GEO 202 Final
1/87
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
88 Terms
Describe the three cycles that influence ice volume on Earth
Eccentricity, tilt, precession
Eccentricity
Change in the shape of Earth’s orbit (100,000 yr cycle)
Tilt
Change in the tilt of Earth’s axis (41,000 yr cycle)
Precession
Change in the wobble of Earth’s axis (23,000 yr cycle)
What do warmer summers mean for glaciers?
More glacier melt
What do colder summers mean for glaciers?
Potential for ice growth
What are the “gains” in a glacial mass budget?
Accumulation
What are the “losses” in a glacial mass budget?
Ablation
When does a glacier indicate advance?
When accumulation is greater than ablation
When does a glacier indicate retreat?
When accumulation is less than ablation
What are the stages of glacial formation?
Snow accumulates, compacts into granular ice, ice flows downhill and forms a glacier.
What are the two manners in which glaciers move?
Ice deformation and basal sliding
What are the three factors that define a glacier?
Perennial mass of snow and ice, originates from densification of snow to ice, shows evidence of internal deformation
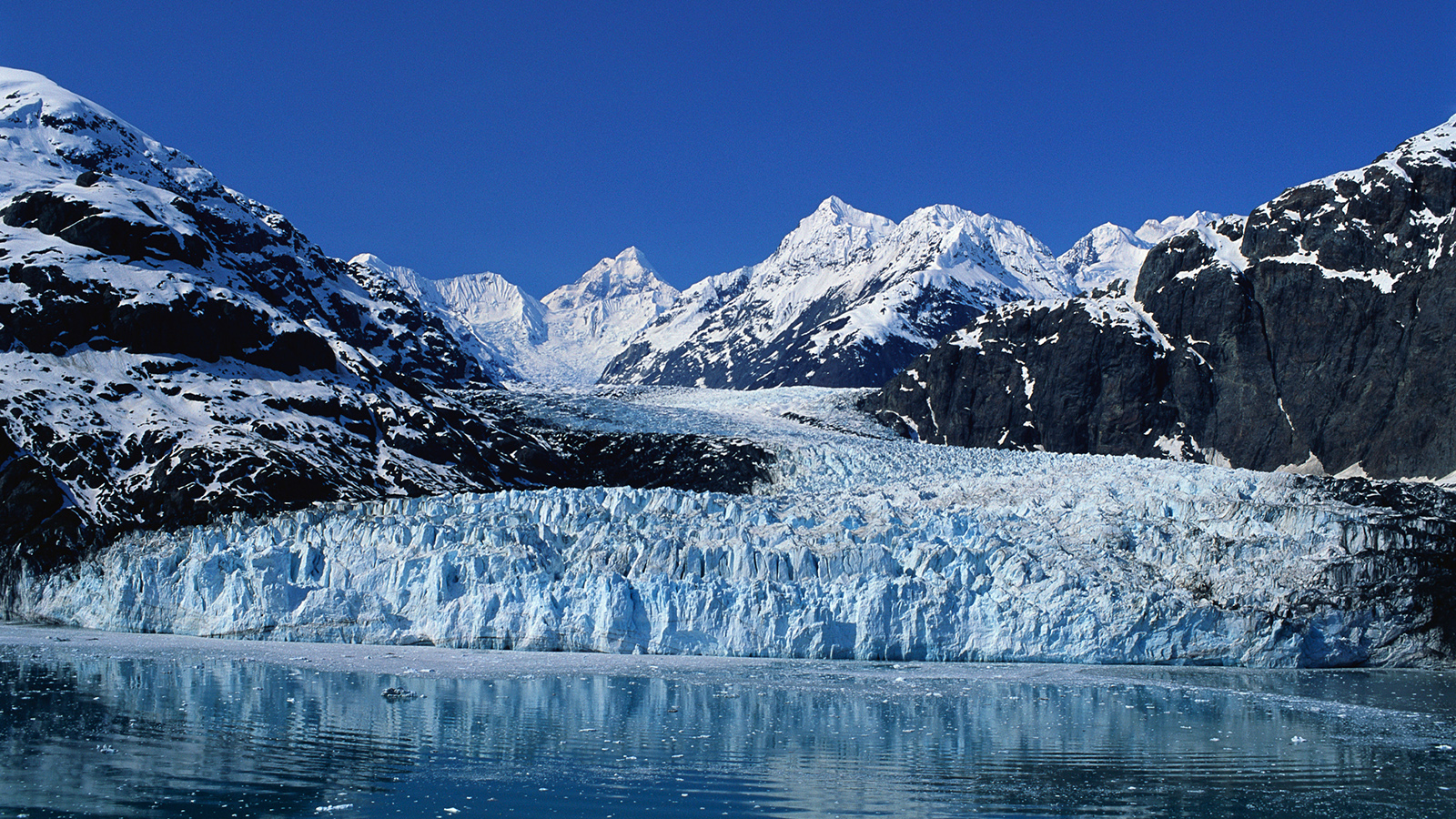

