Hemolymphatic Dz (Bone Marrow, Thymus, Spleen, LN)
1/122
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
123 Terms
Define hematopoiesis
Bone marrow production of cells (myeloid and lymphoid) that is based on peripheral need
Young animal bone marrow characteristics
More active red tissue, less fat
Adult animal bone marrow characteristics
More inactive fatty tissue but there are still sites for hematopoiesis. Extra-medullary hematopoiesis occurs in the spleen
Regenerative anemia clincal/pathological findings
Icterus, splenomegaly, hemorrhage
Regenerative anemia bone marrow findings
Erythroid hyperplasia
Non-Regenerative anemia clincal/pathological findings
Myelofibrosis/bone marrow disease, pallor
Non-Regenerative anemia bone marrow findings
Absence of erythroid precursors/cytosis of other lineages
Causes of non-regenerative anemia
-infectious
-toxins
-medications, estrogens
-CKD
-iron deficiency
-neoplasia
What is aplastic anemia?
Decrease in red and white blood cells leading to pallor, thrombocytopenia, neutropenia, and petechiae/echymoses
Infectious causes of aplastic anemia
-Ehrlichia (dogs and cats)
-Parvovirus (dogs and cats)
-FeLV/FIV (cats)
-EIA (horses)
What is a therapeutic cause of aplastic anemia in dogs?
Estrogen administration
Main lesion of myelofibrosis
Bone marrow fibrosis with macrophages with iron pigment
What are the 3 mechanisms for myelofibrosis development?
1. Scar formation after necrosis
2. High concentration of growth factors with bone marrow injury or activation
3. Idiopathic
What are 3 causes of bone marrow necrosis leading to myelofibrosis?
1. Neoplasia (leukemia/metastatic)
2. Infectious (FeLV/sepsis)
3. Toxins
What are the toxins leading to necrosis and myelofibrosis?
-carprofen
-chemo
-estrogen
-metronidazole
-mitotane
-phenobarbital
-heavy metals
-irradiation
Serous atrophy of fat lesion and main cause
Lesion = gelatinous transformation of bone marrow
Cause = starvation/emaciation
Causes of non-neoplastic lymphocytosis in dogs and cats
o Age/antigenic stimulation in cats
o Epinephrine in cats
o Chronic infection
o Ehrlichia canis
o Addison's disease
o Hyperthyroidism in cats
o Paraneoplastic lymphocytosis
o Cattle = Bovine Leukosis Virus (BLV)
Acute leukemia
-Poorly differentiated
-CD34 expression
-Very poor prognosis (9-56 days)
->20% blast cells in marrow or blood
-Pancytopenia (anemia, neutropenia, thrombocytopenia)
-Median age 7-8 years but wide range in dogs
-Necropsy = pale mucous membranes, bone marrow highly cellular but pancytopenia, splenomegaly, lymph node involvement
Chronic leukemia
-CD8 expression (T cell)
-CD21 expression (B cell)
-Often has incidental lymphocytosis
-Necropsy = splenomegaly, anemia, lymphadenopathy, highly cellular bone marrow
Negative prognostic factors in B cell CLL
-Boxers have shorter survival time
-High lymphocyte count >60,000 = shorter survival
-Higher Ki-67 = shorter survival
Explain the benefits of using flow cytometry in cases of lymphocytosis in dogs and cats
o Distinguishes homogenous from heterogenous expansions
o Identifies aberrant antigen expression
o Provides prognostic information
List three clinical abnormalities that can be seen with multiple myeloma
o Hyperglobulinemia (overproduction by neoplastic plasma cells)
o Hypercalcemia (bone osteolysis)
o Pancytopenia (neoplastic plasma cells replace the normal cells)
What abnormality would you except in the bone marrow in a dog with MM?
Markedly increased plasma cells in the bone marrow (>20-30%)
Identify which cell is infected in equine infectious anemia
Macrophages
How does thrombocytopenia and anemia develop in EIA?
