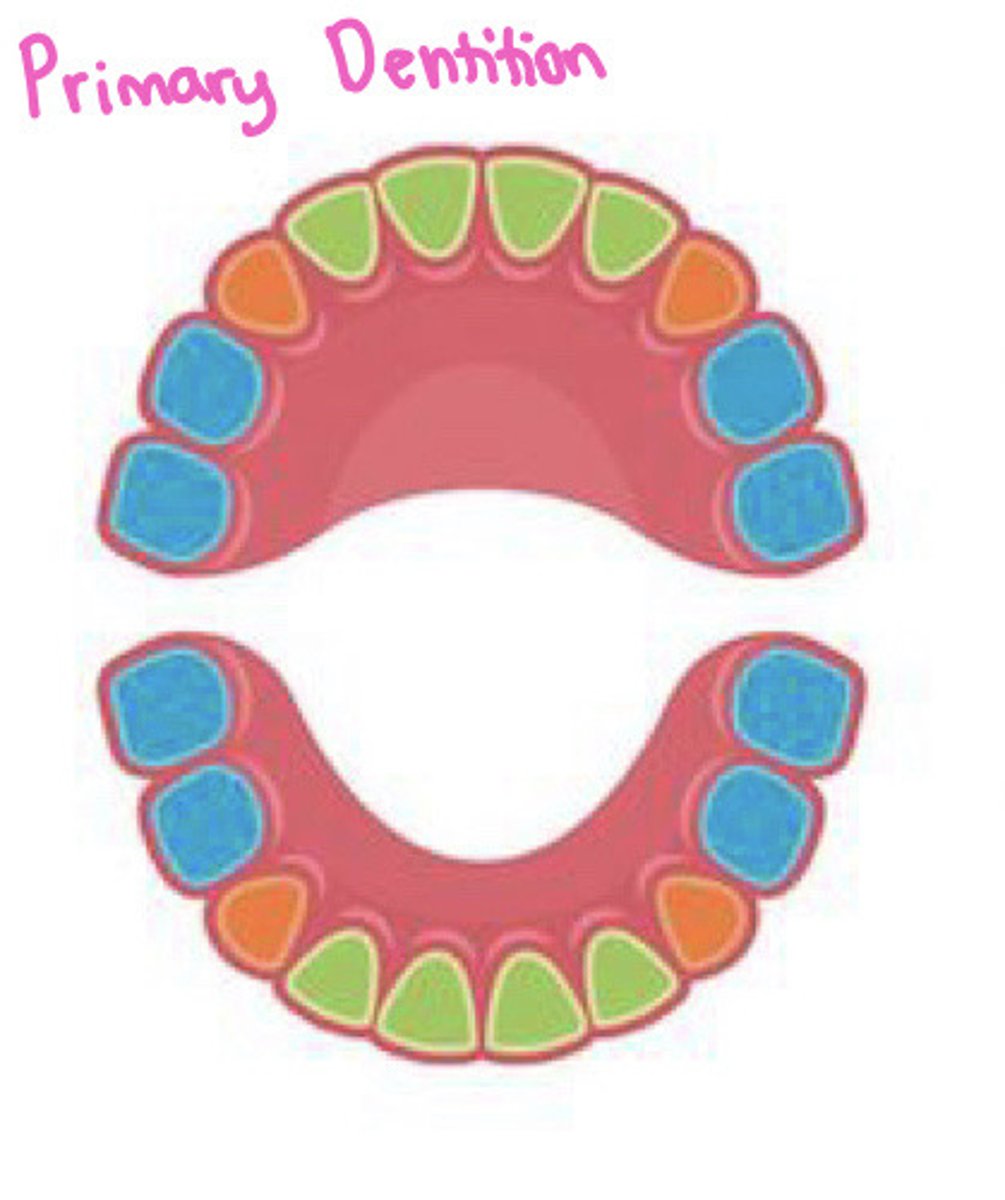
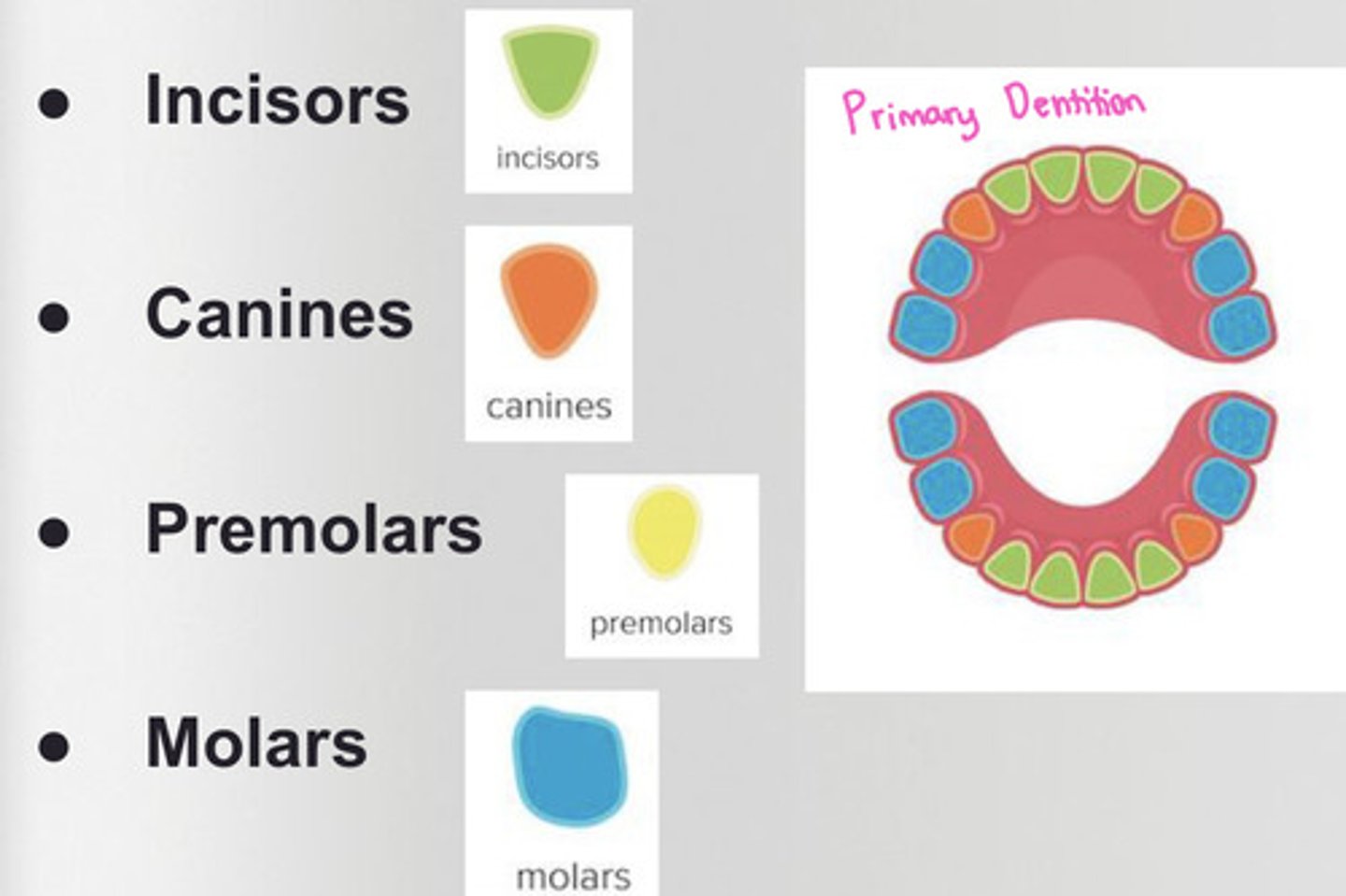
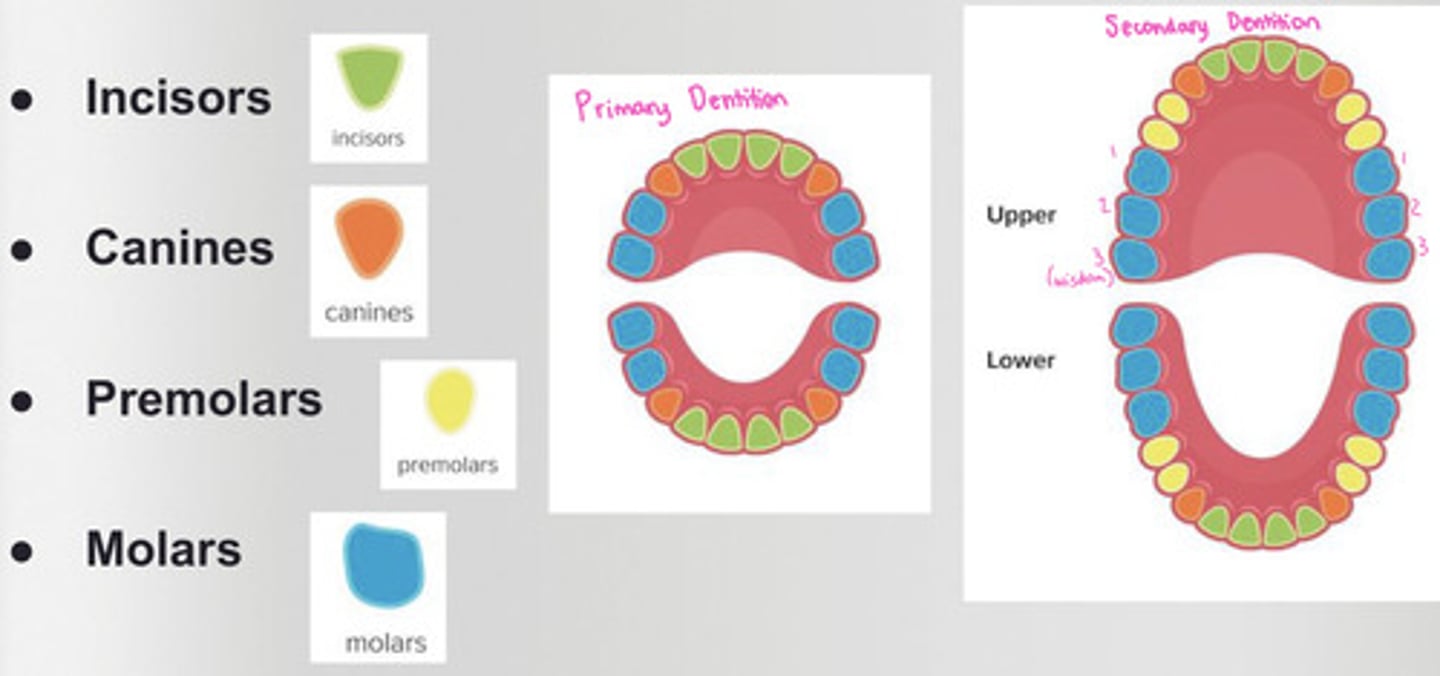
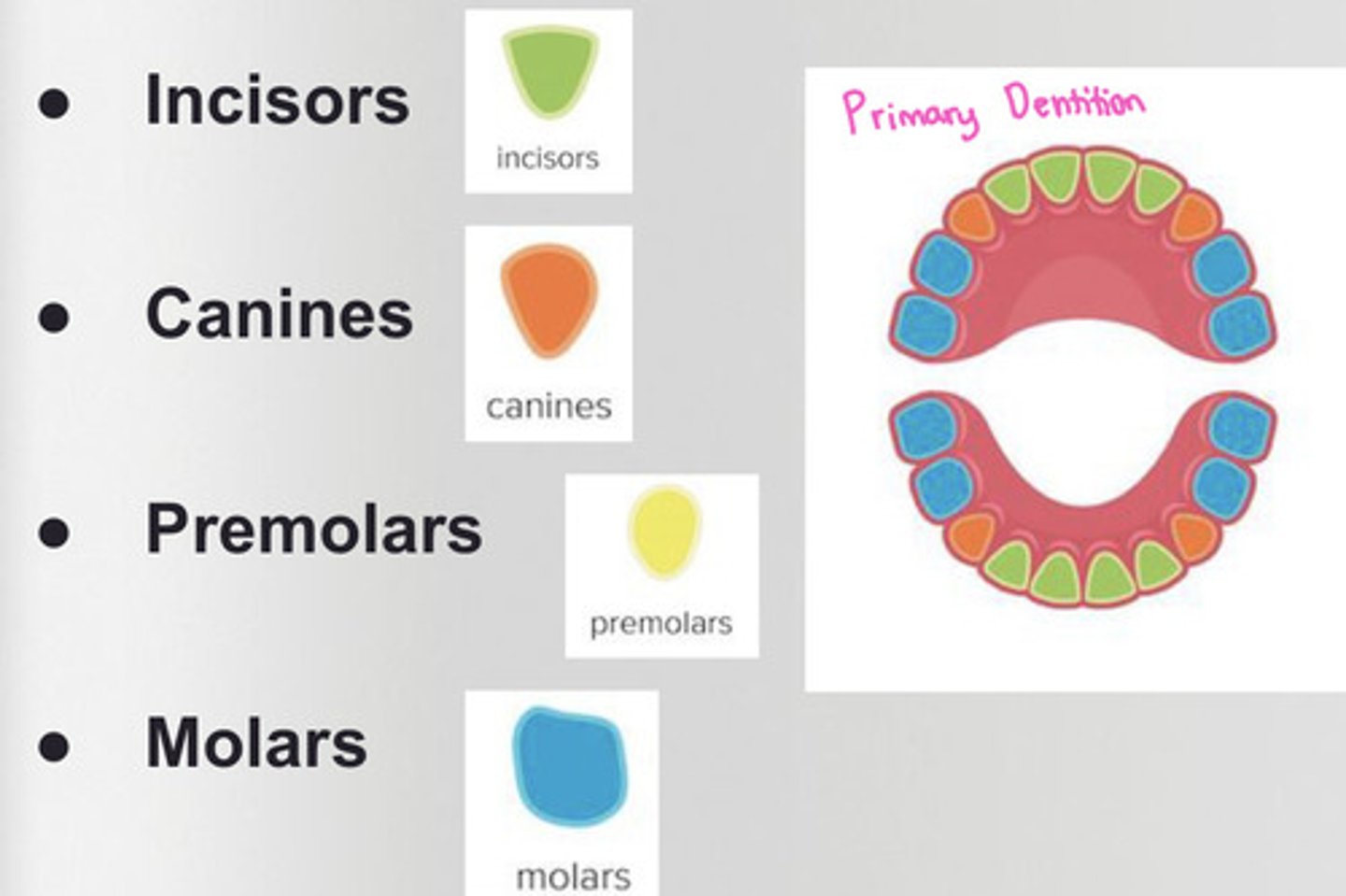
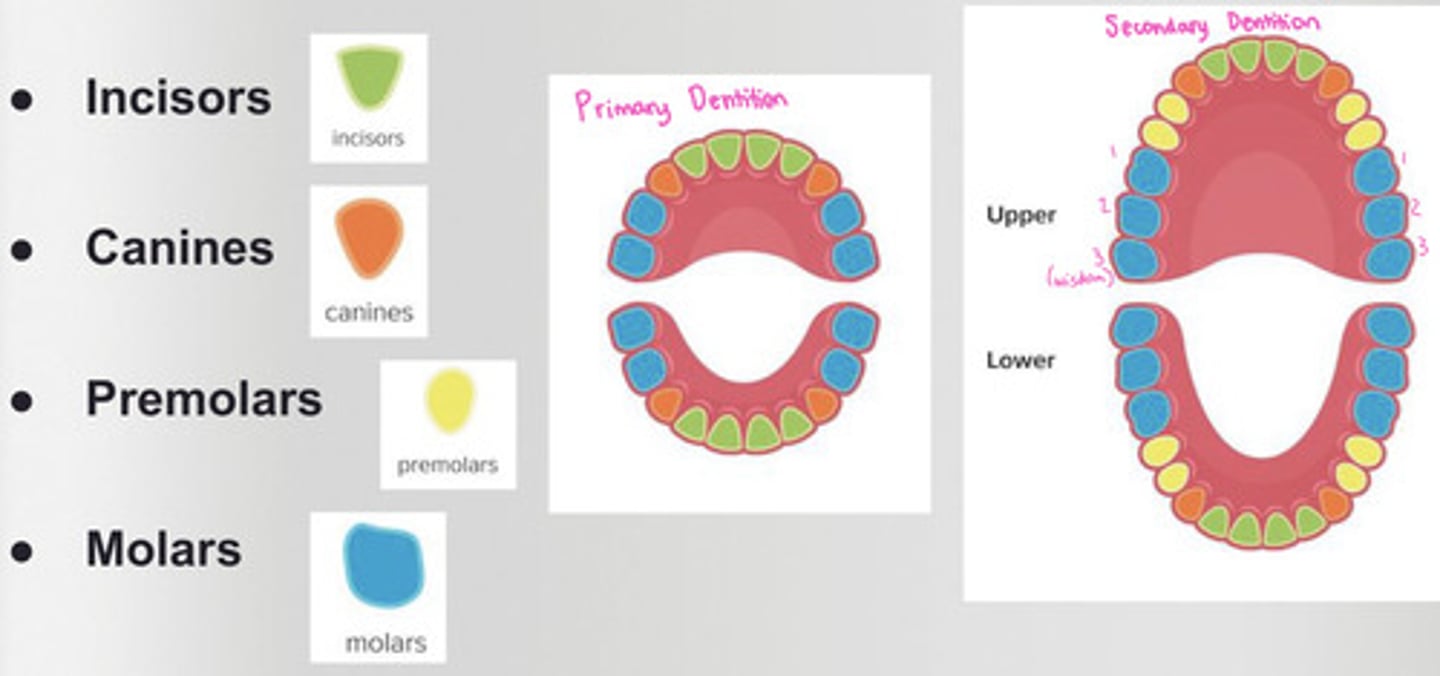
What is the primary dentition?
baby teeth
*20 teeth*
-has incisors, canines, and molars
What is the secondary or permanent dentition?
adult/permanent teeth
*32 teeth*
-Has incisors, canines, premolars, and molars
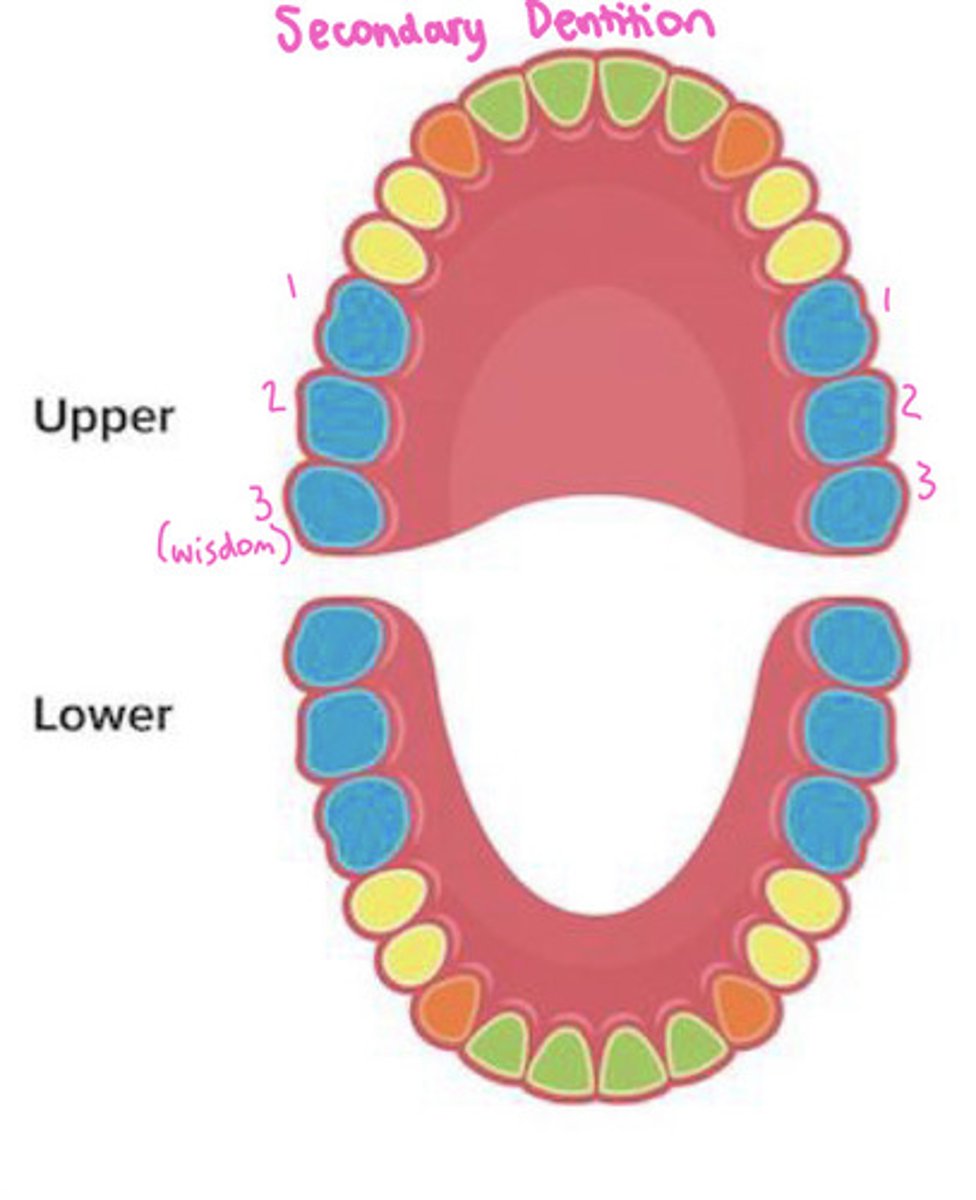
How many incisors are in the primary dentition?
4 maxillary
4 mandibular

How many incisors are in the permanent dentition?
4 maxillary
4 mandibular
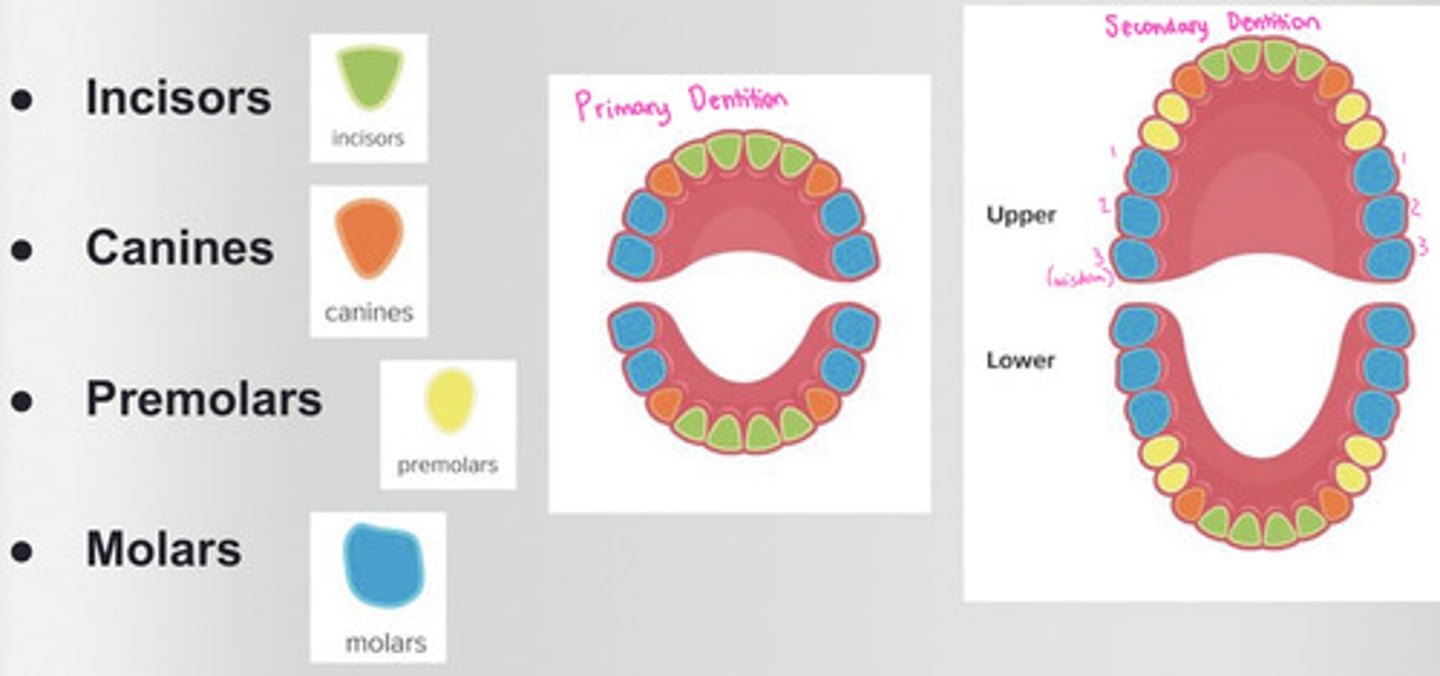
How many canines are in the primary dentition?
2 maxillary
2 mandibular

How many canines are in the permanent dentition?
2 maxillary
2 mandibular
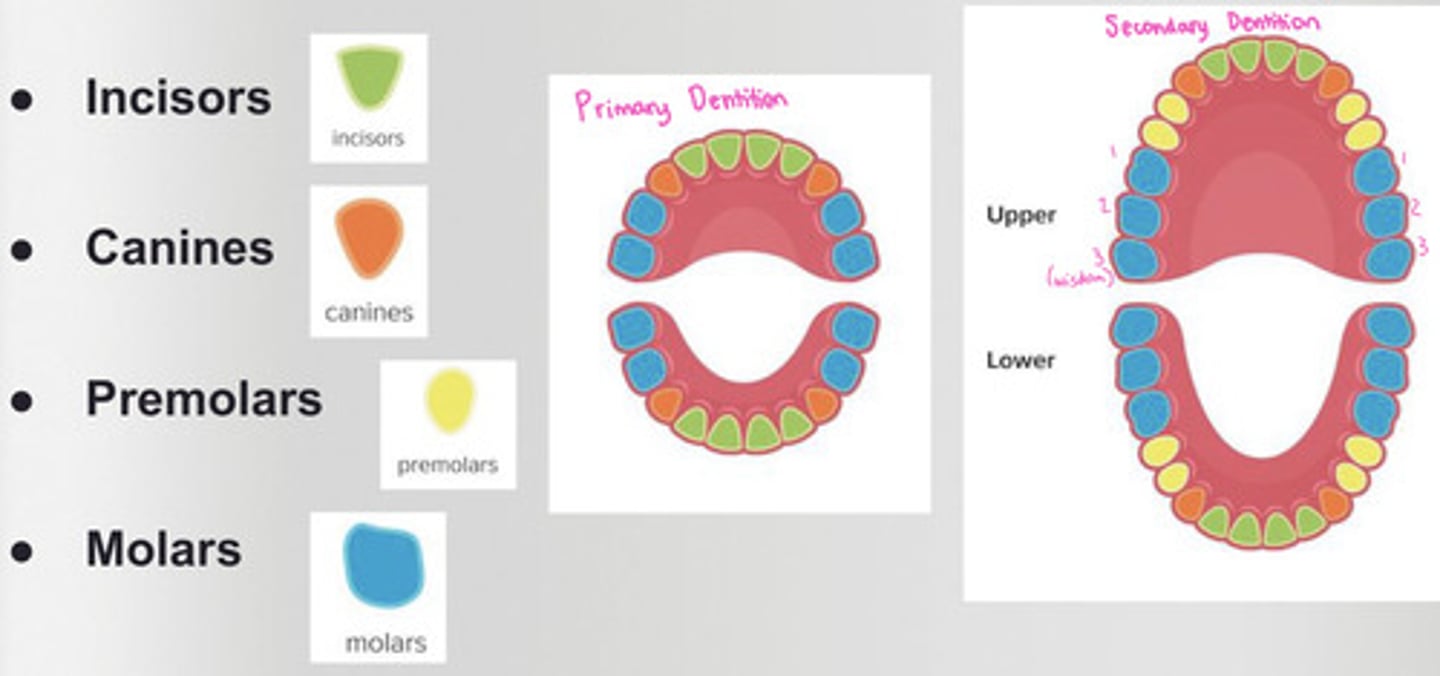
How many premolars are in the primary dentition?
NONE
How many premolars are in the permanent dentition?
4 maxillary
4 mandibular
How many molars are in the primary dentition?
4 maxillary
4 mandibular
How many molars are in the permanent dentition?
