Comprehensive Review of Period 1 Content: Regions, Cultures, and Political Changes
1/112
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
113 Terms
What should you do with your phone during class?
Put it in the locker with the same number as your desk.
What is the homework for the next class?
Take the SBMCQ portion of the Period 1 Test on the Post-Classical Era.
When is the SAQ portion of the Period 1 Test scheduled?
On 9/15.
What is the significance of the feudal system in the Post-Classical Era?
It established distinct classes and provided political stability at the local level.
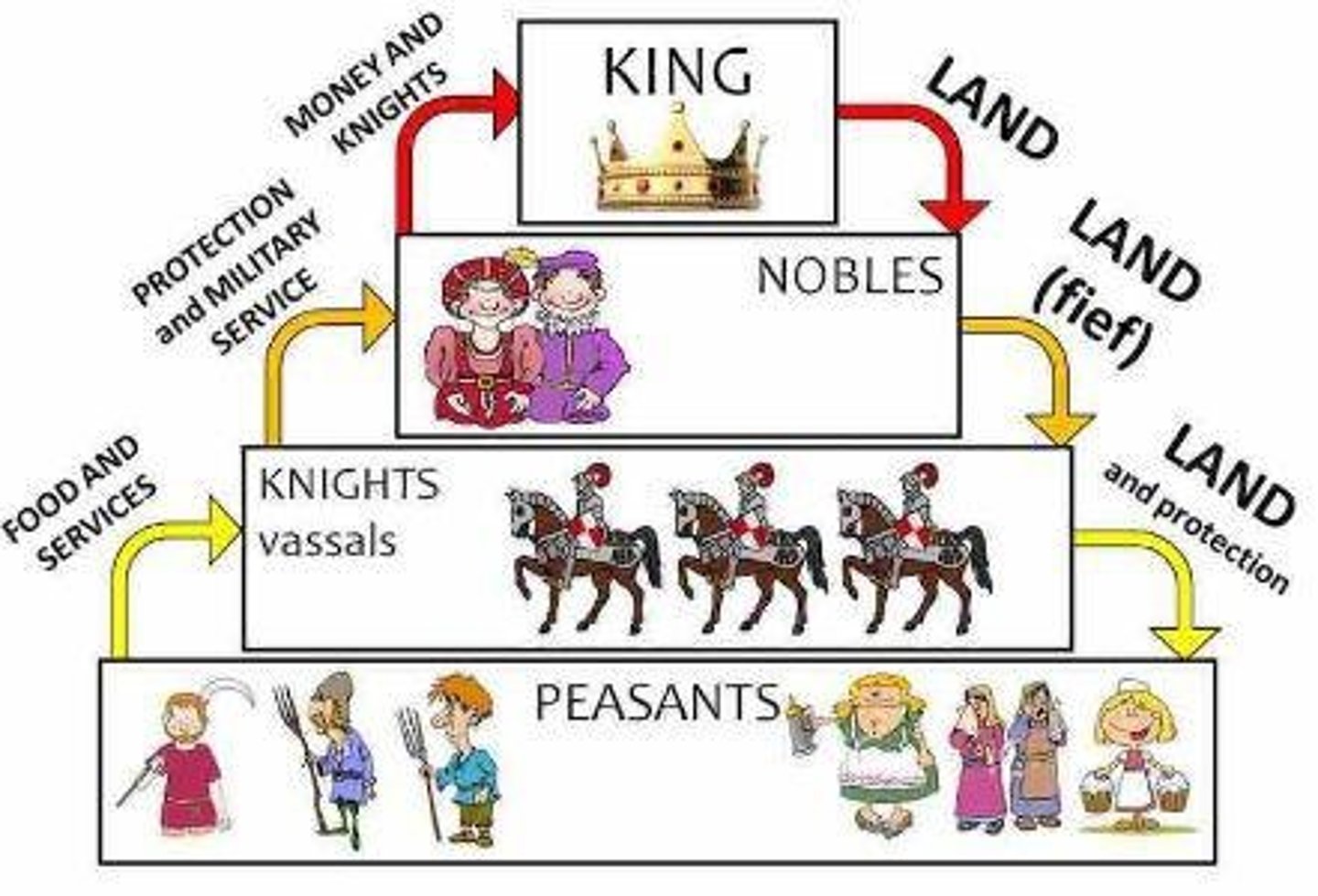
How did the decline of Western Rome affect governance?
