ch.4 Price Controls & Quotas
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
consumer surplus
diff b/w max market price consumer willing to pay for something - the price they actual pay
assessment: George is considering the purchase of some new shirts for work. He is willing to pay $35 for the first shirt, $25 for the second shirt, and $15 for the third one; Oxford Clothiers, his favorite shirt manufacturer, is selling shirts for $28 each.
What is the efficient number of shirts for George to buy?
What is George’s consumer surplus?
35 - 28 = 7
less additional MU from each additional unit of product we purchase
25 - 28 = -3
15 - 28 = -13
buy 2nd price at 50% off
MC = $10
1st shirt = $25 profit margin
2nd shirt = $4 profit margin
producer surplus
diff b/w equil price - minimum price they're willing to accept
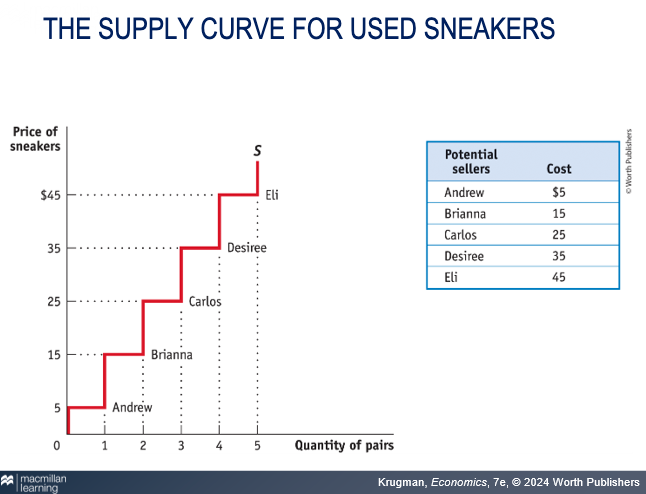
most efficient?
Andrew (lowest price yet still profitable)
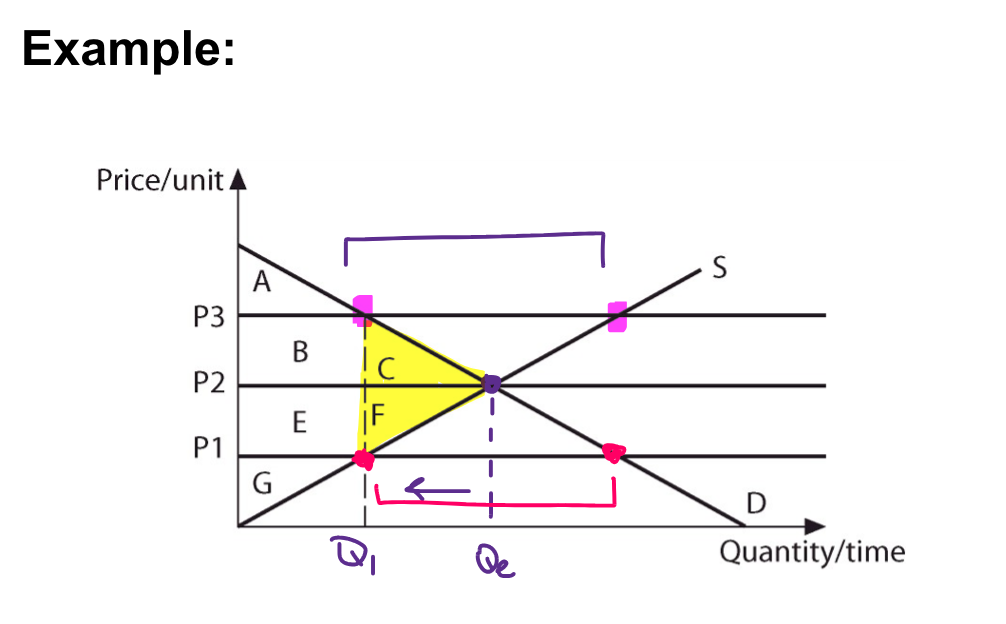
identify PS & CS
p2:
- CS: ABC
- PS: EFG
- transaction
P3:
- CS: A
- PS: BEG
p1:
- Q1
- CF = deadweight
- PS: G
- CS: ABE
CF = deadweight
Price ceiling:
maximum price sellers are allowed to charge for a good or service (Only effective BELOW equilibrium).