6 maxillary
6 mandibular
When we talk about teeth, what is the order we name them in?
arch --> quadrant --> position --> class
-maxillary/mandibular, right/left, distance from midline, tooth
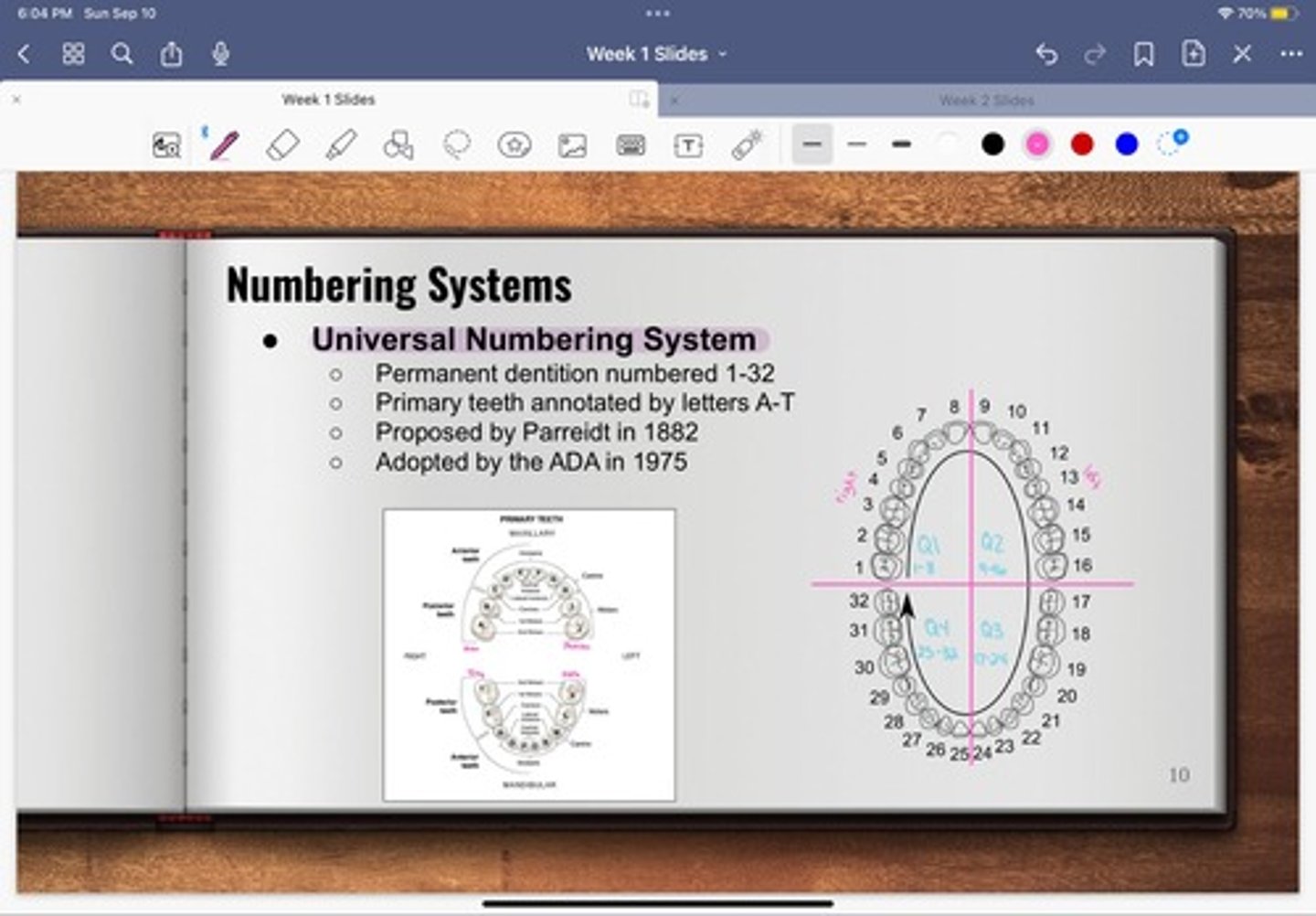
What is the universal numbering system?
-permanent dentition numbered 1-32
-primary teeth annotated by letters A-T
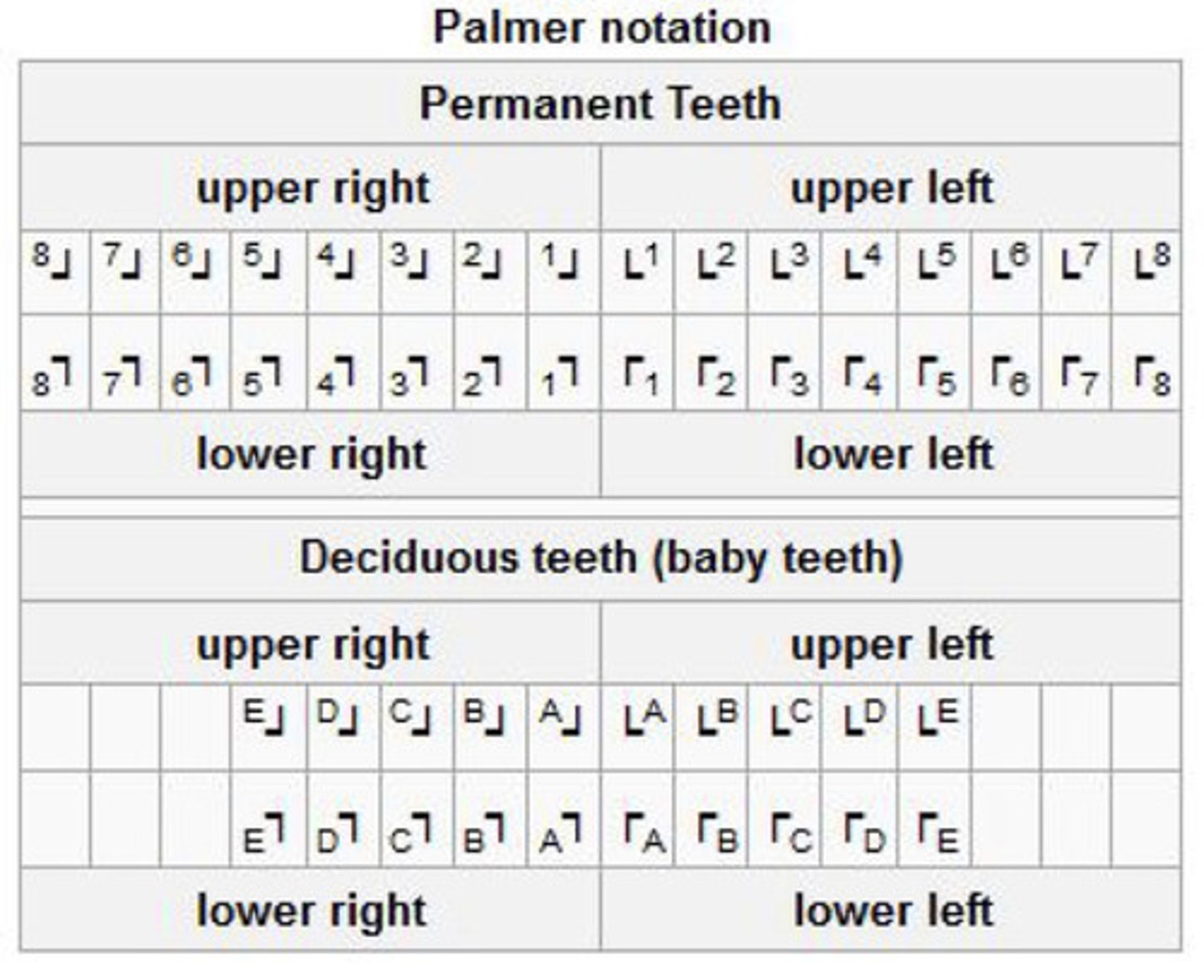
What is palmer notation?
quadrant is identified by bracket position
-teeth are numbered by distance from midline
What is world dental federation notation (FDI)?
uses 2 digits to identify teeth:
-first number relates to quadrant
-second number relates to position from midline
-example: 41 (Q4, tooth first from midline = tooth 25)

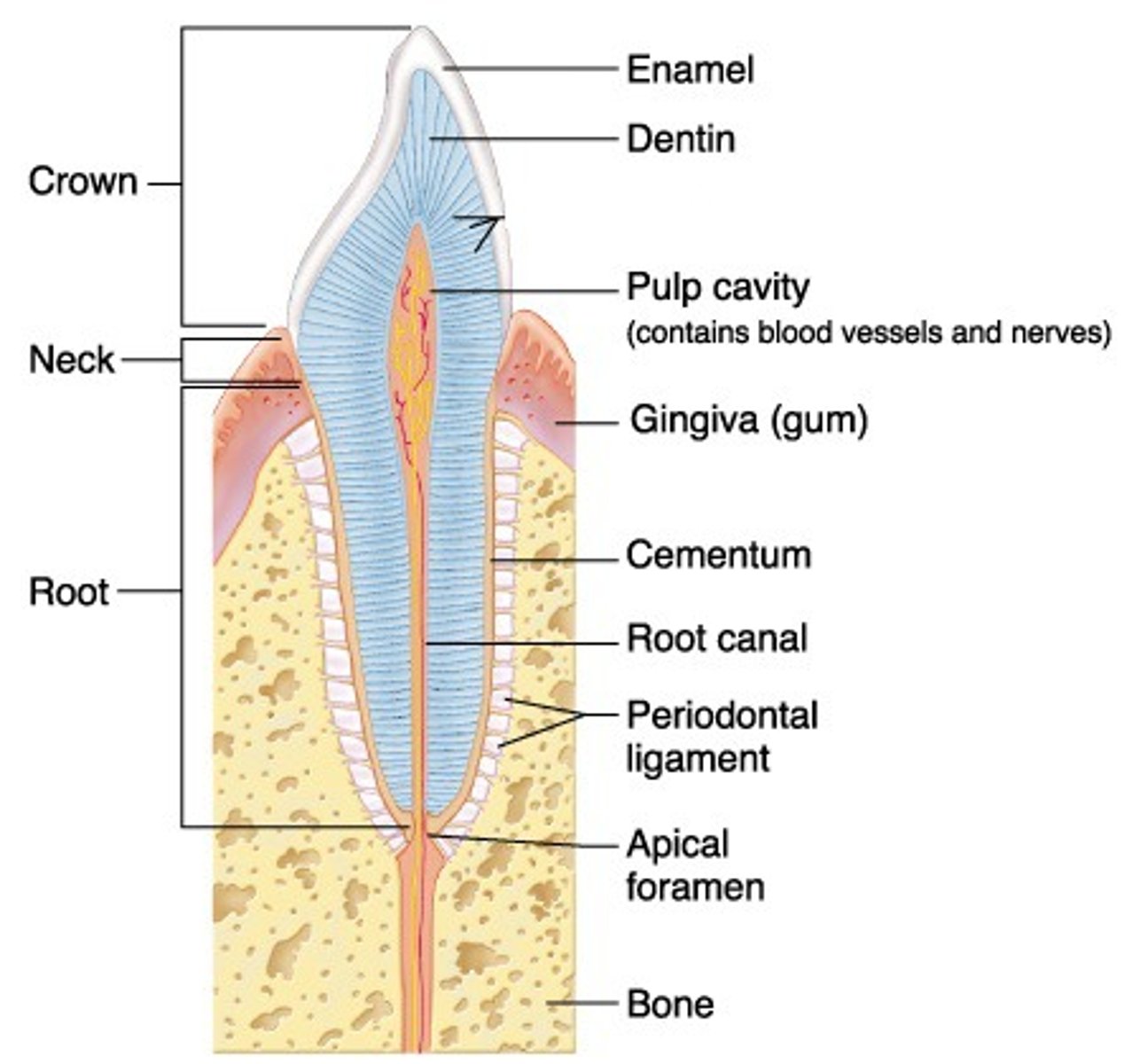
What is cementum?
external layer of anatomic root; covers dentin
-very thin
-65% mineralized
-approximately as hard as bone
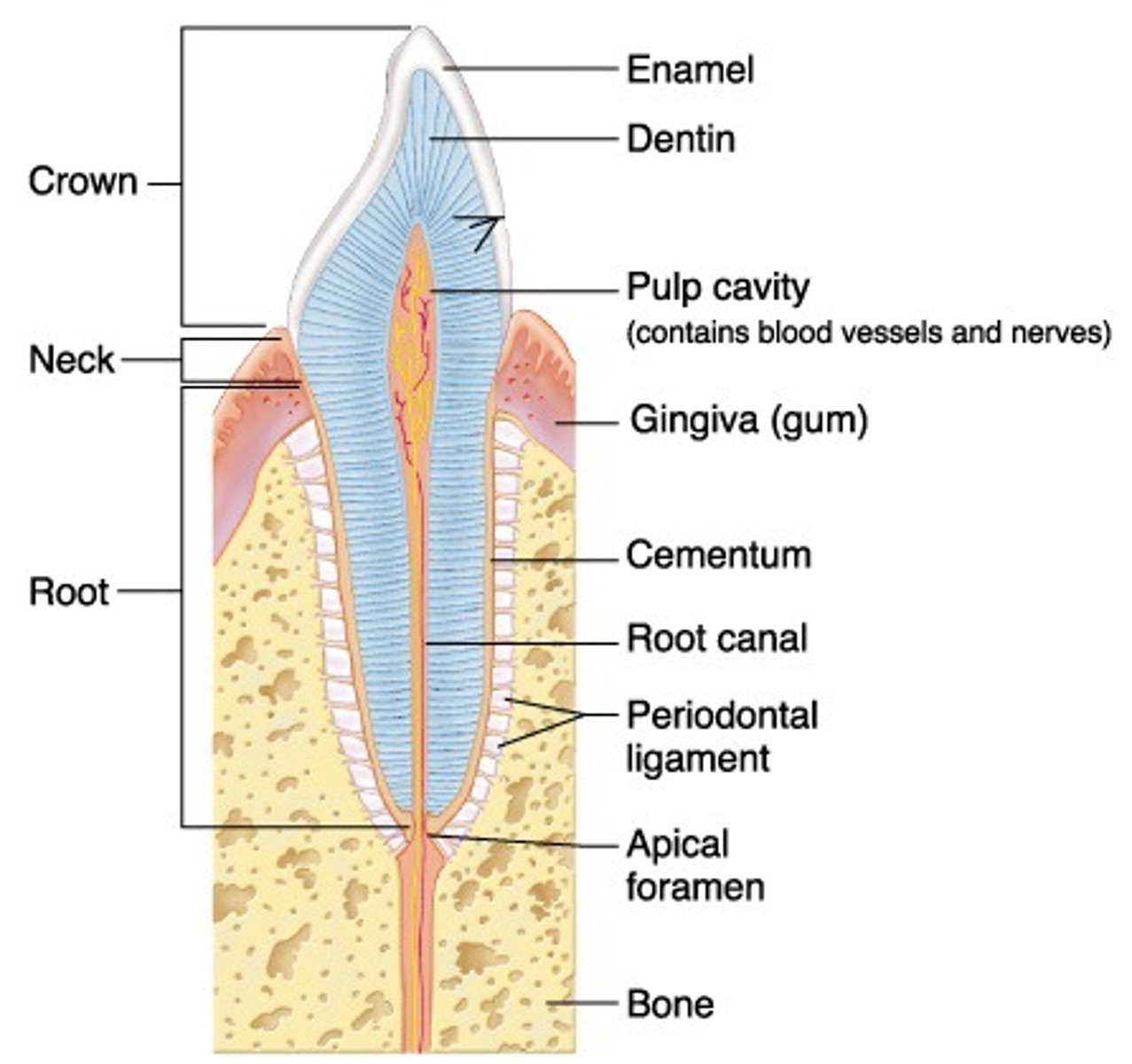
What is dentin?
hard yellowish tissue underlying the enamel & cementum
-70% mineralized calcium hydroxyapatite
What is the anatomical root?
portion of the tooth covered by cementum
-has cementum, dentin, pulp cavity
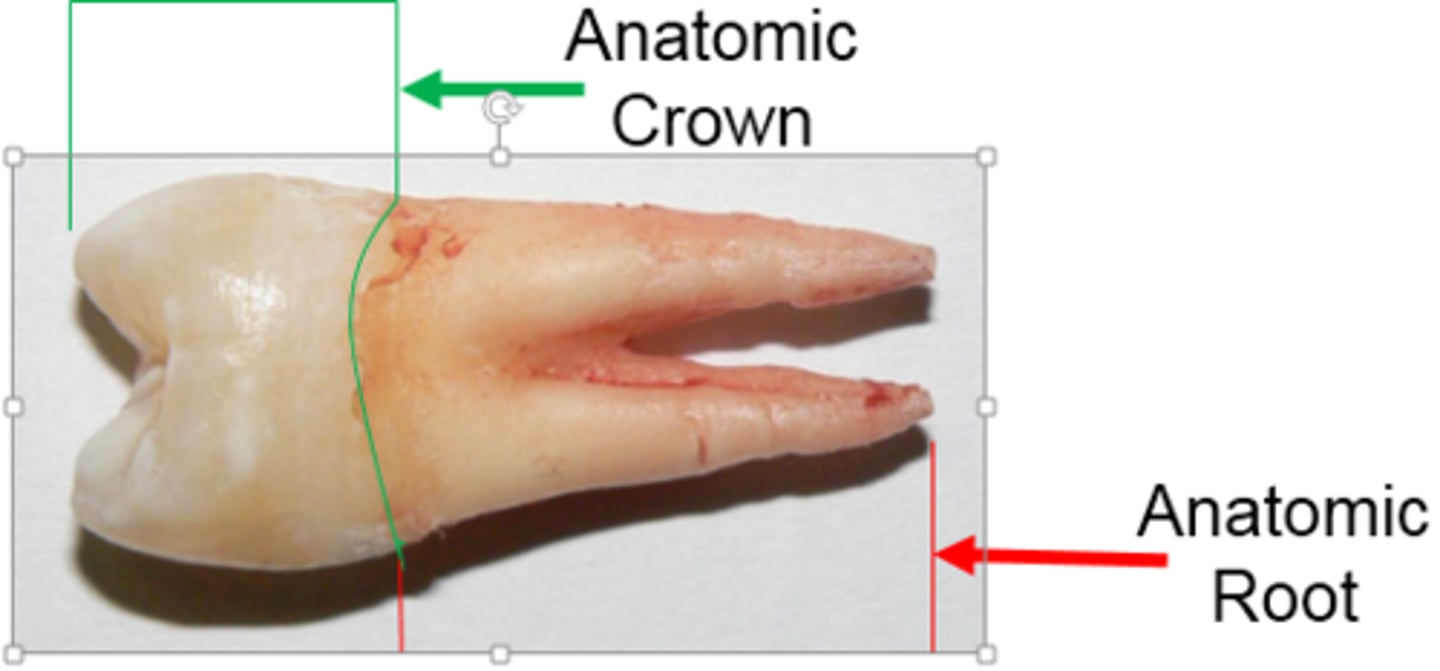
What is the clinical crown?
the amount of tooth that is visible
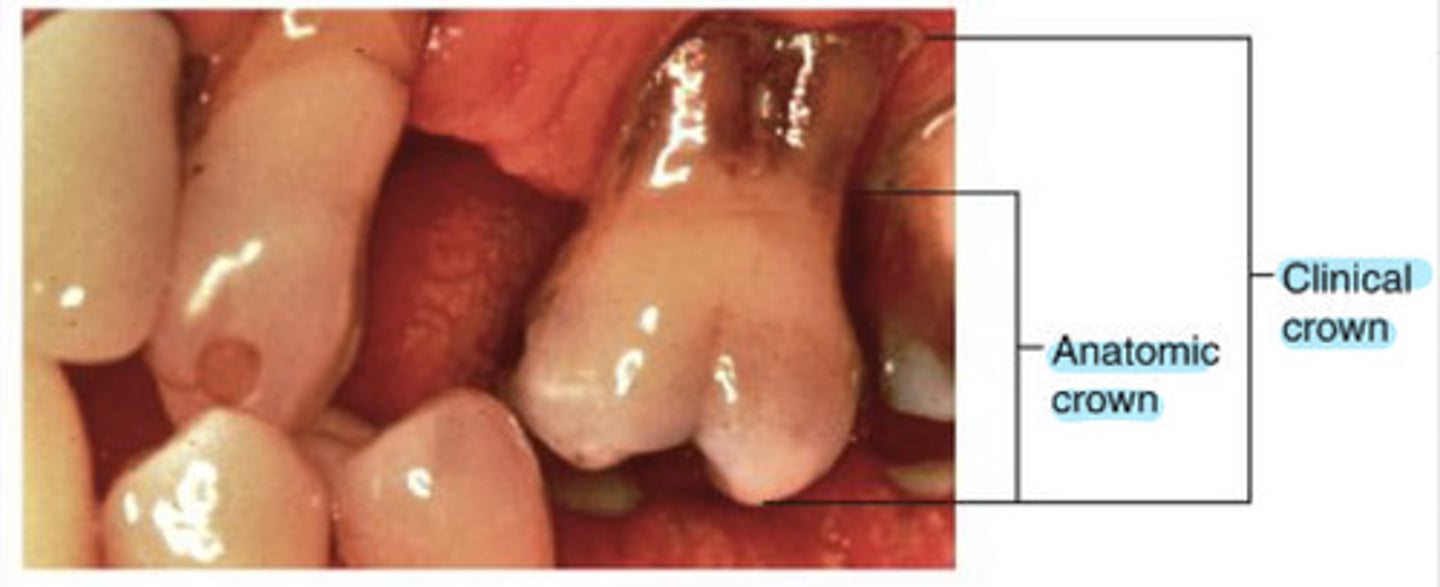
What is the clinical root?
the portion of the tooth not visible in the oral cavity

What is the pulp cavity?
contains pulp chamber, root canal, and apical foramen
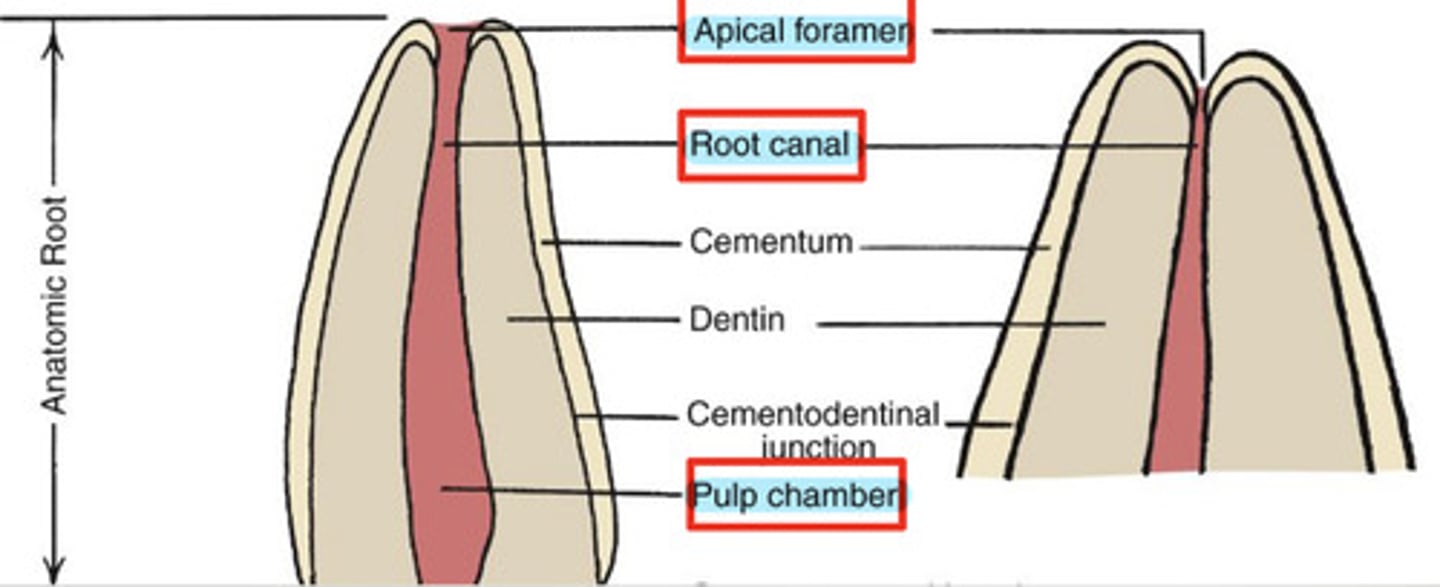
What is the pulp chamber?
coronal portion of the pulp cavity located toward the anatomical crown
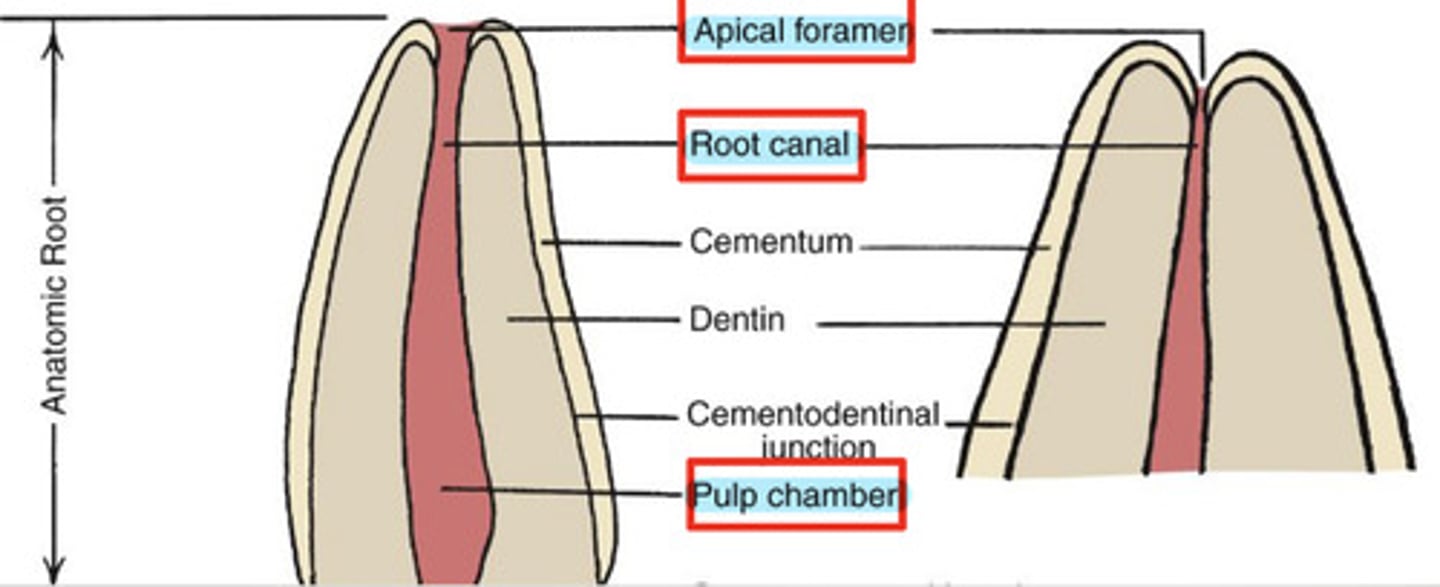
What is the root canal?
portion of the pulp cavity that extends into the root
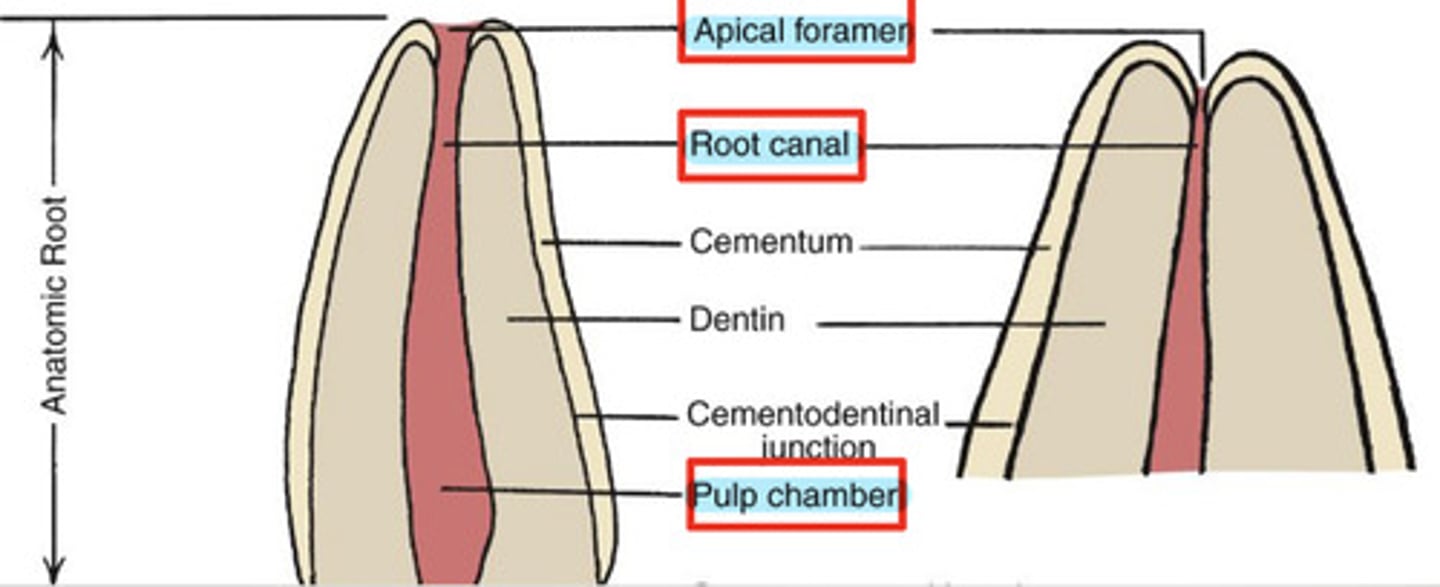
What is the apical foramen?
point of entry for nerves & blood supply
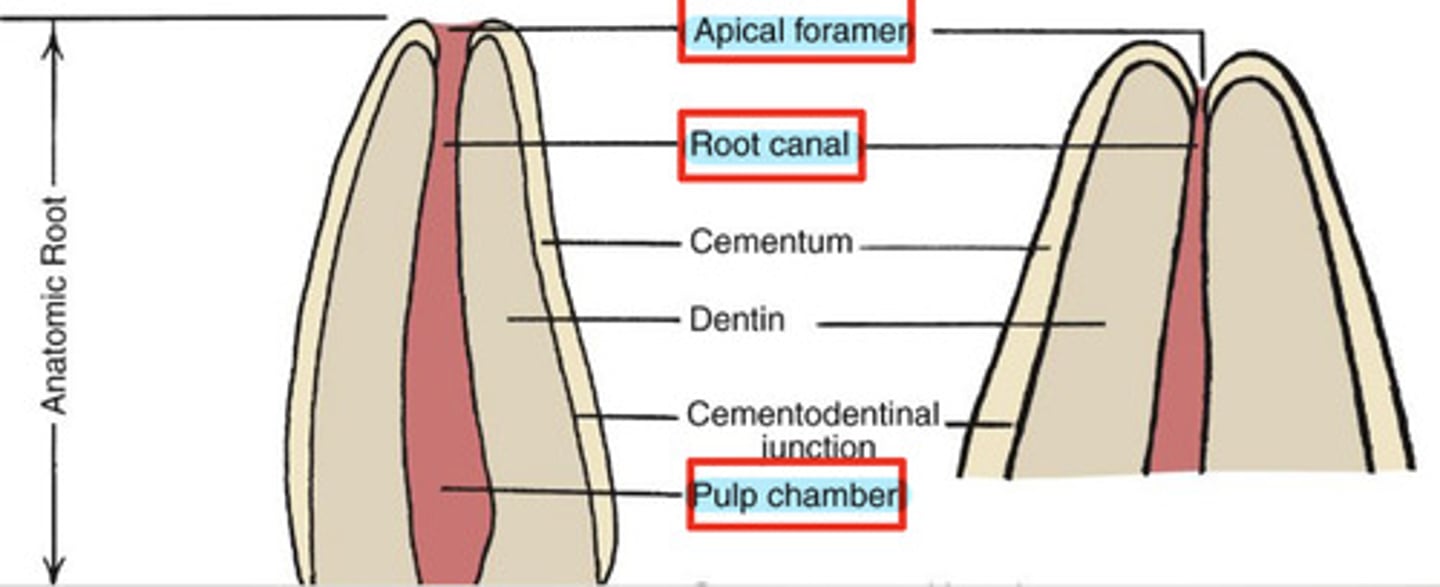
What is pulp?
soft, nonmineralized connective tissue
What are the four functions of pulp?