Immune mediated hemolysis/destruction of platelets
THYMUS SECTION
List 3 viral diseases in dogs or cats that can affect the thymus
o Parvovirus (causes injury AND necrosis)
o Distemper virus
o FIV
List 3 viral disease in other species that can affect the thymus
-EHV-1
-BVDV
-PCV-2
What is the cause of Post-weaning multi-systemic wasting syndrome?
Porcine Circovirus-2
What inflammation is present with PCV-2?
Granulomatous inflammation with multinucleated cells with cytoplasmic viral inclusions
What pathology is seen with PCV-2?
• Thymic enlargement
• Lymph node enlargement
• Interstitial pneumonia
• Poor body condition
Define the neoplastic cell of a thymoma
Neoplastic epithelial cells
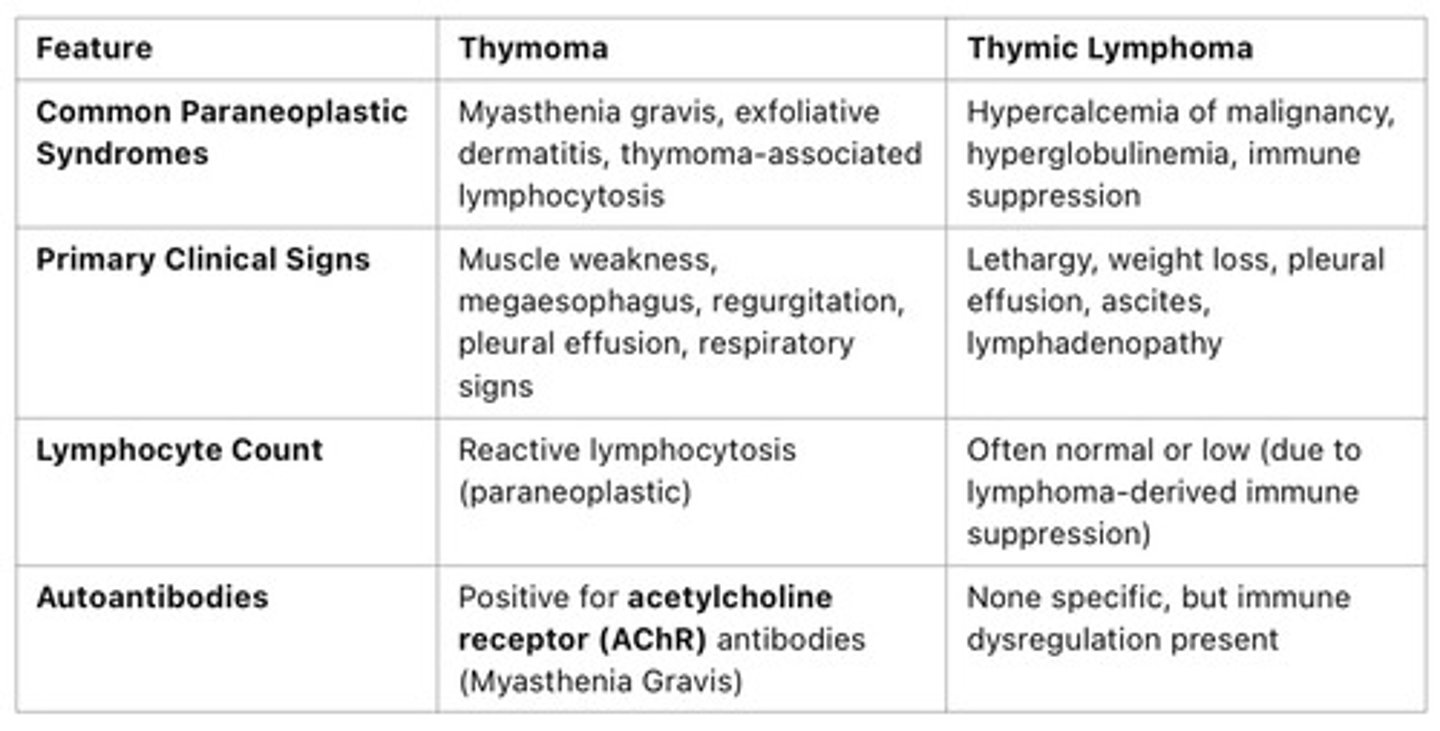
3 paraneoplastic syndromes with a thymoma & pathophysiology
Myasthenia gravis and megaesophagus — defective antigen presentation leading to auto-antibodies against AchRs, neuromuscular dysfunction in esophagus
Thymoma associated lymphocytosis — expansion of non-neoplastic T lymphocytes in response to the tumor. Note that this is different from lymphoma because lymphoma is neoplastic lymphocyte proliferations.