It led to regionalism, the rise of feudal kingdoms, and eventually nation-states.
What role did the Catholic Church play during the Post-Classical Era?
It held significant political power and influenced monarchs.
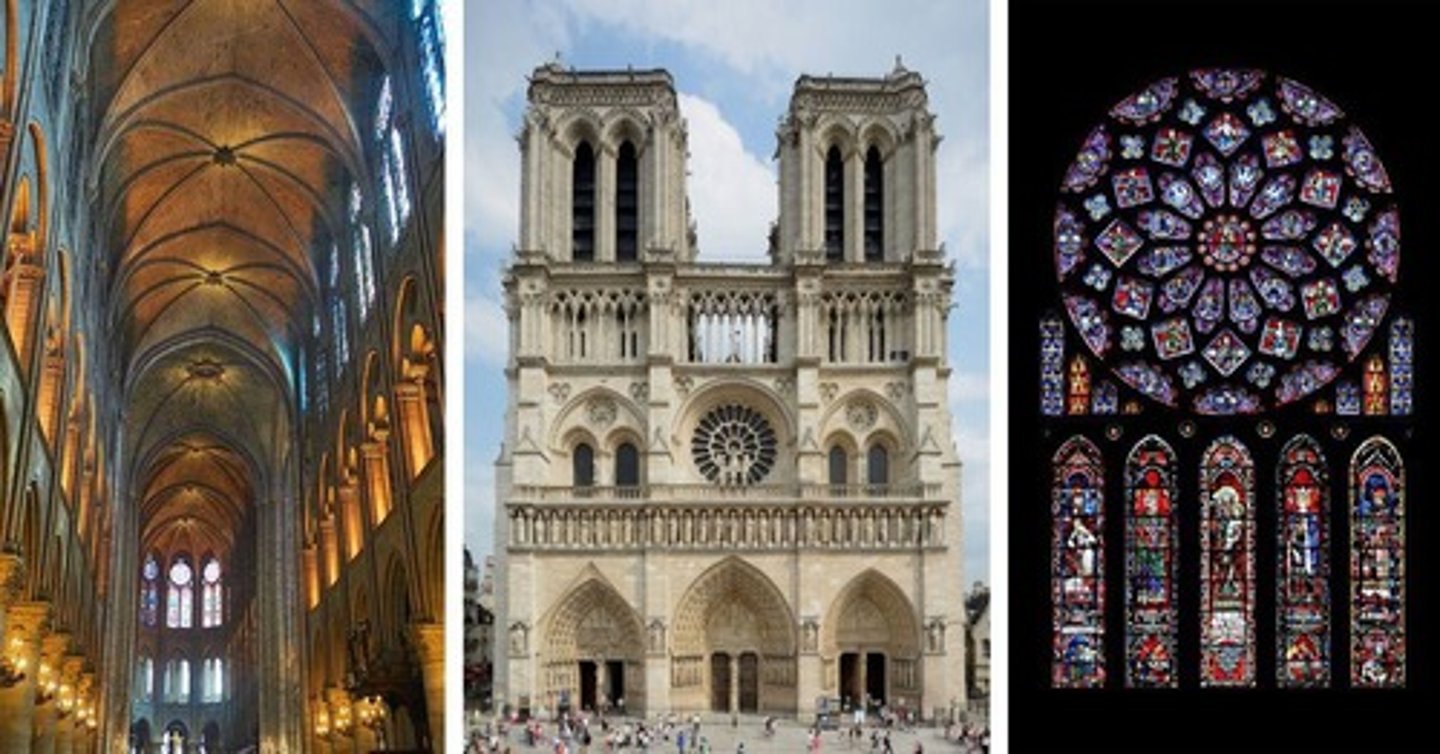

What was the Code of Chivalry?
An ideal that emphasized the need to 'save' women, reflecting patriarchal values.
How did the Black Death impact the power of the Catholic Church?
The Church's power weakened as monarchies became more loyal to kings rather than the Church.
What characterized early Post-Classical interactions?
They were very isolated and focused on self-sufficiency.
What changes occurred in trade during the later Post-Classical Era?
There was increased involvement in trade and conflicts, such as the Crusades.