A glacier is
Confined to a valley and flow is controlled by surrounding topography
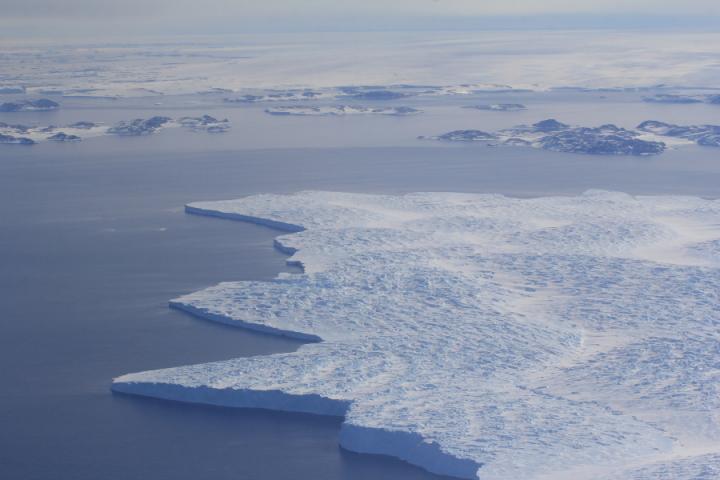

An ice sheet is
Flow controlled by surface slope of ice, independent of underlying topography

A piedmont lobe is
Ice no longer confined, spreads out like an alluvial fan

An ice shelf is
A floating extension of ice
What are the two mechanisms of glacial erosion?
Abrasion and quarrying (plucking)
What is abrasion in a glacier?
Debris dragged across underlying bed
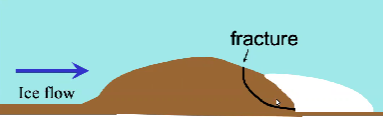
What is quarrying in a glacier?
Rock is quarried from bed by glacier
What are the 5 depositional landscape features carved by glaciers?
Moraine, drumlin, eskers, outwash plains, kettle lakes
What are the 7 erosional landscape features carved by glaciers?
U-shaped valley, cirque, moraine, tarn, arete, horn, fiord
What is a U-shaped valley?
An open valley that is easy to see-through and is in the shape of a “U”

What is a cirque?
An amphitheater carved into the side of a mountain due to quarrying and abrasion
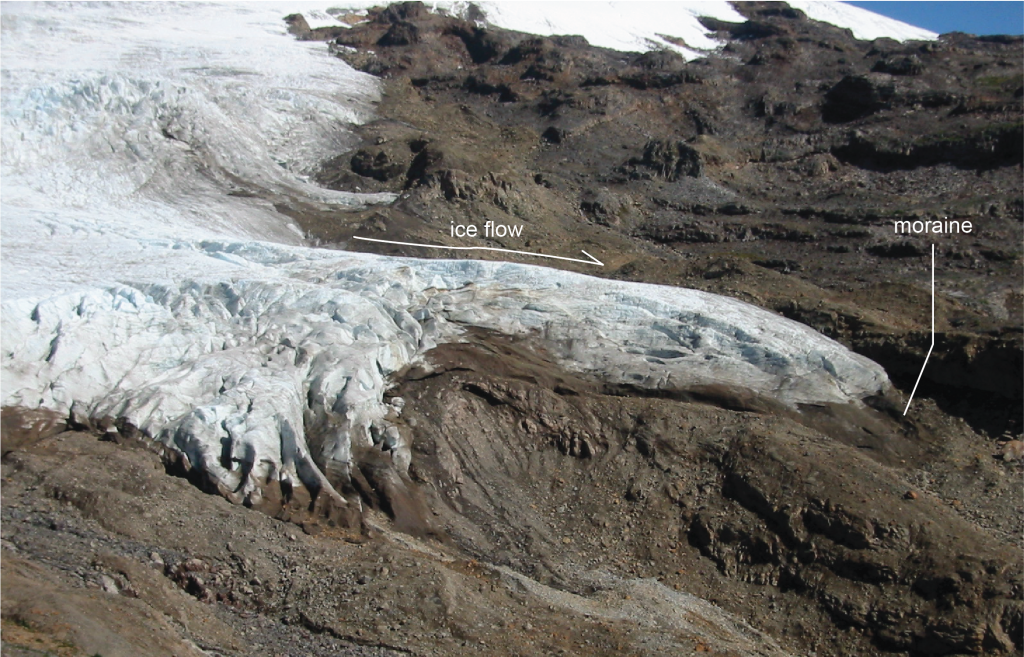