Exfoliative dermatitis — immune mediated attack on epidermal cells
What types of cells can you see in an aspirate of a thymoma?
Double positive T cells (heterogenous population on flow cytometry)
Differentials for a cranial mediastinal mass
o Lymphoma
o Thymoma
o Hemangiosarcoma
o Neuroendocrine tumor
Cattle thymic lymphoma
-less than 2 years old
-NOT associated with BLV
Cats thymic lymphoma
-typically 1-3 years old
-CAN be associated with FeLV/FIV
Dogs thymic lymphoma
-mean age 8 years
-hypercalcemia common
Goats thymic lymphoma
-3 years of age
-mediastinal involvement frequent
Pigs thymic lymphoma
-less then 2 years old
-spontaneous
Thymoma vs. Thymic Lymphoma
SPLEEN SECTION
Recognize gross photos of diffuse enlargement and nodular enlargement of the spleen
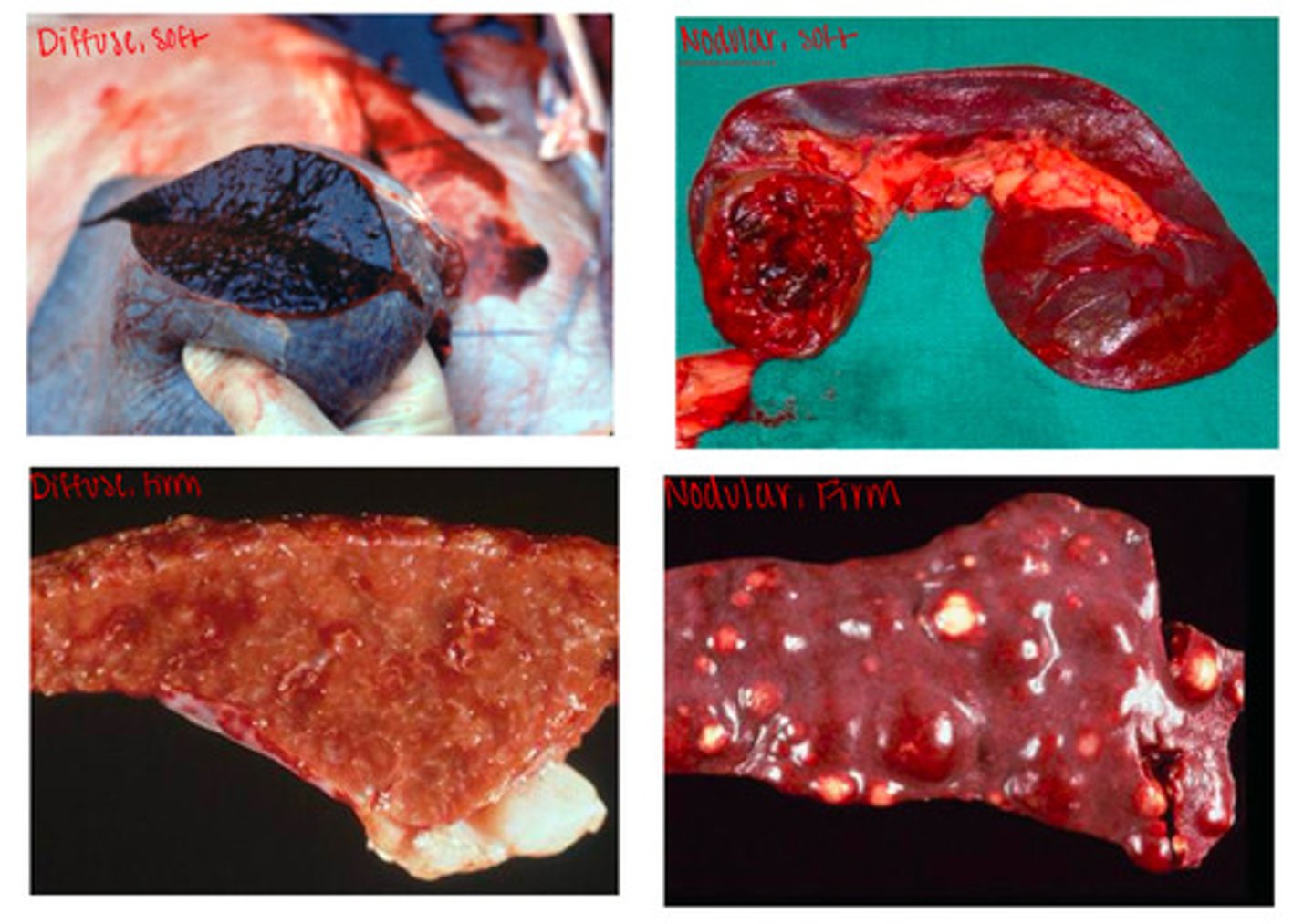
List non-neoplastic causes of diffuse soft enlargement of the spleen
Splenic entrapment/volvulus/torsion
Barbiturate euthanasia/anesthesia/sedation
Acute hyperemia/septicemia (anthrax, salmonella, erysipelothrix)
Acute hemolytic anemia (babesiosis, hemolytic crises in EIA, IMHA)
Why does acute hyperemia/septicemia cause splenomegaly?
this occurs because the number of pathogenic bacteria in circulation exceeds capacity of the splenic macrophages
What is a typical component of soft expansions of the spleen?
Blood
What species are primarily affected by anthrax?
Ruminants (peracute hemorrhage and death)
What is the pathogenesis of anthrax?
1. Ingestion, inhalation, or wound
2. Endospores germinate in macrophages for 1-14 days
3. Spread to lymph nodes and systemic circulation
4. Toxins lead to decreased phagocytosis, increased capillary permeability (edema), and delayed clotting
What can be seen on impression smears of the spleen in anthrax?
Large gram + rods
What should be done to manage an outbreak of anthrax?
-Carcasses, bedding, feces, etc must be cremated or deep burial
-Vaccinate exposed animals to contain and prevent disease