What was the dominant religion during the Post-Classical Era?
Catholicism.
What technological advancements influenced culture in the Post-Classical Era?
The printing press and reintroduction of Greco-Roman ideas.
What was the status of the Kievan Rus during the Post-Classical Era?
It was characterized by independent cities without a single ruler.
What was the Byzantine Empire's relationship with the Kievan Rus?
The Kievan Rus was influenced by the Byzantine Empire and traded with it.
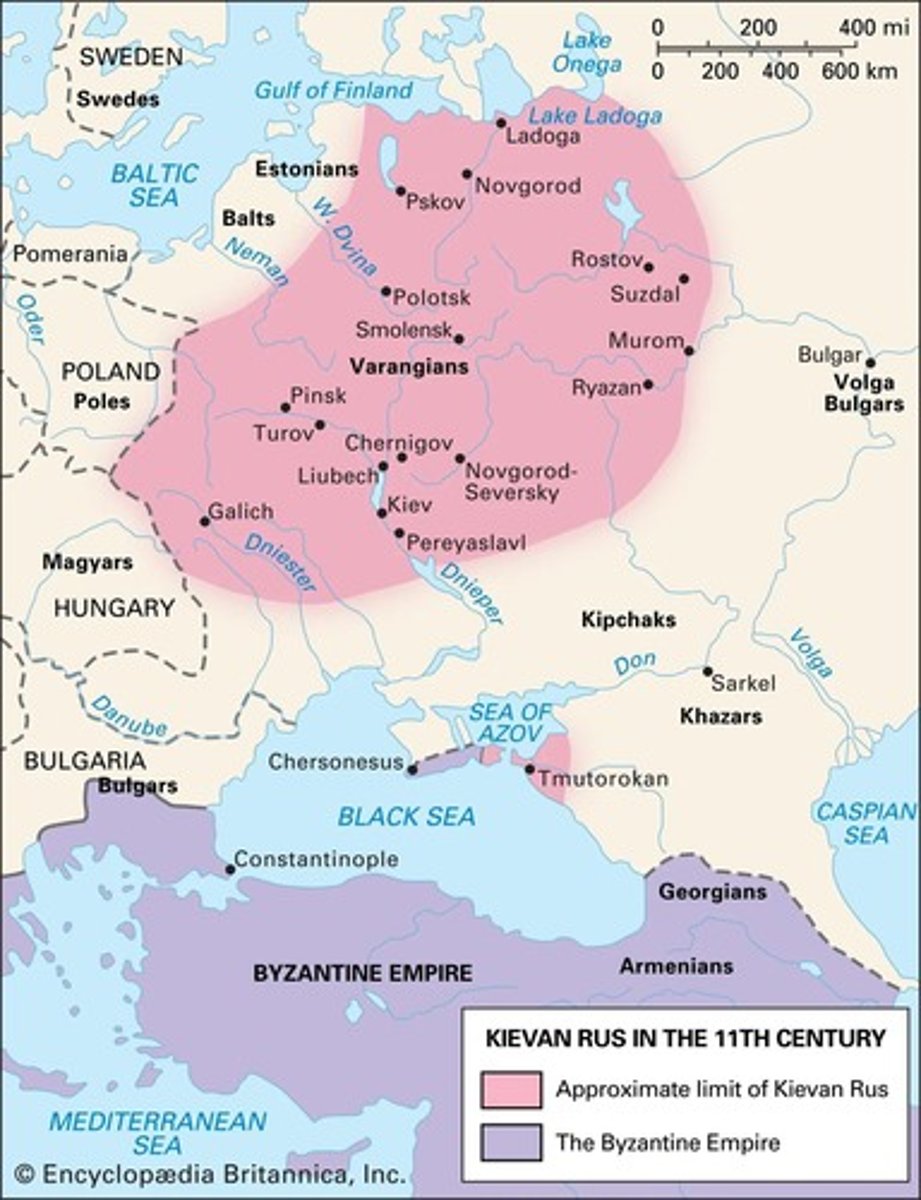
Who was a major ruler of the Byzantine Empire?
Justinian.
What is 'Caesaropapism'?
A political system where the head of state is also the head of the church.
What architectural example is associated with the Byzantine Empire?
The Hagia Sophia.
