Le Chatelier's Principle
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
8 Terms
A system will remain at equilibrium as long as…
rate of forward and reverse reaction are equal
A system will no longer be at equilibrium if a change in what? How does it affect the reaction?
reaction conditions or stress
unequally affects the rates of the reactions
What is Le Chatelier’s Principle?
if a dynamic
equilibrium is disturbed by a change in the reaction conditions, the balance between the forward and reverse processes will shift to counteract the change and return the system to equilibrium
What are the stresses which can be applied to systems?
Change in Concentration
Change in Temp.
Change in Pressure
Addition of a Catalyst
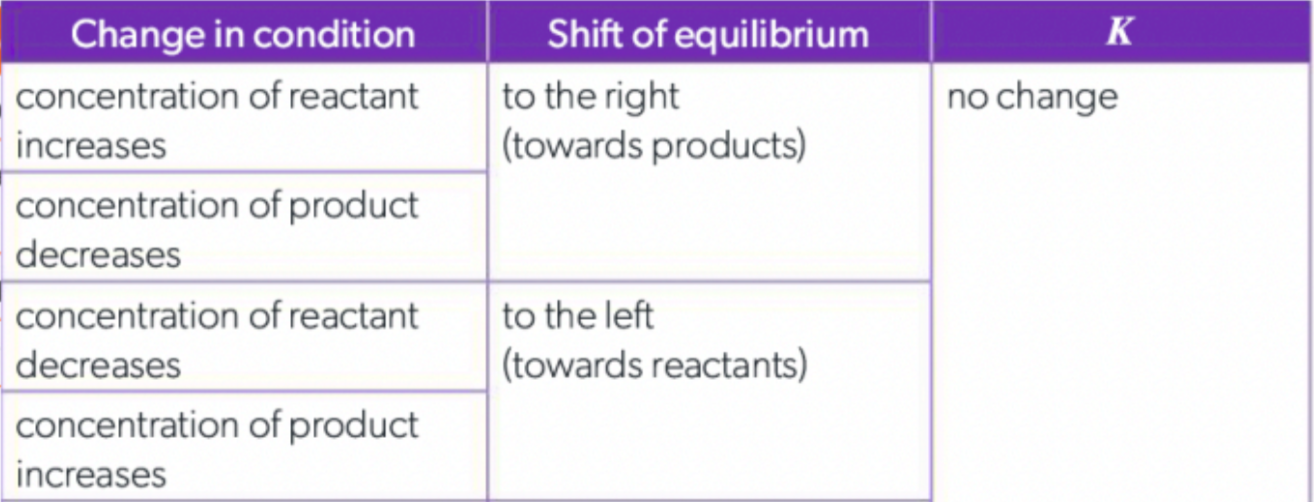
How does changing Concentration affect reactions?
when you add a reactant/product, the system will shift the opposite way
if you increase concentration of reactants, the system will increase the forward reaction (R → P) to create more products to return to equilibrium
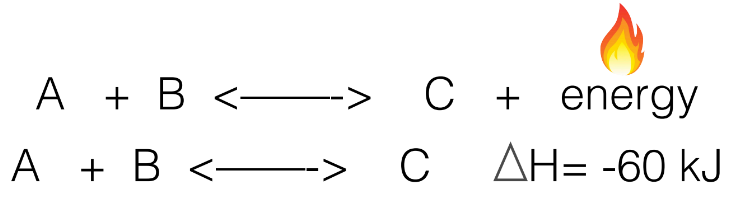
How does changing Temperature affect reactions?
does affect K
Think of it as: the energy needs to stay the same so:
if the product is exothermic (R → P +energy), if you increase temp., it will increase the reverse reaction to use up that energy
How does changing Pressure affect reactions?
remember that in gaseous form, molecules want to be as far away from each other as possible
If you increase pressure/decrease volume, the reaction will shift to the side with less moles
If you decrease pressure/increase volume, the reaction will shift to the side with more moles (to fill up the space)
How does adding a catalyst affect reactions?
forward and reverse reactions pass through the same transition state
due to catalysts, both are lowered in Ea equally
no position change in equilibrium
no change in K
speeds up time to reach equilibrium
used in industrial processes