Lecture Six: Cornea
1/82
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
83 Terms
- Tear film
- Epithelium
- Stroma
- Descemet's membrane
- Endothelium
What are the 5 layers of the cornea?
Maintaining clarity
What is the ultimate goal of the cornea?
- Smooth ocular surface
- Deliver oxygen and nutrients
- Remove waste
- Allow for optical transparency
- Immunology
What are the 5 functions of the tear film?
- Lipophilic
- Hydrophilic
The epithelium is (hydrophilic/lipophilic) and the stroma is (hydrophilic/lipophilic).
- 75% water, 25% collagen
- Relatively acellular (some keratocytes)
What are the components of the stroma?
Endothelium's basement membrane
Descemet's Membrane?
Active dehydration of the stroma
What is the role of the endothelium
False
T/F: the endothelium is regenerative
Cornea
What is the most densely innervated tissue in the body?
CN 5
What nerve innervates the cornea?
Superficial
On the cornea, are most of the nerve endings superficial or deep?
brachiocephalics
less nerves in who?
reflex uveitis with corneal ulceration
cycloplegic (Atropine)
axonal reflex?
treatment?
- Loss of transparency
- Change in thickness
What are the 2 over-arching categories of corneal disease?
- Precise arrangement of collagen lamellae
- Relative dehydration
- Absence of pigment, blood vessels, and keratinization of the surface epithelium
What 3 factors result in corneal transparency?
Lipid, mineral, fibrosis
white in the cornea =
Edema
blue in the cornea =
Blood vessels, hemorrhage
red in the cornea =
- Pigment
- Necrosis (sequestrum)
- Foreign body
- Neoplasia
- Dermoid
- Iris prolapse
brown in the cornea =
Cellular infiltrate
yellow in the cornea =
Corneal dystrophy
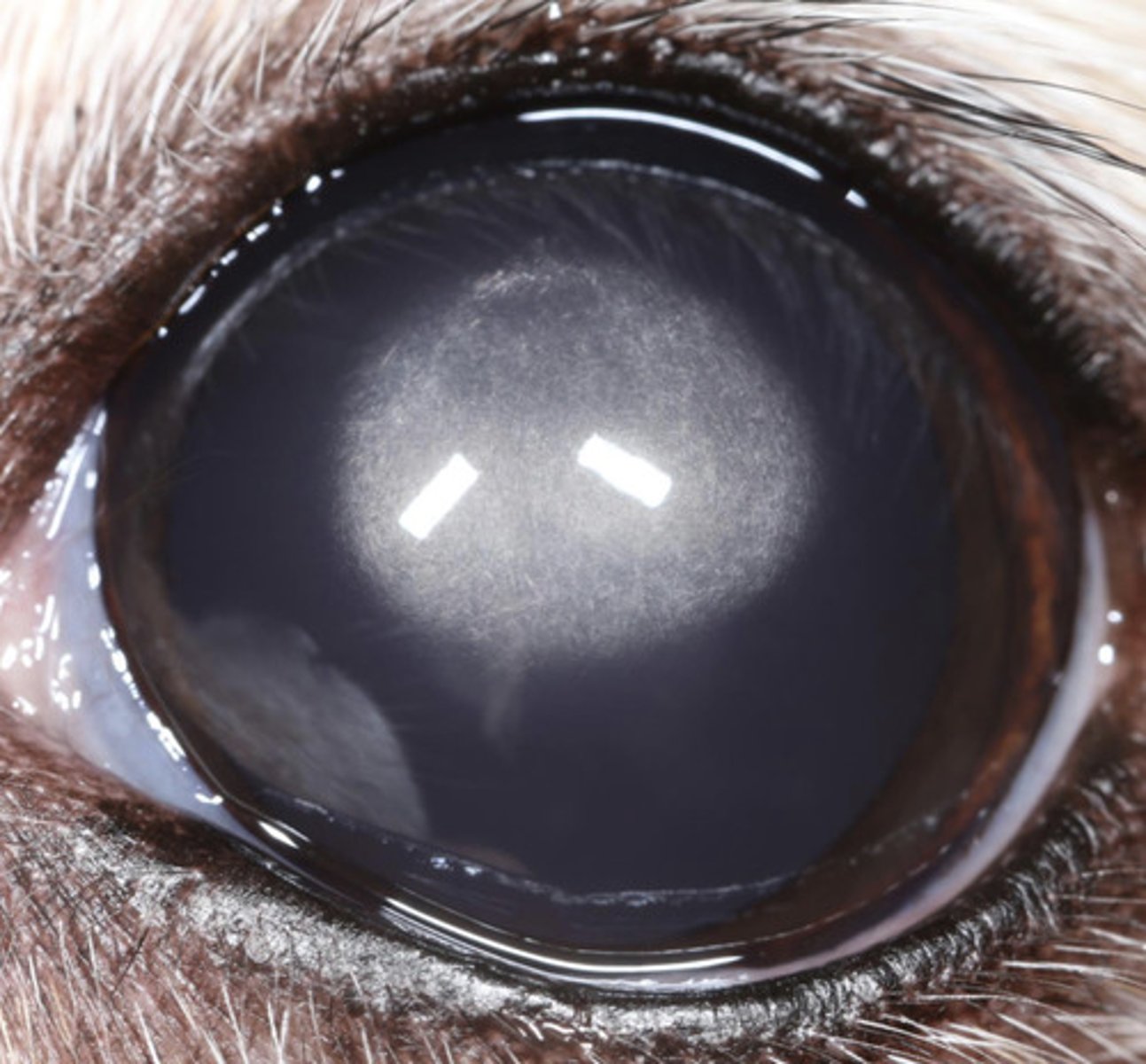
What am I describing?