What is a moraine?
Winding ridge-like feature deposited at the edge of a glacier
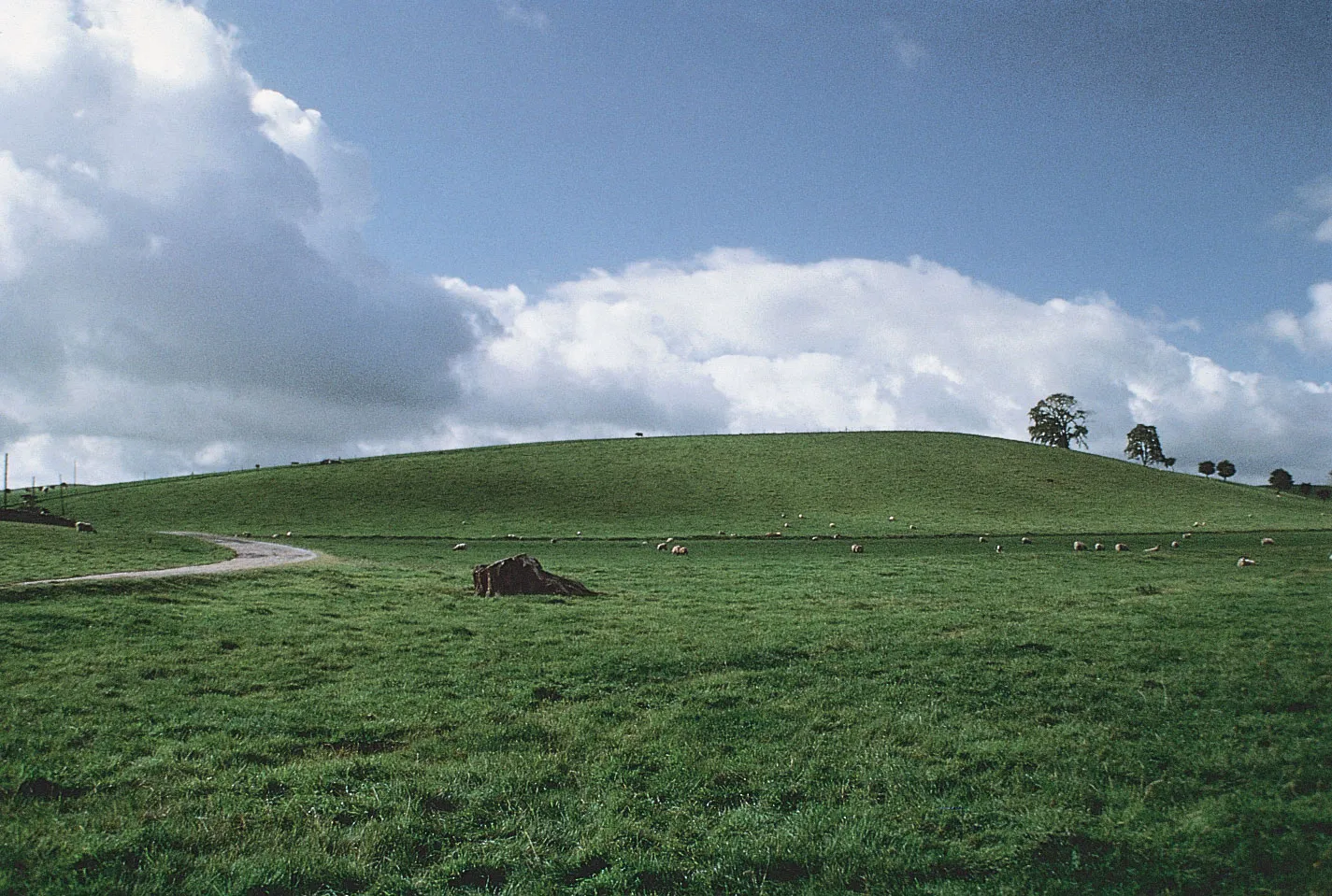

What is a drumlin?
Tear-dropped shaped hills, asymmetric

What is an esker?
Deposited by subglacial rivers, looks like a long snake/stream

What are outwash plains and kettles?
They are formed in front of a retreating glacier