-nutritive: blood vessels transport nutrients, get waste products out
-formative: odontoblast produce dentin through the tooth's life (secondary dentin)
-sensory: nerve endings relay the sense of pain
-defensive/protective: injury or decay results in reparative dentin
What is enamel?
external surface layer of anatomic crown
-highly calcified/mineralized: 95% calcium hydroxyapatite
-hardest substance in body
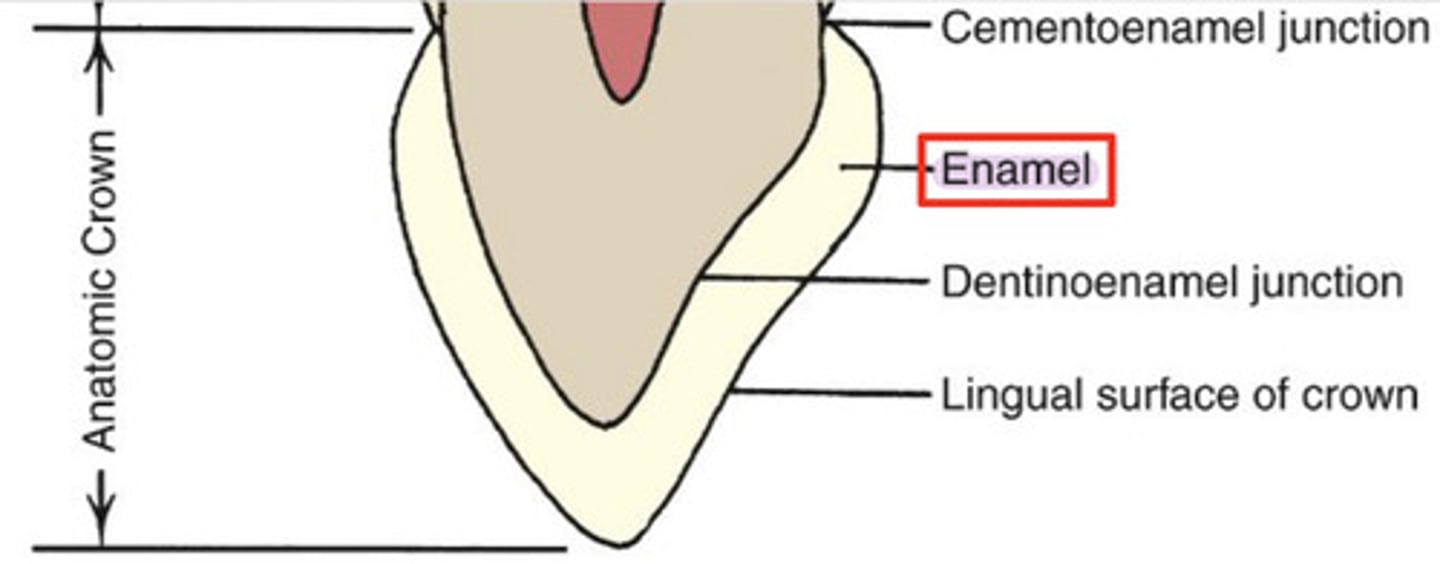
What is alveolar bone?
bone that surrounds the roots of the teeth
-outer bone: made up of cortical/compact bone plates
-inner bone: made up of spongy/cancellous bone
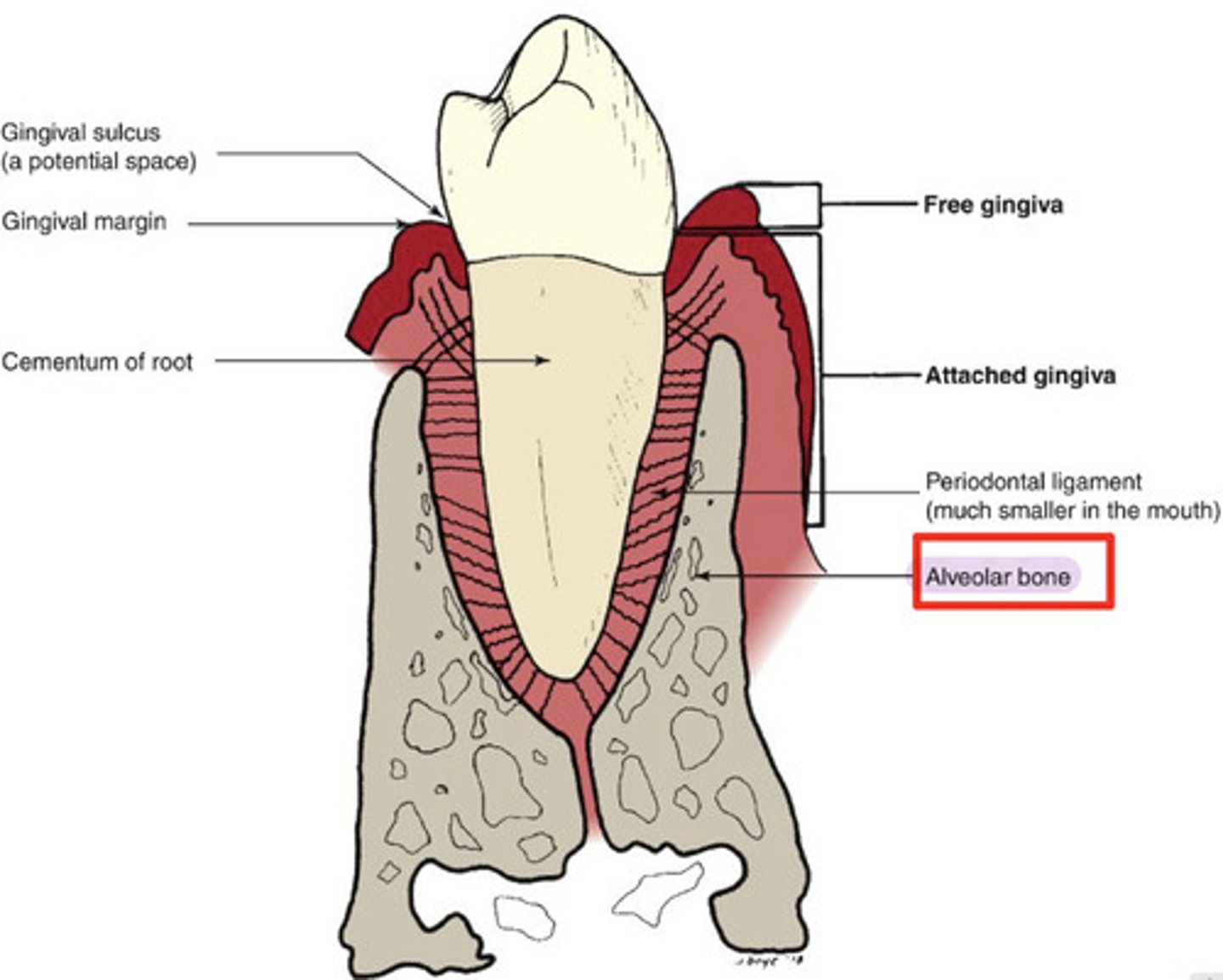
What is gingiva?
soft tissue that covers the alveolar bone

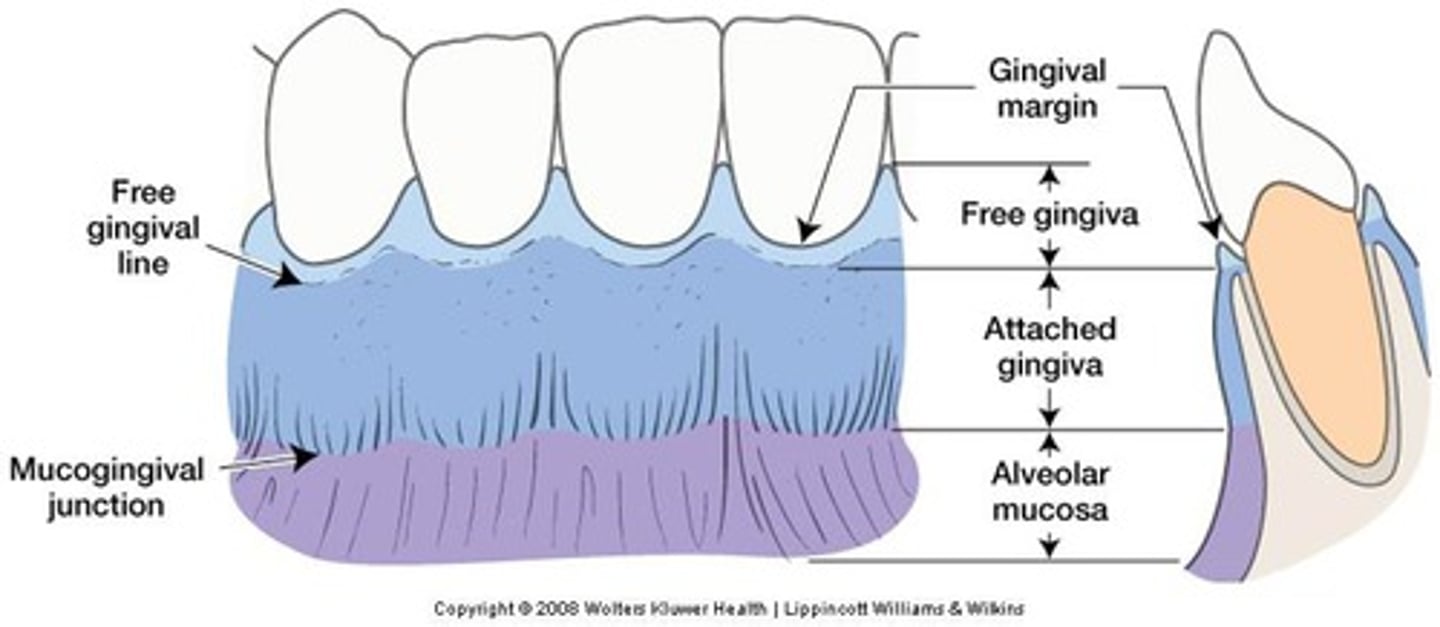
What is attached gingiva?
firmly bound to underlying alveolar bone
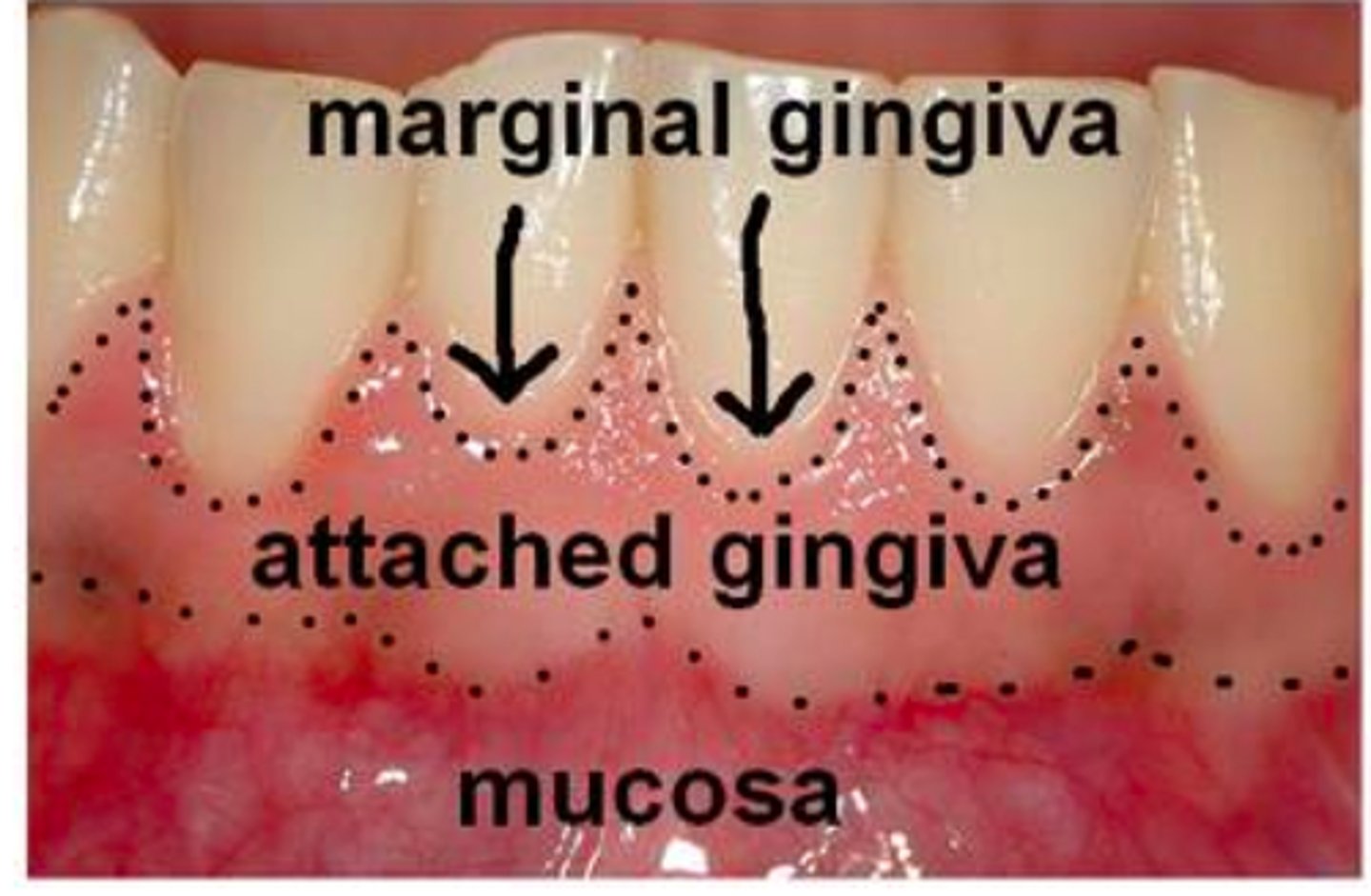
What is free gingiva?
collar gingiva that surrounds tooth
-not attached to bone, creates pocket measured w/ probe
-healthy: 1-3 mm pocket
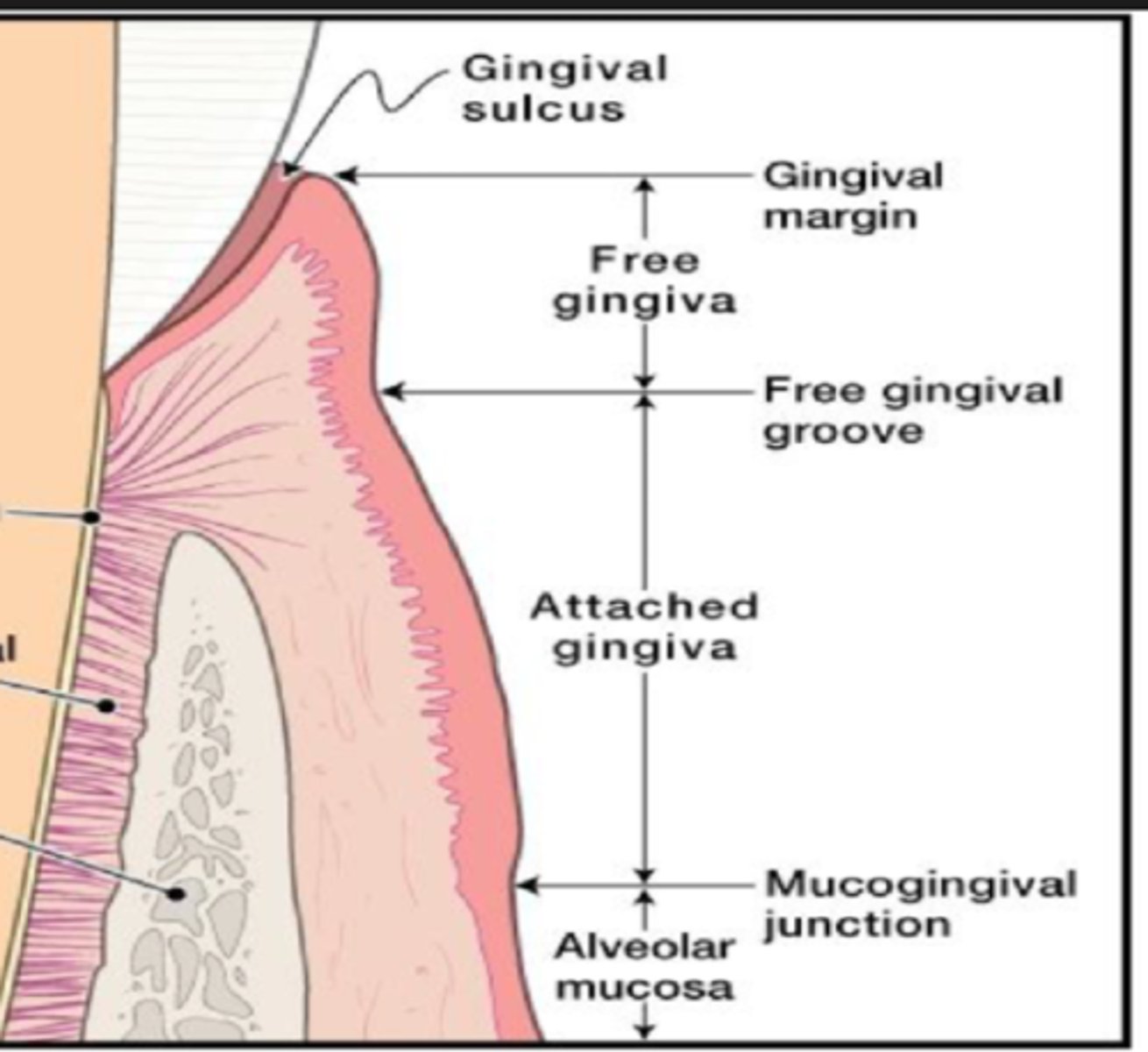
What is the gingival margin?
provides access to the space between gingiva & the tooth
-gingival sulcus (crevice)
What is the periodontal ligament?
attaches tooth to alveolar bone
-1-4x thickness of human hair
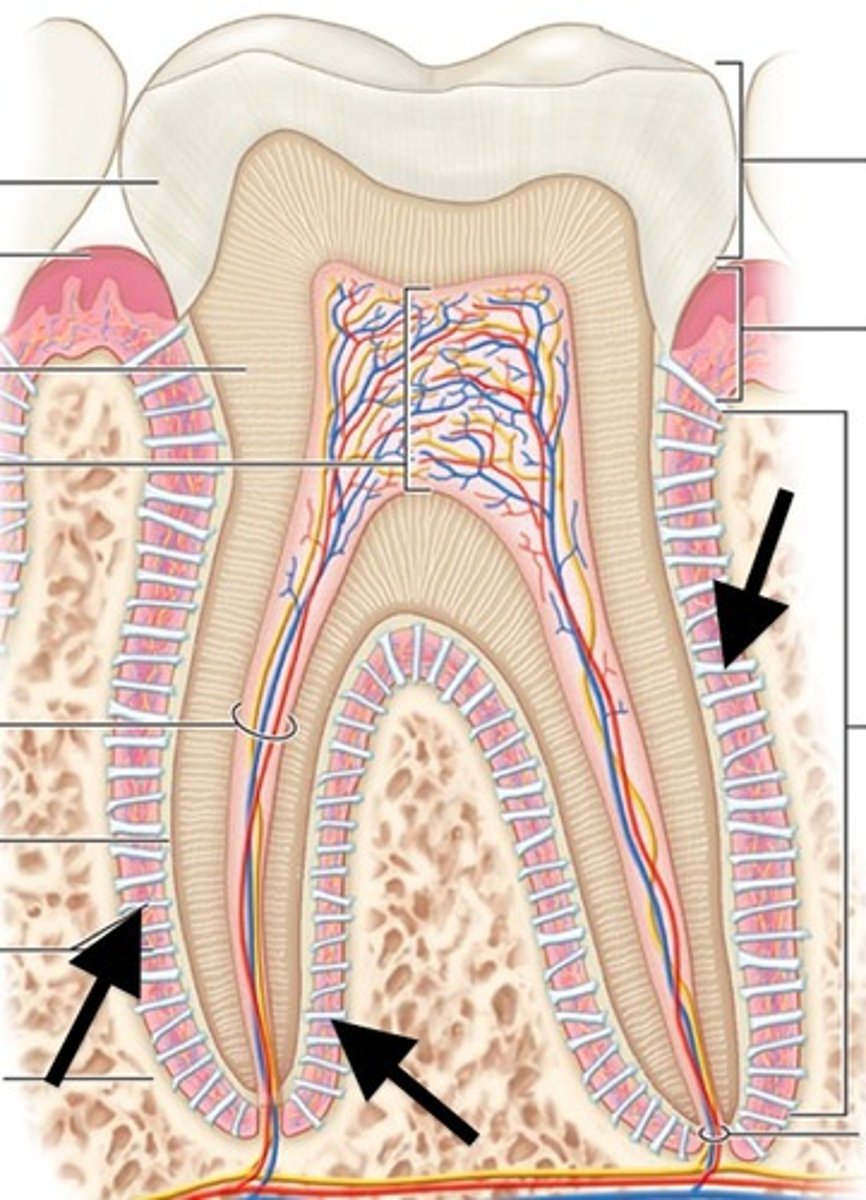
What is interdental papilla?
free gingiva between teeth
What are the outer surfaces of a tooth?
facial, buccal, labial
What is the facial surface?
surfaces towards face (all teeth)
What is the buccal surface?
surfaces towards cheek

What is the labial surface?
surfaces towards lips

What are the inner surfaces of a tooth?
lingual & palatal
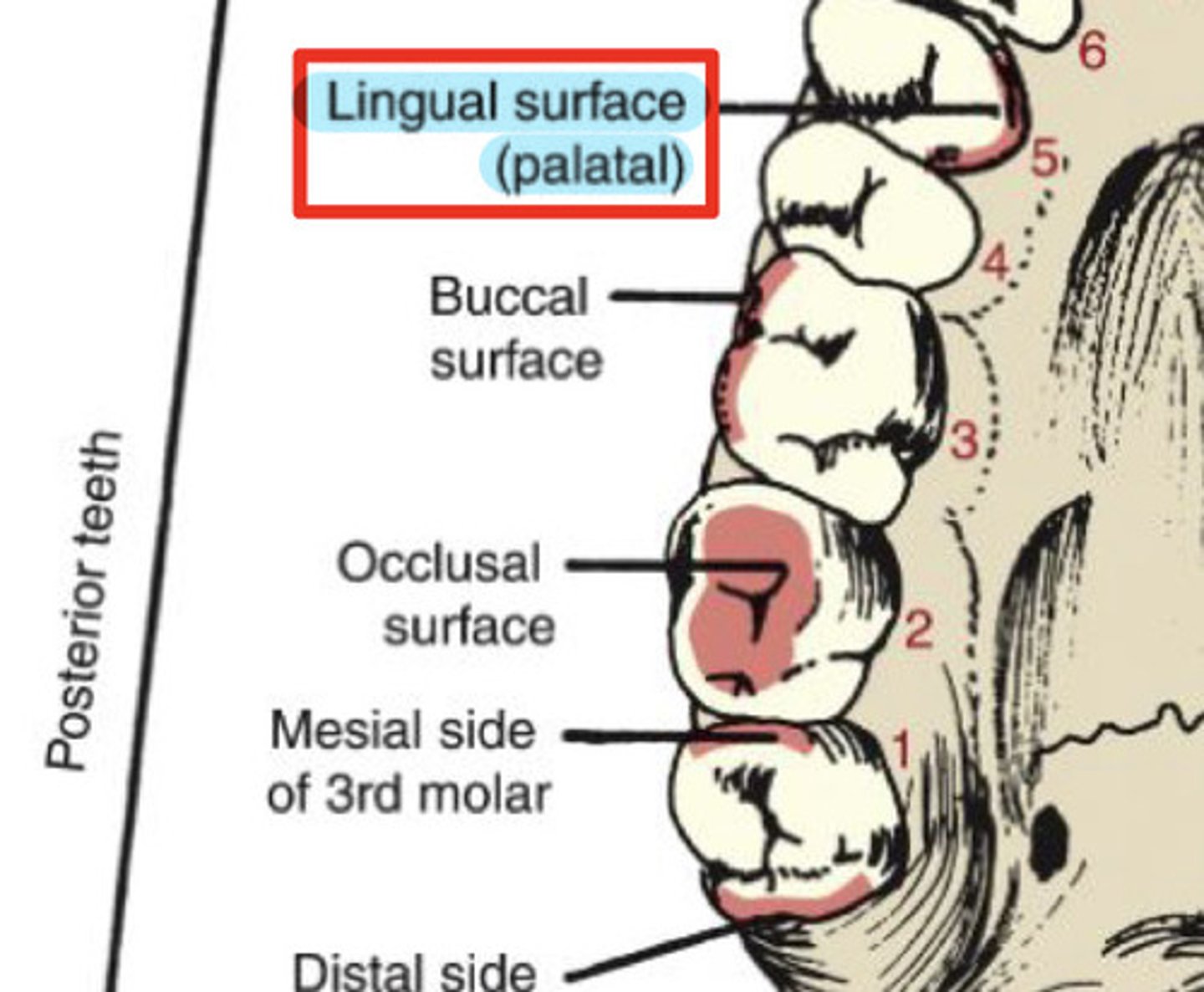
What is the lingual surface?
surfaces towards tongue (all teeth)
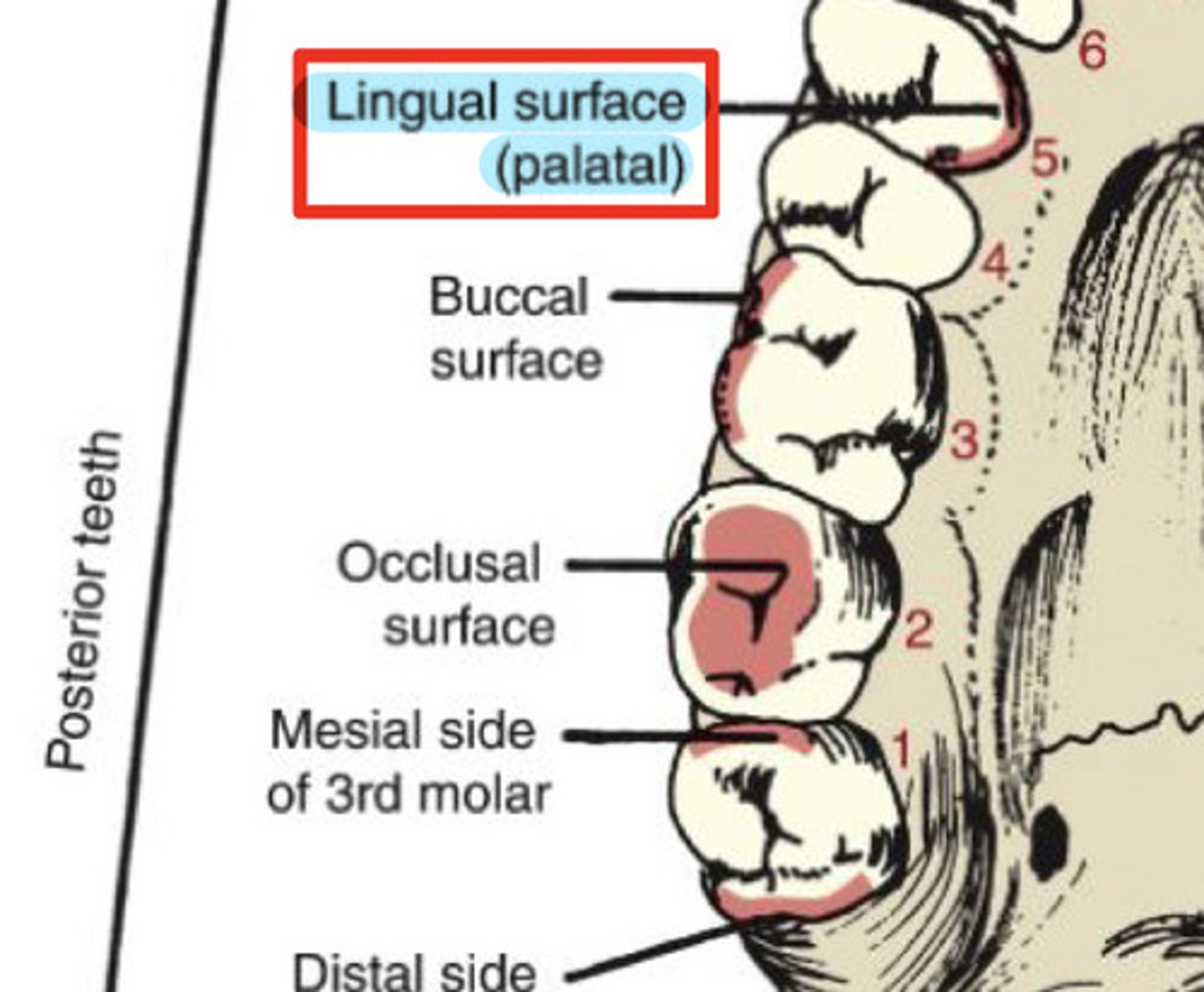
What is the palatal surface?