- White opacities
- Bilateral, symmetrical
- Seen in purebred dogs
- Non-painful, non-progressive
- No concern
None
What is the treatment for corneal dystrophy?
Corneal degeneration
What am I describing?
- White opacities
- Unilateral or bilateral, asymmetric
- Due to ocular surface or intraocular disease
- May have systemic implications
- Often vascularized
- Can result in ulceration
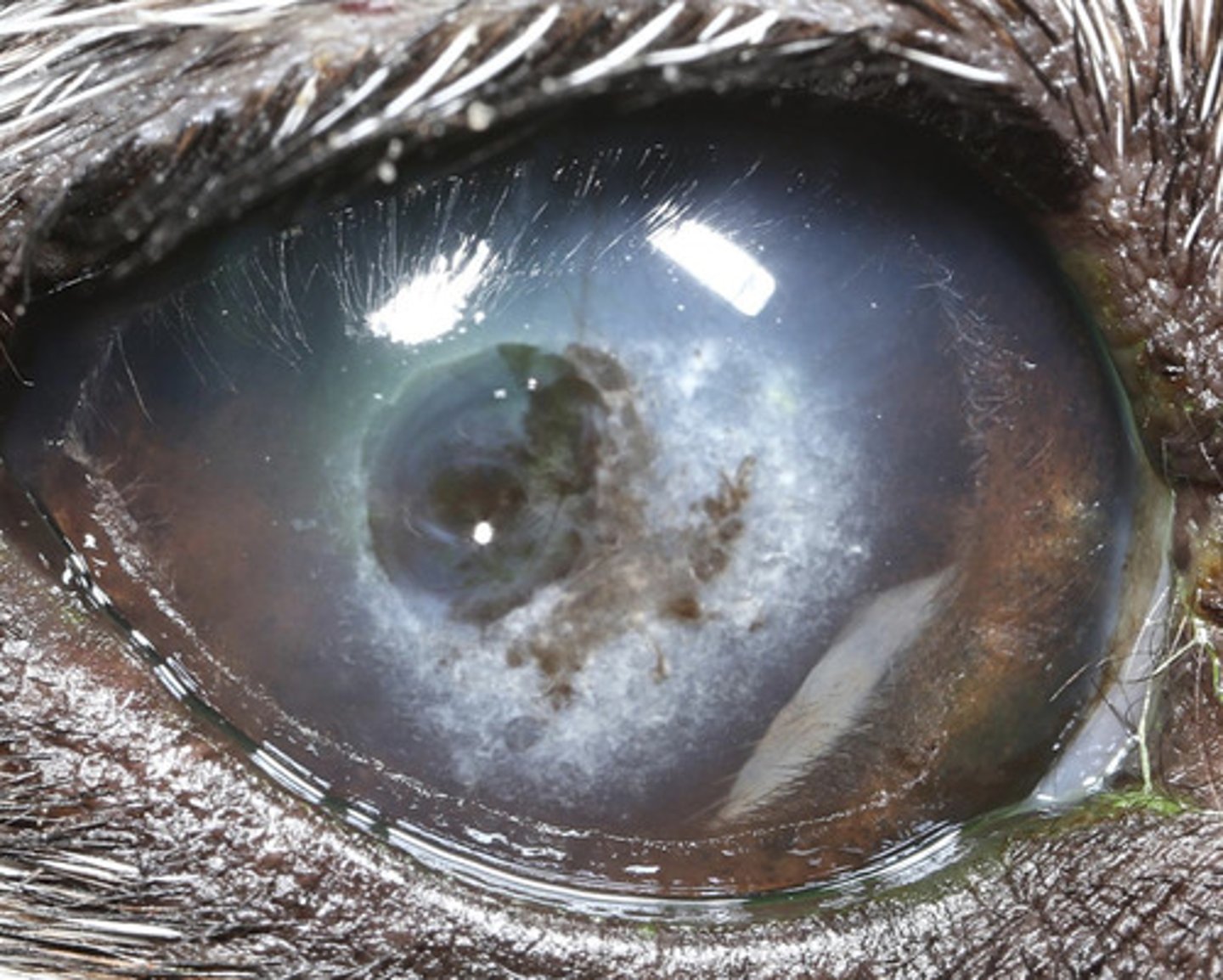
- Identify ocular/systemic diseases and treat
- Consider referral
What is the treatment for corneal degeneration?