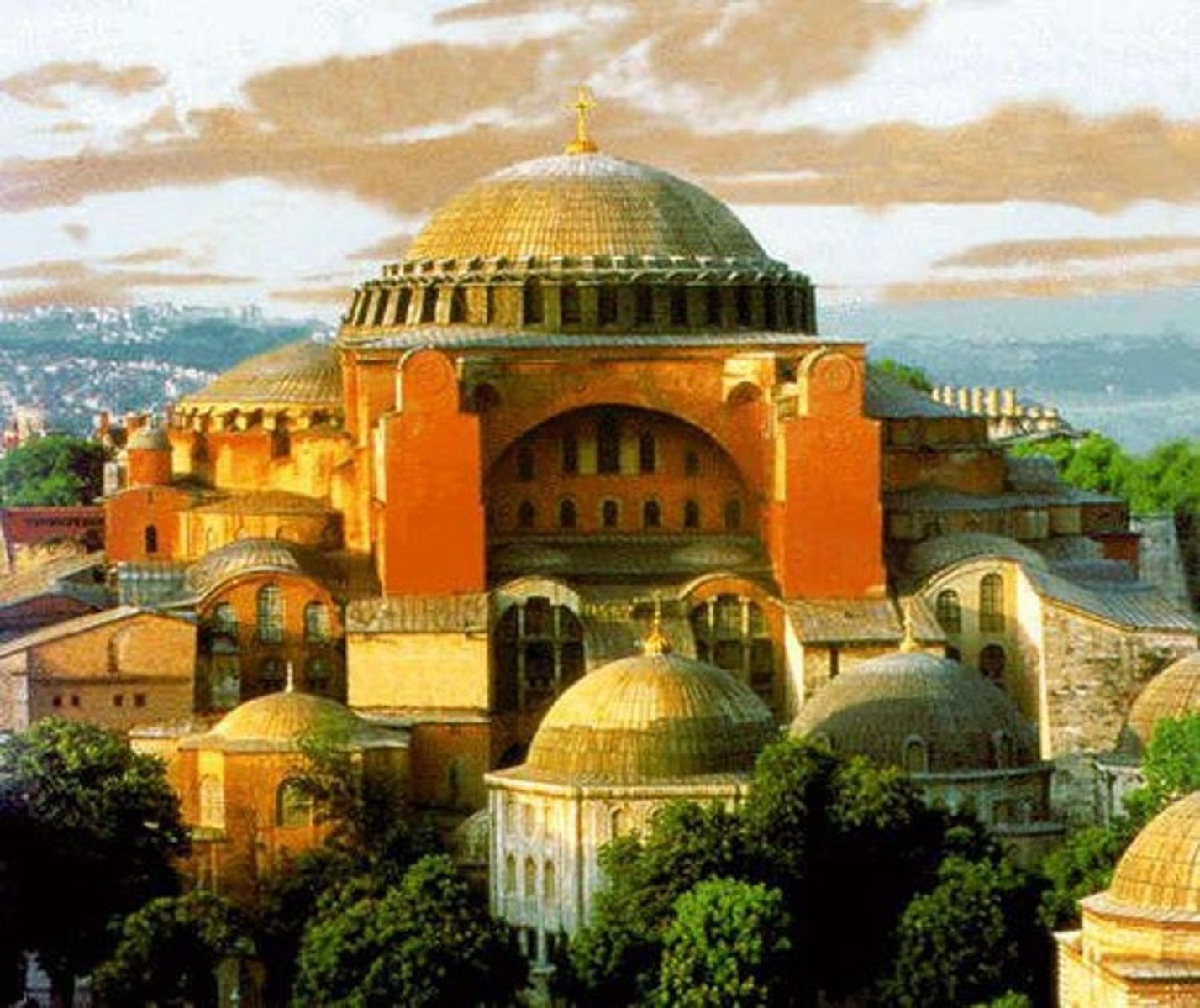

What was the political structure of the Byzantine Empire?
It had no feudal system and utilized a theme system for land ownership.
What happened to the Byzantine Empire in 1453 CE?
It was taken over by the Ottomans.
How did social structures change over time in the Post-Classical Era?
They evolved from clan-based systems to more formal hierarchies as centralized kingdoms developed.
What was the impact of the Crusades on culture?
