Class 10 - Assessment & Management of PPA & End of Life Care
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
R.A.I.S.E Framework for PPA Assessment:
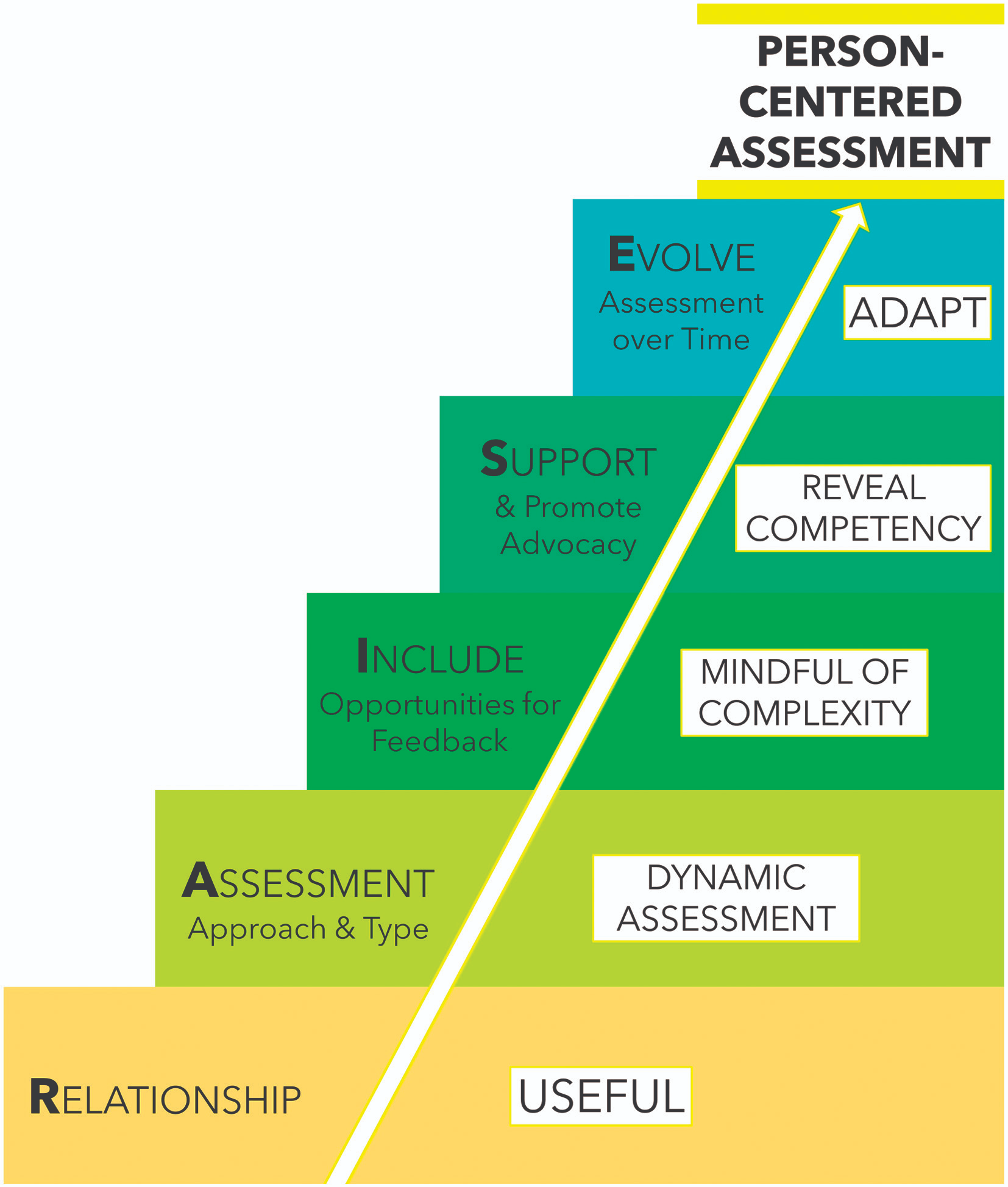
What are assessment suggestions for general PPA Diagnosis?
Can start w/ screeners
Standard aphasia batteries may be used, but classifications (e.g., Broca’s aphasia) should not be used
Western Aphasia Battery-Revised
Boston Diagnostic Aphasia Exam
Comprehensive Aphasia Test
What other cognitive domains should be assessed?
Extralinguistic cognitive domains!
Visuospatial processing & visual memory: complex figure copy & recall
Emotional processing: Emotional Evaluation subtest of the Awareness of Social Inference Test
Cognitive decline will not begin after 2 years!
What is a specific standardized test for PPA subtypes?
Sydney Language Battery
What factors should you consider when formulating a diagnosis vs. suspicion?
What is the neurological evidence?
Consider the patient’s symptoms
Do they meet the criteria for PPA?