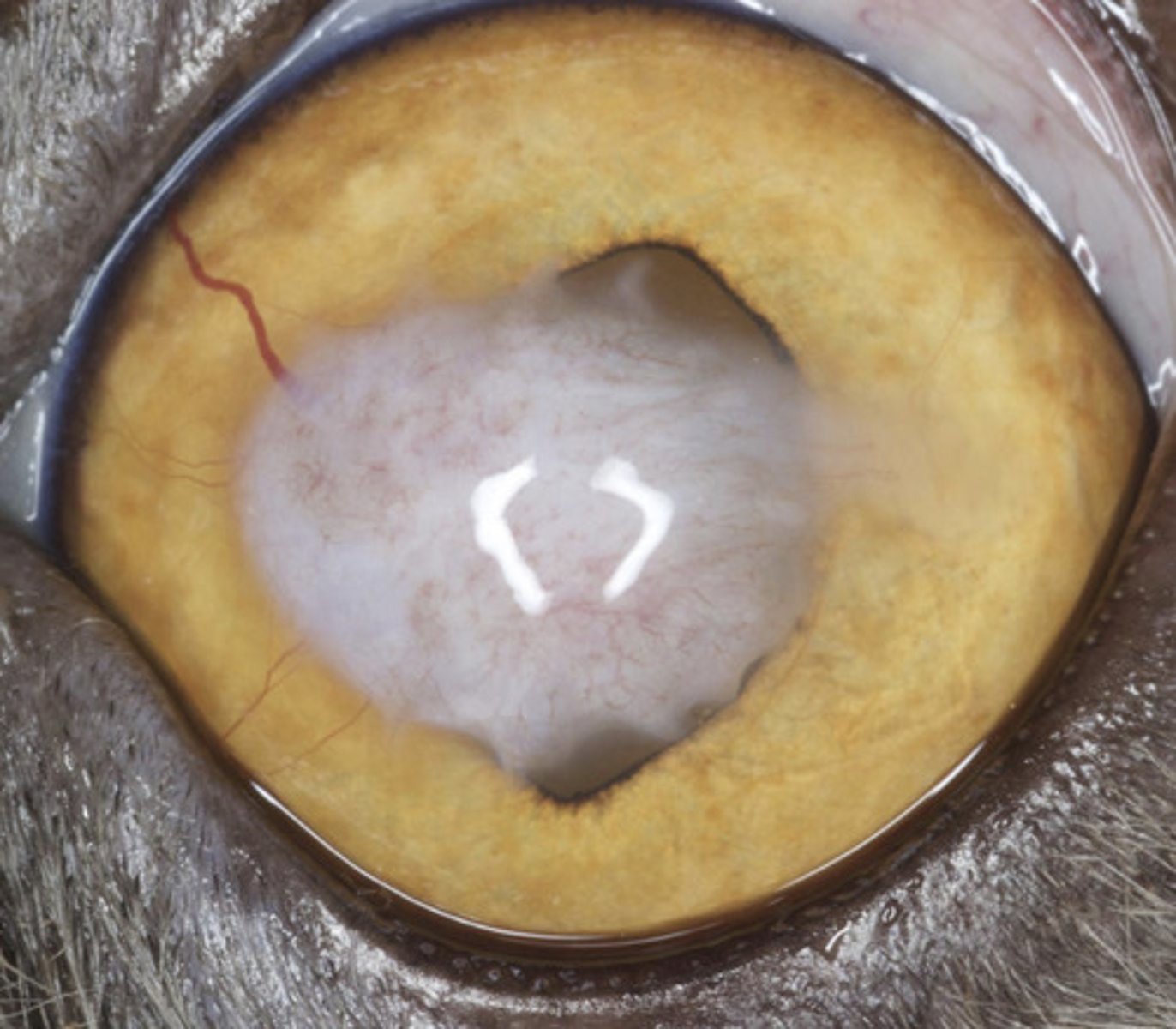
Corneal fibrosis
What am I describing?