List three differentials for nodular, soft, enlargement of the spleen
1. Hematomas
2. Hemorrhagic infarcts (classical swine fever)
3. Neoplasia (hemangiosarcoma)
Important note about classical swine fever and african swine fever
African swine fever cause diffuse soft splenomegaly but often the lesions are indistinguishable from classical swine fever
Tumor cell type hemangiosarcoma
Endothelial cells
3 breeds commonly affected with hemangiosarcoma
-Golden retrievers
-German shepherds
-Portuguese water dogs
What are the two primary sites of hemangiosarcoma?
1. Spleen
2. Right auricle of heart
Hemangiosarcoma gross changes
single or multifocal to coalescing dark red-purple masses which are variably bloody/cavitated to solidly cellular on cut section
Hematomas gross changes
red to dark red, soft, bulging, usually solitary mass of varying size
Hemorrhagic infarcts gross changes
wedge shaped hemorrhagic lesions (chronic = pale)
List three causes of diffuse firm enlargement of the spleen
1. Diffuse granulomatous disease (histoplasmosis)
2. Neoplasms (round cell tumors)
3. Storage disease/amyloidosis
Important note about lymphoma
Can be diffuse firm OR nodular firm
Important note about storage disease/amyloidosis
RARE AF
List differentials for firm nodules in the spleen
-Lymphoid and complex nodular hyperplasia
-Primary OR metastatic neoplasia
-Granulomas/abscesses
-Extramedullary hematopoiesis
2 bacteria that cause splenic abscesses
1. Rhodococcus equi
2. Trueperella pyogenes
2 bacteria that cause splenic granulomas
1. Tularemia
2. Mycobacteria
Nodular firm neoplasia
Primary = lymphoma, histiocytic sarcoma, splenic stromal sarcomas, solid hemangiosarcomas, myelolipomas
Metastatic = sarcomas, carcinomas, malignant round cell tumors
Cell of origin histiocytic sarcoma
Monocytic/histiocytic origin (dendritic cells and macrophages)
Important note about histiocytic sarcoma pattern
Can be diffuse firm and nodular firm
What are common tissues affected by histiocytic sarcoma?