When neuro referral is needed…
Suspected primary progressive aphasia
When neuro evidence exists before SLP testing…
“_____ type PRIMARY PROGRESSIVE APHASIA”
PPA Subtyping - Assessment Suggestions:
svPPA
lvPPA
nfvPPA
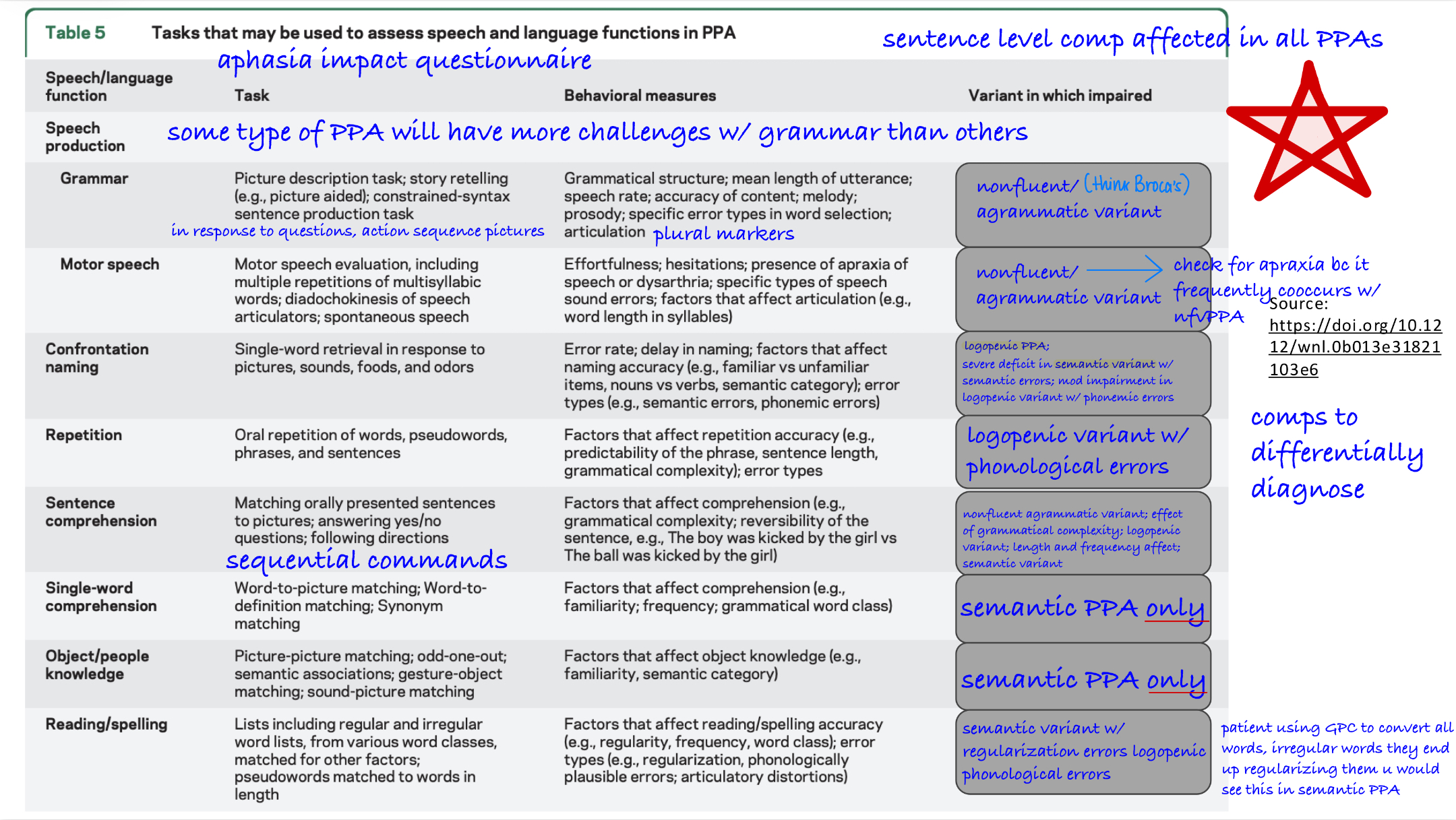
Picture description svPPA:
fluent with high frequency nouns, pronouns & verbs; normal speech rate; prominent word finding difficulties
Picture description lvPPA:
intermediate speech rate between svPPA & nfvPPA; fewer syntactic errors than nfvPPA; word finding difficulties NOT as severe as svPPA; phonemic paraphasias
Picture description nfvPPA:
nonfluent, agrammatic, & slow; frequent speech distortions
On aphasia batteries, what would svPPA present with?
difficulty w/ naming subtests; poor performance on auditory comprehension tests
On aphasia batteries, what would lvPPA present with?
difficulty w/ naming subtests; impaired repetition
On aphasia batteries, what would nfvPPA present with?
distortions in naming subtests; impaired repetition may be observed, but due to apraxia of speech &/or grammatical processing impairment; poor performance on subtests assessing grammatical processing impairment
(Goal Management for PPA) STGs:
We want to “compensate for progression of language loss (not stimulate the language system to regain skills).”