surfaces towards palate - only on maxillary arch
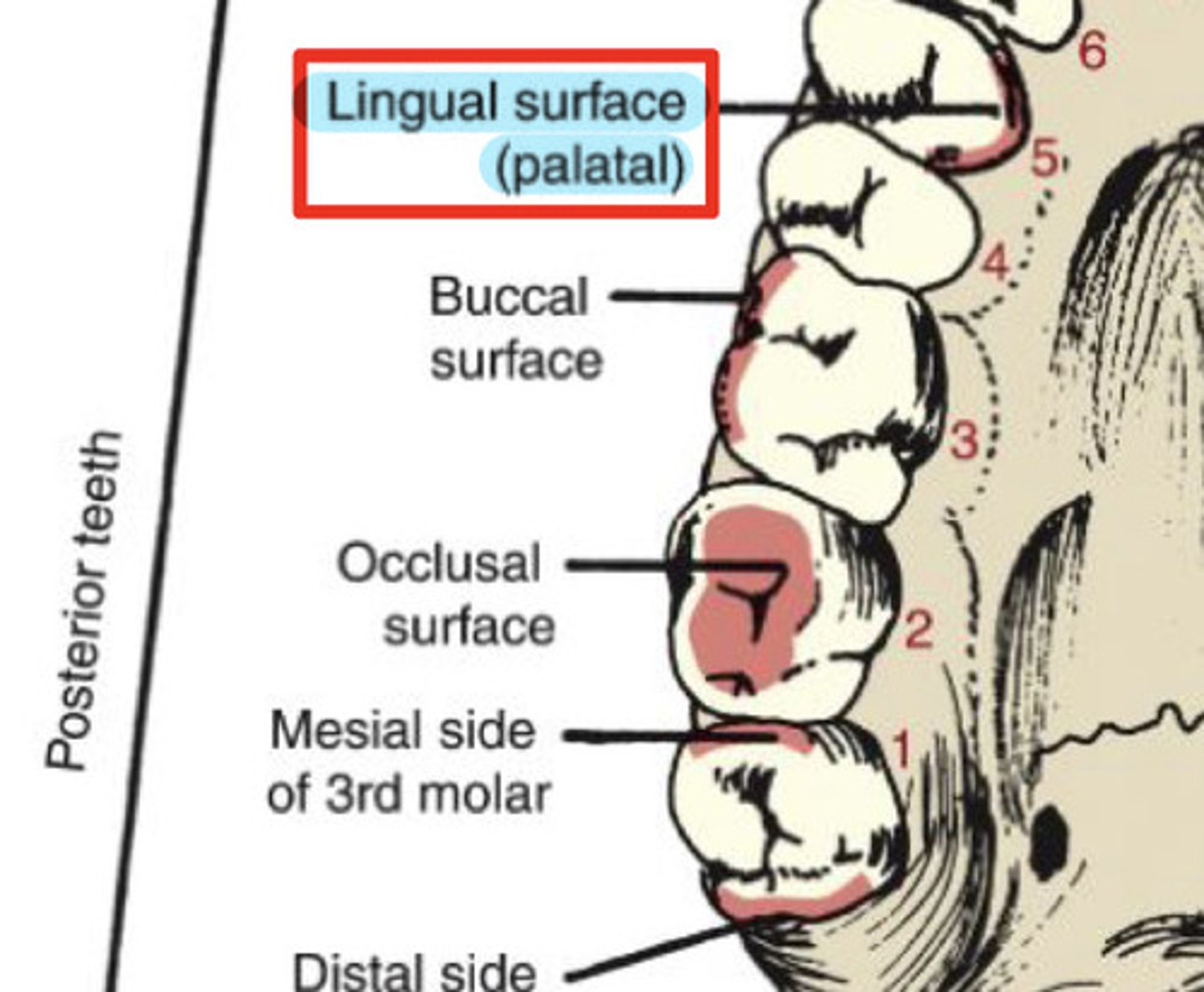
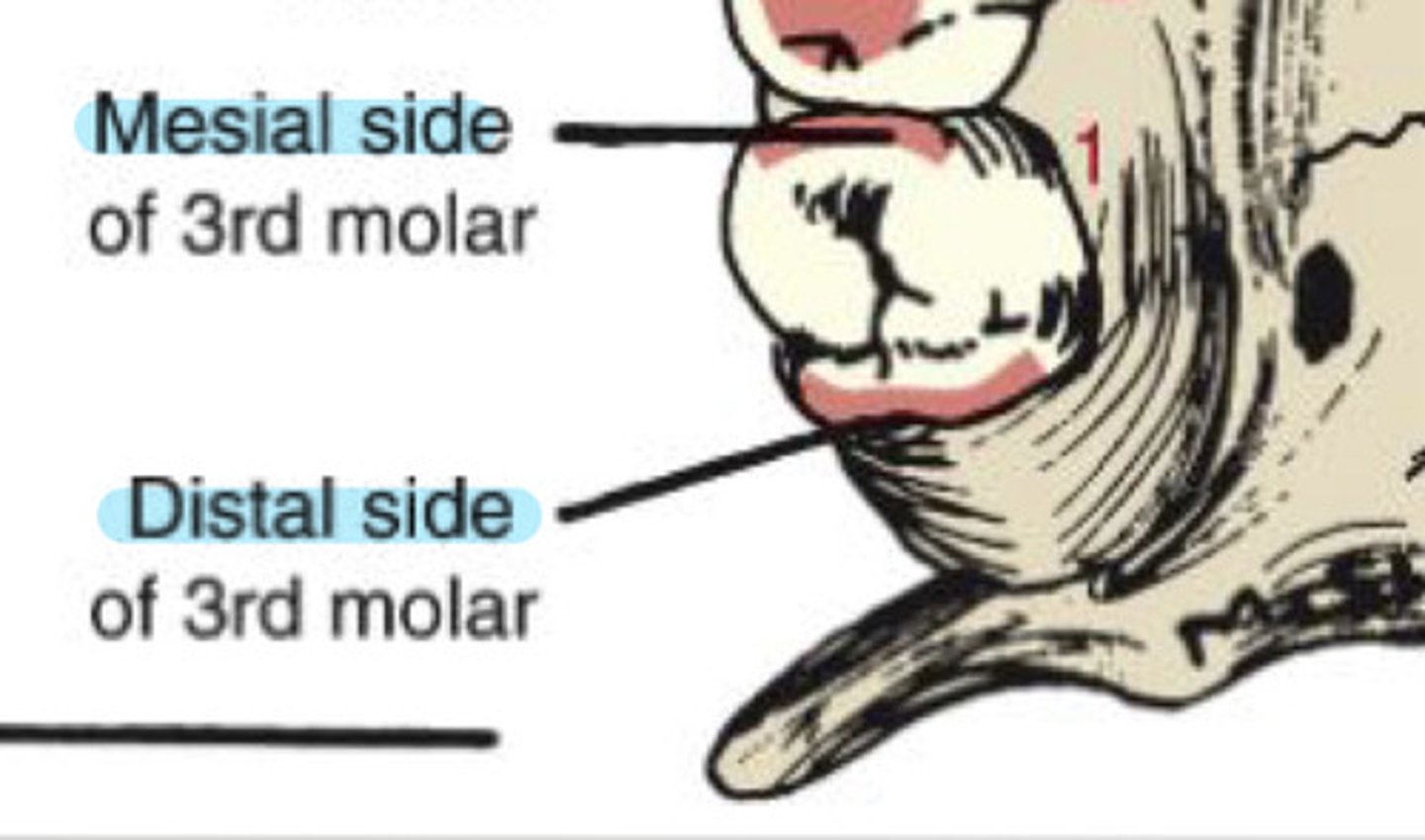
What is the mesial surface of a tooth?
surfaces towards the midline
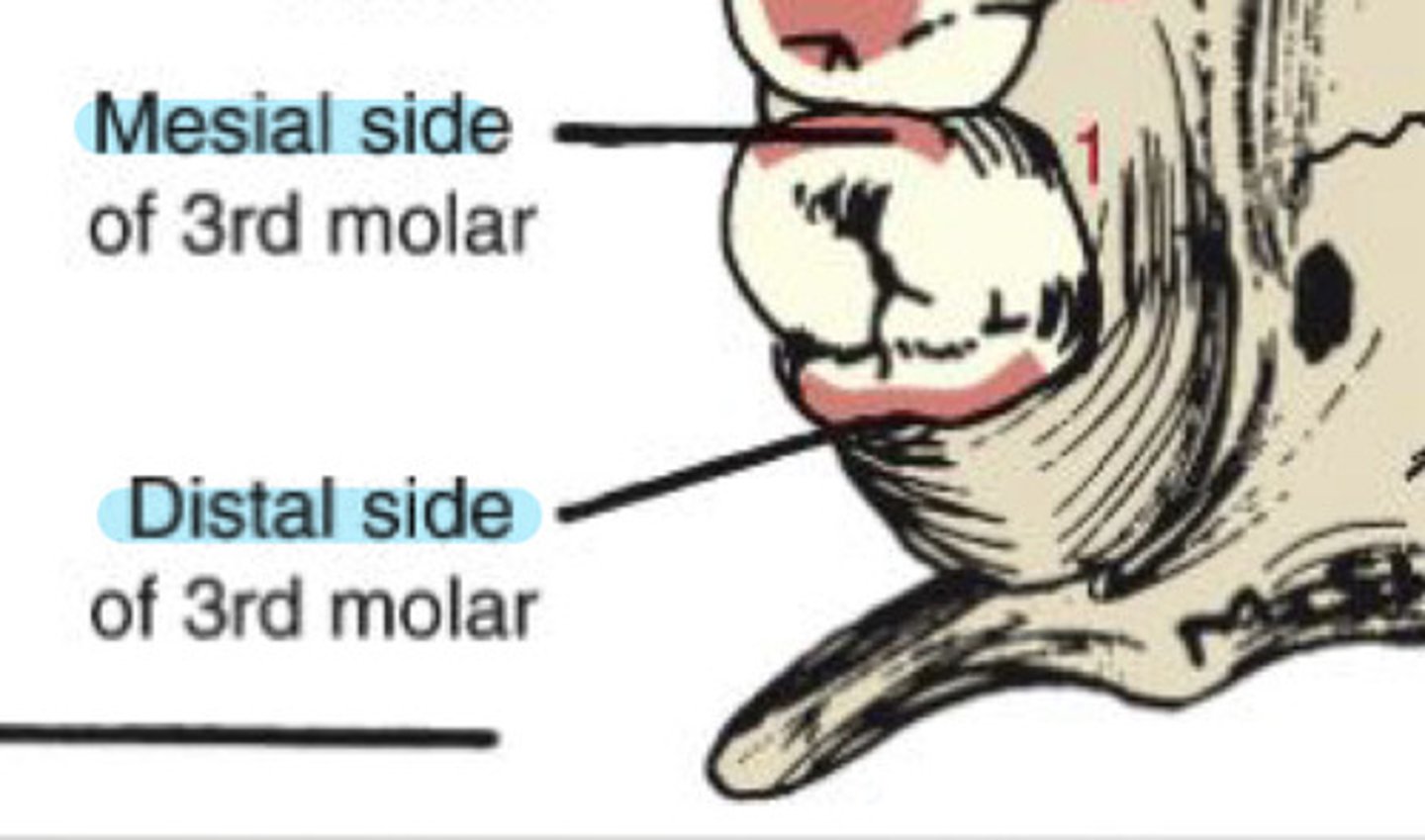
What is the distal surface of a tooth?
surfaces away from the midline
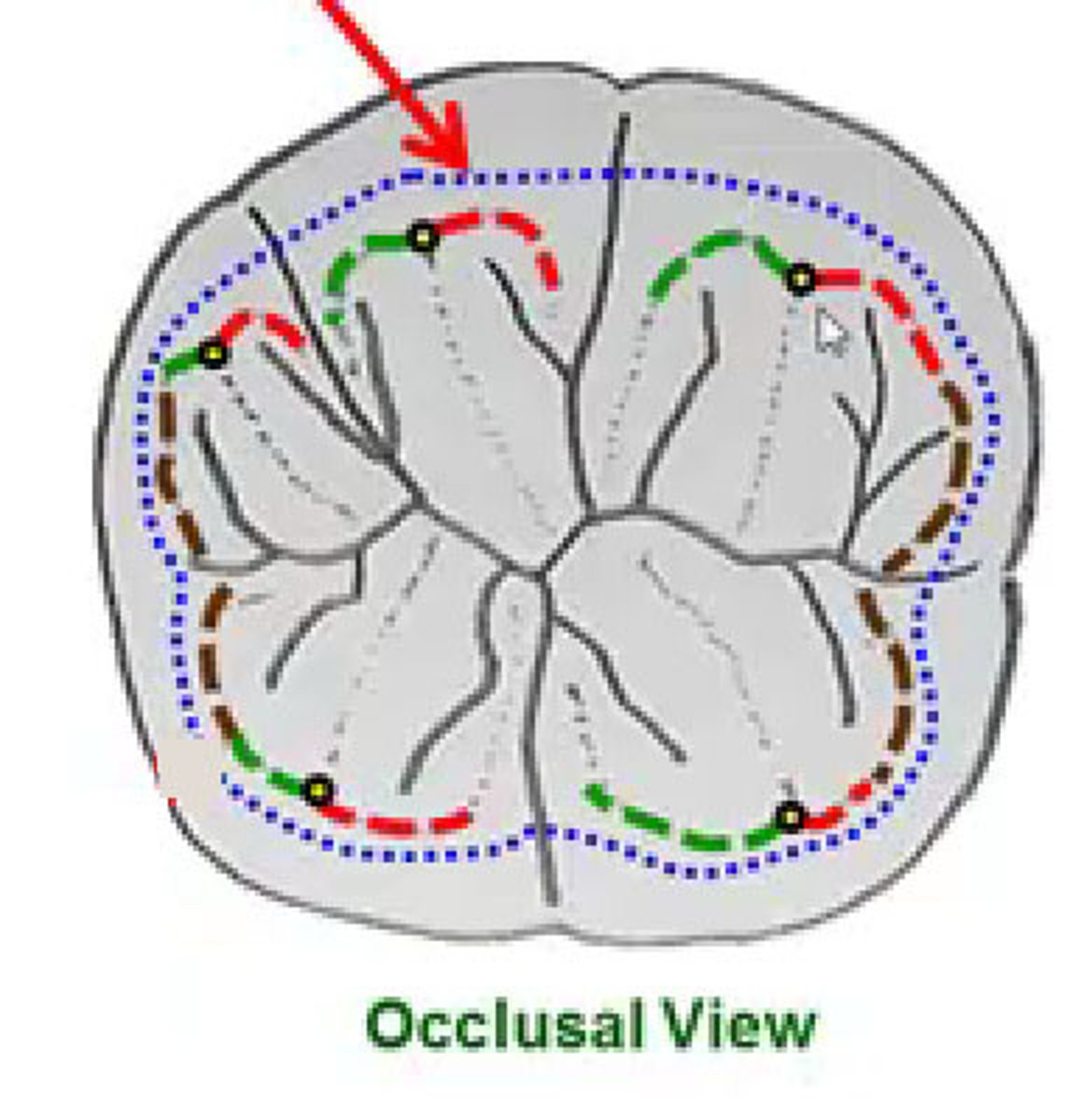
What is the occlusal surface?
Chewing surface of a posterior tooth
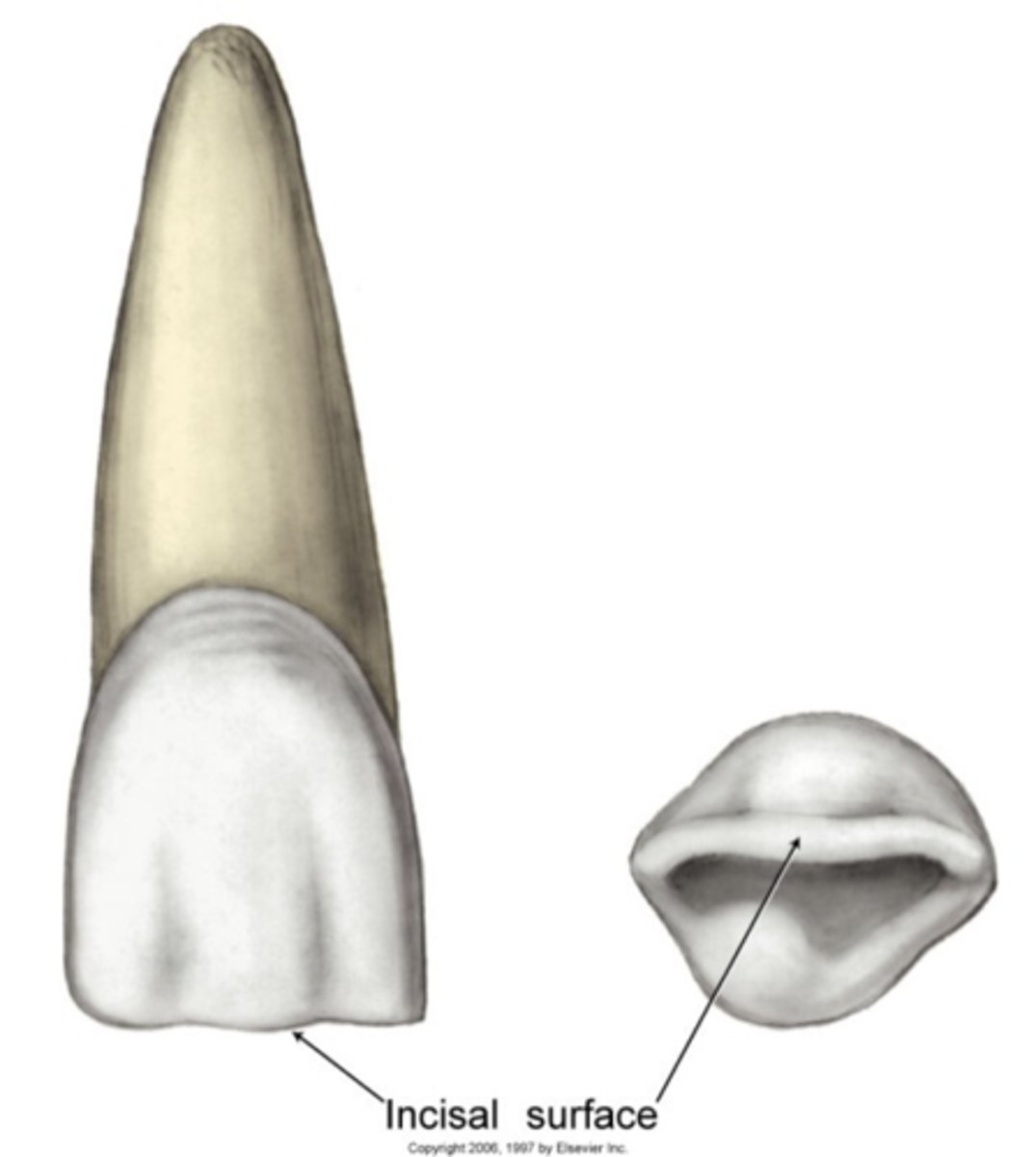
What is the incisal edge?
cutting/biting edge of anterior teeth
What is the proximal surface of a tooth?
any surfaces facing another tooth
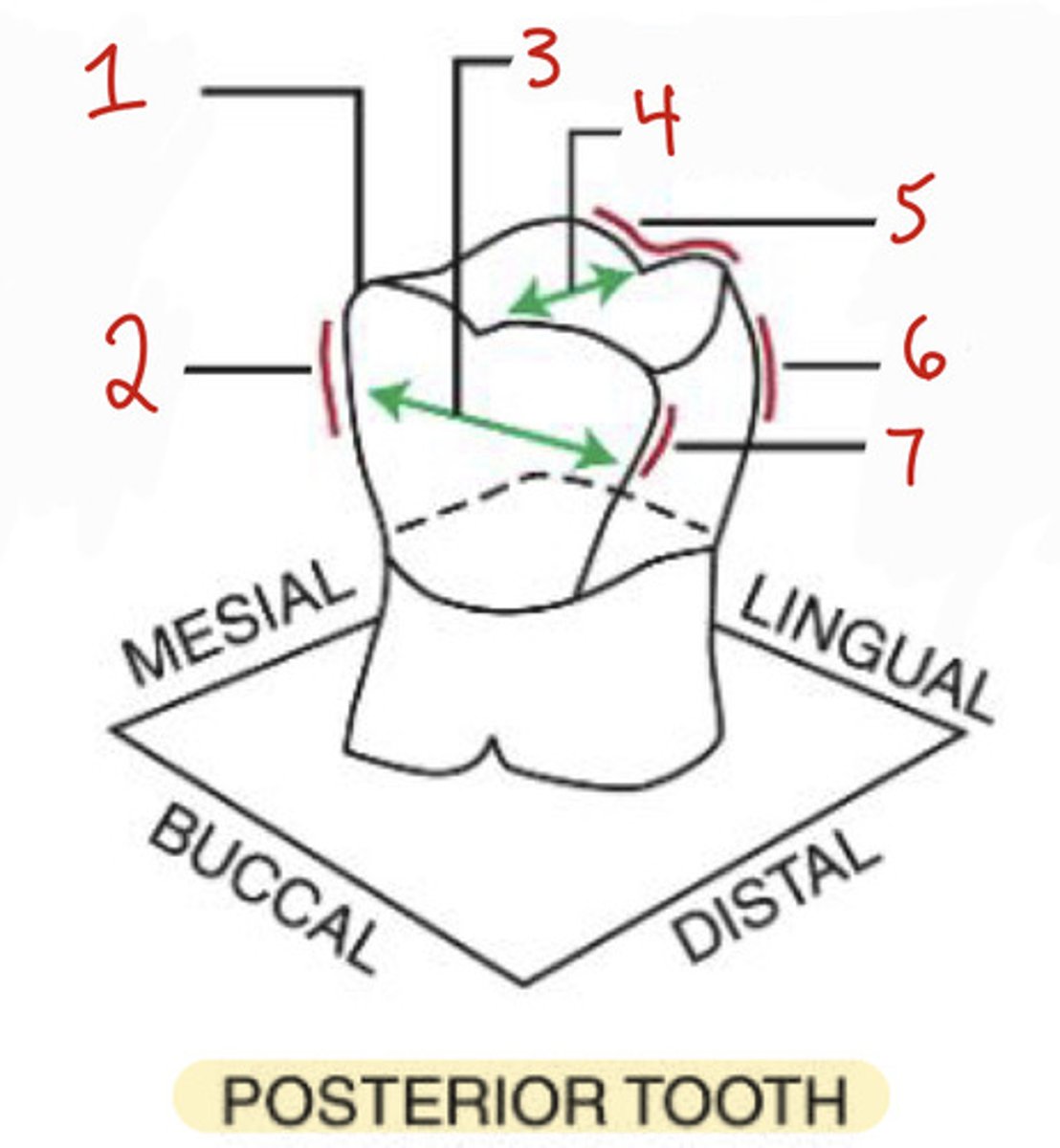
What is the mesiolabial line angle on an anterior tooth?
1
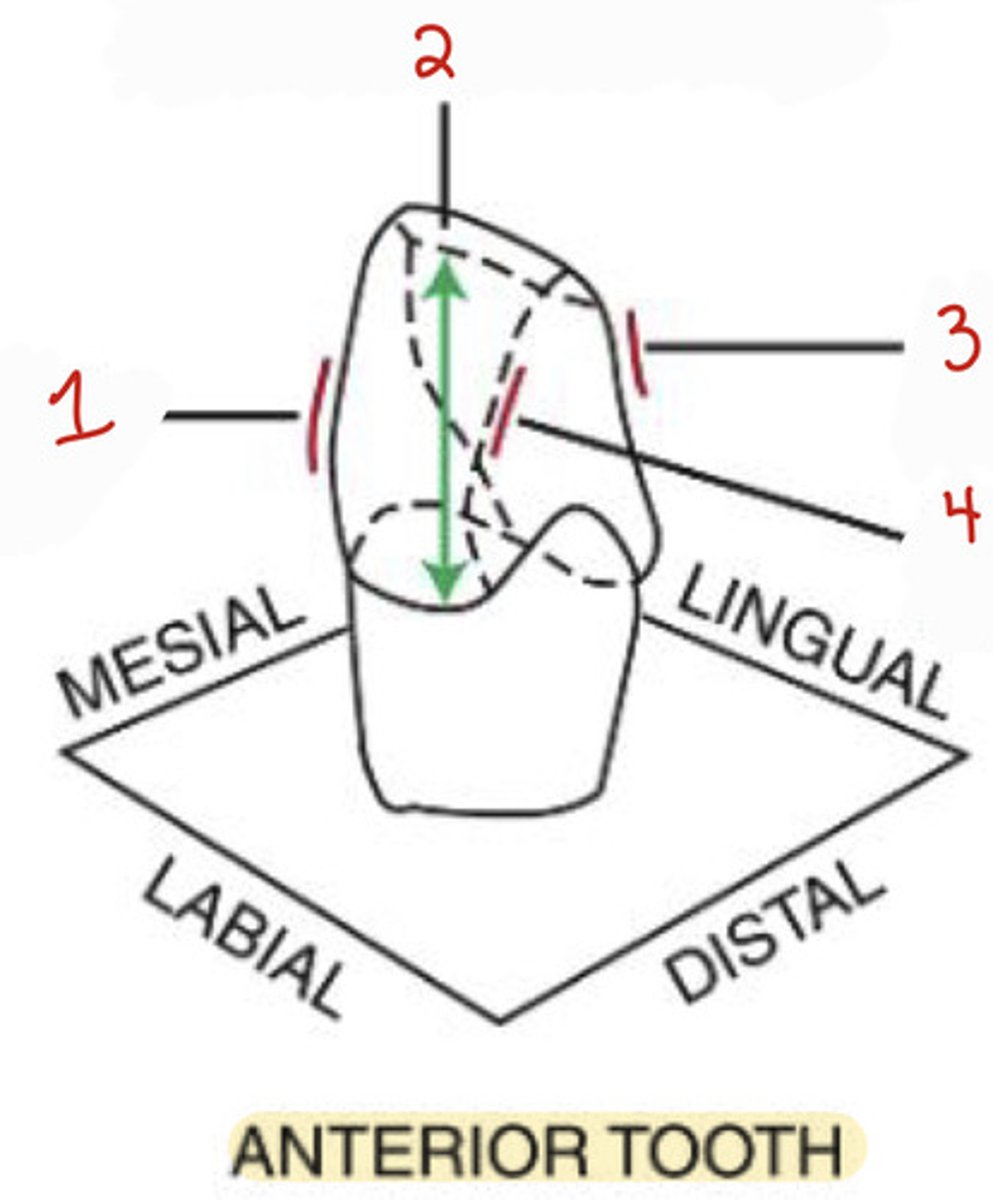
What is the incisocervical dimension on an anterior tooth?
2
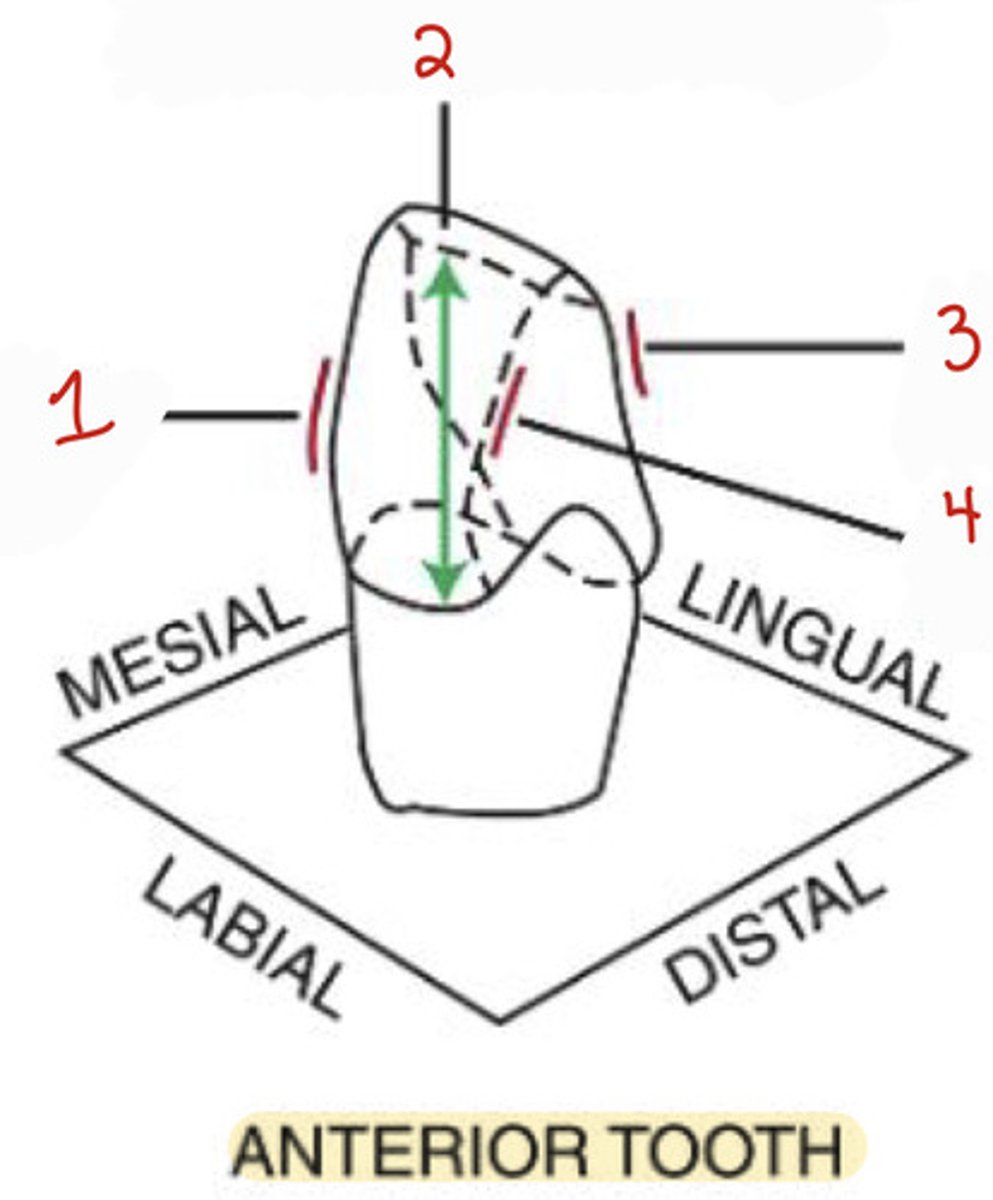
What is the distolabial line angle?