Spleen, lung, liver, skin, articular surface of joints, bone marrow
What are common breeds affected by histiocytic sarcoma?
-Bernese mountain dogs
-Flat-coated retrievers
-Golden retrievers
LN/LYMPHATICS SECTION
Recognize normal architecture and pattern of LNs
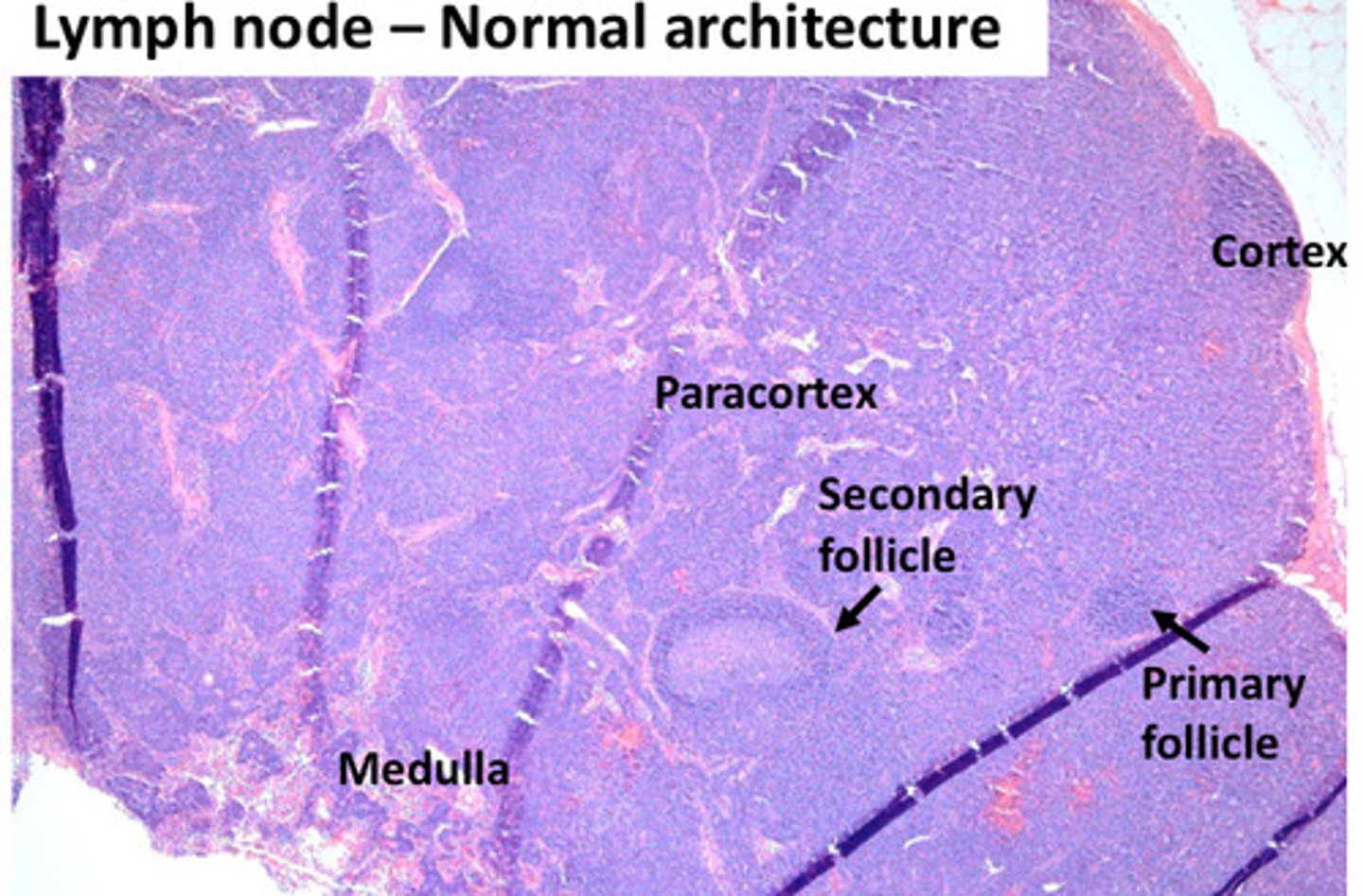
Where do T cells live in the LN?
