REED 430 MIDTERM
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
Simple View of Reading
decoding x language = reading comprehension
Dyslexia
inability to understand spoken language
Hyperlexia
inability to recognize sounds when reading
Ehri’s phases : Pre-Alphabetic
little to no knowledge of alphabetic principle (ex. A child sees the stop sign and knows it means stop without reading)
Ehri’s phases: partial-alphabetic
emerging – use of initial grapheme to read word (uses the letter /S/ to spell stop)
ehri’s phases: full alphabetic
decoding sound by sound (ex. /s/ /t/ /o/ /p/ stop)
ehri’s phases: consolidated alphabetic
using chunking to decode (ex. /st/ /op/ stop)
ehri’s phases: automatic phase
reading effortlessly and automatically (ex. “what’s this word?” ‘stop!’)
Scarborough’s rope
Word recognition and language comprehension have to go together
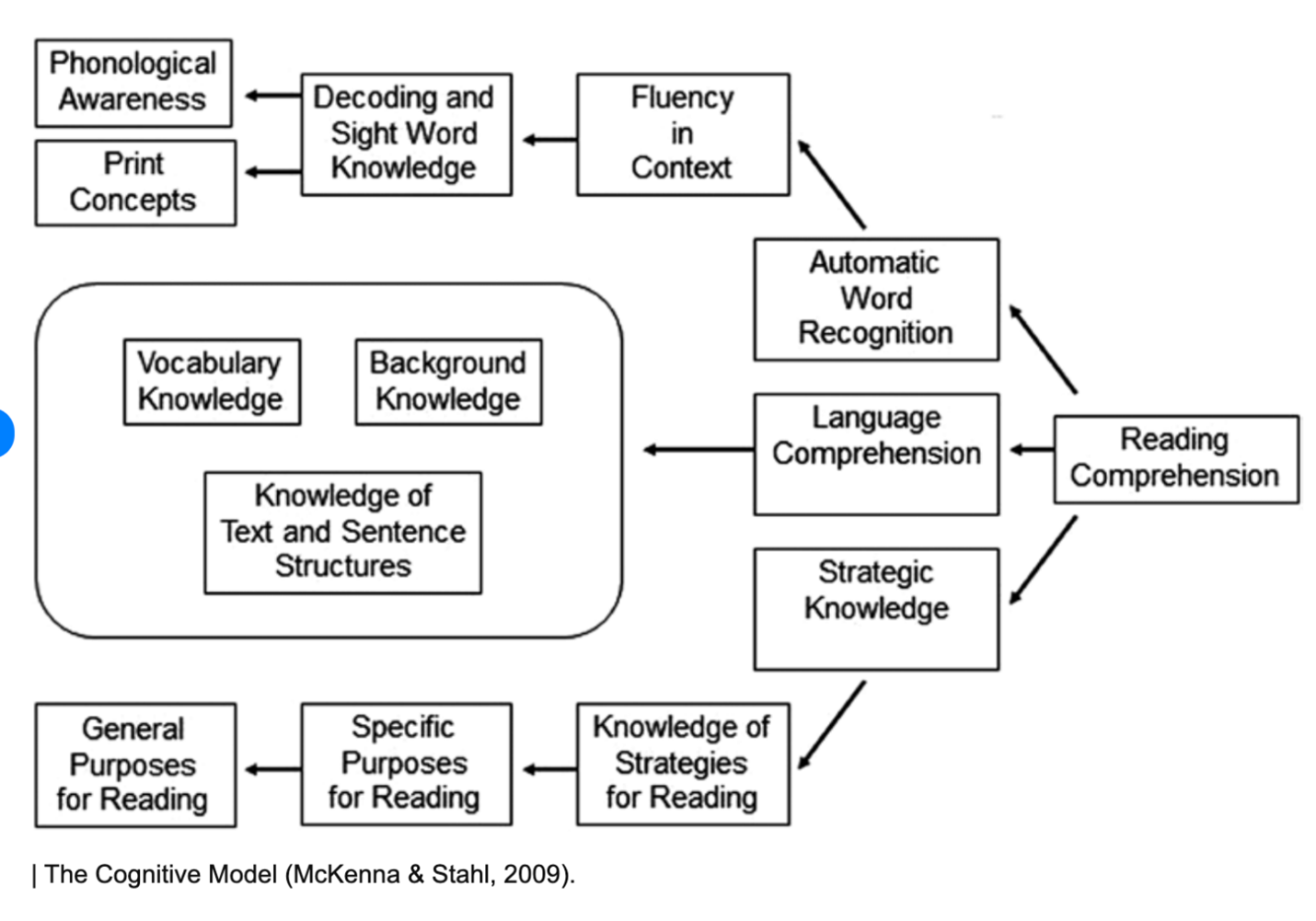
cognitive model
Phonological awareness and print concepts > decoding and sight words > fluency >automatic word recognition > reading comprehension
The Big 5 from the National Reading Panel
Phonemic awareness, phonics, fluency, vocabulary, comprehension
phonemic awareness
o The ability to focus on and manipulate individual sounds in spoken words.