What is a kettle lake?
Formed by ice buried in outwash, filling with melt water
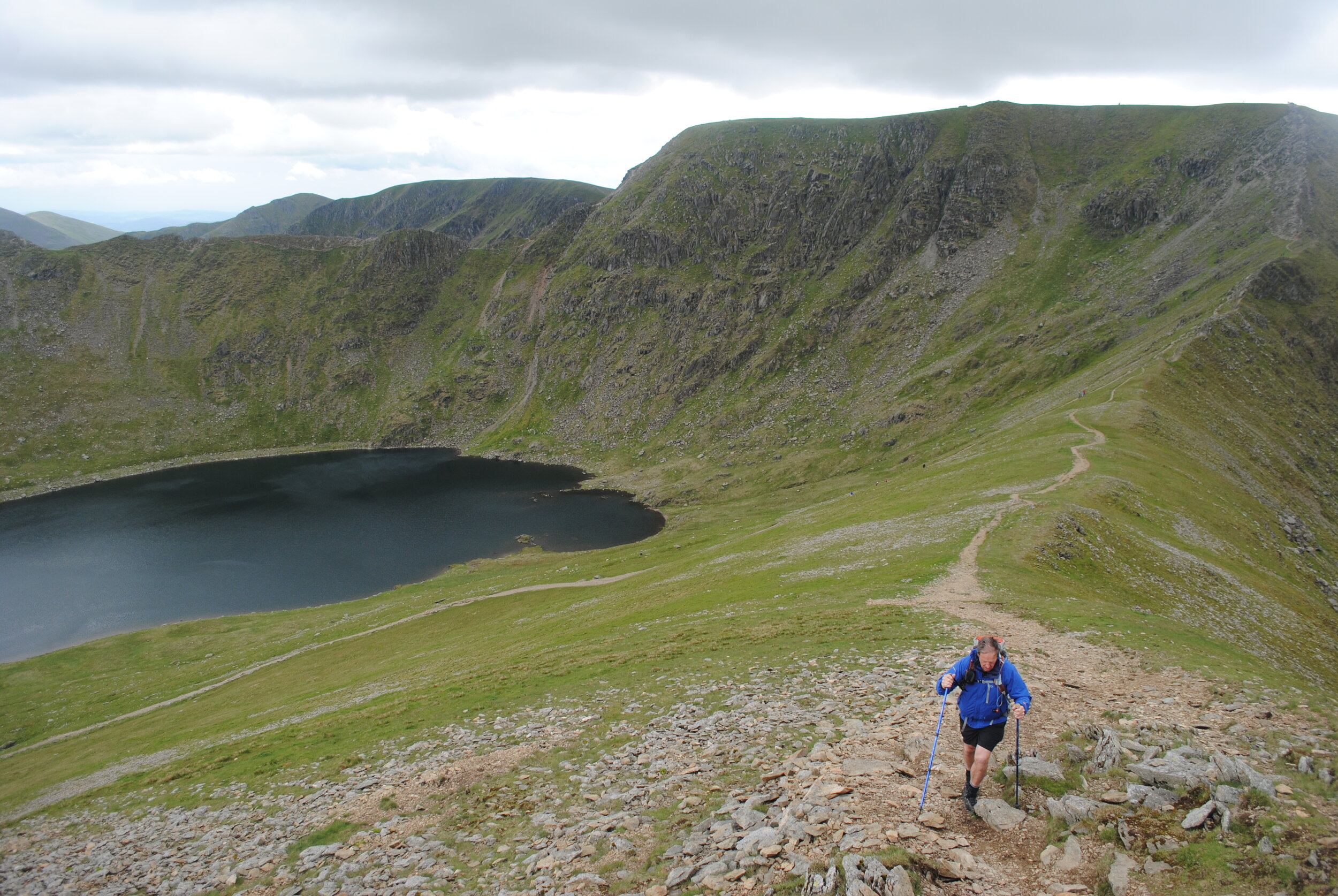

What is a tarn?
Lake at the bottom of a cirque
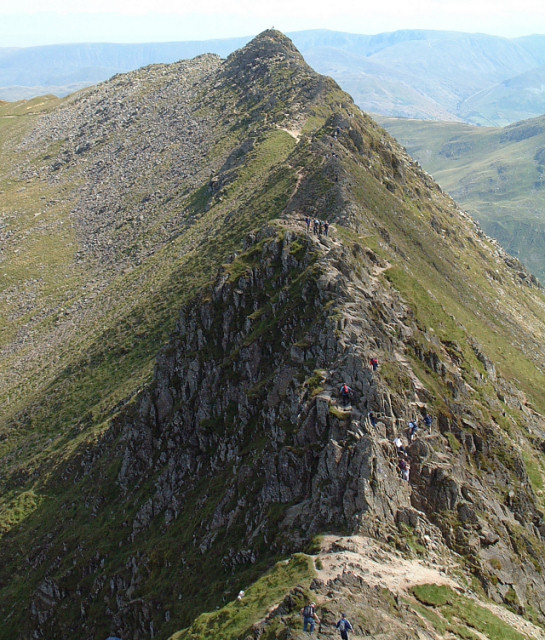