4
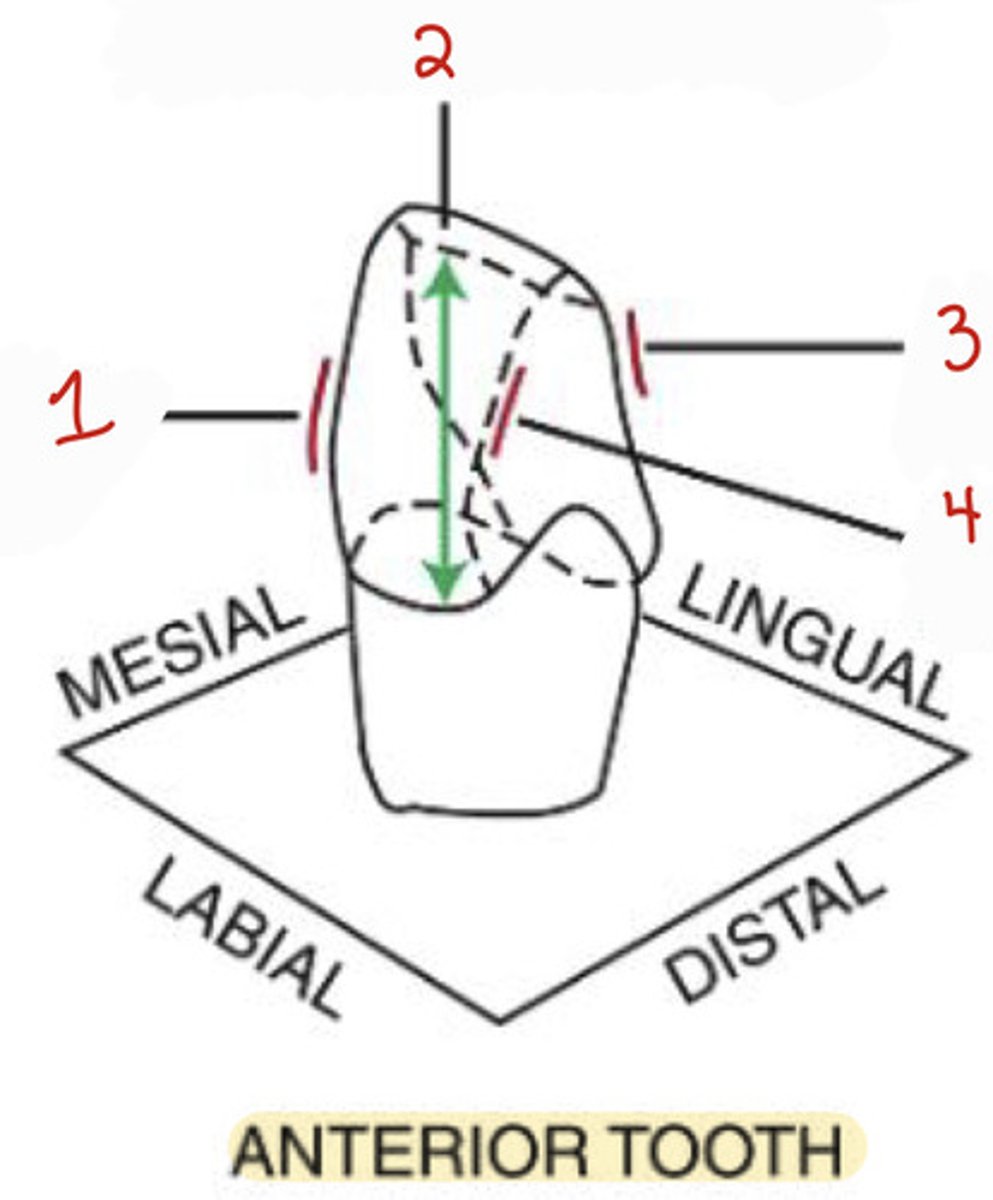
What is the distolingual line angle on an anterior tooth?
3
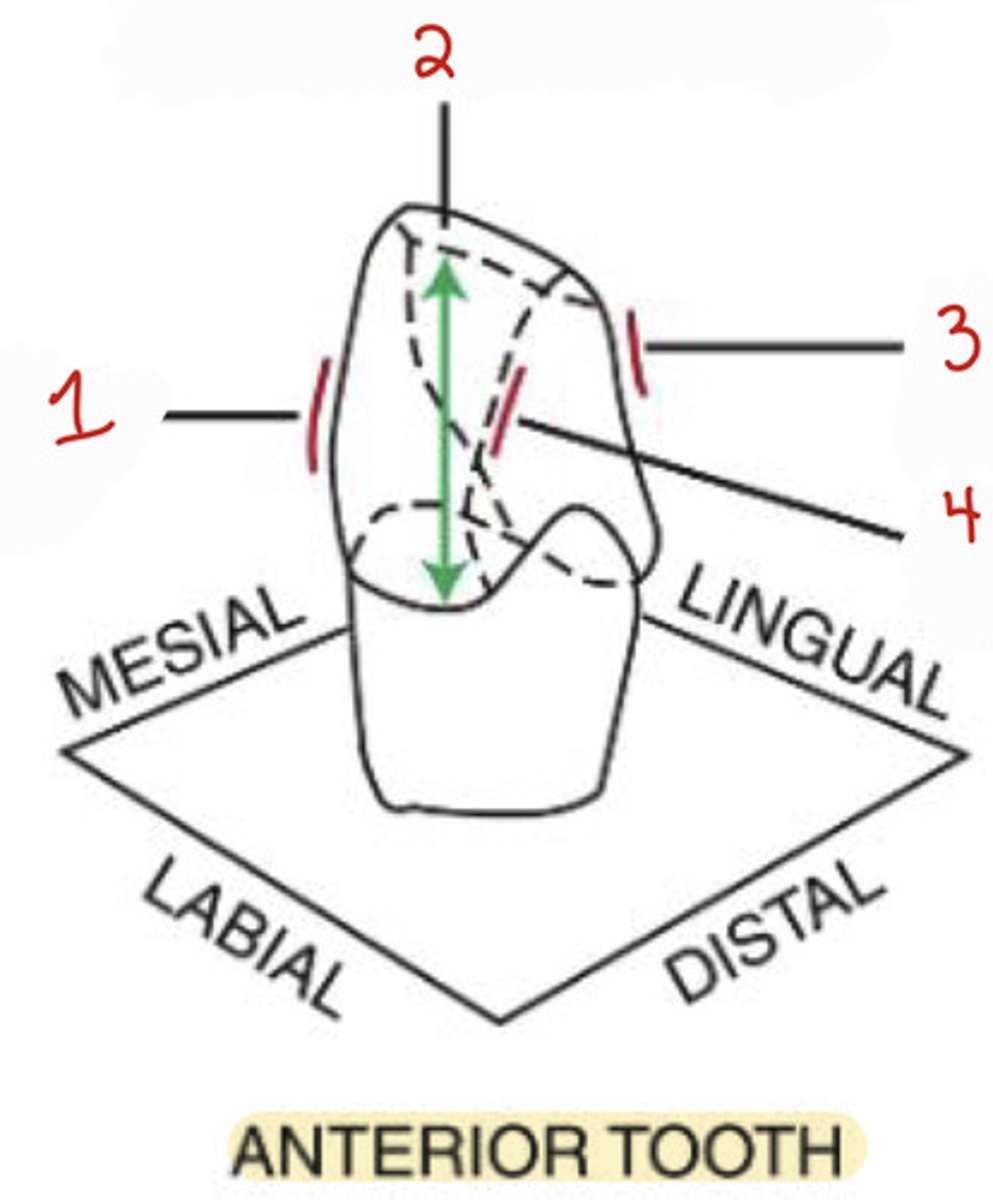
What is the mesiobuccal-occlusal point angle?
1
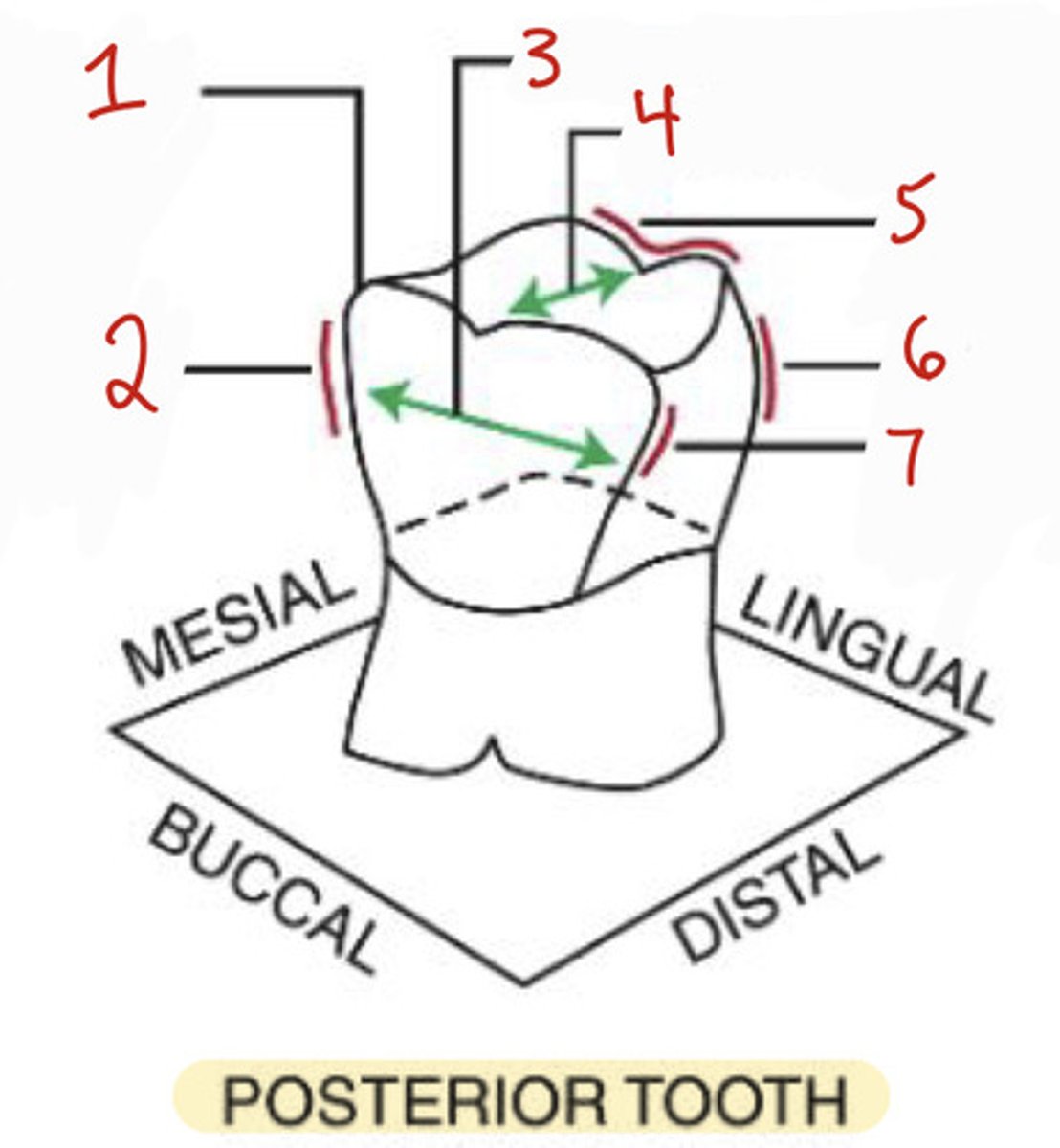
What is the mesiobuccal line angle?
2
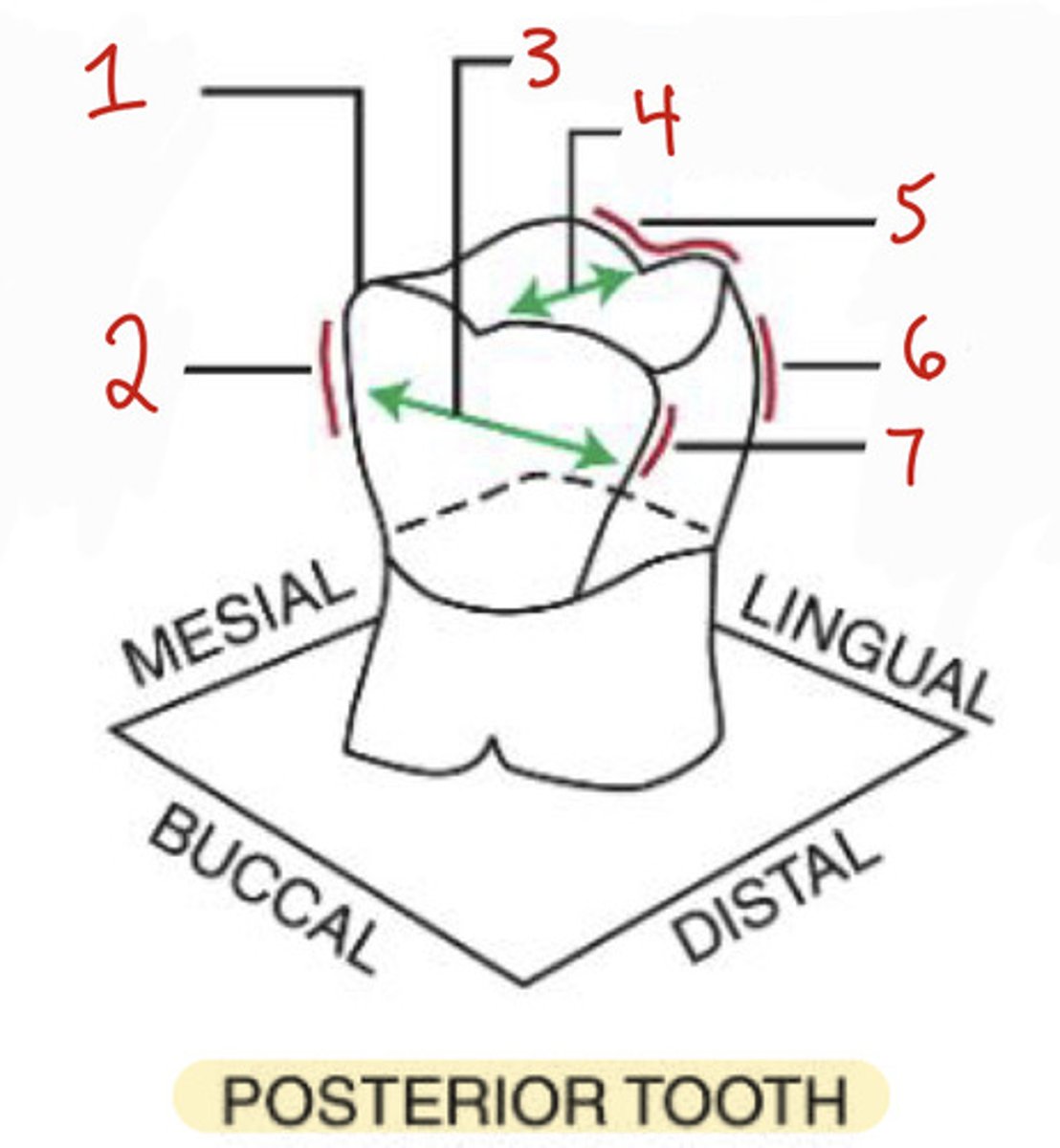
What is the mesiodistal dimension?
3

What is the buccolingual dimension?
4
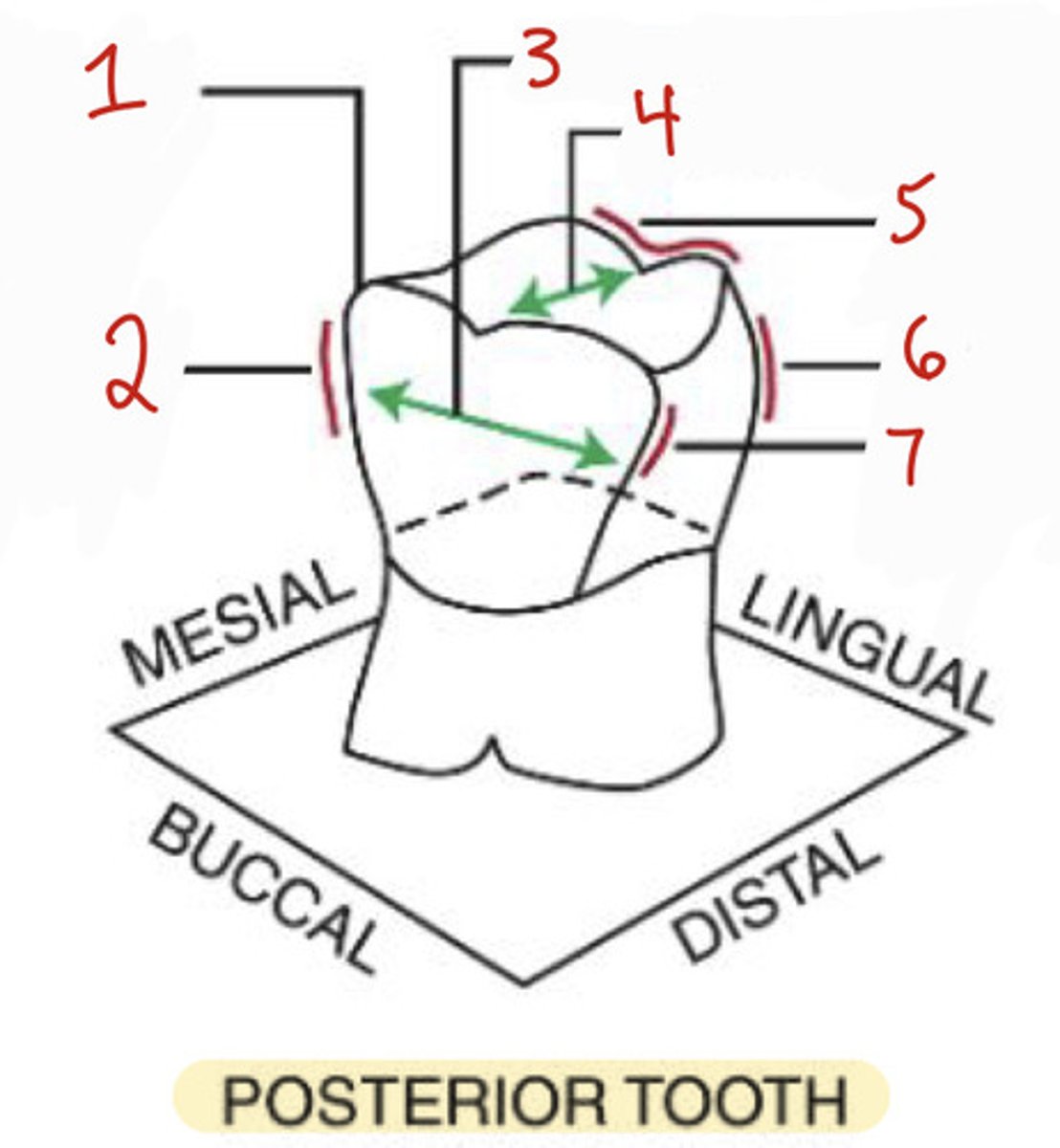
What is the distobuccal line angle?
7
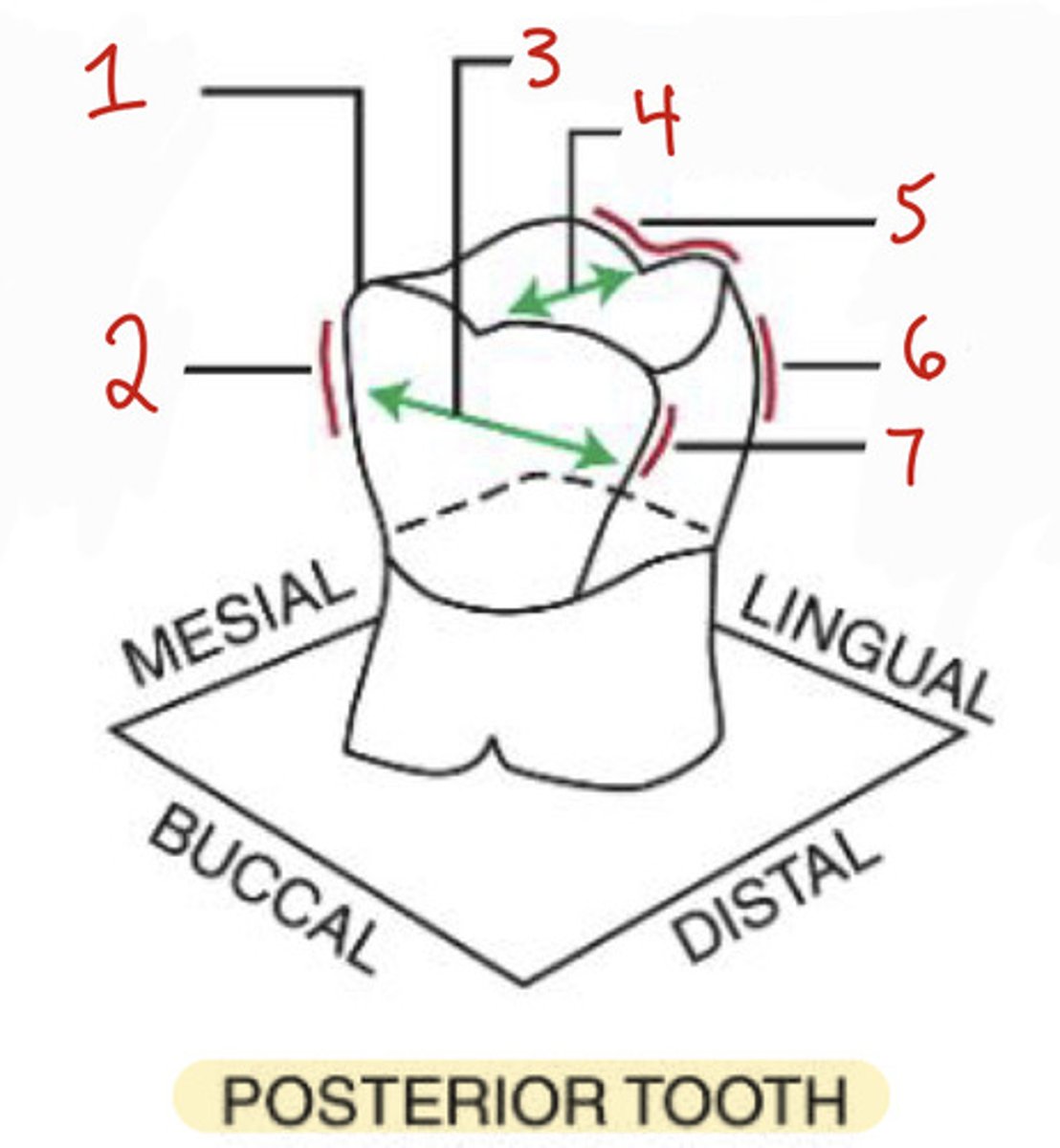
What is the linguo-occlusal line angle?
5
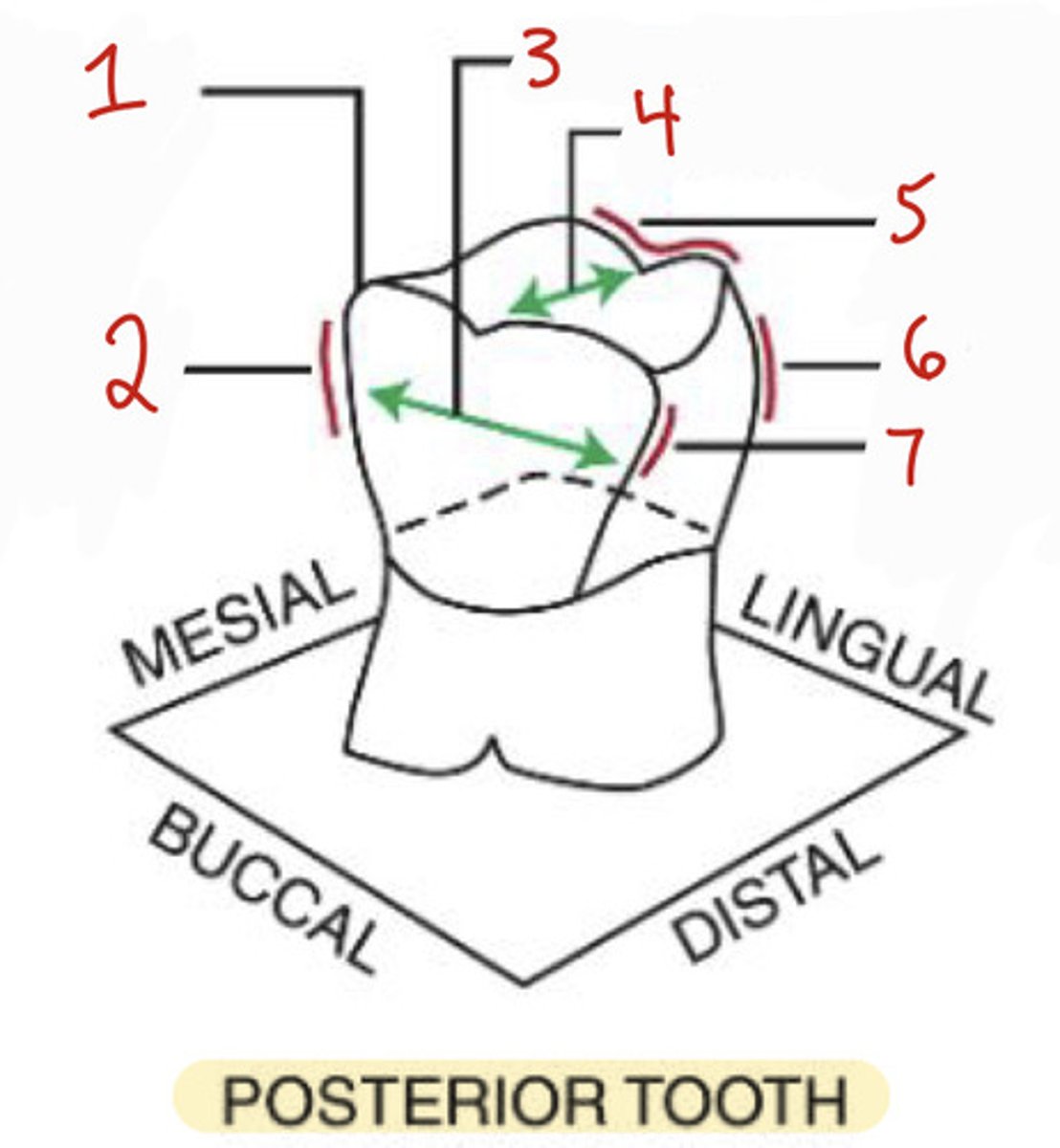
What is the distolingual line angle on a posterior tooth?