phonics
The systematic and predictable relationship between spoken sounds (phonemes) and written letters (graphemes) that allows readers to identify or "decode" words.
fluency
o The ability to read orally with appropriate speed, accuracy, and proper expression.
vocabulary
o The knowledge of words, both spoken and written, that is necessary for comprehension.
Comprehension
The cognitive process of understanding what a reader has read.
Language Scaffolds: recasts:
provide a corrected version of what the child says
Language scaffolds: expansions
add to child’s utterances
language scaffolds: modeling
demonstrate to student without expectations
language scaffolds: following the child’s lead
communication between student and teacher is based on students’ responses
4 domains of print
o Print as an object of meaning: a period means to pause, enviormental print
o Book organization and print conventions: we read left to right
o Alphabet knowledge: recognize the names of letters.etc
o Concept of word : a students awareness of letter sounds
concept of print assessment
o an understanding of how print, reading, texts/books, etc. work
- Evaluate a child’s understanding of print, where to start on a page: which way a book turns, etc
phonological awareness: word level
Sentence segmentation: Understanding sentences can be broken down into words.
Rhyme: cat, bat
Alliteration: peter piper picked a patch of pickled peppers
Syllable: breaking words into smaller parts (every part has a vowel sound)
-hel-i-cop-ter
phonological awareness: on-set rime
Onset: the sounds at the beginning of a single-syllable word prior to the vowel /c/ /at/
Rime: the sounds from the vowel to the end of the word /c/ /at/
phonological awareness: phonemic awareness
Recognizing and manipulating the smallest unit of sound in words (phonemes) /c/ /a/ /t/
phonological awareness progression
matching, isolation, blending, segmenting, deletion, substitution
Connection between word recognition and decoding
Phonological awareness is about manipulating sounds and this is a foundation of decoding
phoneme
smallest unit of sound in spoken word
phonological awareness
The ability to hear, recognize and manipulate the sounds in spoken language.
alphabetic principle
: connecting letters with their sound to read and write
grapheme
symbol that represents a phoneme
blend
consonants keep sound (bl, st,tr)
diagraphs
2 letters make one sound (sh,ch ph)
Diphthongs
letters make a gliding sound (oi)
R controlled
r makes the dominant sound
decodeable text
: Most of the text is made of letter sound correspondences students already know or are learning.
predictable texts
: encourages memorizing whole words and sentences
pattern texts
a text that follows a pattern or structure
heart words
words a student can’t decode and has to know by
Heart (the,you, of,)
invented spelling
Students’s use what they know to spell
-provides a foundation to learn about spelling
-strengthens phonological skills and awareness
Bears spelling strategies
Letter formation
Orthography: understanding of how letters create sounds which become words
composing
spelling stages from words their way assessment
emergent > letter name alphabetic > within word pattern > syallabulles and affixes> derivational relations
Spelling Stage: emergent
short vowels, diagraphs, blends
Spelling stages: within word patterns
common long vowels and other vowels
Spelling stage: syllables and affixes
inflected endings, syllable junctures, unaccented final syllables,
derivational relations
harder suffixes and bases or roots