Exam 2 Basic Procedures
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/97
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
98 Terms
1
New cards
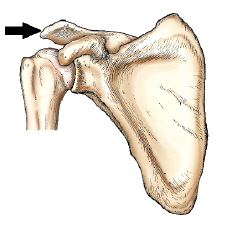
What is the arrow pointing to
acromion
2
New cards
The area of the proximal humerus located directly below the tubercles, which is the site of many fractures, is called the:
surgical neck
3
New cards
Which of the following methods is used to demonstrate the carpal canal?
Gaynor-Hart (tangential)
4
New cards
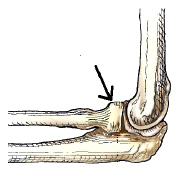
What anatomy is indicated by the arrow in this figure?
Radial head
5
New cards
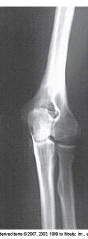
What projection and position is depicted in the image below?
AP oblique, lateral rotation position
6
New cards
In an image of an AP axial projection of the clavicle, the clavicle should be demonstrated with:
1. most of the clavicle projected above the ribs.
2. only the lateral end superimposing the coracoid process.
3. only the medial end superimposing the first or second ribs
1. most of the clavicle projected above the ribs.
2. only the lateral end superimposing the coracoid process.
3. only the medial end superimposing the first or second ribs
1 and 3 only
7
New cards
Which of the following methods best demonstrates the supraspinatus outlet (coracoacromial arch)?
Neer
8
New cards
The first bone located on the proximal row and lateral side of the wrist is called the:
Scaphoid
9
New cards
The respiration phase for an AP projection of the shoulder should be:
Suspended
10
New cards
The hand consists of how many bones?
27
11
New cards
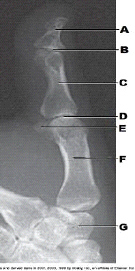
Which bone is labeled as letter A in the figure above?
Distal phalanx
12
New cards
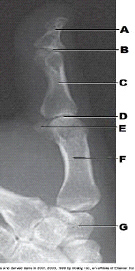
What is labeled as letter B in the figure above?
IP joint
13
New cards
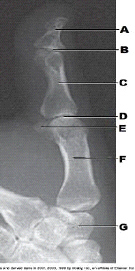
What is labeled as letter C in the figure above?
Proximal phalanx
14
New cards
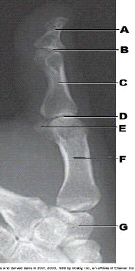
What is labeled as letter D in the figure above?
MCP joint
15
New cards
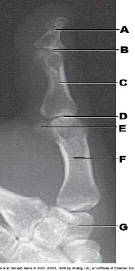
What is labeled as letter F in the figure above?
1st metacarpal
16
New cards
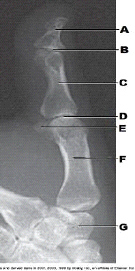
What is labeled as letter G in the figure above?
Trapezium
17
New cards
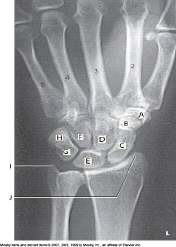
Which bone is labeled as letter A in the figure above?
Trapezium
18
New cards
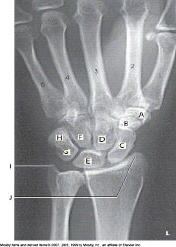
Which bone is labeled as letter B in the figure above?
Trapezoid
19
New cards
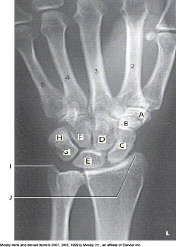
Which bone is labeled as letter C in the figure above?
Scaphoid
20
New cards
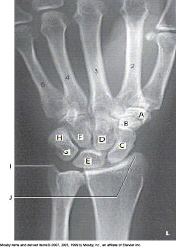
Which bone is labeled as letter D in the figure above?
Capitate
21
New cards
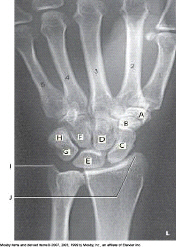
Which bone is labeled as letter E in the figure above?
Lunate
22
New cards
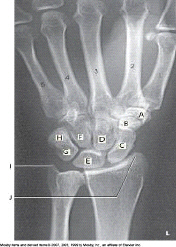
Which bone is labeled as letter F in the figure above?
Hamate
23
New cards
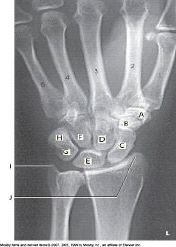
Which bone is labeled as letter G in the figure above?
Triquetrum
24
New cards
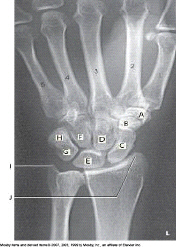
Which bone is labeled as letter H in the figure above?