They led to a 'culture clash' with Western Europe influencing the Middle East more than vice versa.
What agricultural advancements were made during the Post-Classical Era?
New plows and crop rotation techniques were introduced.
What was the significance of trade routes like the Hanseatic League?
They helped develop European trade networks during the Post-Classical Era.
What social structure characterized early African societies?
Clan-based systems where kin was the core unit, evolving into more formal hierarchies with the development of centralized kingdoms.
What major social trend occurred in Africa as kingdoms grew?
An increase in the enslaved population due to conquest.
How does the patriarchal structure in Africa compare to other regions?
Africa was less patriarchal than other regions, even with more formal social divides.
What was the primary economic activity in West and East Africa during the period?
Most people engaged in agriculture, but trade increased, especially through Trans-Saharan routes in West Africa and Indian Ocean routes in East Africa.
What geographical obstacle affected trade in Sub-Saharan Africa?
The Sahara Desert, which required camels and saddles to traverse.
What natural resources contributed to trade in Africa?
Gold and salt were significant natural resources that brought wealth through trade.
What role did monsoons play in East Africa's economy?
Monsoons influenced agricultural practices and trade in East Africa.
How did conquest affect social structures in Africa?
Conquest led to the establishment of centralized kingdoms and increased enslavement.
What was the influence of Islam on culture in East and West Africa?
Islam influenced trade and led to some syncretism with indigenous beliefs.
What is an example of cultural syncretism in East Africa?
The Swahili language, which developed along the East African coastline.
What political systems were present in the Inca Empire?
The Inca had a theocratic and bureaucratic system to manage their empire.
What was the Mit'a system in the Inca Empire?
A reciprocal labor system where land was owned by the government, and people worked it, keeping a percentage of the crops.
How did the Aztec Empire manage its conquered regions?
Through a tribute system that dictated payments based on the reaction to Aztec rule.
What agricultural innovation did the Aztecs use?
Chinampas, or floating gardens, to enhance agricultural production.
What was a key agricultural practice of the Inca?
Terrace farming, which allowed them to farm on mountainous terrain.
What were the primary religious practices of the Aztecs?
Polytheism with gods tied to nature, rituals involving sacrifice, and pyramids as religious sites.
What was the impact of Mongol conquests on the Silk Road?
Increased trade and stability, known as Pax Mongolica, which facilitated the movement of goods and ideas.
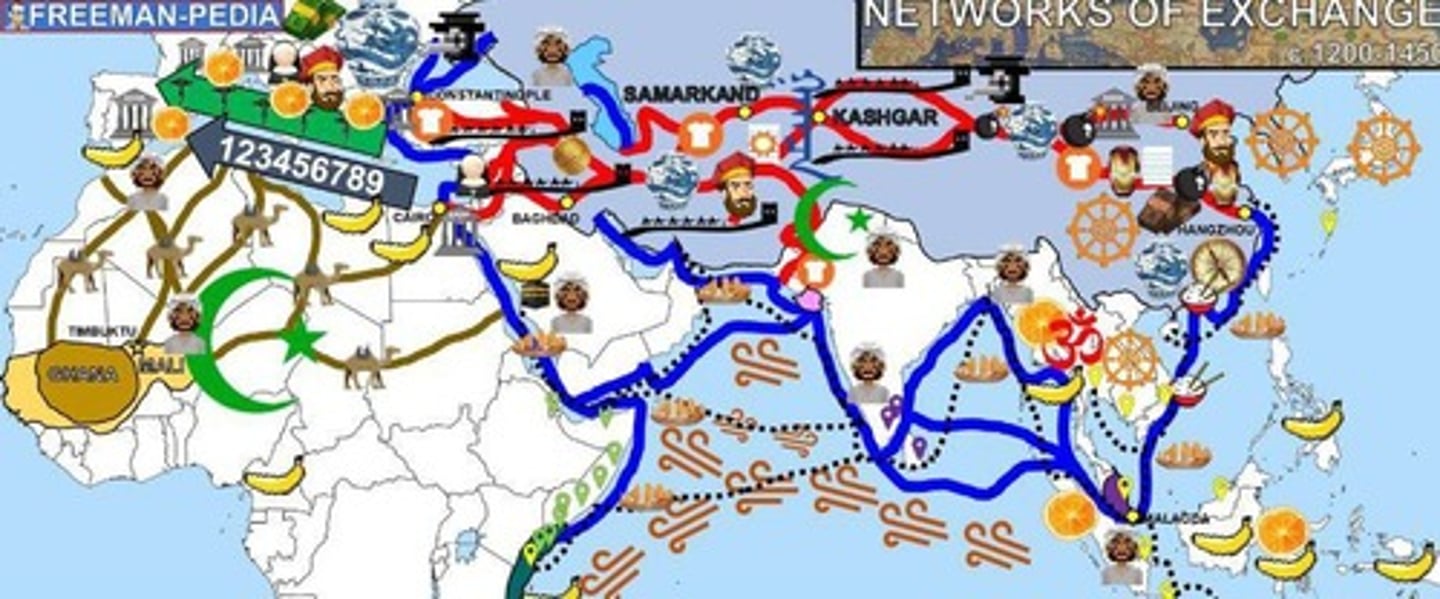
What technological advancements spread due to increased exploration and trade?