What is an arete?
A knife-like feature or ridge that forms when two cirques erode into each other

What is a horn?
A steep mountain peak/pyramid that results from 3 or more cirques eroding into each other.
What are the factors that control the locations of deserts on Earth’s surface?
Atmospheric circulation, cold ocean currents, and rain-shadow effect
What is atmospheric circulation?
Uplifting air at 0 degrees and 60 degrees (wet), subsiding air at 30 degrees latitude (dry)
What are cold ocean currents/coastal deserts?
Desert near a “cold” ocean that can’t hold much moisture in the air
What is the rain-shadow effect?
An uplift of warm moist air that expands & cools, rises, then evaporates due to compression and warming
What are the geologic roles of weathering and running water in an arid system?
Wind erosion, ephemeral streams, and flash flooding
What are the ways wind transports sediments?
Suspension, saltation, and bedload
What is suspension?
Wind suspending fine-sized particles into the air
What is saltation?
Causes sand to leap, hit other sand grains, and impact objects.
What is bedload?
Small gravel and sand getting rolled along the ground.
What are the two general erosion processes common in deserts?
Deflation and abrasion
What is deflation?
Removal of sediment
What is abrasion?
Blowing sand that abrades rock
What landscape features can deflation create?
Desert pavement
What landscape features can abrasion create?
Rocks with stripped bases and ventifacts
What creates sediment sorting in arid environments?
Wind erosion (suspension, saltation, bedload)
What’s the first step in a dune moving?
Sand moving up the back of a dune
What’s the second step in a dune moving?
Sand reaches the crest
What’s the third step in a dune moving?
Sand is deposited on the downwind side (suspension/avalanching)
What are the 2 factors that control dune morphology?
Distance from sand supply & wind direction
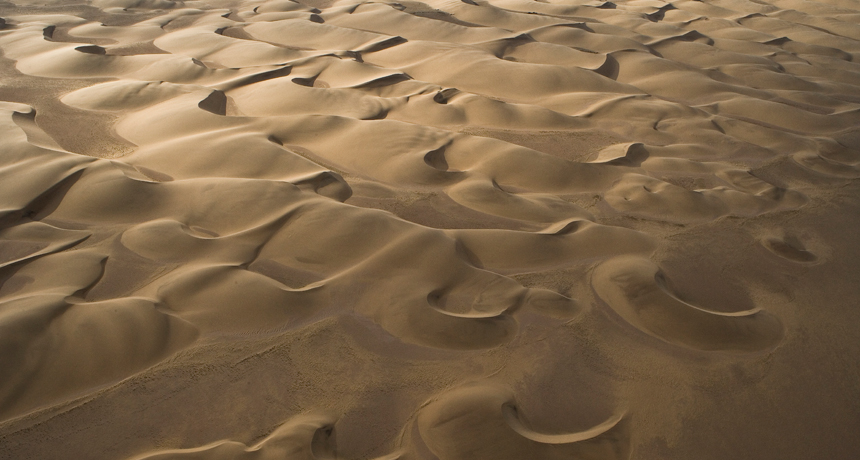