6
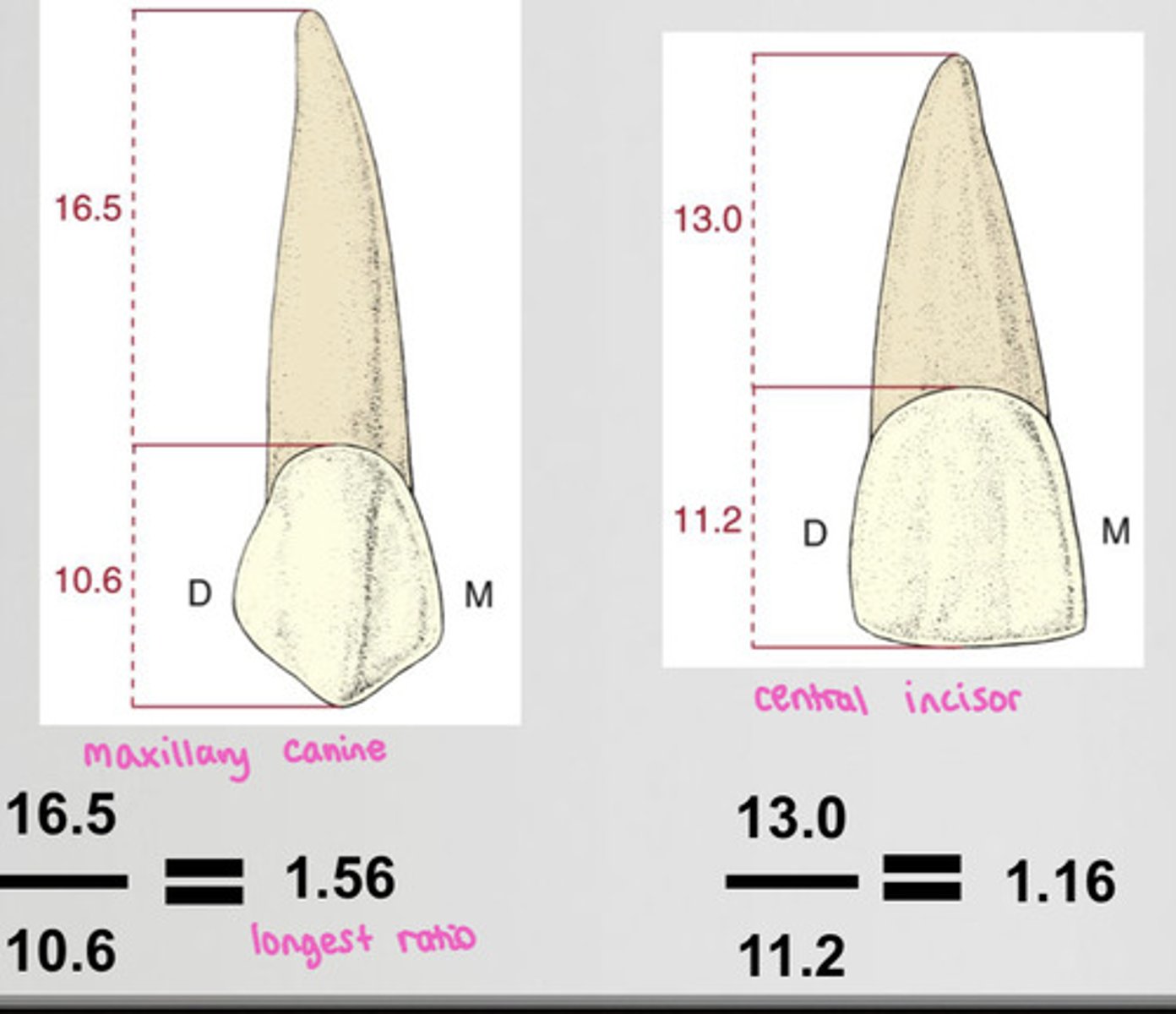
What is the root-to-crown ratio?
root length divided by crown length
-the bigger the ratio, the better a crown would do on a tooth
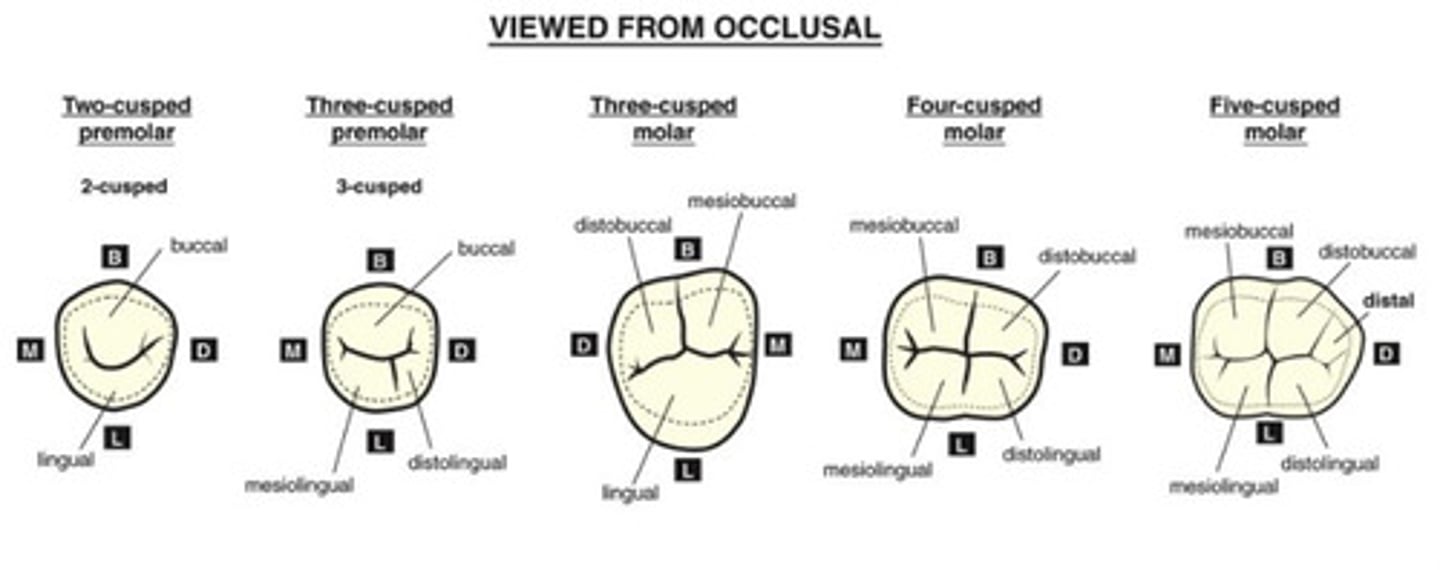
What is a cusp?
pyramidal elevation with a peak = cusp tip
-found on molars, premolars, and canines
-named by their location on tooth
What are cusp ridges?
each cusp can be thought of having 4 ridges that intersect at the cusp tip
-each ridge is named for the surface it extends from
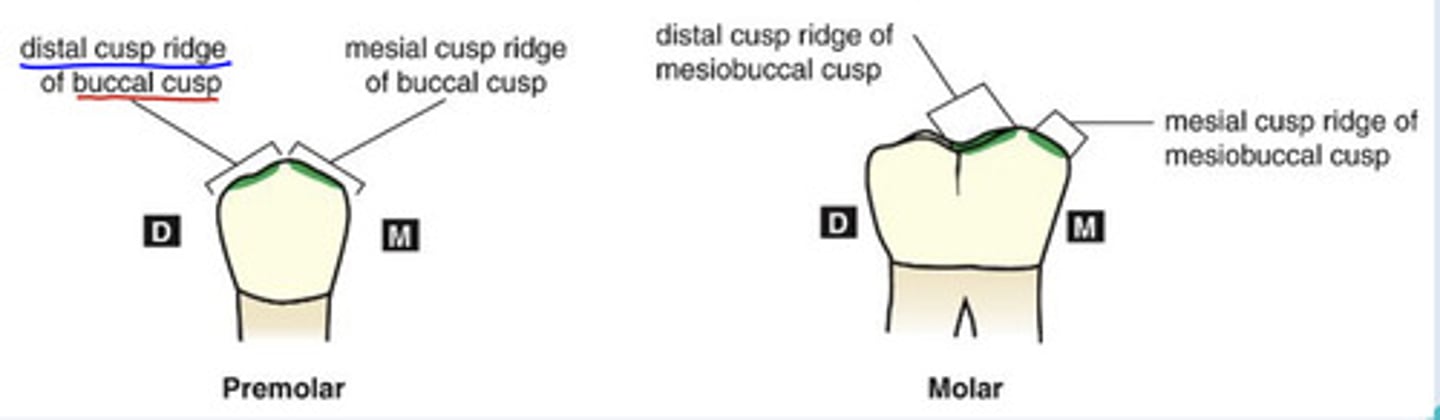
What are triangular ridges?
cusp ridges that descend from the cusp tips toward the central part of the occlusal table
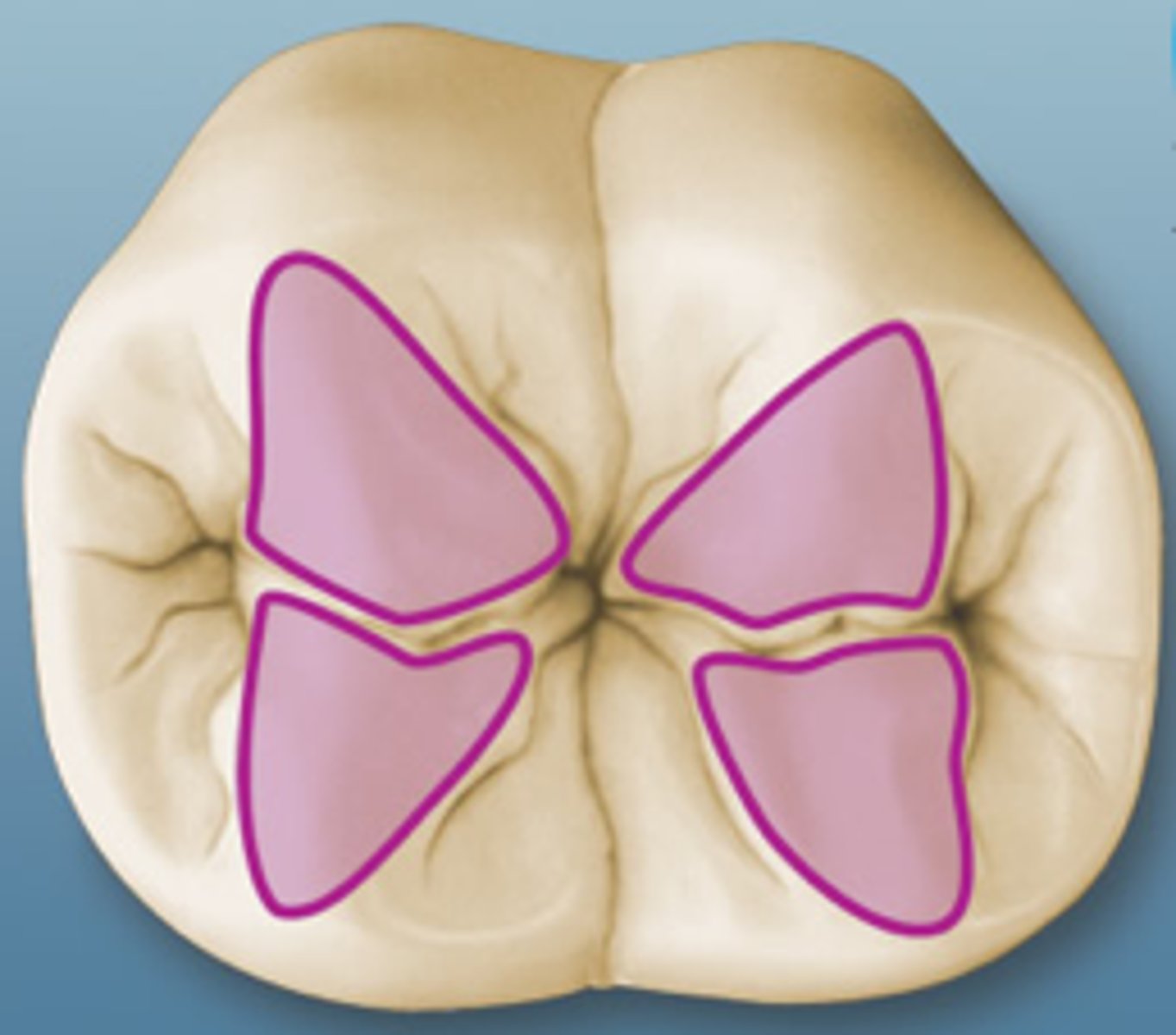
What are transverse ridges?
formed by the junction of two triangular ridges
-crosses occlusal surface buccolingually
What are oblique ridges?
formed by the junction of the mesiolingual cusp (distal ridge) and distobuccal cusp (triangular ridge)
-crosses occlusal surface obliquely
-will only have oblique ridge if transverse ridge is present

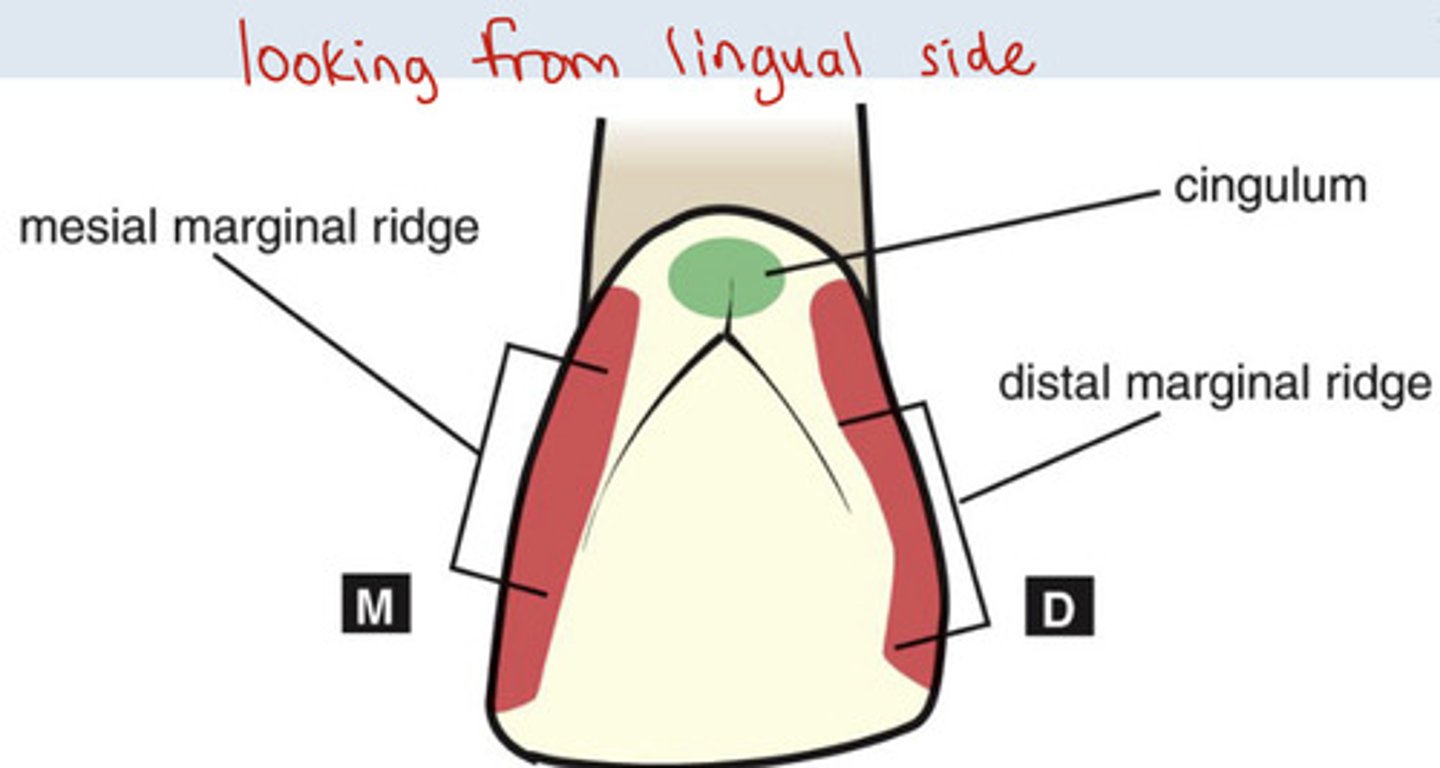
What is the cingulum?
bulge in lingual cervical third of anterior teeth
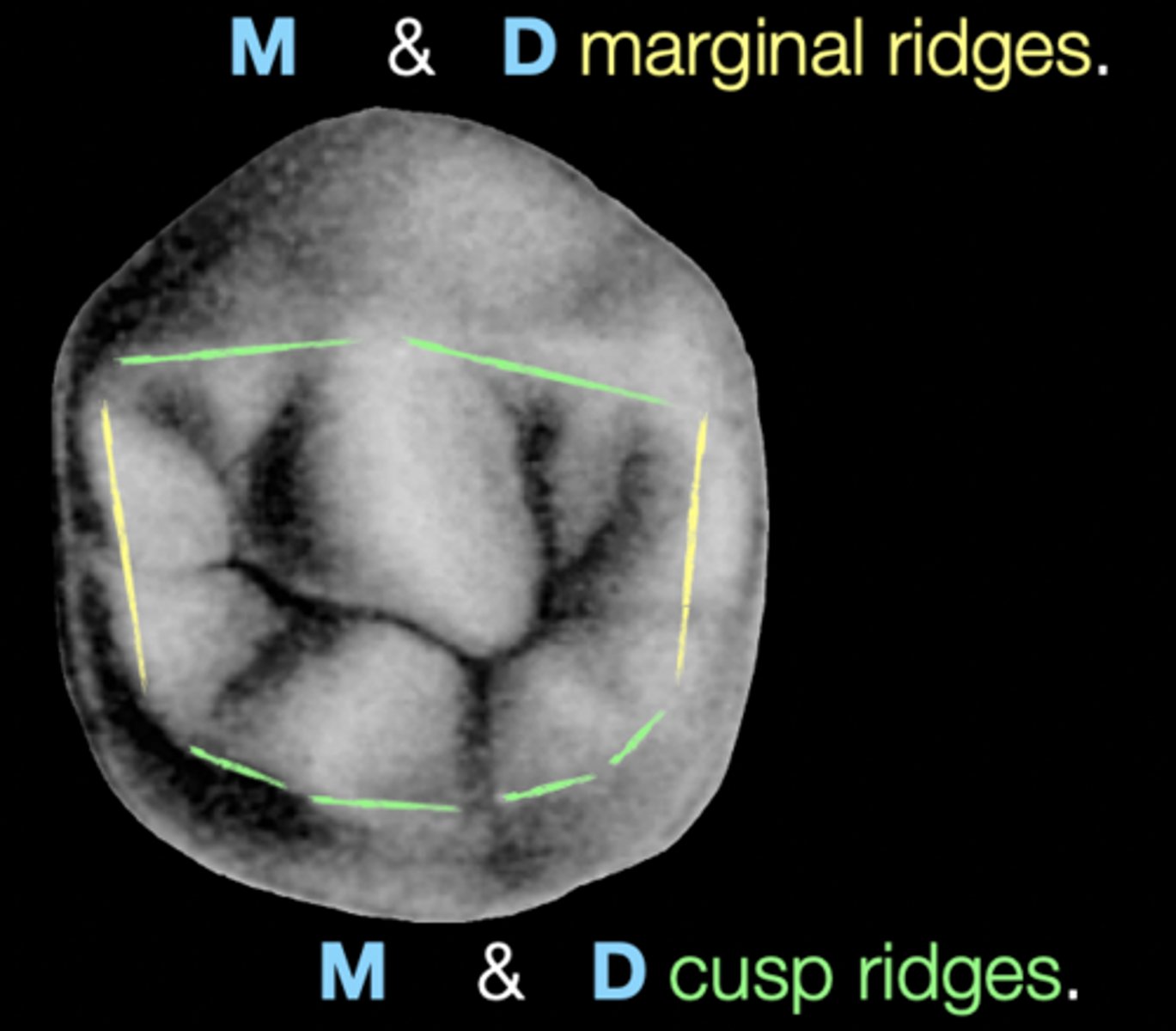
What is the mesial marginal ridge?
forms mesial border of lingual surface
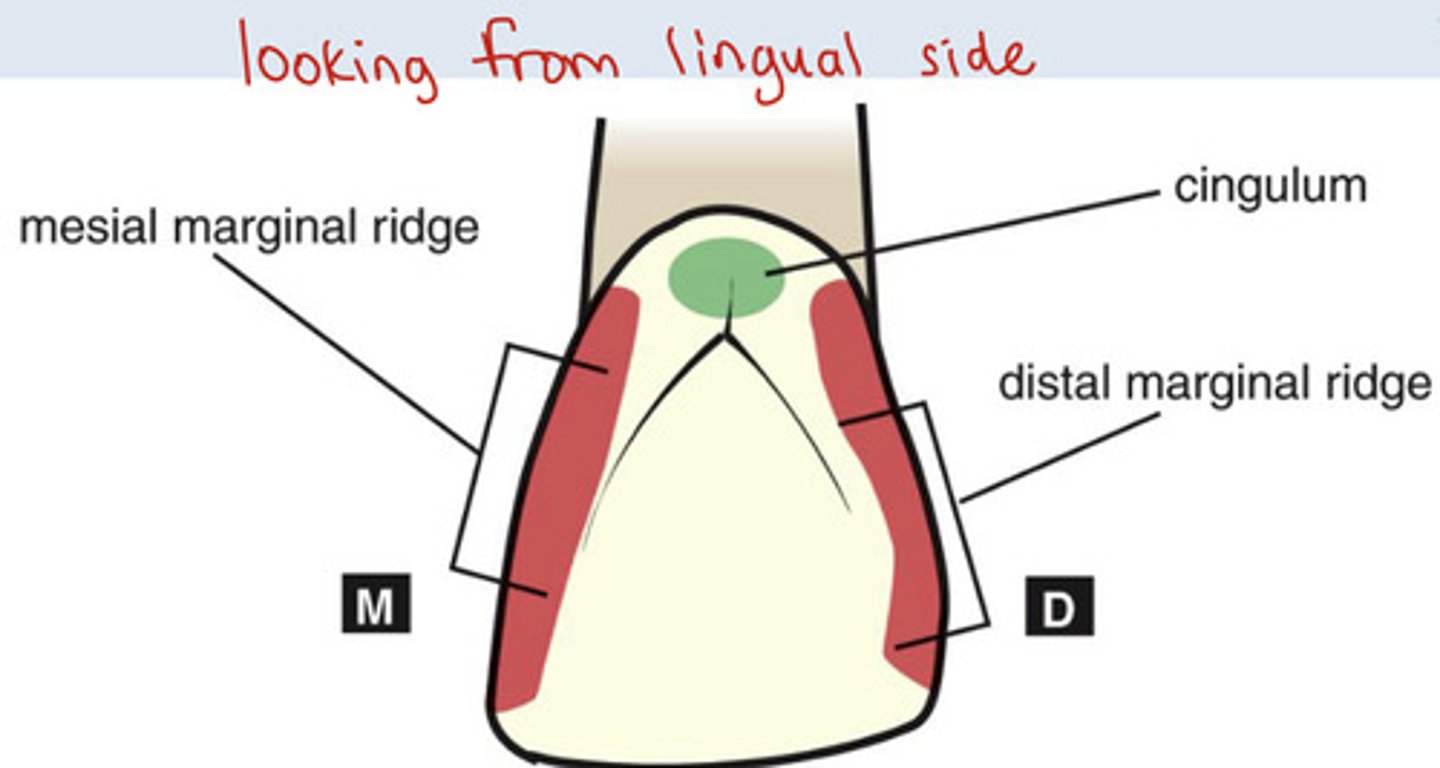
What is the distal marginal ridge?
forms distal border of lingual surface
What is the occlusal crown outline?
Outer outline of the entire tooth crown from the occlusal view
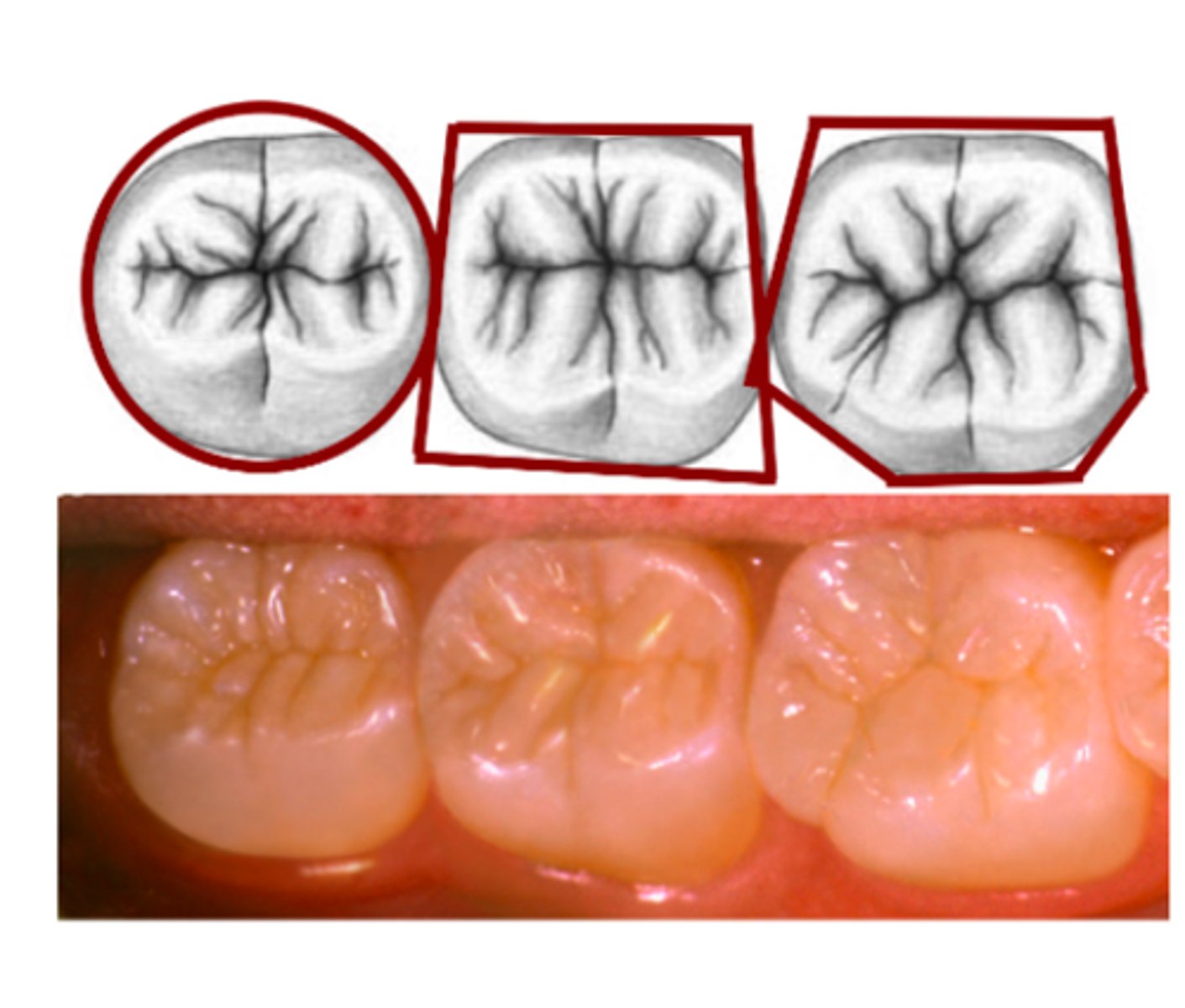
What is the occlusal table?
occlusal surface that is bounded by the continuous cusp ridges & marginal ridges
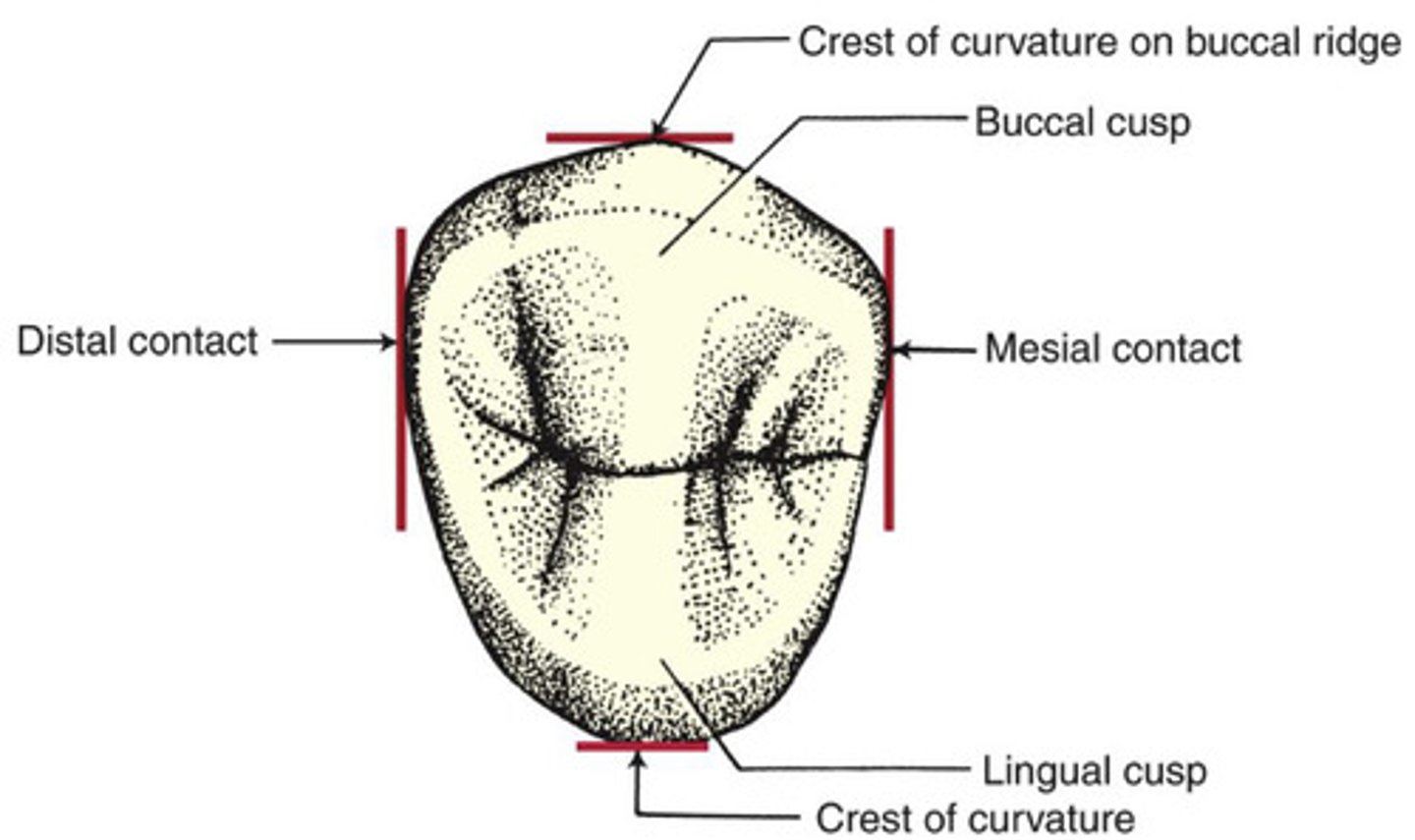
What is the Crest of Curvature?