The astrolabe, compass, lateen sail, and deeper-hulled boats.
Which religions spread into new regions during this period?
Buddhism spread into East and Southeast Asia, while Islam spread into South and Southeast Asia, West and East Africa, and Spain.
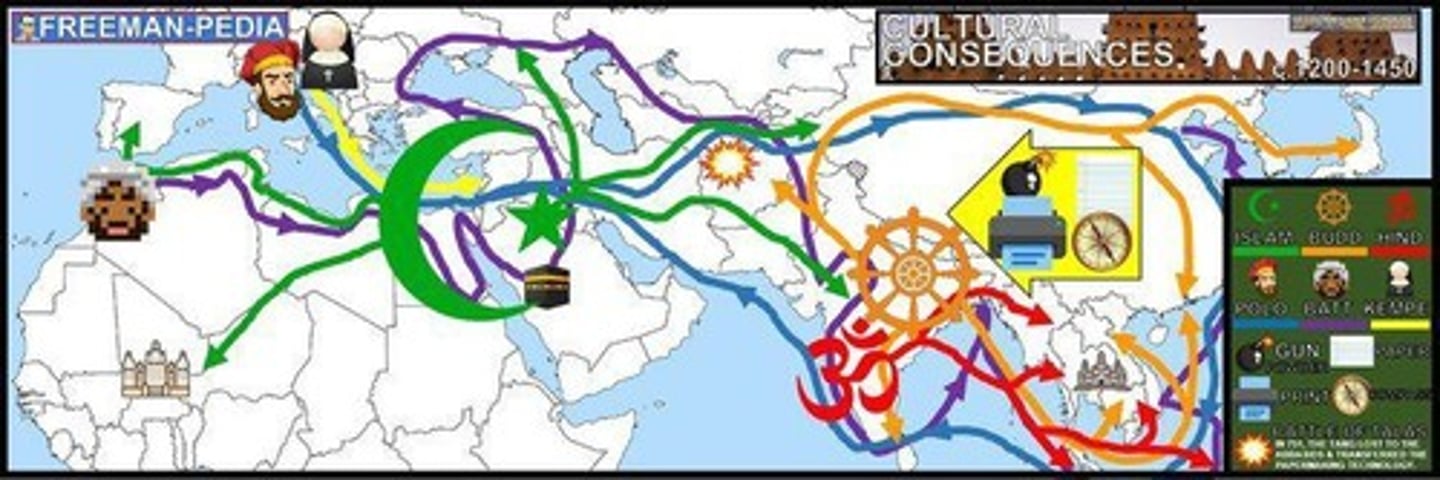
What characterized the economic systems of the Aztecs and Incas?
The Aztecs relied on agriculture and a tribute system, while the Incas utilized agriculture through the Mit'a system and were largely self-sufficient.
What was the significance of caravanserais during the Mongol Empire?
They provided safe havens for travelers and traders along the Silk Road, enhancing trade.
How did the Aztec and Inca empires remain disconnected from the Eastern Hemisphere?
They developed large, self-sufficient empires in the Americas, isolated by geography.
What regions saw increased exploration and trade during this period?
East Asia (especially China) and the Middle East.
Which regions experienced less exploration and trade?
Europe and the Americas.
What societal structure dominated across regions during this time?
