AST201 Week 1
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/35
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
1
New cards
solar system
our solar system is made up of the sun, planets, and their moons, rockey asteriods and icy comets
2
New cards
galaxy clusters
groups of galaxies with many more large members
3
New cards
astronomical unit (AU)
earths average distance from the sun
4
New cards
light year (LY)
the distance that light can travel in 1 year, about 10 trillion km
5
New cards
age of the universe
14 billion years
6
New cards
big bang
where the expansion of the universe began, most galaxies including our own milky way formed within a few billion years after
7
New cards
star birth
when gravity compresses the material in a cloud to the point at which the centre becomes dense enough and hot enough to generate energy by nuclear fusion
8
New cards
star life cycle
it ‘lives’ as long as it can shine with energy from fusion, and ‘dies’ when it exhausts its useable fuel
9
New cards
supernova
when a massive star dies, it throws it energy back out into space
10
New cards
chemical elements in early universe
hydrogen and helium (trace of lithium)
11
New cards
earths orbit speed
average speed of 100,000 km/hr
12
New cards
axis tilt
almost directly at the North Star
13
New cards
constellation speed
incredibly slow speed, but over time will be unrecognizable and they previously have been shaped differently as well
14
New cards
dark matter
matter which is completely invisible to our telescopes
15
New cards
dark energy
the expansion of the universe is getting faster with time, this means there is some invisible energy that is a lot of the unvierse
16
New cards
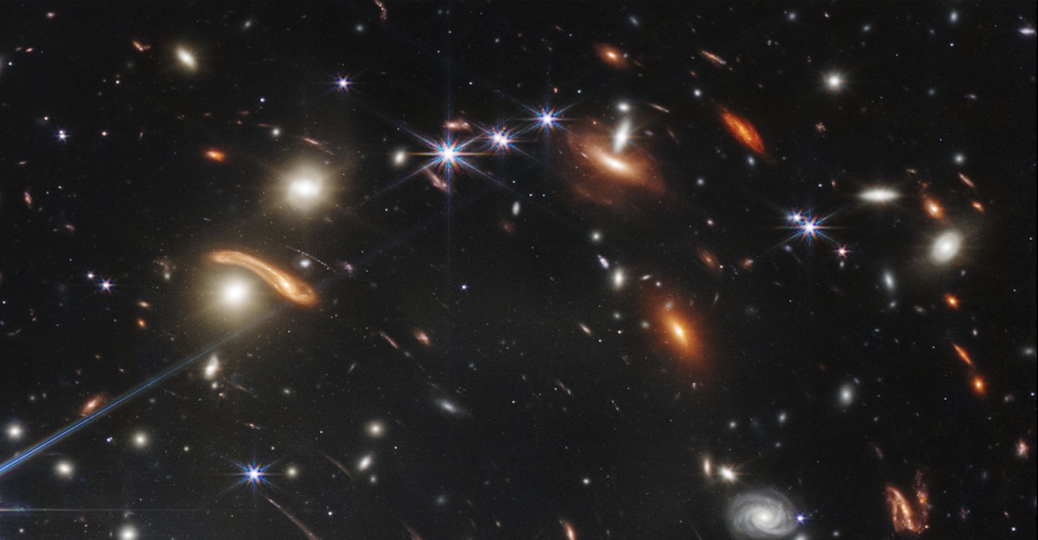

galaxies
all smudges are galaxies
17
New cards
looking out is looking back
when you look up at the sky you are looking back in time
18
New cards
contents of the universe (1920s)
most (99.9%) is stars, galaxies, planets, gas, dust, etc
19
New cards
fritz zwicky (1898 - 1974)