What are barchan dunes?
Dunes that form in extremely arid environments with U-shaped pits/wings that point toward the direction of the wind
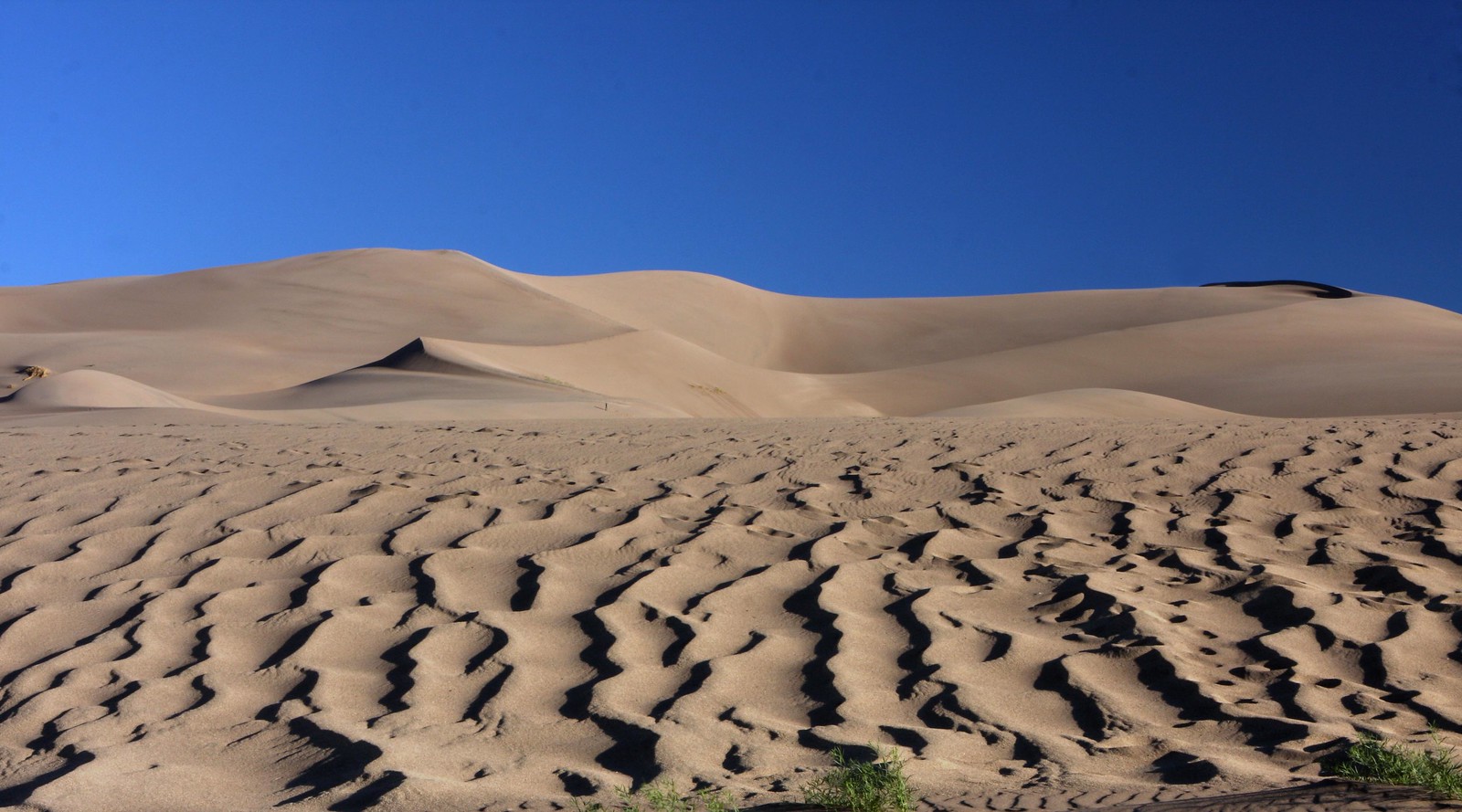

What are barchanoid dunes?
Dunes that form from two barchans coming together, forming an extremely wavey shape.

What are transverse dunes?
Dunes that are formed from strong wind blown in a singular direction, causing subtle wave-like shaped dunes. Occurs mostly in coastal deserts.

What are longitudinal dunes?
Dunes caused by two wind directions, forming mostly straight long ridge shaped dunes.