Patriarchy.
What navigational advancements were made during this period?
The astrolabe, compass, lateen sail, deeper-hulled boats, Chinese junks, and Indian dhows.
How did Buddhism and Islam spread during this period?
Buddhism spread further into East and Southeast Asia, while Islam spread into South and Southeast Asia, West and East Africa, and Spain.
What were the main characteristics of the Aztec civilization?
Located in Mesoamerica, they had a tribute system, chinampas, and extensive trade.
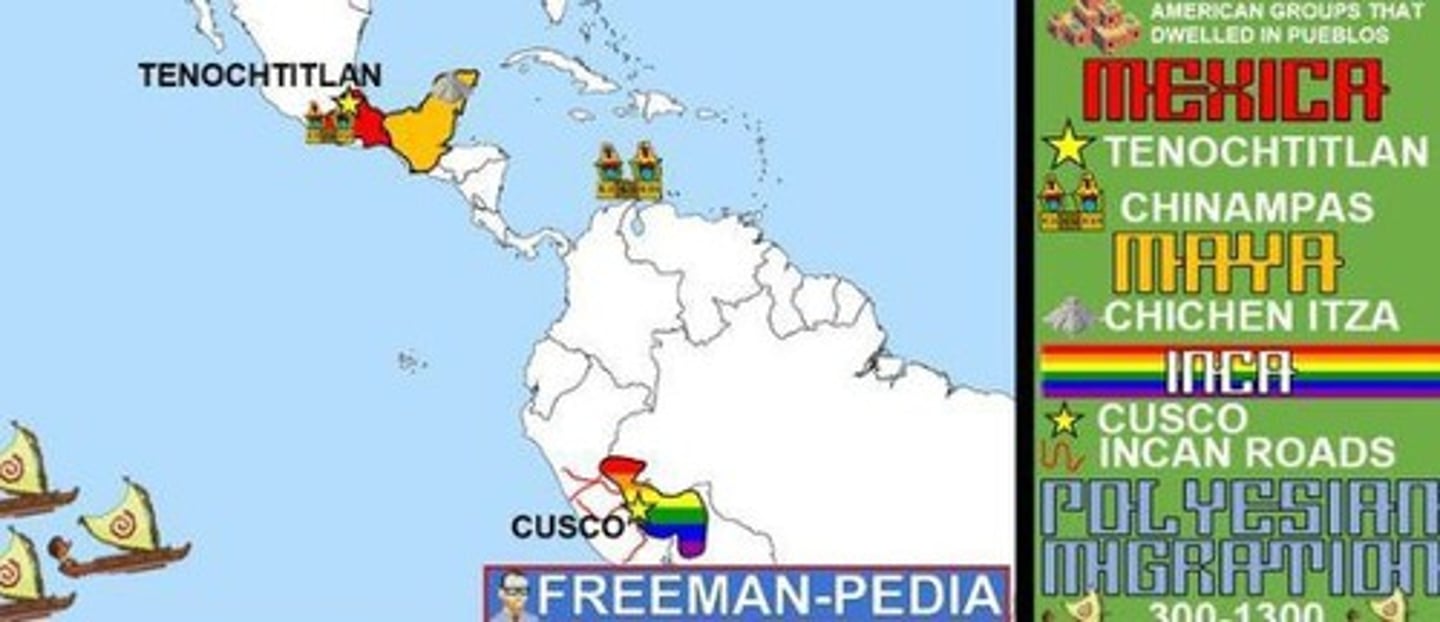
What were the main characteristics of the Inca civilization?
Located in South America, they practiced terrace farming, had provinces, and utilized the mit'a labor system.
What was the primary engine of interactions between different regions?
Trade.
What is the significance of the tribute system in Aztec society?
It was a method of economic control and resource distribution.
What role did the Chinese junks and Indian dhows play in trade?
They allowed for more extended travel away from the coastline.
What is the mit'a system used by the Inca?
A labor system that required citizens to work on state projects as a form of taxation.
What agricultural innovation is associated with the Aztecs?
Chinampas, which are floating gardens used for farming.
What was the impact of trade routes on religious spread?
Trade routes facilitated the spread of religions like Buddhism and Islam into new regions.
What is the significance of the reading check mentioned in the notes?
It is an open-note, timed assessment that counts towards the student's grade.