Price floor:
minimum price buyers are required to pay for a good or service (Only effective ABOVE equilibrium).
in price ceilings
Prevents prices from performing it’s rationing function in a free market system.
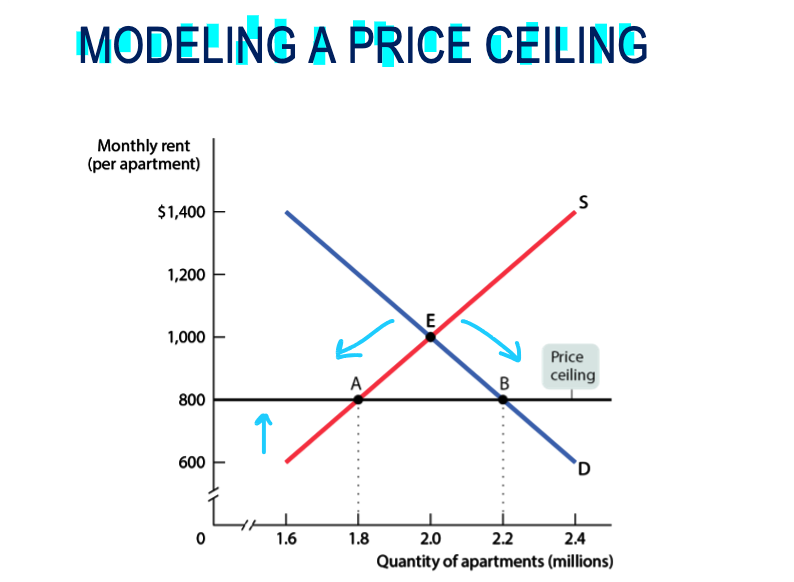
this is a ____
shortage
Qd > Qs
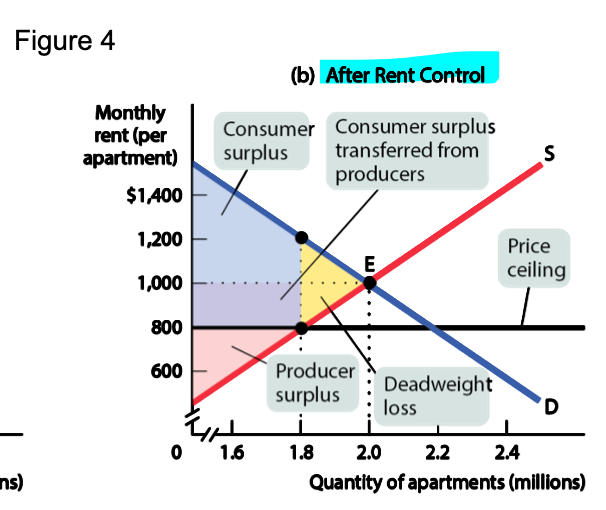
how are they allocated w/ price ceiling?
Consumer Surplus:
Increases: Consumers pay less, boosting consumer surplus.
Shortages: If demand exceeds supply, some consumers can't buy the product, reducing overall surplus.
Producer Surplus:
Decreases: Producers earn less, shrinking producer surplus.
Reduced Incentives: Lower prices may discourage production, leading to fewer goods available.