- White opacities
- Increased and/or disorganized collagen
- Historical keratitis
- Often associated with vascularization
- Non-painful
- No treatment
None
What is the treatment for corneal fibrosis?
Descemet's striae
What am I describing?
- White opacities
- Cracks in descemet's membrane leaving scars
- Associated with glaucoma
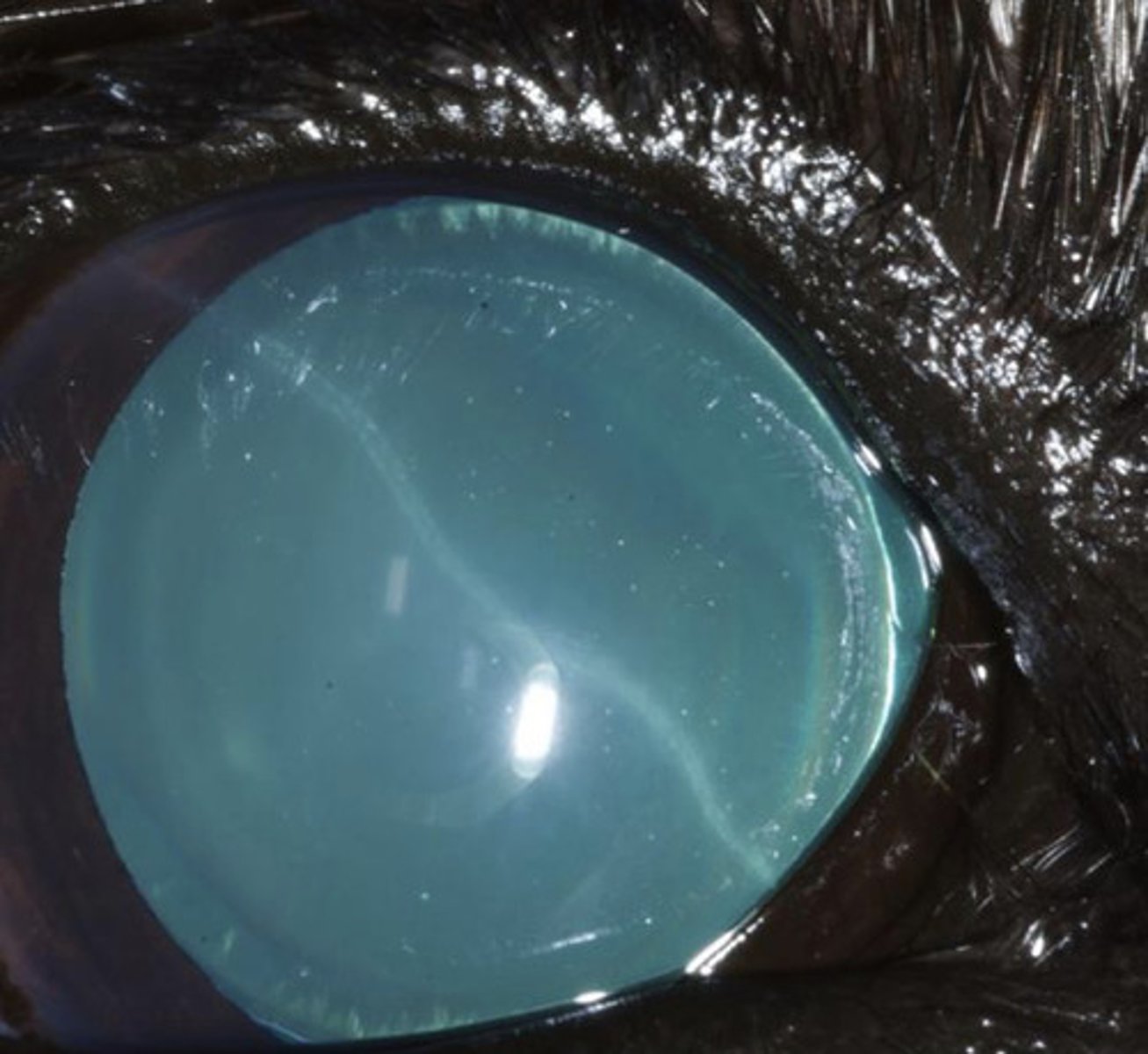
Glaucoma
Descemet's striae is associated with what?