Paracortex
Where do histiocytes and macrophages live in the LN?
Medulla
Where do B cells live in the LN?
Cortex
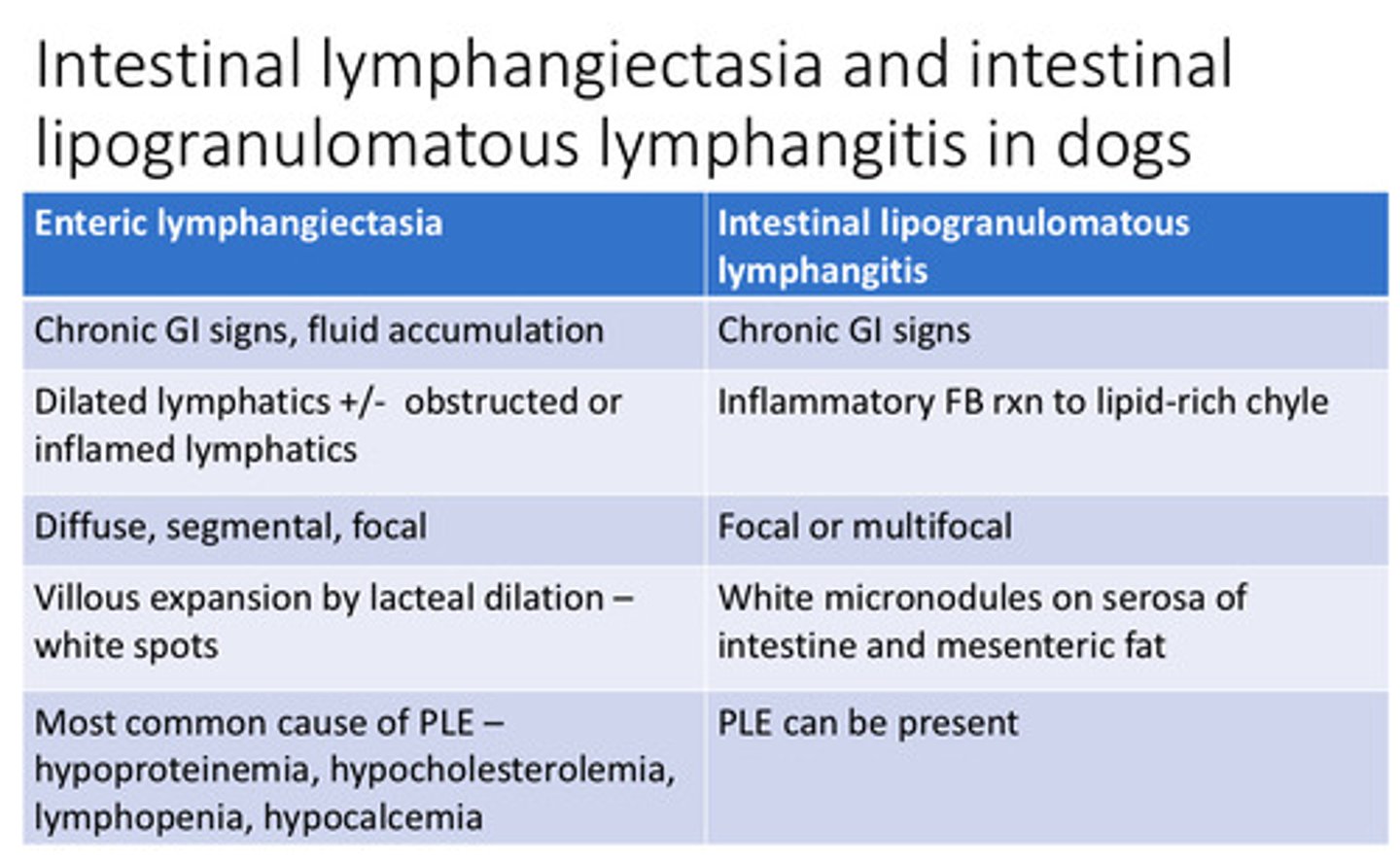
Enteric lymphangiectasia/itis in the dog gross findings
Will see the lymphatics and pinpoint dots inside of the mucosa
Enteric lymphangiectasia/itis in the dog clinical findings
chronic diarrhea, wasting, hypoproteinemia, lymphopenia, hypocalcemia, hypocholesterolemia
Enteric lymphangiectasia/itis in the dog histo
Dilated lymphatics
What is the cause/pathogenesis of serosal lesions?
Intestinal lipogranulomatous lymphangitis = accumulations of granulomatous inflammation forming white masses
Enteric lymphangiectasia VS intestinal lipogranulomatous lymphangitis
4 causes of chylothorax
o Idiopathic
o Trauma
o CHF
o Chest tumors
Clin path finding of chylothorax
lymphopenia due to loss of lymphocytes in fluid
Causes of lymph node atrophy
-Primary immunodeficiency disease
-Lack of antigenic stimulation
-Viral infections
-Cachexia & malnutrition
-Aging
-Radiation
Viruses that can injure lymphoid tissue
-Parvovirus
-FIV
-BVDV
-Distemper
-Ehrlichia
Name common species to be affected by Yersinia pestis
Squirrels, prairie dogs, rabbits, wood rats
How is plague spread?
Bite by infected flea or consumption of infected animal
Gross findings of plague in cats
Fever, loss of appetite, lethargy, enlarged LNs