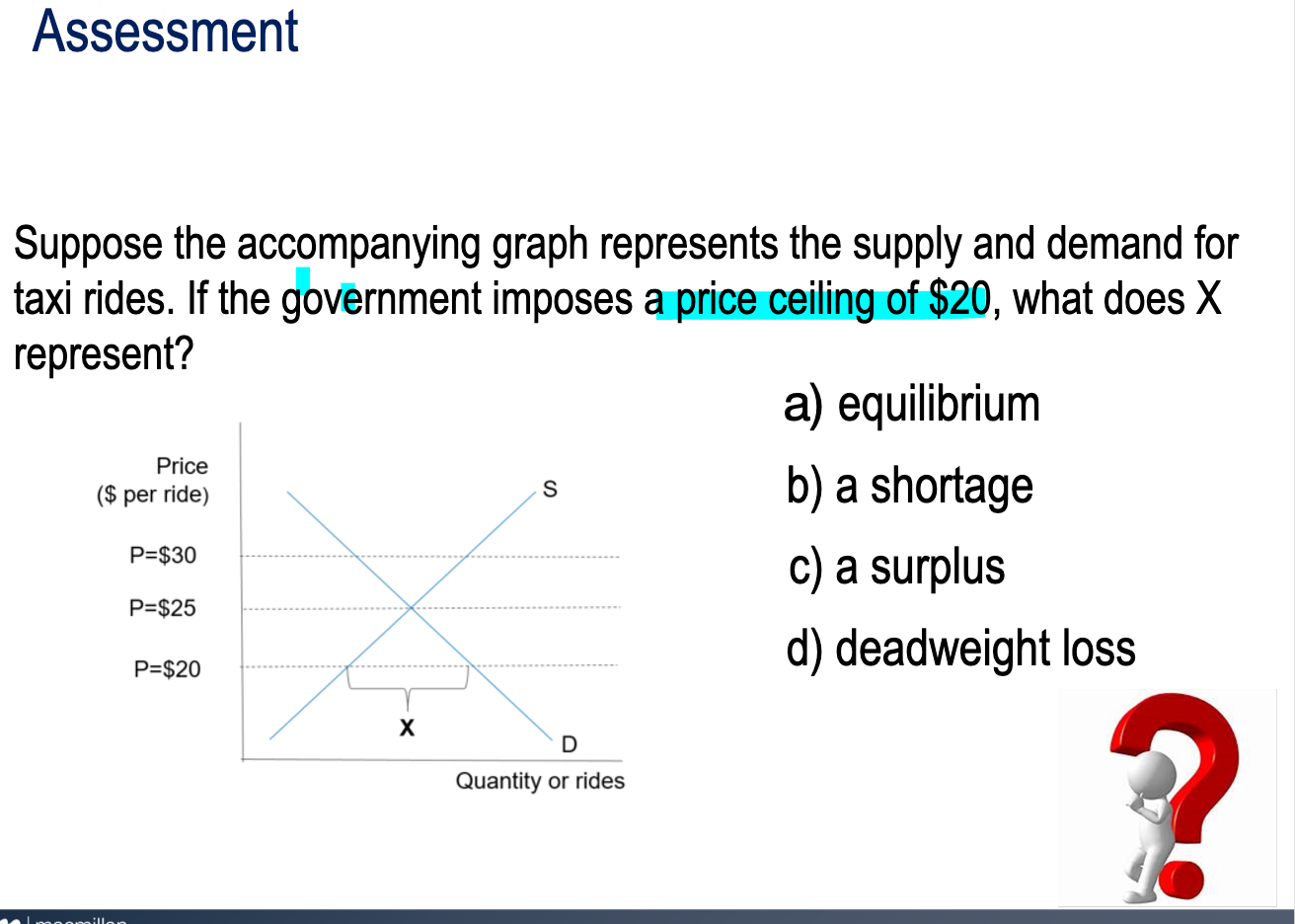
Suppose the accompanying graph represents the supply and demand for taxi rides. If the government imposes a price ceiling of $20, what does X represent?
shortage
Binding price ceiling or price floor
one that must be adhered to by all people.
Non-binding price ceiling or price floor
one that does not change the market.
a price floor below equilibrium;
non-binding & has no effect

Solve