the height of countour
-furthest projection of enamel for that surface
-widest point of surface; what sticks out the most

What is the cervical ridge?
bulge running mesiodistally in the cervical 3rd of the buccal surface
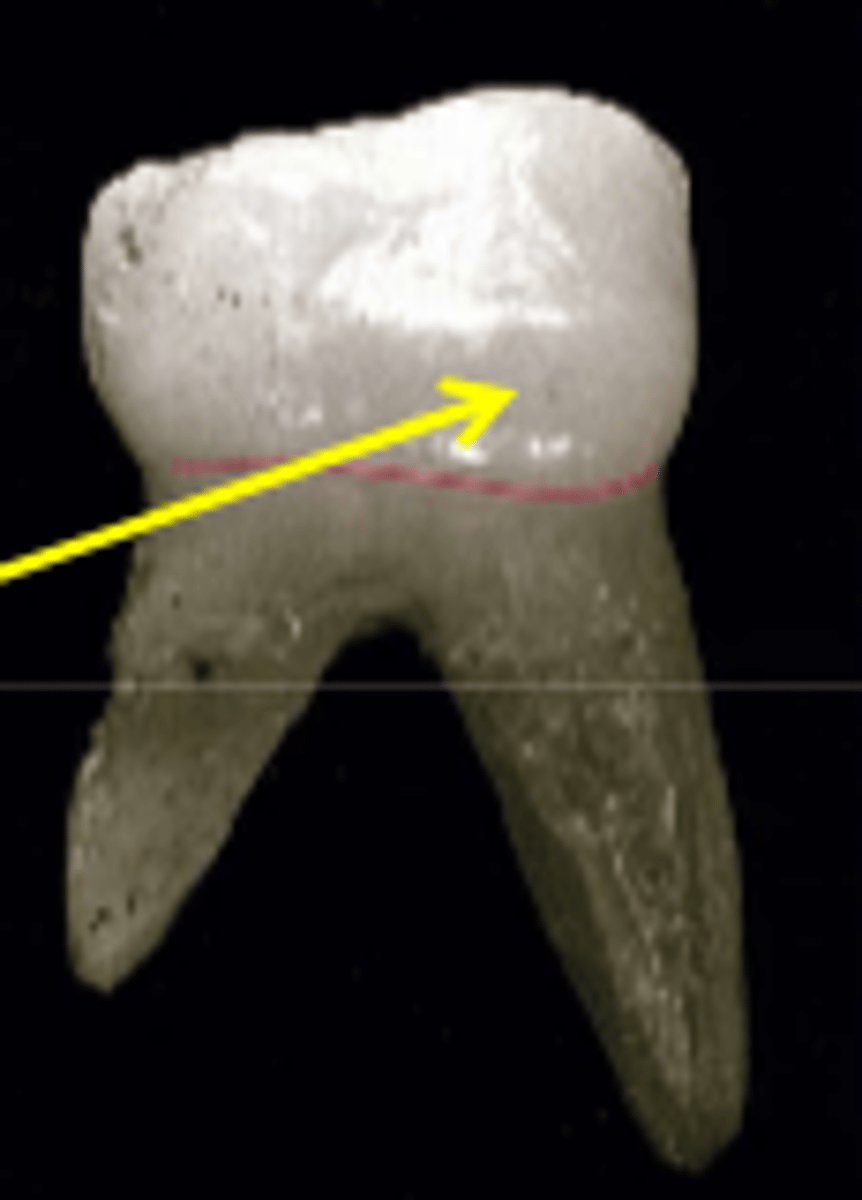
What are mamelons?
small rounded bumps on incisal of newly erupted incisors
-indicates a freshly erupted permanent tooth
-generally, they wear down
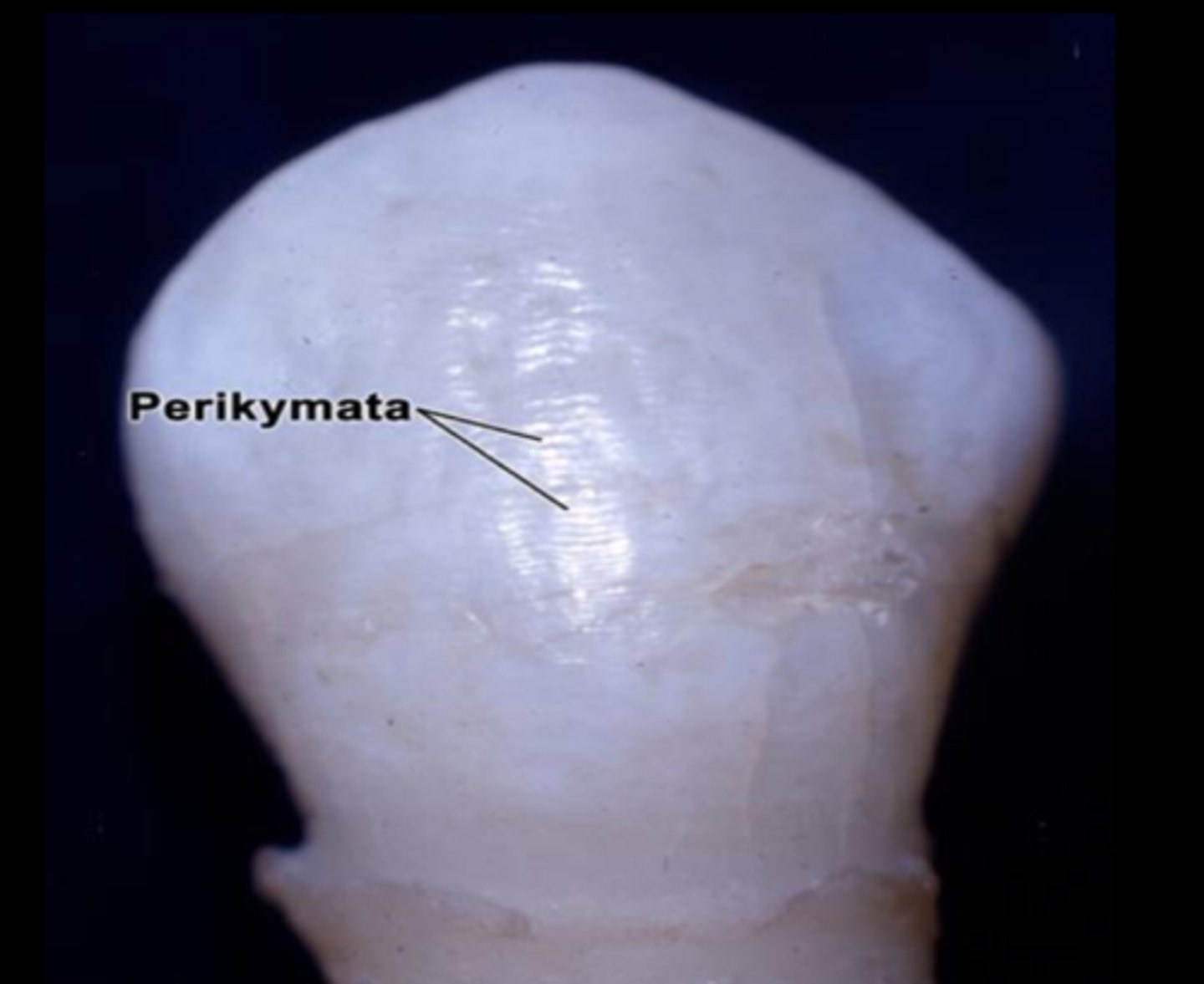
What are perikymata?
small ridges visible on the labial surface of incisors
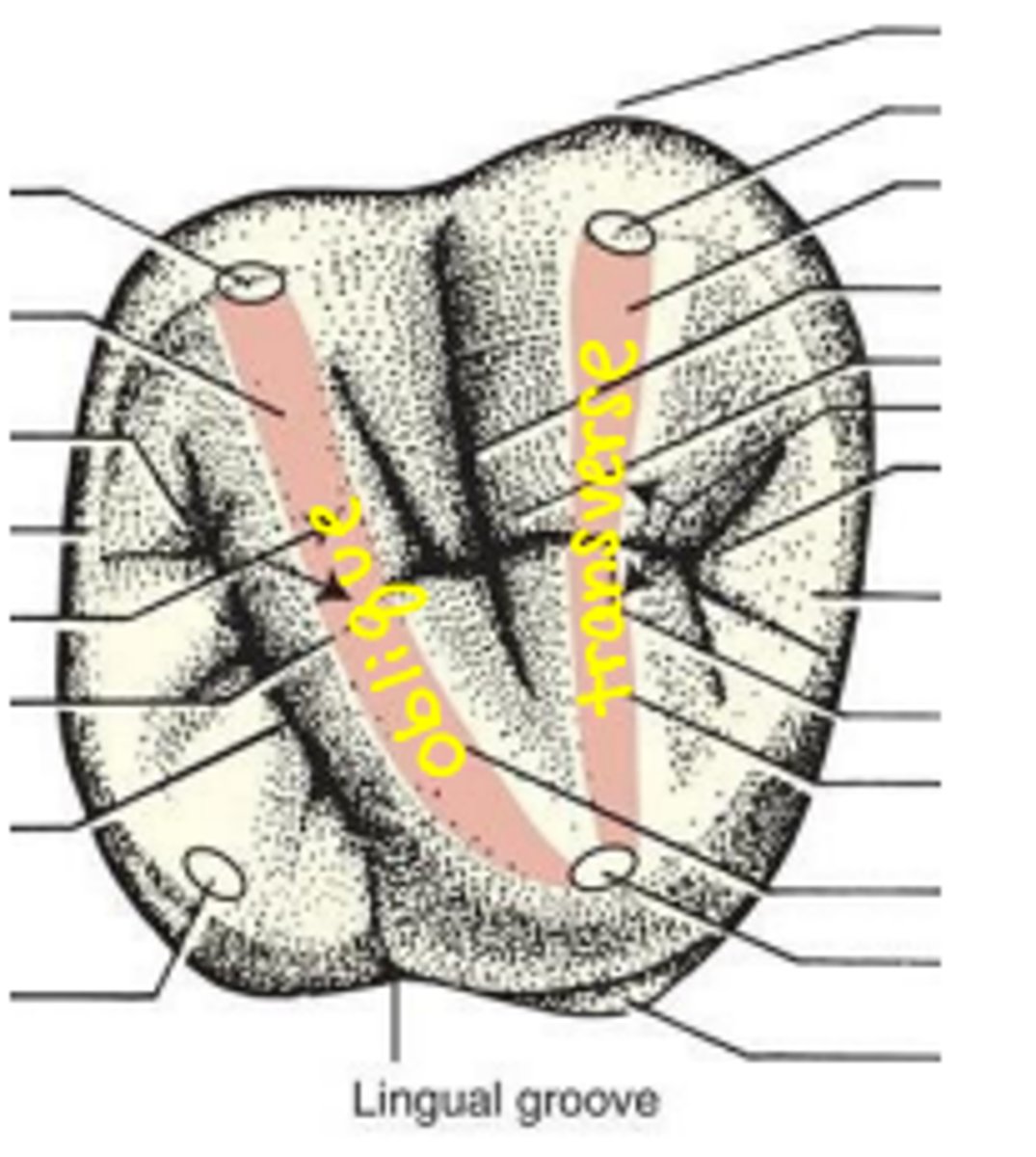
What are developmental grooves?
separate major portions of a tooth; formed by developmental lobes

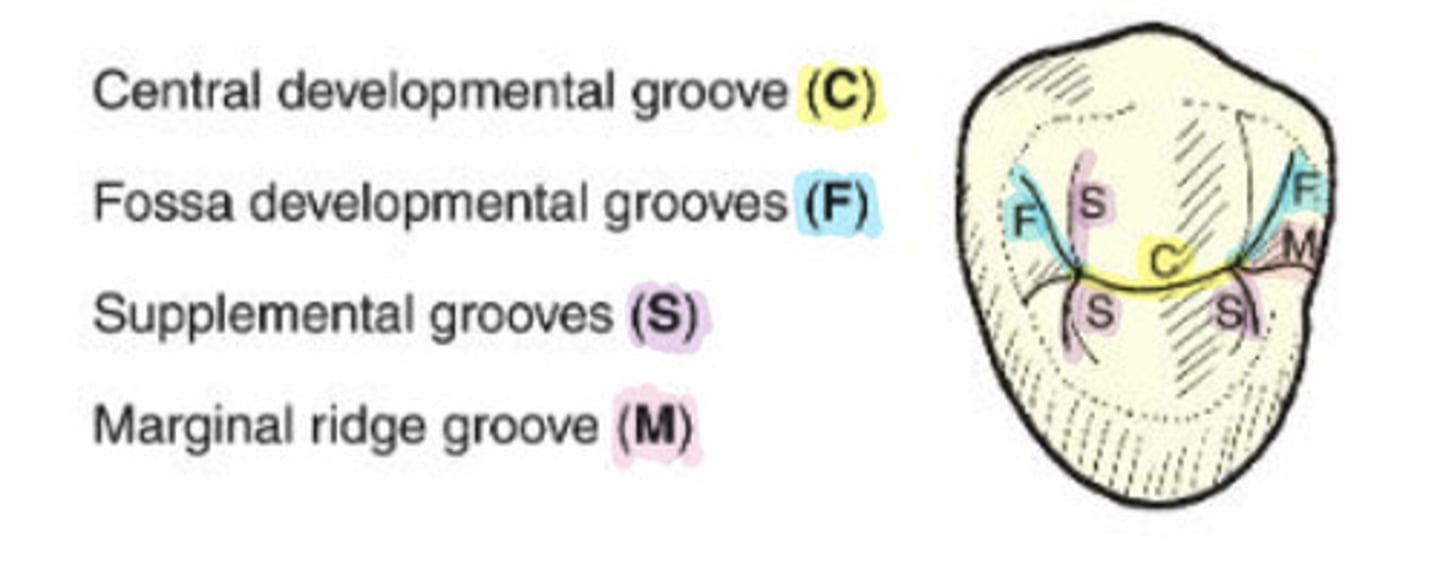
What is the central developmental groove?
C
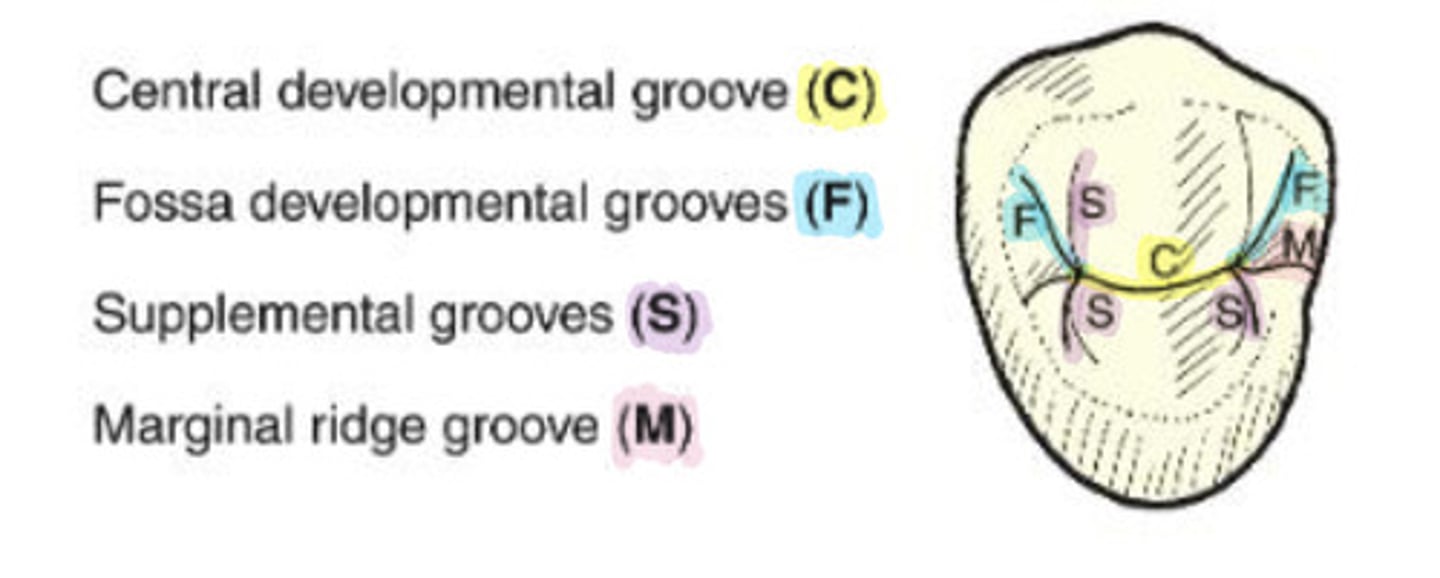
WHat are marginal ridge grooves?
groove that crosses a marginal ridge
-M
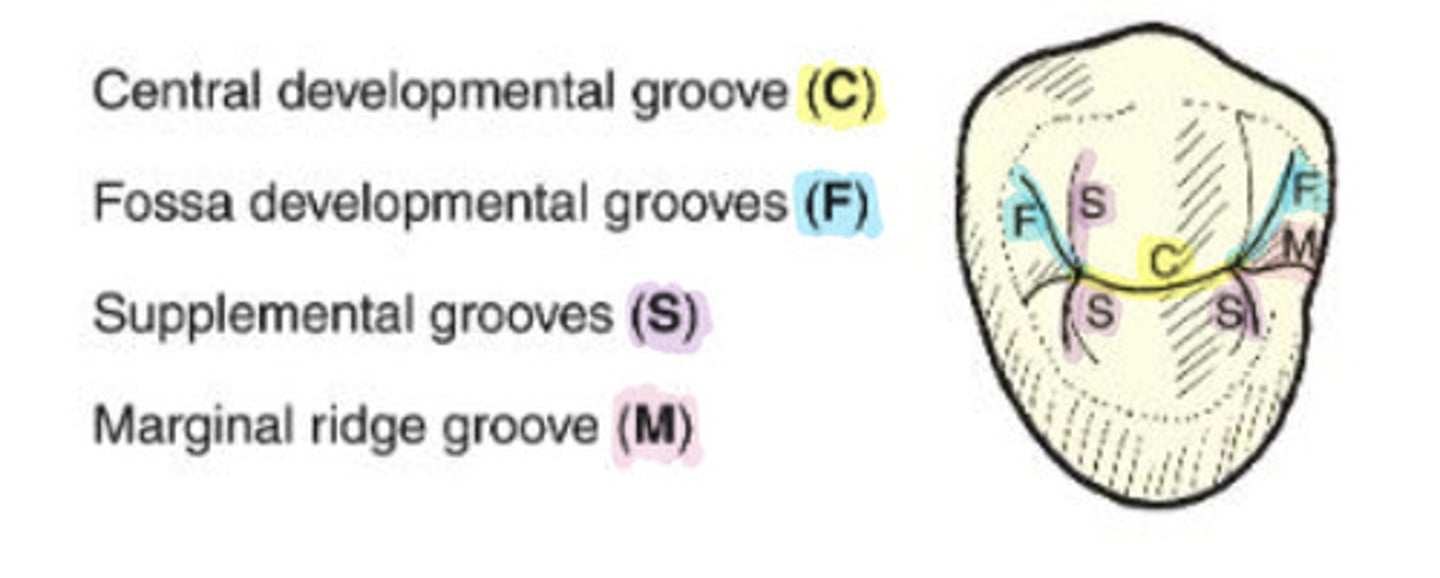
What are fossa grooves?
split off of the ends of the central groove directed toward the line angles of the tooth
-F
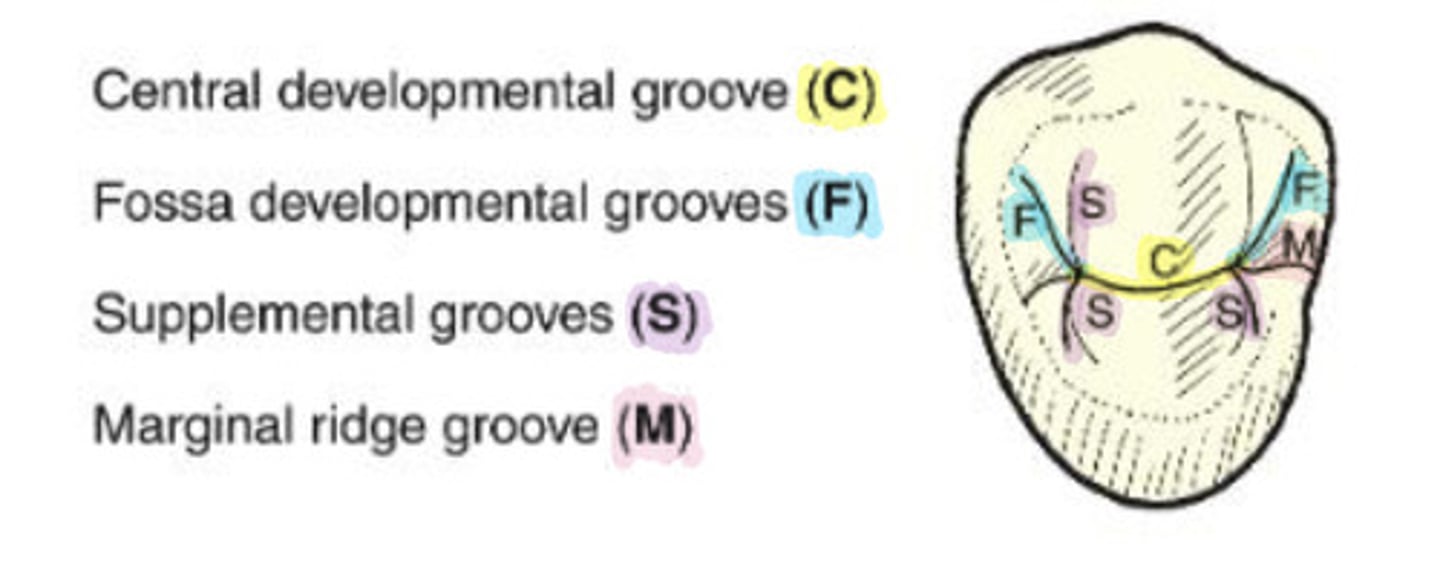
What are supplemental grooves?
additional occlusal grooves that are non developmental
-S
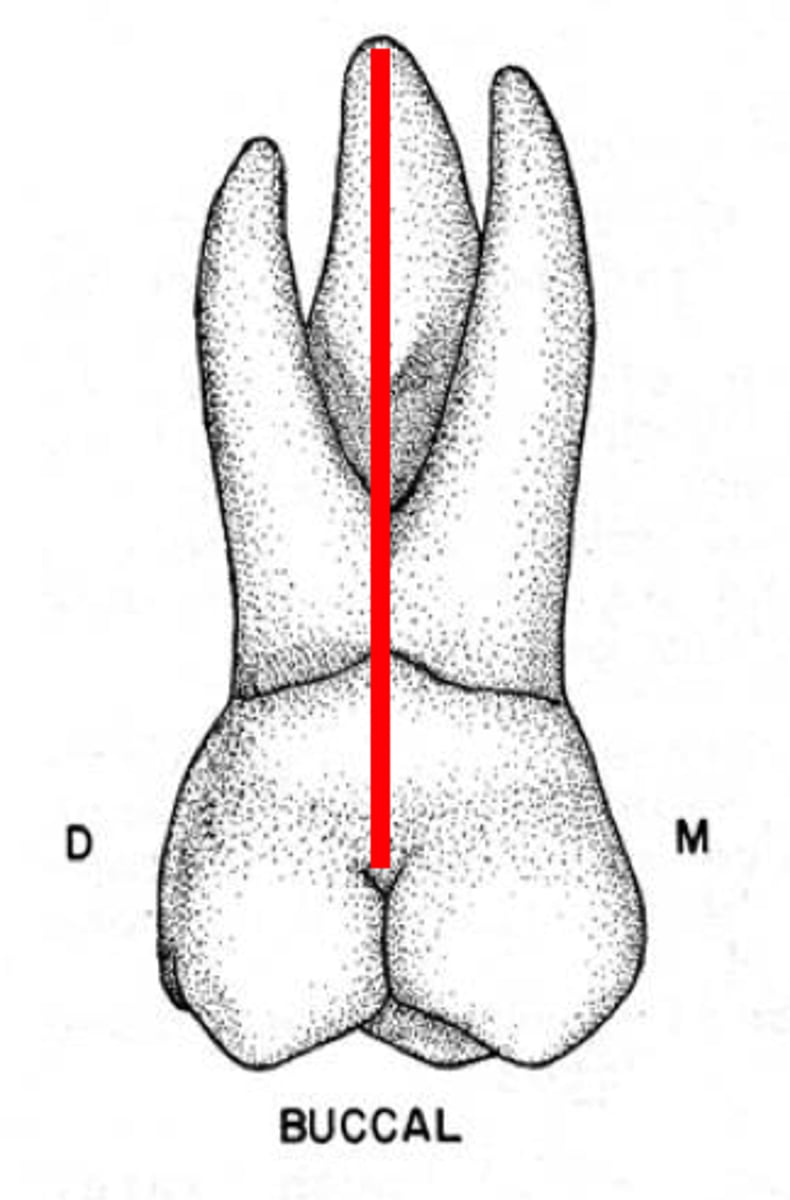
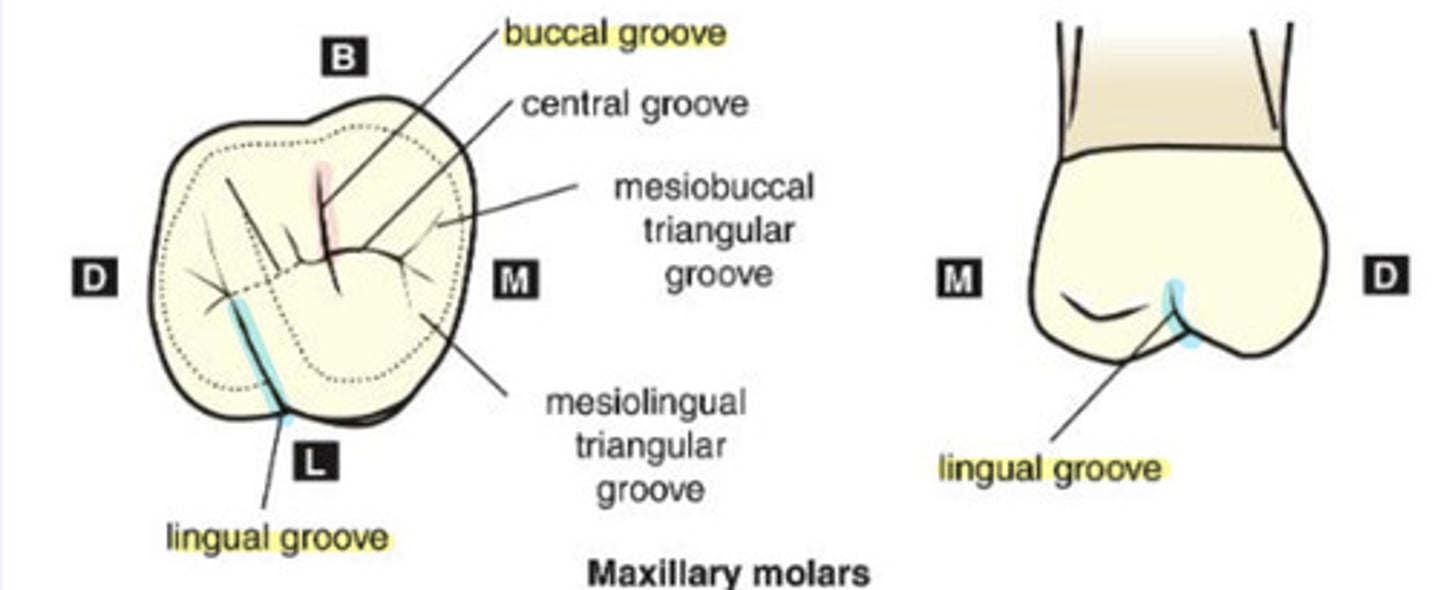
What is the buccal groove?
developmental groove that separates mesiobuccal and distobuccal cusps
-likely to extend onto buccal surface
-mandibular molars with 3 buccal cusps have 2 grooves separating the 3 buccal cusps
What is the lingual groove?
groove separating the mesiolingual and distolingual cusps
-commonly on maxillary molars
-usually only one
Why are pits bad?