Pisiform
25
New cards
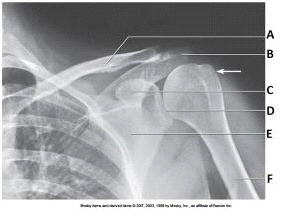
The projection in the image below was obtained with the arm positioned in:
External rotation
26
New cards
The thumb is also known as the:
First digit
27
New cards
How many phalanges are there in the hand?
14
28
New cards
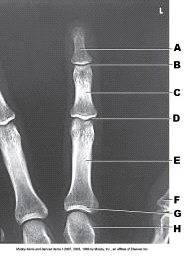
What projection of the third digit is demonstrated in the image?
PA
29
New cards
If the patient places the palm of the hand against the thigh, the humerus will be in:
Neutral position
30
New cards
The acromial extremity of the clavicle articulates with the:
Acromion process of the scapula.
31
New cards
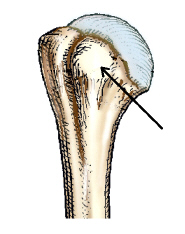
The small, rounded, elevated process identified by the arrow in this figure is the:
Lesser tubercle
32
New cards
If the patient cannot elevate the unaffected shoulder for a transthoracic lateral projection (Lawrence) of the shoulder, what central ray orientation is needed?
10 to 15 degrees cephalad
33
New cards
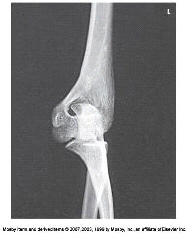
What projection and position is demonstrated in the image?
AP oblique, medial rotation
34
New cards
For the AP projection of the forearm, the hand is:
Supinated
35
New cards
The scapula is classified as a(n) _____ bone.
Flat
36
New cards
The lesser tubercle is situated on which surface of the humerus?
Anterior
37
New cards
PA oblique projection of the shoulder (scapular Y) is performed to evaluate:
Dislocations
38
New cards

The part identified on the clavicle in this figure is the:
Acromial extremity
39
New cards
The small, synovial fluid–filled sacs, which relieve pressure and reduce friction in joint tissues, are called:
Bursae
40
New cards
The PA projection of the wrist in ulnar deviation clearly demonstrates the:
Scaphoid
41
New cards
The clavicle is classified as a(n) _____ bone.
Long
42
New cards
To elevate the clavicle above the ribs and scapula for the AP axial projection, the phase of respiration should be:
Full inspiration
43
New cards
For a PA oblique projection of the first digit (thumb), the hand is positioned in:
Pronation
44
New cards
Which of the following passes through the carpal canal?
Radial vein
Radial nerve
Median vein
Median nerve
Radial vein
Radial nerve
Median vein
Median nerve
Median nerve
45
New cards
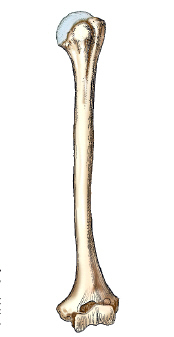
What bone is shown in this figure?
Humerus
46
New cards
The central ray for a PA projection of the wrist is directed to enter the:
Midcarpal area
47
New cards
What is the largest carpal bone
Capitate
48
New cards
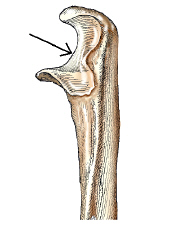
The area on the bone labeled with the arrow is this figure is the:
Trochlear notch
49
New cards
What is an impacted fracture of posterolateral aspect of the humeral head with dislocation
Hill-Sachs defect
50
New cards
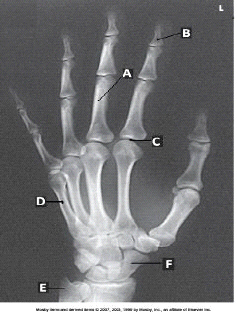
Letter B in the figure above labels the _____ phalanx of the _____ digit.
distal; second
51
New cards
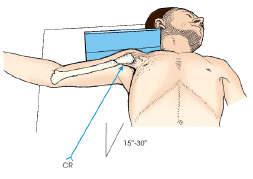
The projection of the shoulder demonstrated in this figure is the:
Inferosuperior axial (Lawrence).
52
New cards
Patients often arrive in the radiology department with trauma to the shoulder. Which of the following positions is recommended for x-ray examination of the shoulder on these patients?
Upright
53
New cards
The carpal bones articulate with the:
Radius
54
New cards
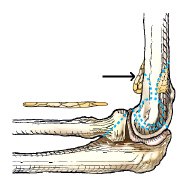
Which fat pad is identified by the arrow in this figure?
Anterior
55
New cards
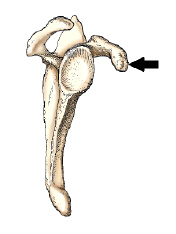
The bone part identified by the arrow in this figure is the:
Coracoid Process
56
New cards
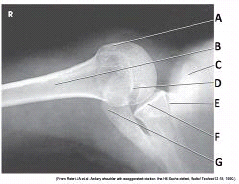
What projection (method) is demonstrated in the image?
