Fields and Consequences
1/122
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
123 Terms
What is a field?
An area in which an object experiences a non-contact force
Are fields vectors or scalars?
Vectors
How can fields be represented on diagrams?
Field lines
How do field lines show the strength of a field?
Closer lines represent a stronger field
When is a gravitational field formed?
During the interaction of masses
When is an electric field formed?
During the interaction of charges
Is gravity an attractive or repulsive force?
Always attractive
State Newton’s law of gravitation.
The magnitude of the gravitational force between 2 masses is directly proportional to the product of the masses and inversely proportional to the square of the separation
State the equation for gravitational force.
F = GMm/r²
State the 2 types of gravitational field.
Uniform and Radial
What is a uniform field?
The same gravitational force is exerted on a mass anywhere in the field
What is a radial field?
The force exerted depends on the position of the mass in the field. As an object moves further away from the bigger mass M, the force on it decreases
What type of gravitational field is around the earth?
Radial, but can be assumed to be uniform close to the surface
What is gravitational field strength?
The force per unit mass exerted by a gravitational field on an object
How does gravitational field strength vary in different types of fields?
In a uniform field, the field strength is constant
In a radial field, the field strength decreases with distance from the object
State the formula for gravitational field strength in a uniform field.
g = F/m
State the formula for gravitational field strength in a radial field.
g = GM/r²
What is gravitational potential?
The work done per unit mass against gravitational force to move an object from infinity to a given point
What is the value of V at infinity?
0
Why is gravitational potential always negative?
As an object is moved from infinity to a point, its GPE is reduced from 0
What is gravitational potential difference?
The energy required to move a unit mass between 2 points
State the equation for work done in a gravitational field.
(delta)W = m x (delta)V
What is an equipotential surface?
A line in a field where the the potential is constant along it
What is the work done when moving along an equipotential surface?
Zero
Where are equipotential lines compared to field lines?
Perpendicular to them
Draw a graph to represent the relationship between V and r
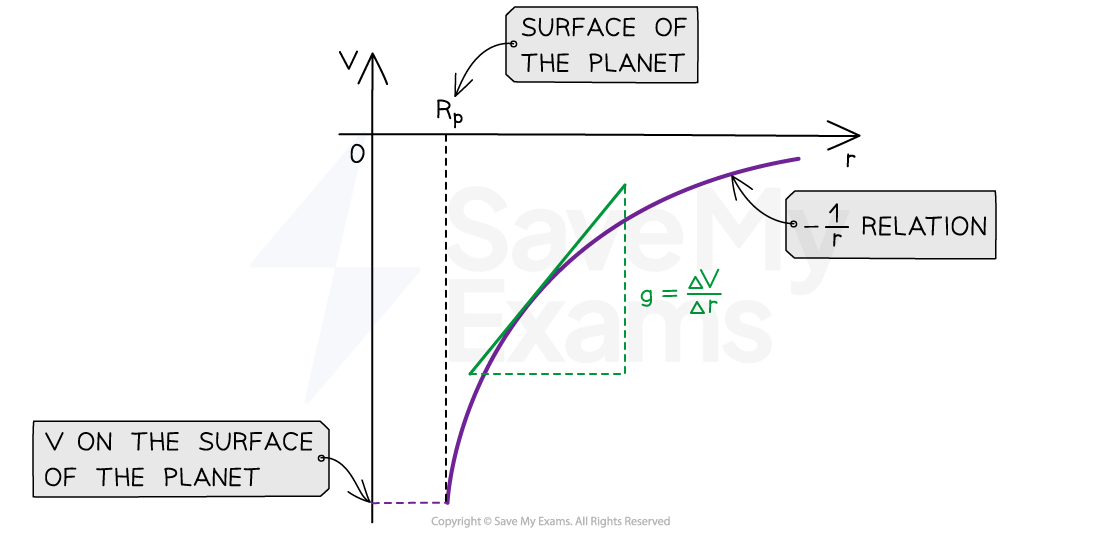
How can g be calculated from a V against r graph?
Draw a tangent to the curve and calculate the gradient, then multiply by -1
Draw a graph to represent the relationship between g and r.

How can potential difference be calculated from a g r graph?
The area under the curve
State Kepler’s third law.
The square of the orbital period is directly proportional to the cube of the radius
Derive Kepler’s third law.
mv²/r = GMm/r²
v² = GM/r
v = 2pi/r so v² = 4pi²r²/T²
4pi²r²/T² = GM/r
T² = 4pi²/GM x r³
4pi²/GM is a constant, so T² = kr³
How is the total energy of a satellite calculated?
kinetic energy + potential energy
Why is the total energy of a satellite always constant.
e.g if height is decreased, GPE will decrease, but KE will increase, maintaining the total energy
Define escape velocity.
The minimum velocity a body must travel at in order to escape the gravitational field at the surface of a mass
When does escape velocity occur?
When KE = GPE
State the equation for escape velocity.
v = (root)2GM/r
What quality of the moving body is its escape velocity independent of?
Its mass
What is a synchronous orbit?
An orbit that has a period the same as the rotational period of the object it is orbiting
What is a geostationary satellite?
A satellite above the earth that has a period of 24hrs and always sits at the same point above the earth
Where does a geostationary satellite orbit?
Directly above the equator
Why are geostationary satellites used for and why?
TV and telephone signals
They sit at the same point above earth, so you do not need to alter the plane of an aerial or a transmitter
State the equation used to find the orbital radius of a geostationary satellite.
r³ = GMT²/4pi²
Why do low orbit satellites have a much smaller orbital period than higher ones?
They are much closer to the earth, so travel at a much greater speed
What are low-orbit satellites useful for?
Monitoring the weather, making scientific observations and military applications
State Coulomb’s law.