What are star dunes?
Dunes formed by wind blowing in multiple directions, causing star-like shapes to form.
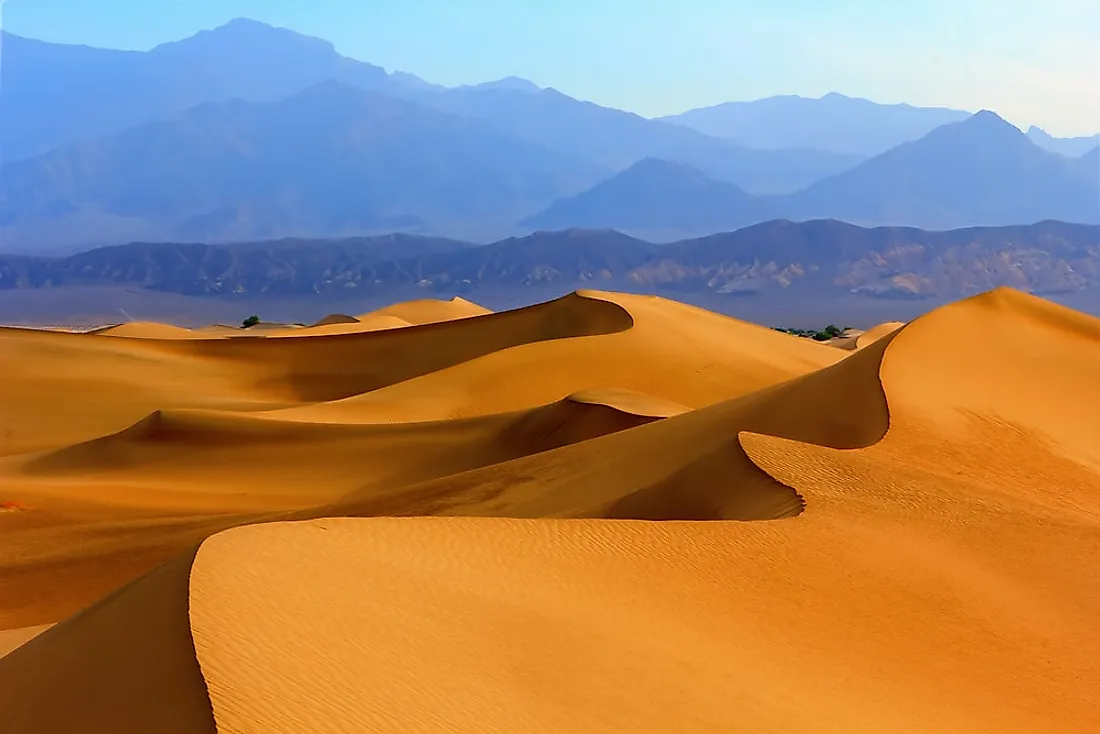

What are parabolic dunes?
Dunes with wings that go against the wind direction with the slip face on the inward side. Common in coastal environments.
How do horst and graben complexes form?
Extension takes place where the crust stretches, developing faults with horsts and grabens.
How do horst and graben complexes evolve?
They can evolve into different landforms.
What landforms can horst and graben landscapes evolve into?
Alluvial fans, playa lakes, bajadas, inselbergs
How do mesa and scarp landscapes evolve and what do they turn into?
Buttes and pillars due to weathering
Why are shorelines considered dynamic interfaces?
Because shorelines are constantly changing due to sea level, storms, and wave action.
How does a wave gain motion?
Waves move forward (not the water), and as a wave moves forward, the water moves in a circle (orbital motion).
What is wave refraction?
How waves bend
Why is wave refraction important for wave erosion and deposition?
The bending of waves has an impact on the strength of erosion that takes place and the movement of sediment
How do waves erode?
By impact and abrasion
How does longshore transport of sediment occur?
Waves push sand and sediment along the beach sideways, moving it in the direction the waves are hitting the shore.
What landforms are formed due to wave action/erosion?
Wave-cut platforms, marine terraces, sea stacks, and sea arches.
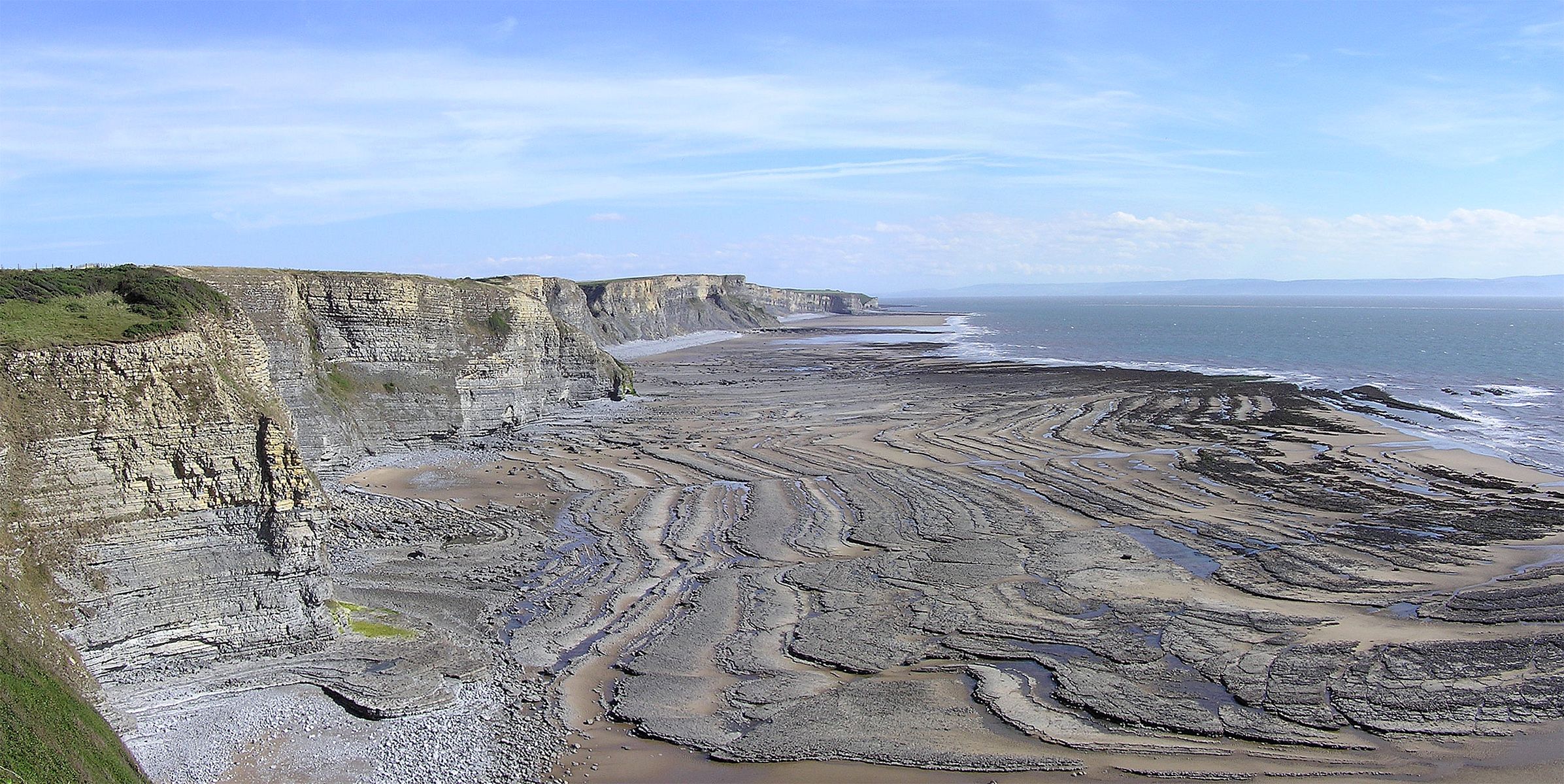

