Botany Class 2
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
New
Card Sorting
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
1
New cards
sieve cells
long, slender connecting cells in phloem
sieve tube elements are cells in angiosperms, sieve cell in gymnosperm
assoicated with specialized parenchyma cells called albuminous cells
usually not derived from the same cell by mitosis, but perform similar role as companion cell
sieve tube elements are cells in angiosperms, sieve cell in gymnosperm
assoicated with specialized parenchyma cells called albuminous cells
usually not derived from the same cell by mitosis, but perform similar role as companion cell
2
New cards
sieve tube elements
found in phloem
aligned end to end into sieve tubes
associated with specialized parenchyma cells (nucleated companion cells)
derived from the same cell by mitosis and have numerous plasmodesmatal connections
both function together in phloem transport
aligned end to end into sieve tubes
associated with specialized parenchyma cells (nucleated companion cells)
derived from the same cell by mitosis and have numerous plasmodesmatal connections
both function together in phloem transport
3
New cards
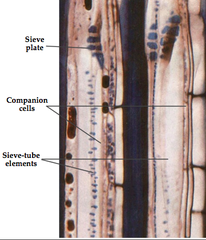
sieve tube elements and companion cells
P-proteins staunch wounds
continuous wall called a sieve plate
continuous wall called a sieve plate
4
New cards
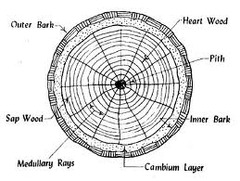
Medullary rays
"pith rays"
composed primarily of parenchyma and transport for nutrients
for occlusion of xylem vessels
for deposition of terpenes in formation of heartwood
composed primarily of parenchyma and transport for nutrients
for occlusion of xylem vessels
for deposition of terpenes in formation of heartwood
5
New cards
Vascular bundle:Eudicot
In secondary growth, the vascular cambium forms between the primary xylem and primary phloem and produces new xylem to the inside and new phloem to the outide
6
New cards
Protoxylem
the part of the primary xylem that differentiates early, while adjacent cells are still elongating
7
New cards
Phloem
Living vascular tissue that carries sugar and organic substances throughout a plant
produced in primary and secondary growth
produced in primary and secondary growth
8
New cards
Protophloem
The part of the primary phloem that differentiates early, while adjacent cells are still elongating during primary growth
often stretched and destroyed as part of expansion and elongation
analogous to protoxylem
often stretched and destroyed as part of expansion and elongation
analogous to protoxylem
9
New cards
Protophloem vs. protoxylem
both elongate, dead at maturity, heavily lignified, provide support but also conduct water and mineral nutrients inside the stem
10
New cards
companion cells
the active cells found next to sieve tube elements that supply the phloem vessels with all of their metabolic needs
11
New cards
where is protoxylem
12
New cards
Pectin
a soluble gelatinous polysaccharide that is present in ripe fruits and is extracted for use as a setting agent in jams and jellies
13
New cards
primary wall
alive during maturity
14
New cards
secondary wall
if lignified, dead a maturity
if not lignified, marenchyma, alive at maturity
if not lignified, marenchyma, alive at maturity
15
New cards
Xylem froms and function
tracheary elements, tracheids, and
vessel elements- conduct/transport water and minerals
fibers- support and sometimes storage
parenchyma- storage
vessel elements- conduct/transport water and minerals
fibers- support and sometimes storage
parenchyma- storage
16
New cards
vessel elements
A short, wide, water conducting cell found in the xylem of most angiosperms and a few nonflowering vascular plants. Dead at maturity, vessel elements are aligned end to form micropipes called vessels.
17
New cards
Phloem form and function
sieve elements- long distance transport of food
Sieve and albuminous cells, sieve-tibe elements- materials and signaling molecules
Scelerenchyma, fibers, sclereids- support, sometimes storage
parenchyma-storage
Sieve and albuminous cells, sieve-tibe elements- materials and signaling molecules
Scelerenchyma, fibers, sclereids- support, sometimes storage
parenchyma-storage
18
New cards
Dermal