Medicinal Chemistry of ADHD Treatments
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
What class do amphetamines belong to?
Phenethylamines
How do amphetamines increase neurotransmitter levels?
Inhibit reuptake, inhibit MAO, increase release, reverse reuptake
What is the SAR order for N-substitution in amphetamines?
N–CH₃ > NH₂ > NHR > NR₂.
Which amphetamine enantiomer is more active?
S(+) (dextro) over R(–) (levo).
What does the "3:1 ratio" in Adderall refer to?
3 parts S(+)/dextro to 1 part R(–)/levo.
What are the key metabolism points for amphetamines?
t½ ~7 h; ~23% excreted unchanged, ~18% as p‑hydroxy.
(Blank card for amphetamine image)
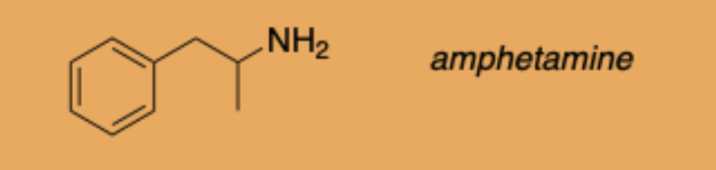
Name an amphetamine prodrug used in ADHD.
Lisdexamfetamine (Vyvanase).
What is methylphenidate chemically?
Methyl ester of phenidate.
Which stereoisomers of methylphenidate are active in ADHD?
Threo isomers; (+)-threo (Ritalin).
How does Focalin differ from Ritalin?
Focalin is pure (+)-TMP, ~10× more potent.
How is methylphenidate metabolized?
Hepatic conversion to inactive ritalinic acids
What is the MOA of atomoxetine?
Selective NET inhibition
What is atomoxetine’s brand name?
Strattera
What is the role of bupropion in ADHD treatment?
Modest NDRI (inhibits NE & DA reuptake)
How do certain blood pressure meds work for ADHD?
Centrally acting; stimulate α₂ receptors and nonadrenergic receptors.
How do stimulants differ from non-stimulants in ADHD?
Stimulants directly raise NE & DA; non-stimulants modulate NE
What are the metabolism details for atomoxetine?
t½ 3–6 h (17–21 h in poor metabolizers); via CYP2D6
SAR
S(+) > R(-)