Name three other bacterial causes of lymphadenitis/adenomegaly
-Mycobacterium avium ssp paratuberculosis
-Rhodococcus equi
-Streptococcus equi ssp equi
Name a fungal cause of lymphadenitis/adenomegaly
Histoplasmosis
Name two causes of bacterial lymphadenitis in horses
-Streptococcus equi ssp equi (Strangles)
-Rhodococcus equi
Streptococcus equi ssp equi
-Term for systemic spread = bastard strangles
-Purpura hemorrhagica (type III) from repeated exposure
Rhodococcus equi
-Foals up to 6 months old causing bronchopneuonia
-50% develop progranulomatous ulcerative enterotyphlocolitis of Peyer's patches
-Pyogranulomatous inflammation with phagocytized bacteria
3 bacterial causes of bacterial lymphadenitis in cattle or sheep
1. Johne's Disease
2. Bovine Tuberculosis
3. Caseous Lymphadenitis
Johne's disease cause
mycobacterium avium paratuberculosis
Johne's disease gross findings
Enteritis and granulomatous lymphadenitis
Johne's disease stain
Acid fast within macrophages
Bovine tuberculosis cause
Mycobacterium bovis
Bovine tuberculosis gross findings
Necrotic and suppurative/abscessed lymph nodes
Bovine tuberculosis human infection
Raw milk
Caseous lymphadenitis cause
gram + intracellular bacterium corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis
Caseous lymphadenitis transmission
enters through skin wounds —> drain to regional LN —> disseminate in lymph and blood