Keratic precipitates
What am I describing?
- White opacities
- Clumps of cells, protein, fibrin, lipid adhered to endothelium, forming a scar
- Pathognomonic for anterior uveitis
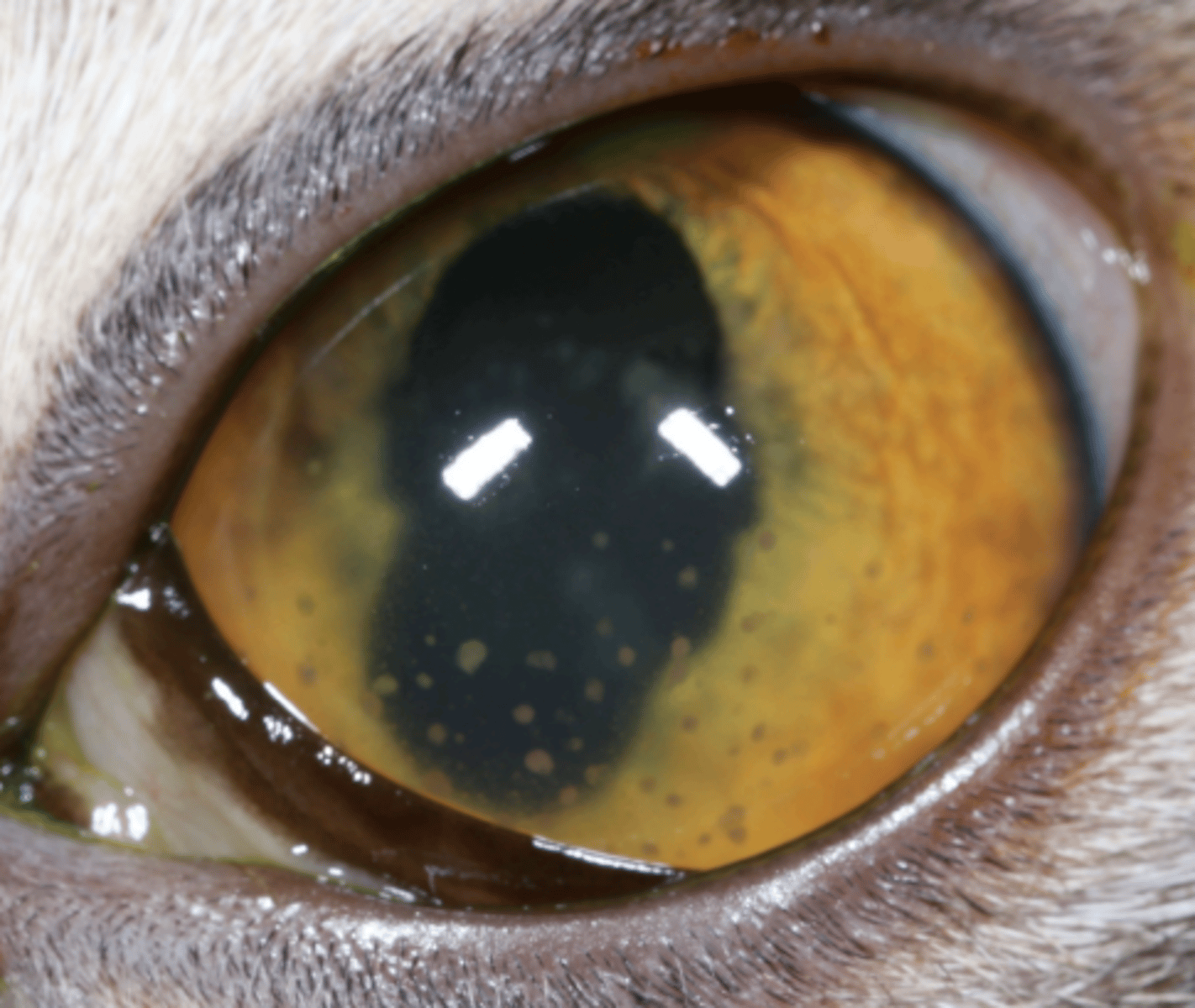
Keratic precipitates
What is pathogneumonic for anterior uveitis?