The magnitude of the force between 2 point charges in a vacuum is directly proportional to the product of their charges and inversely proportional to the square of the separation
State the equation for force between 2 point charges.
F = 1/4piE0 x Q1Q2/r²
State the value of E0.
8.85 × 10-12
Where is charge assumed to act from in a charged sphere?
The centre
How can the charges on the points be used to determine the nature of the force between them?
If they have the same sign, the force is repulsive, and if the have different signs, it is attractive
Are electrostatic forces between subatomic particles greater or less than gravitational forces and why?
Greater, the charges of subatomic particles are very large compared to their masses
What is the difference between the electrostatic and gravitational forces between 2 protons?
Electrostatic force is 1.24×1036 x greater
What is electric field strength?
The force per unit charge experienced by an object in an electric field
State the formulas for electric field strength in a uniform field.
E = F/Q or E = V/d
State the formula for electric field strength in a radial field.
E = 1/4piE0 x Q/r²
Electric field lines show the direction of the force acting on what type of charge?
Positive charge
What is the strength of a radial field dependent on?
The distance between the 2 charges
State the formula for work done to move a charged particles between 2 charged plates?
(delta)W = Q x (delta)V
How can charged plates be used to determine the charge on a particle?
Fire the particle in between the plates at right angles to the field and the particle will accelerate towards one of the plates in a parabolic shape depending on whether it is negatively or positively charged
What is electric potential?
The potential energy per unit charge of a positive point charge a that point in the field
State the formula for electric potential in a radial field?
V = 1/4piE0 x Q/r
What type of force corresponds to a positive potential?
A repulsive force
How can the electric field strength be calculated from a V r graph?
Draw a tangent to the graph ( E = (delta)V / (delta)r )
What is electric potential difference?
The energy needed to move a unit charge between 2 points
State the equation for work done in an electric field.
(delta)W = Q x (delta)V
How much work is done when a charge moves along an equipotential surface?
None
How can potential difference be found from an E r graph?
Find the area underneath the curve
What is induced when a current flows through a long, straight conductor?
A magnetic field
What shape is the magnetic field formed around a current carrying wire?
Concentric circles
What is a tesla?
A force of 1N acting on 1m of wire carrying 1A of current perpendicular to a magnetic field
What force is exerted on a wire if it is parallel to the magnetic field?
0N
Give the equation for the force on a current carrying wire perpendicular to the magnetic field.
F = BIL
State which finger corresponds to which component in Fleming’s left hand rule.
1st = magnetic flux density / field
2nd = current (conventional)
thumb = force
What direction does the magnetic field follow around a bar magnet?
North to south
Give the equation for the force acting on a charged particle in a magnetic field.
F = BQv
What needs to be changed about Fleming’s left hand rule when dealing with charged particles?
The direction of motion is reversed when considering a negative charge
What direction is the force exerted on a charge particle?
Perpendicular to its motion
Why do charged particles follow a circular path in a magnetic field?
The force acts perpendicular to the particle’s motion, providing a centripetal force for the particle
Derive a formula for the radius of the circle travelled by a charged particle in a magnetic field.
F = mv²/r and F = BQv
mv²/r = BQv
Rearrange
r = mv/BQ
Give some uses of cyclotrons.
Producing ion beams for radiotherapy
Radioactive tracers
What is a cyclotron?
2 semi-circular electrodes (dees) with a uniform magnetic field acting perpendicular to the plane of the electrodes, and a high frequency alternating voltage between them
Describe the motion of a particle within a particle accelerator.
Particles move from the centre of one electrode in a circular path (due to the magnetic field) until it reaches the gap between the electrodes
They are the accelerated across by the alternating electric field, increasing the radius of their path
Define magnetic flux.
The magnetic field lines passing through a given area
How is magnetic flux calculated when the area is perpendicular to the field?
magnetic flux = BA
How is magnetic flux calculated when the area is at an angle to the field?
magnetic flux = BAcosX
Which angle is measured when calculating magnetic flux?
The angle between the normal and the field lines
What is the unit for magnetic flux?
Wb
What is the magnetic flux in a coil parallel to the field lines?
0Wb
Define magnetic flux linkage.
Magnetic flux multiplied by the number of turns in the coil
Give the equation for magnetic flux linkage perpendicular to the field?
magnetic flux linkage = BAN
Give the equation for magnetic flux linkage at an angle to the field?
magnetic flux linkage = BANcosX
What happens when a conducting rod moves relative to a magnetic field?
The electrons in the rod will experience a force and build up on one side of the rod, causing an emf to be induced
How is a current induced from electromagnetic induction?
If a bar magnetic moves relative to a coil of wire that is connected to a complete circuit
State Faraday’s Law.
The magnitude of induced emf is equal to the rate of change of flux linkage
State Lenz’s Law.
The direction of induced emf opposed the change in magnetic flux that produces it
Describe the motion of a bar magnet falling through a coil of wire?
As the magnet approaches the coil, there is a change of flux through it, so an emf is induced
Due to Lenz’s law, the direction of the current opposes the motion of the magnet (the same pole as that in the approaching end of the magnet is induced in the coil to repel it)
The magnet slows due to EM repulsion
As it leaves the coil, there is a change in flux so an emf is induced, this time in the opposite direction (the opposite pole is induced as the end of the magnet leaving the coil to attract it back in), so the magnet slows again
For a magnet in free-fall through a coil, at which point is the induced emf the greatest?
At the bottom, as the speed is greater so the change in time is less
State the equation for Faraday’s law.
emf = N x (change in flux/change in time)
How does the equation for emf change based on lenz’s law.
The emf becomes negative
State an equation for emf using length, speed and flux density.
emf = Blv
How can emf be calculated for a coil rotating at a constant frequency in a magnetic field.
emf = BANwsin(wt)