Inferosuperior axial (Lawrence)
57
New cards
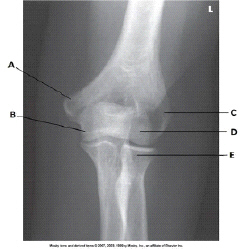
What anatomy is labeled as letter A in the image below?
Medial epicondyle
58
New cards
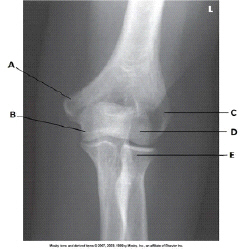
What anatomy is labeled as letter C in the image below?
Lateral epicondyle
59
New cards
The third metacarpal of the hand articulates with the:
Capitate
60
New cards
The palm of the hand is formed by:
5 metacarpals
61
New cards
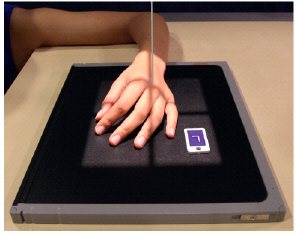
What anatomy is not well demonstrated when the PA oblique hand is performed as show in this photograph?
Distal phalanges and IP joints
62
New cards
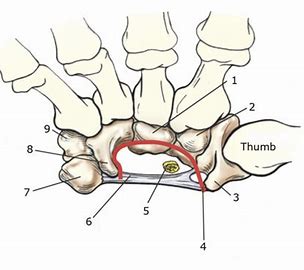
What is number 4
Carpal sulcus
63
New cards
Where do you center for images of the second through fifth digits?
PIP joint
64
New cards
Where do you center for images of the thumb
MCP joint
65
New cards
Where do you center for PA and oblique projections of the hand
3rd MCP joint
66
New cards
Where do you center for lateral projections of the hand
2nd MCP joint
67
New cards
How many degrees should the IR be angled for the Stecher method
20
68
New cards
What is the Stecher method used to demonstrate
Scaphoid
69
New cards
What is the central ray angulation for the Gaynor-Hart method?
25-30 degrees
70
New cards
The heads of metacarpals articulate with the:
Phalanges
71
New cards
What kind of bone are metacarpals classified as?
Long
72
New cards
The bases of the metacarpals articulate with the:
Carpals
73
New cards
What type of bone are carpals classified as?
Short
74
New cards
What is the most commonly fractured carpal bone?
Scaphoid
75
New cards
What is a sign of a scaphoid fracture?
Tenderness in the anatomical snuff box
76
New cards
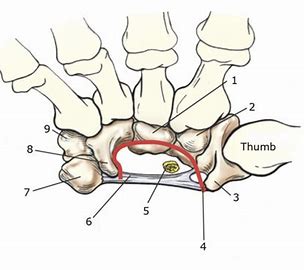
What is number 6?
Flexor retinaculum
77
New cards
What type of joint are the MCP joints?
Ellipsoidal
78
New cards
What type of joint are the 2nd-5th CMC joints?
Gliding
79
New cards
What type of joint is the 1st CMC joint?
Saddle
80
New cards
What type of joints are the IP joints?
Hinge
81
New cards
What type of joints are intercarpal joints?
Gliding
82
New cards
What type of joint is the radiocarpal joint?
Ellipsoidal
83
New cards
Which portion of the humerus articulates with the
radial head?
radial head?
Capitulum
84
New cards
Fracture at the base of the first
metacarpal
metacarpal
Bennett's fracture
85
New cards
Fracture of distal radius with
anterior (palmar) displacement
anterior (palmar) displacement
Smith fracture
86
New cards
Where is the radial tuberosity facing on a lateral forearm image?
Anteriorly
87
New cards
What should be seen clearly in an AP oblique elbow with medial rotation?
Coronoid process
88
New cards
What should be seen clearly in an AP oblique elbow with lateral rotation?
Radial head
89
New cards
How many degrees is the CR angled for the Coyle method
45
90
New cards
What is the Coyle method used to visualize?
Radial head and coronoid process
91
New cards
What is the projection for an image of the 2nd or 3rd digits?
Mediolateral
92
New cards
What is the projection for an image of the 4th or 5th digits
Lateromedial
93
New cards
Where is the CR centered for the Stecher method?
Scaphoid
94
New cards
Which carpal bone is in profile and free of superimposition in the Gaynor-Hart method?
Pisiform
95
New cards
Soft tissue radiographs of the elbow in the lateral position are often ordered to demonstrate:
Fat pads
96
New cards
The most common oblique projection of the second through fifth digits is _____ with _____ rotation.
PA; lateral
97
New cards
For a PA oblique projection of the first digit (thumb), the hand is positioned in:
Pronation
98
New cards
Flexing the fingers for a PA wrist image does what to the carpal bones?
Brings them closer to the IR