-incomplete fusion of enamel in deep pits
-nearly impossible to clean
-prime location for decay (pit and fissure caries)
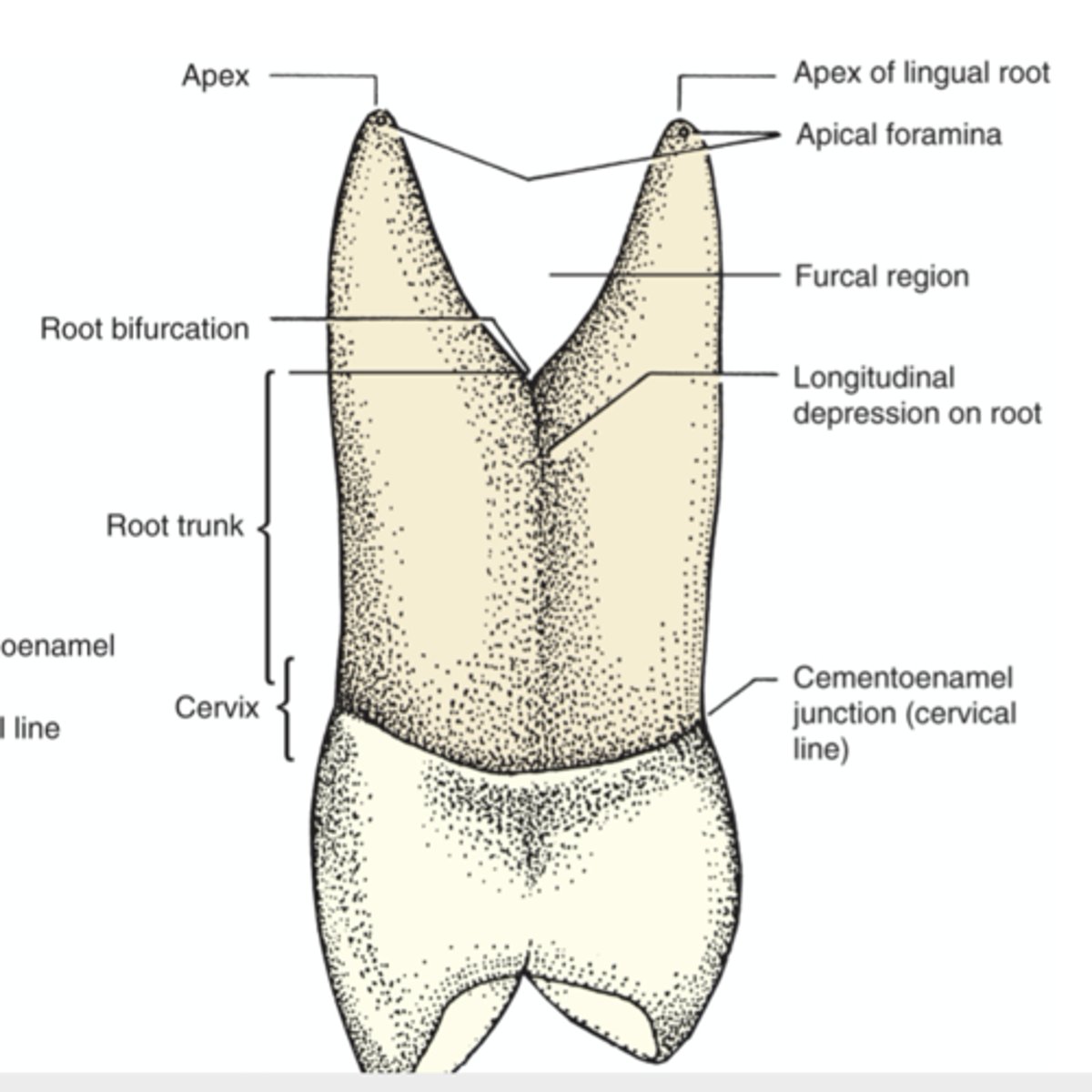
What is the apex of the root?
tip or peak at the end of the root
-apical foramen: opening at apex
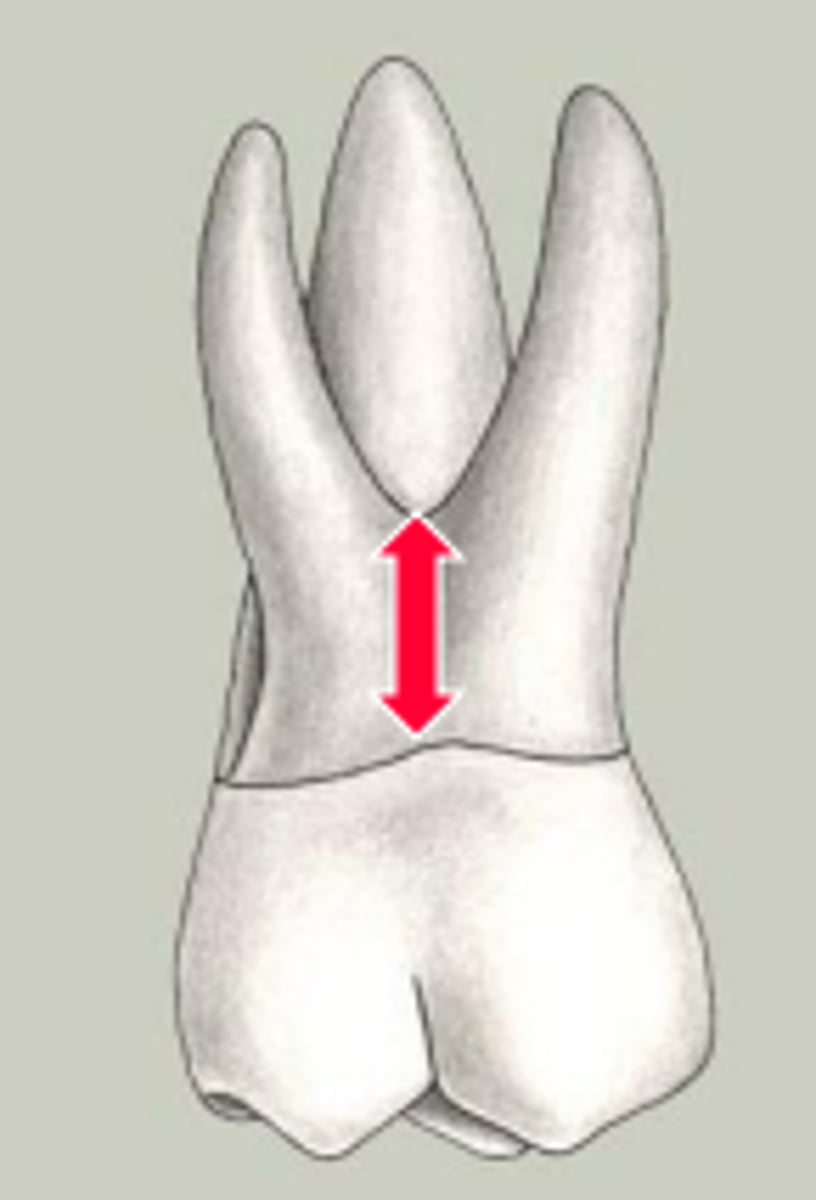
What is the cervix of the root?
constricted region surrounding the junction of the crown and root
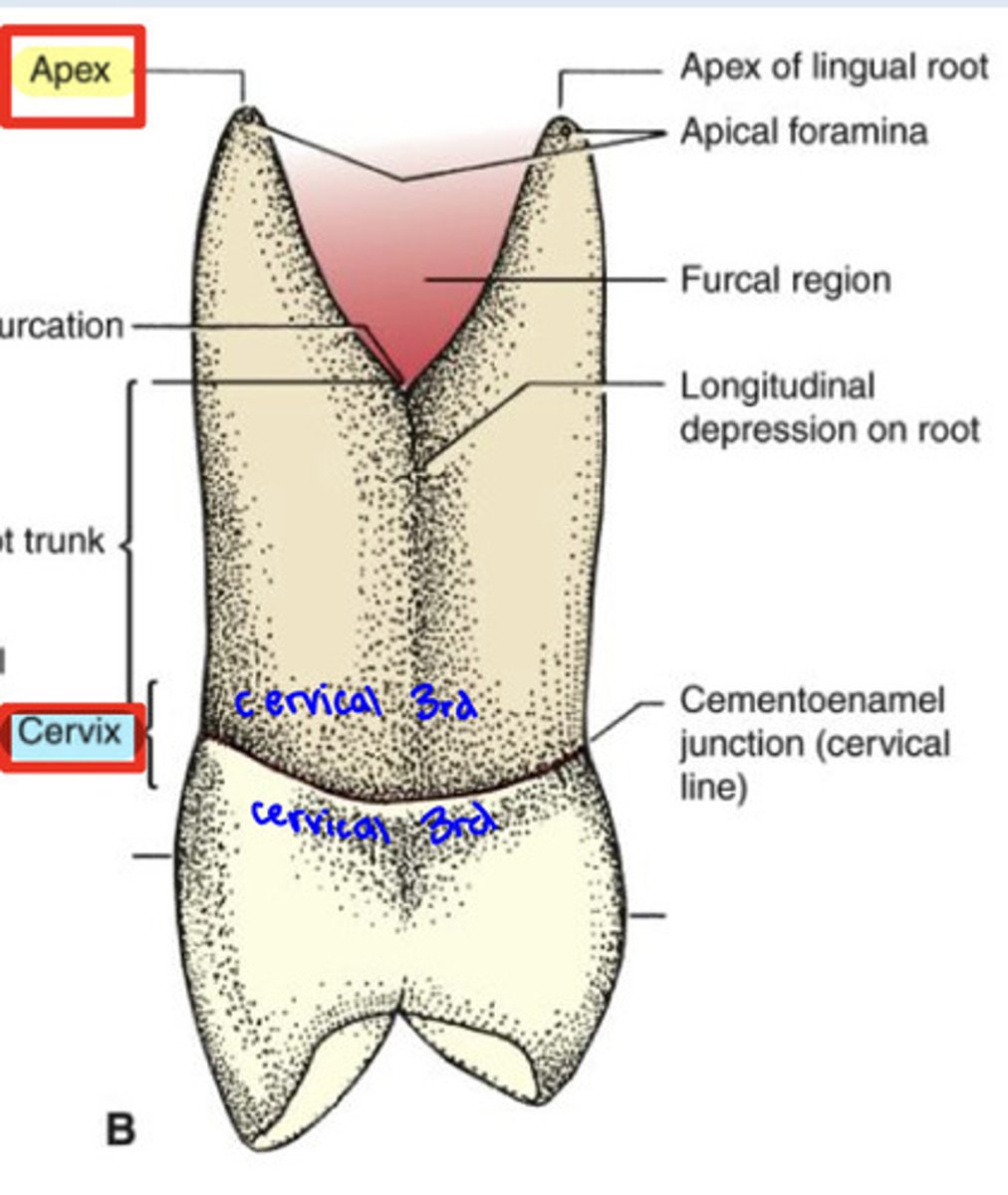
What is the root trunk?
portion of multirooted tooth that is not split or furcated
What is furcation?
portion of multirooted teeth that is split into multiple roots

What is the furcal region?
the space between two or more roots
What is the longest tooth overall?
maxillary canine
Which tooth has the longest root?
maxillary canine
What is the ideal alignment of teeth?
all buccal and lingual cusp tip surfaces follow imaginary parabolic lines that are parallel to one another
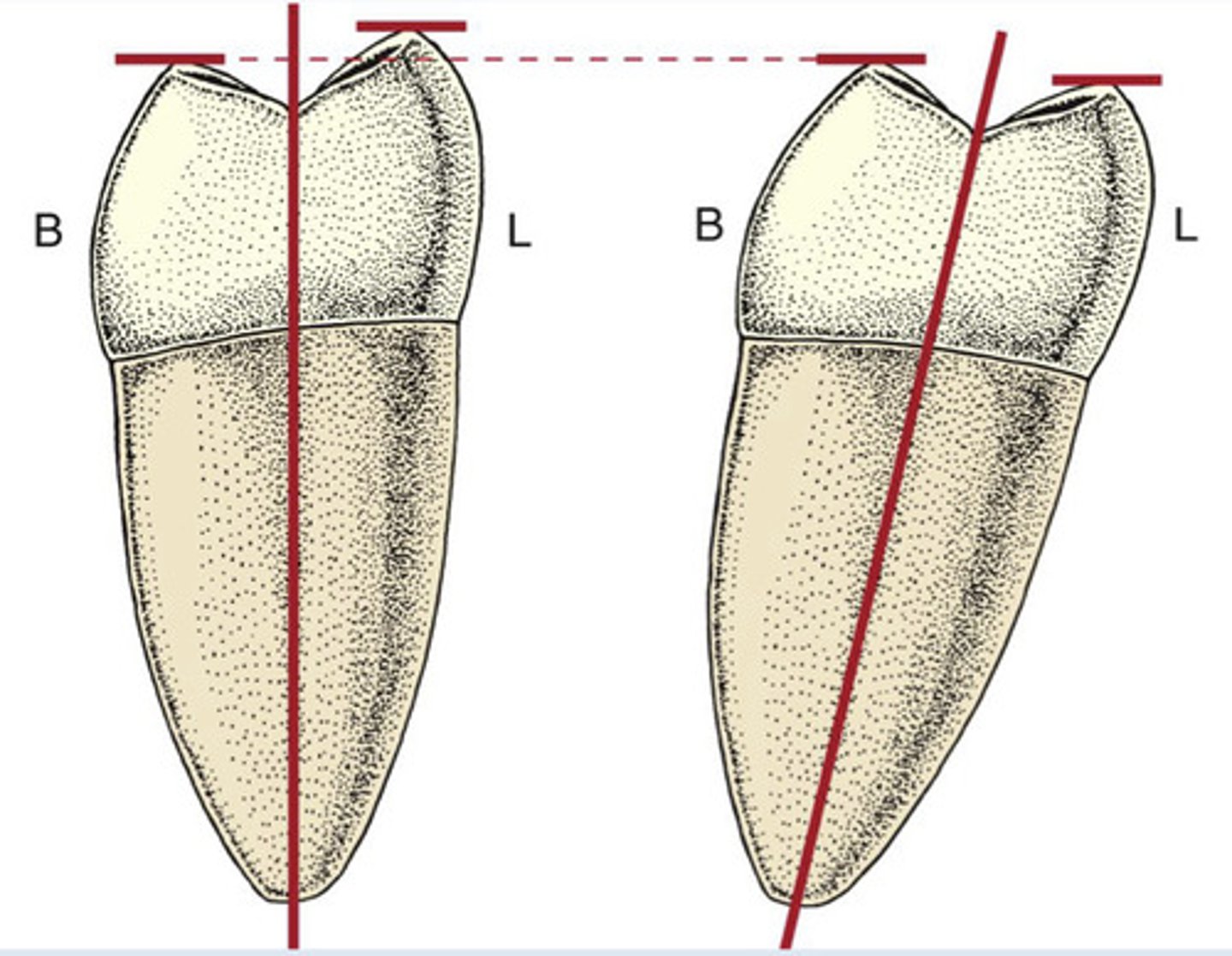
What is the root axis line?
imaginary line through the center of the tooth root
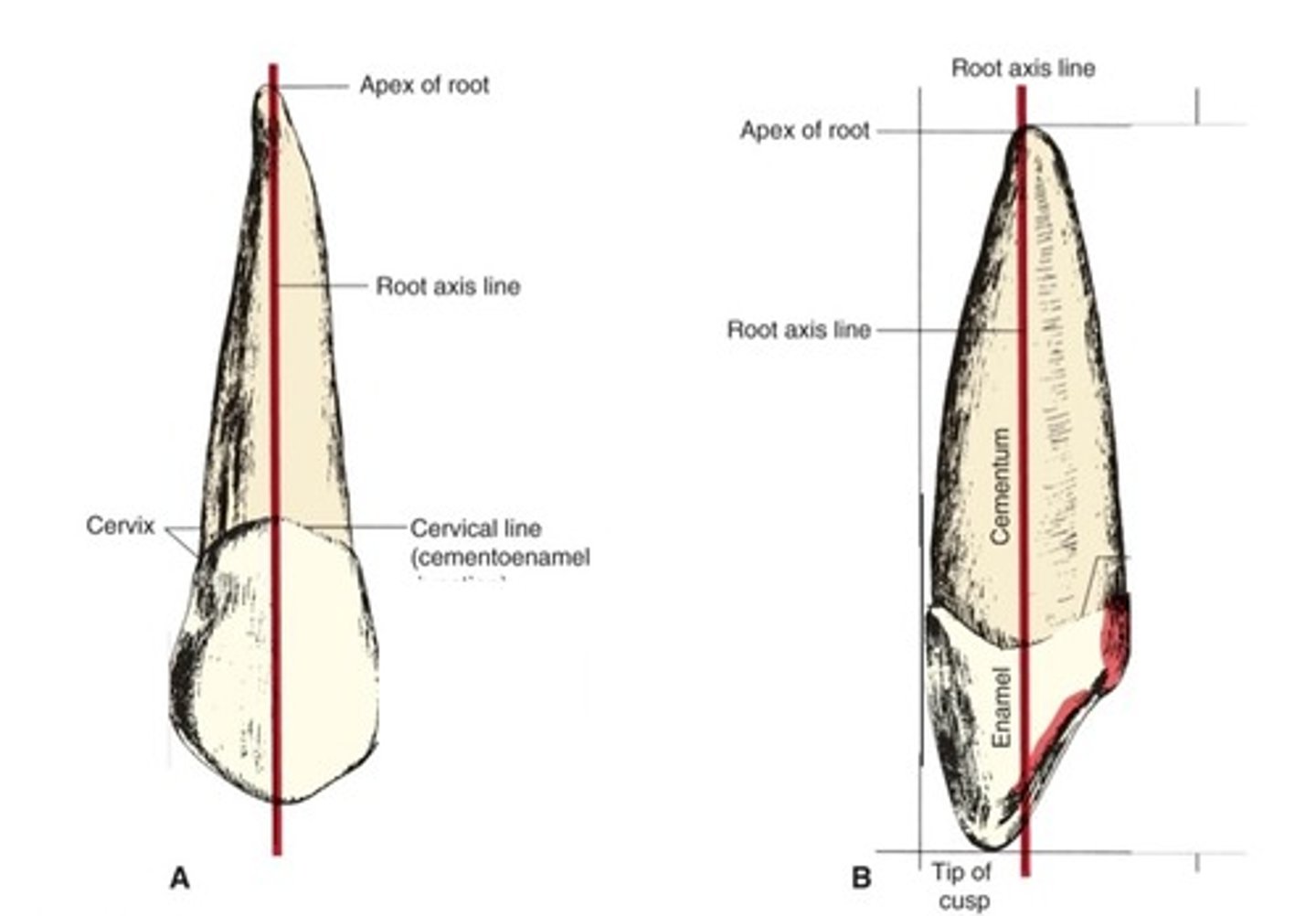
What is essentially the same as contact?
crest of curvature
-parallel to the midroot axis line
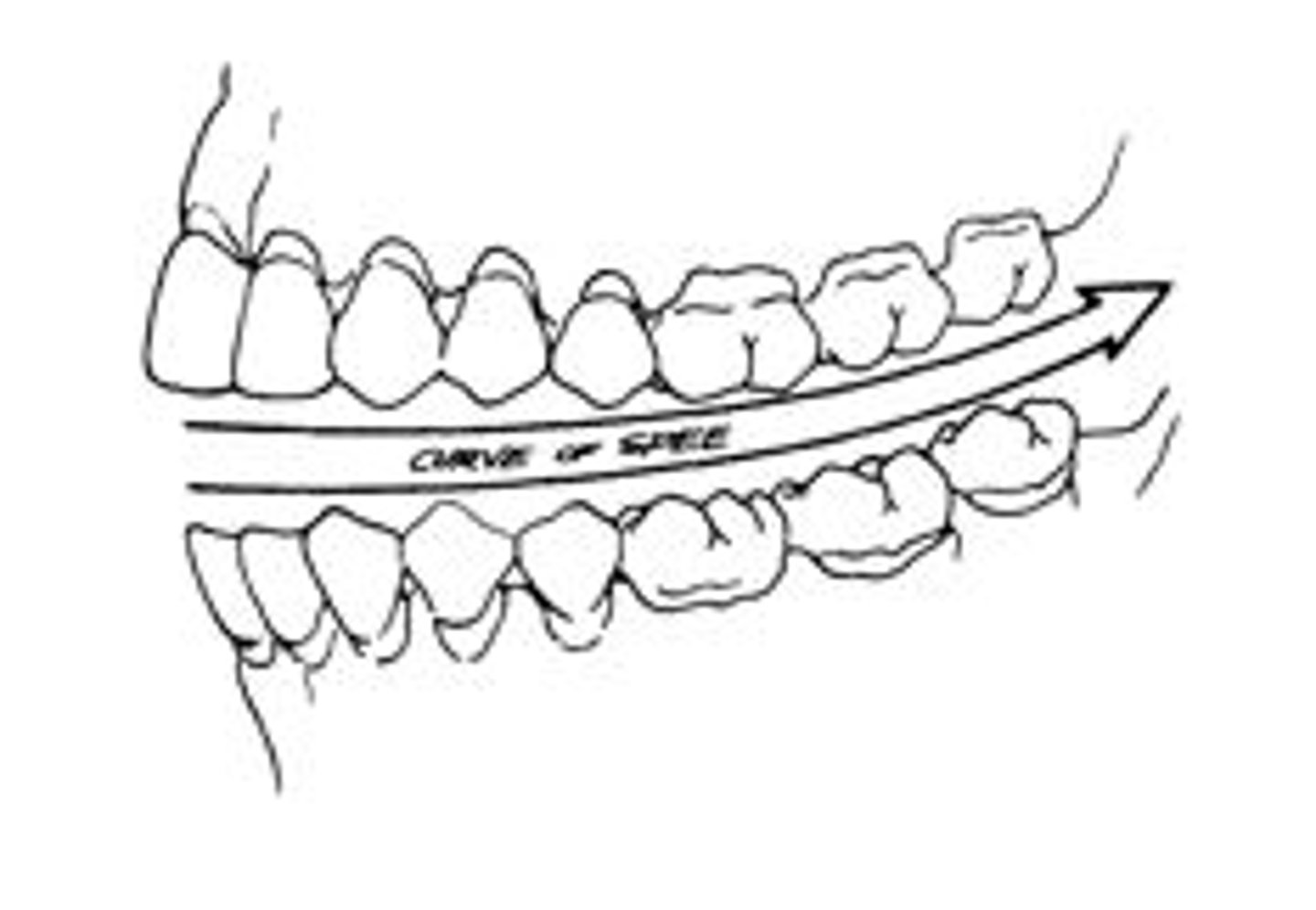
What is the anteroposterior curve?
axial alignment changes gradually from posterior to anterior teeth
-gradual convex in maxillary arch
-concave in mandibular arch
-also known as the Curve of Spee
-curvature of max. and man. arches that fit w/ each other
What is the mediolateral curve?
imaginary line connecting opposite teeth (buccal & lingual cusp) of the same arch
-maxillary posterior teeth are axially tilted facially, whereas mandibular posterior teeth are tilted lingually
-aka Curve of Wilson

Is the lingual cusp of a mandibular molar longer than the buccal cusp?
yes, if it is held straight on its vertical midroot axis
-appears nearly level in the mouth due to the lingual tilt of the molar
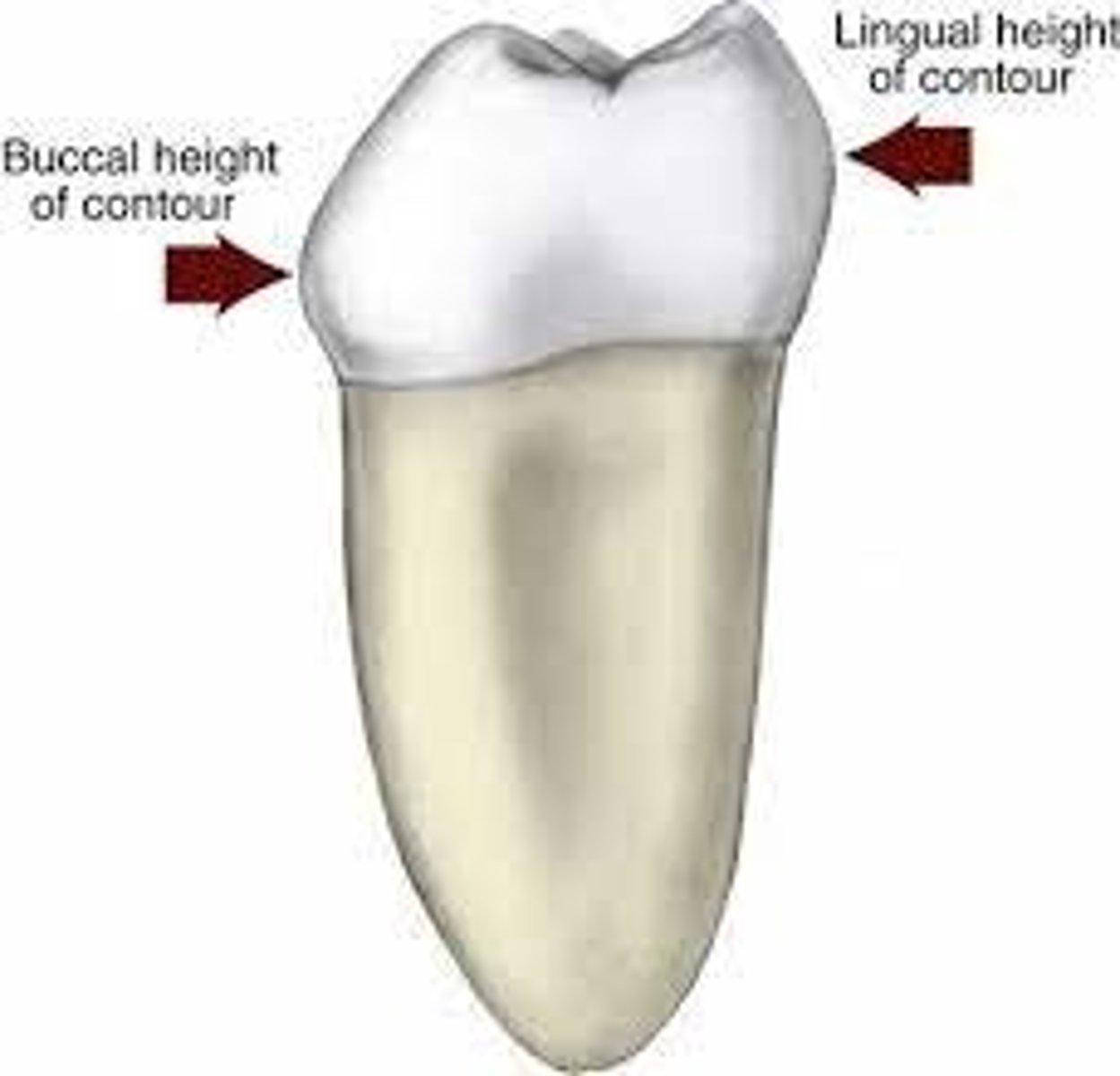
What is the function of the Crest of Curvature?
allows food and debris to shed away from the gingiva
-critical for healthy gingiva
Where on the tooth is the facial height of contour?
both anterior & posterior located in cervical third
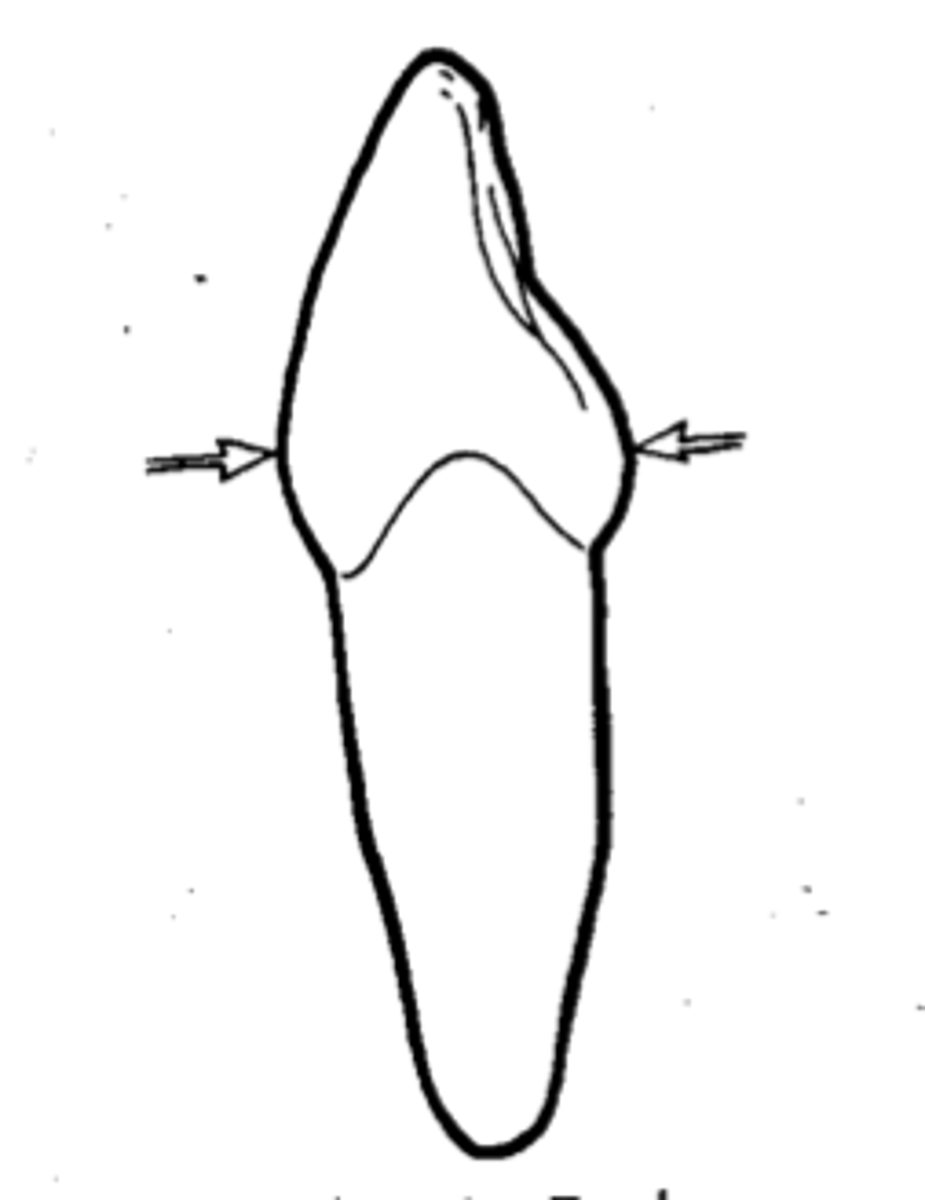
Where on the tooth is the lingual height of contour?
-lingual anterior cervical third
-posterior in middle third
What is the mesial & distal height of contour?
essentially the same as contact
-becomes flatter with time