started looking at clusters of galaxies, idea of “missing mass”
20
New cards
vera rubin (1928 - 2016)
measure how fast a galaxy spins
21
New cards
milky way galaxy spin
takes 100 million years to rotate once
22
New cards
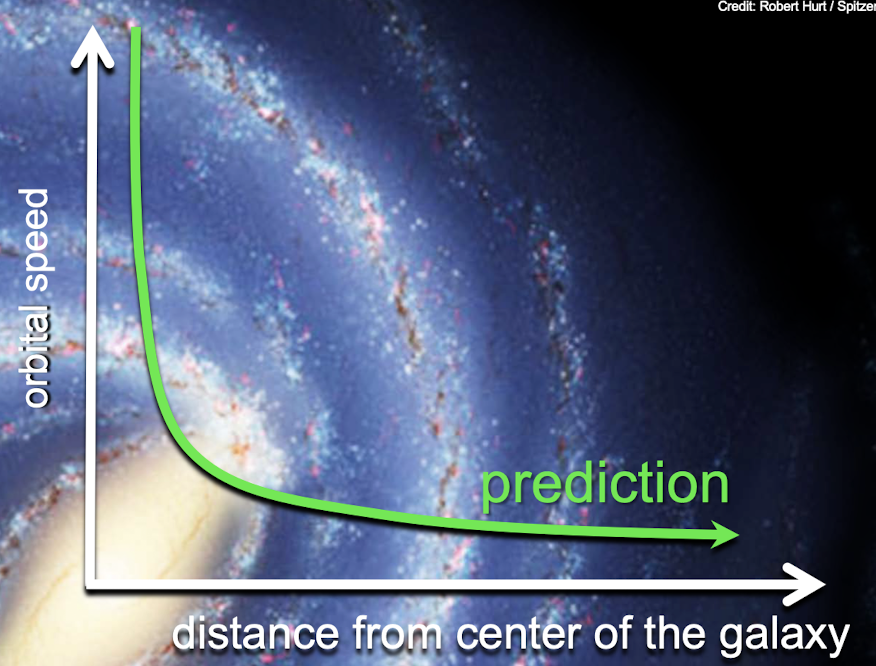
original observation of galaxy rotation speed
the further from the center of the galaxy, the slower the orbital speed
23
New cards
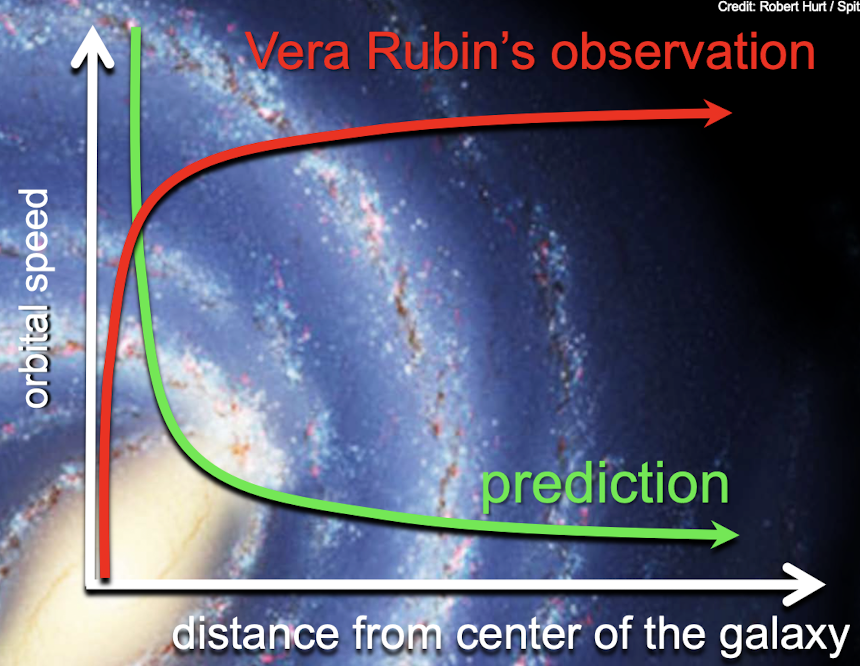
vera rubin’s observation of galaxy rotation speed
the further from the center of the galaxy, the faster the orbital speed, mass is concentrated on the outside and is invisible
24
New cards
contents of the universe (1980s - 1990s)
most (95%) is invisible dark matter, little (5%) is stars, galaxies, planets, gas, dust etc
25
New cards
contents of the universe (2023)
normal matter = 4.9%, dark matter = 26.6%, dark energy = 68.5%
26
New cards
relativity
we can only measure motion RELATIVE to a given frame of reference
27
New cards
speed of light
use the constant c, 300,000 km/s
28
New cards
light around the earth
7\.5 times per second
29
New cards
speed of light rules
light always travels at c, no object w/ mass can ever reach or exceed light speed
30
New cards
speed of light in experiment
no matter how the experiment is done, all observers measure the same speed of light, the speed of light is the same in all frames of reference
31
New cards
speed of the bowling ball
is different in different “frames of reference”
32
New cards
invariant
unchanging, the speed of light
33
New cards
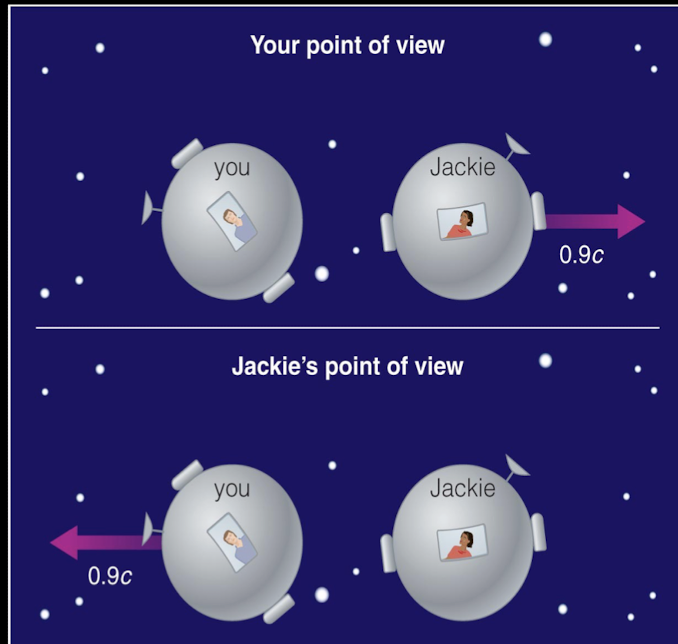
different frames of reference
povs are different so they see time and lengths differently
34
New cards
foundations of special relativity
1. we can only measure speeds of objects relative to one another
2. the speed of light is invariant
35
New cards
time dilation
if someone is moving relative to you, their clock will appear to run slower to you
36
New cards
length contraction
if someone is moving relative to you, their lengths will all appear shorter to you