What resources are available for studying for the Period 1 Test?
Practice SBMCQ questions, SAQ responses, review videos, and other materials in the 'Period 1 Review Materials' folder.
What is the due date for the review packet?
December 15.
What is the format of the reading check?
Typically multiple choice, with roughly one minute per question.
What is the importance of the regular schedule with recharge mentioned in the notes?
It outlines the daily class schedule and timing for each period.
What should students do with their phones during class?
Phones should be placed in the locker at the back of the classroom.
What is the purpose of the bellringer activity?
To engage students at the start of class and address any questions.
What is the significance of the SBMCQs and SAQs mentioned?
They are assessments that will occur on specific dates as part of the Period 1 Test.
How long do students have to complete the reading check?
Approximately 12 minutes.
What should students do if they finish the reading check early?
They should raise their hand for the teacher to collect their check.
What are the major empires mentioned in the political section?
Umayyad, Abbasid, Seljuks, Byzantine, Mongols.
How did the Umayyad Empire expand?
Through conquest.
What challenges did the caliphates face?
New groups like the Seljuks and Ottomans posed challenges.
What was the impact of the Crusades on the Middle East?
The impact was less significant for the Middle East.
How were conquered peoples treated under the caliphates?
The treatment varied, often influenced by the caliph's policies.
What role did agriculture and trade play in the economy?
They were crucial for sustaining the population and facilitating trade.
What was the significance of the Abbasid 'golden age'?
It was marked by advancements in science, math, and technology, and the establishment of the House of Wisdom.
What does the term 'Sinification' refer to?
The influence of Chinese culture on neighboring regions like Korea, Japan, and Vietnam.
What was the role of Confucianism in governance?
It influenced government policies and the behavior of leaders.
What was the social structure in Tang and Song dynasties?
It was characterized by a patriarchal system with divisions between aristocrats and peasants.
What economic innovations emerged during the Tang and Song dynasties?
Paper money and a credit system were developed, along with advancements in agriculture.
What was the significance of the equal field system in the Tang dynasty?
It aimed to distribute land more equitably among the peasantry.
How did the population growth affect food production?
Increased diversity of crops helped meet the demands of a growing population.
What was the role of Islam in the cultural landscape?
Islam was the dominant faith, spreading through trade, Sufis, and jizyah.
What is the significance of the caste system in South Asia?
It structured society based on occupation and social hierarchy.
What characterized the political landscape of Southeast Asia?
Regional kingdoms like the Delhi Sultanate, Srivijaya, and Khmer replaced each other.
How did trade influence cultural exchanges in Southeast Asia?
Trade facilitated the exchange of new ideas and religions.
What is the relationship between population growth and urbanization?
Urban centers grew larger as populations increased, benefiting from trade.
What innovations are attributed to the Song dynasty?
Innovations included gunpowder and woodblock printing.
What was the role of the scholar-gentry in the Song dynasty?
They influenced bureaucracy and governance, contributing both positively and negatively.
What were the religious dynamics in Southeast Asia?
Hinduism, Buddhism, and Islam coexisted, with indigenous beliefs also present.
What was the significance of maritime and land trade routes?
They positioned empires advantageously for trade and cultural exchange.
What was the impact of population growth on food production in the Abbasid Empire?
It led to the cultivation of more diverse crops to sustain the growing population.
What architectural example reflects syncretism in Southeast Asia?
Temples, such as Angkor Wat.
What economic differences exist between kingdoms in South Asia and Southeast Asia?
South Asia is more land-based and agricultural, while Southeast Asia is more trade-oriented, especially in island kingdoms.
How did new religions and populations spread in South Asia?
Through conquest (e.g., Muslims establishing the Delhi Sultanate) and trade.
What role did trade play in Southeast Asia?
Trade introduced new ideas and religions.
What is a significant agricultural example from Southeast Asia?
Khmer agriculture.
Which kingdom controlled the Strait of Malacca?
Srivijaya.
What geographical feature impacted trade and the spread of ideas in the Indian Ocean?
Monsoon winds.
What are the dominant religions in the Indian Subcontinent (ISC)?
Hinduism is dominant, with Islam and Buddhism also present.
What religions are prevalent in Southeast Asia?
Hinduism, Buddhism, Islam, and indigenous beliefs.