How are wave-cut platforms formed?
Cliff retreats, wave cut-notch forms, then as it recedes a wave-cut platform begins to form
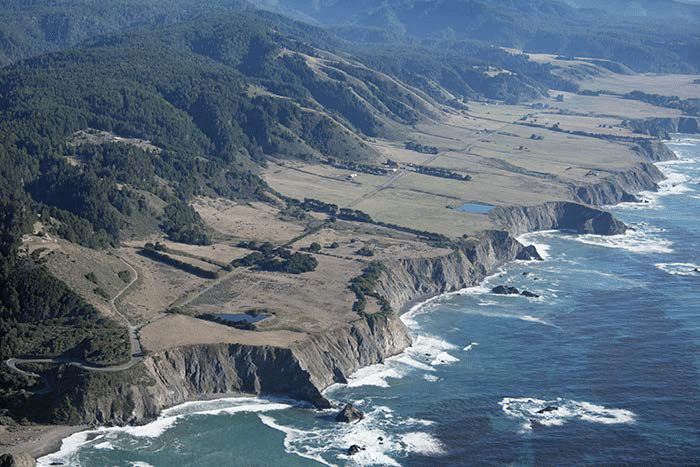

How are marine terraces formed?
Uplift happens, and wave-cut action starts at the base.

How are sea arches formed?
Crack opens and forms a cave due to abrasion, eventually eroded to form an arch.

How are sea stacks formed?
When an arch erodes and collapses due to wave action.
What are the three depositional features that occur where longshore drift is present?
Spits, Tombolos, and Barrier Islands
What is a spit?
An elongated ridge of sand that projects from land into sea
What is a tombolo
Elongated ridge of sand that projects from land to an island
Barrier Islands
Elongated ridge of sand that parallels the coast
What type of weathering do you see in warm and wet climates?
Chemical
What type of weathering do you see in cold and dry climates?
Physical
How does climate change alter rivers/streams?
Increases discharge, velocity, and erosion rates.
How does climate change alter mass movement?
Frequency (none to common)
How does climate change affect groundwater?
Height of water table
How does climate change affect glaciers/ice sheets
Extent, erosion, sea level
How does climate change affect deserts?
Extent
How does climate change affect coasts?
Location & Intensity
What is the first forcing that controls Earth’s climate?
Changes in the sun
What is the second forcing that controls Earth’s climate?
Changes in Earth’s orbit around the sun
What is the third forcing that controls Earth’s climate?
Volcanic Eruptions
What is the fourth forcing that controls Earth’s climate?
Greenhouse gas emissions