We also want to start early. “Begin compensatory treatment as soon as possible. Be proactive so the person w/ PPA can learn to use communication strategies & tools.”
Finally, we want to “include primary communication partners in all aspects of training, w/ outreach to multiple partners.”
(Goal Management for PPA) LTGs:
Decrease frustration & increase communication
Enhance overall understanding in the functional communication setting
E.g: “PWA will be able to express pain related to illness or mood”
E.g: PWA will increase independence & safety
How do you differentially diagnose at more severe stages?
Look at functional assessments
stage of PPA matters a lot (mild to more severe stages) At mild, easier to differentially diagnose bc it’s consistent w/ subtypes. In more severe stages, patient may present w/ difficulties we’re not aware of, making it more challenging to box patient into specific subtypes
If this is the case, more functional assessment measures. Obtain strong case history, if you take naming, repetition, if it is logopenic type, repetition would be the weakest component early on → this helps tell you based on how patient is performing what their diagnosis was more consistent w/ early on & where they were at initially
Impairment-Based Approach:
Enhancing verbal expression or auditory comprehension by direct training of highly significant lexical terms
Participation-Based Approach:
Enhancing life participation by providing access to & training the use of supportive resources
What is the goal of Lexical Retrieval Treatment?
Goal: Developing personally relevant mini lexicons:
Training using cueing hierarchies
Lexical Retrieval Treatment:
Personally relevant mini lexicons →
Training using cueing hierarchies
Semantic Feature Analysis (SFA)
Pairing cues - spoken + written
Research shows that there is long-lasting gains from such tx in svPPA, nfvPPA, & lvPPA
Video-Implemented Script Training for Aphasia (VISTA):
Repeated practice talking about important topics using “scripted” content developed collaboratively w/ the clinician
Largely homework-based (unison speech production w/ video)
Practice using scripts in conversation
Other Direct Interventions:
Spaced Retrieval Training
Vanishing Cues
Direct Verbal Instructions
What are participation-based/indirect interventions?
Communication Partner Training
Use of AAC & other nonverbal communication (Voice banking)
Memory stations
Montessori-based intervention
AAC & speech-generating devices:
practice repeating words or phrases in everyday life
easily add or edit icons, words, or phrases
create a digital memory book & preserve your voice
Use text-to-speech inputs to vocalize your thoughts
Memory Stations:
personalized visual memory & communication aids, such as book, wallets, & signs, can help ppl w/ memory loss recall info that is important to them
What can books & wallets contain?
Photos from LTM to help w/ reminiscence
Important info to help w/ orientation & daily schedule
Answers to repetitive questions
Key words, names, & photos to help word recall
Scripts for daily convos
Montessori-Based Interventions (MI):
Montessori activities involve everyday practical tasks & engage the learning-by-doing system, thus relying on implicit memory (usually spared) rather than explicit or declarative memory
Reading Roundtable:
Montessori-based group activity; aimed at increasing positive engagement & verbal discussion
Capitalizes on relatively spared oral reading skills in many PWD
Specifically developed stories, designed & adapted w/ ease of communicative access:
Stories have a supportive sensory format (e.g., large font, high-contrast printing),
Accompanying questions to spark discussion
Positively engages residents & fosters reminiscence
Participate in conversation (e.g., turn taking, listening, making on-topic statements)
Overview of End-of-Life Care:
Palliative care & hospice: a continuum of health care services for persons with serious illness from the time of diagnosis of a medical condition through death & bereavement care
In palliative care, the goal is to adjust day-to-day activities in response to the continuous progression of the condition to enhance well-being, promote client autonomy, & involve clients & care partners in the process of clinical decision making
Hospice is a type of palliative care & is implemented as patients approach the end of life (EoL)
Who are the care members of the interdisciplinary team?
Patients, Family, & Friends
Medical & Nursing Staff
SLP, OT, PT, SW, Music/Art therapists, Counselors
Chaplains, Other religious/spiritual leaders
The role of the SLP in palliative care:
Consultation with patients, families, & members of the hospice team regarding choices in the areas of communication, cognition, & swallowing function
Consultation regarding strategies & tools in the area of communication to support the patient’s active participation in decision making, to maintain social closeness, & to assist the patient in fulfillment of end-of-life goals
Assistance in optimizing function related to dysphagia symptoms to improve patient comfort & eating satisfaction & to support positive mealtime interactions w/ family members
Collaborative consultation w/ members of the interdisciplinary team to provide & receive input related to overall care
What could we improve & how?
Learning how to manage our emotional responses related to death & dying
Expanding our views to consider death & dying a part of the human experience
Arrange time for self-care practices to maintain our own mental & physical health
logopenic variant:
nonfluent can occur with sentence repetition, however, they will still be able to recall some words this is different from logopenic where they will not be able to recall any