Epithelial inclusion cyst
What am I describing?
- White opacities
- Benign entrapment of epithelium within the stroma
- Non-painful, no problems
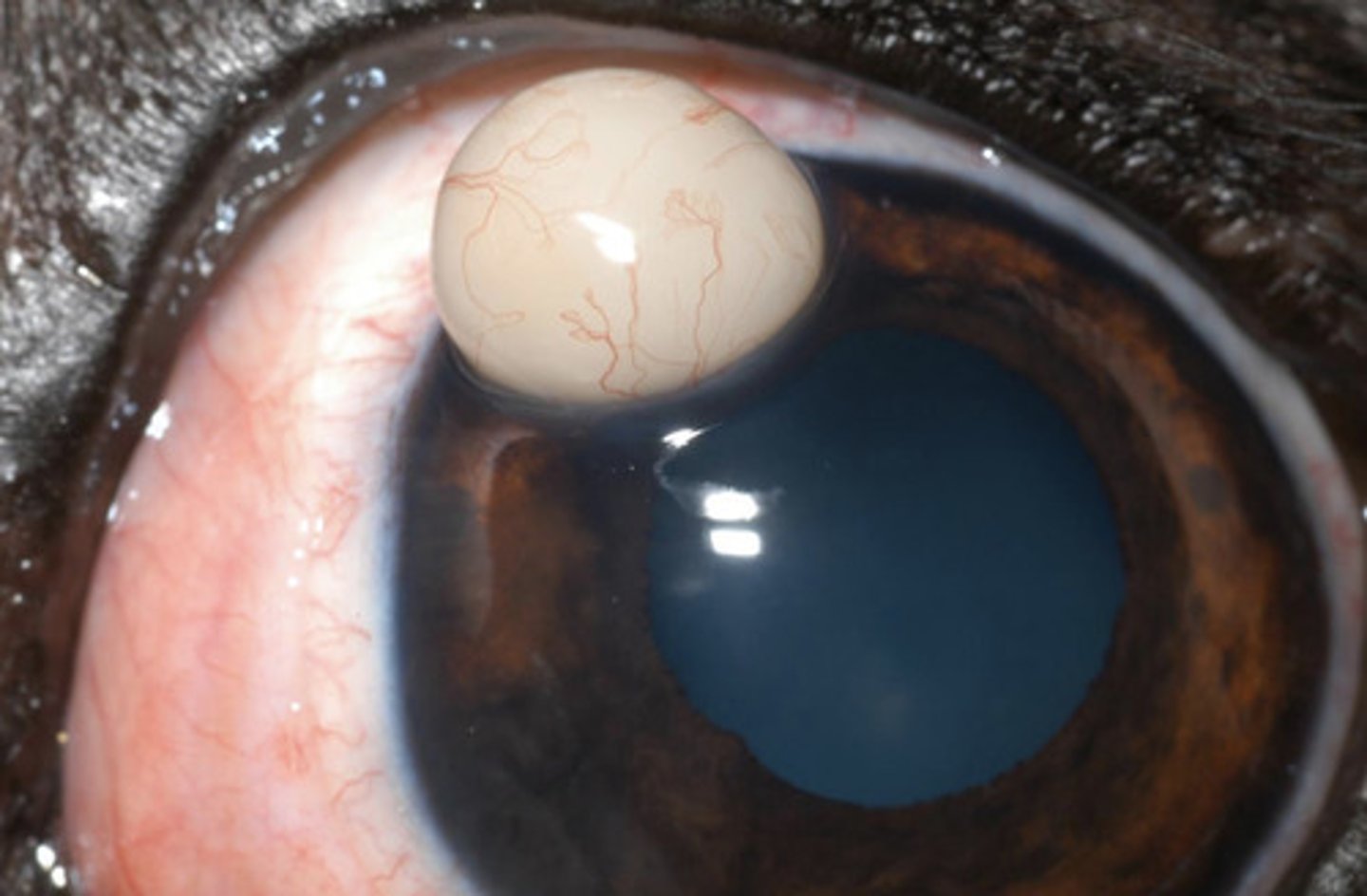
Surgical excision (refer)
What is the treatment for epithelial inclusion cysts and neoplasia?
- SCC*
- Papilloma
- Lymphoma
- also HSA
Top 3 corneal neoplasias?
Corneal edema
What am I describing?
- Blue opacities
- Can be due to an epithelial or endothelial defect
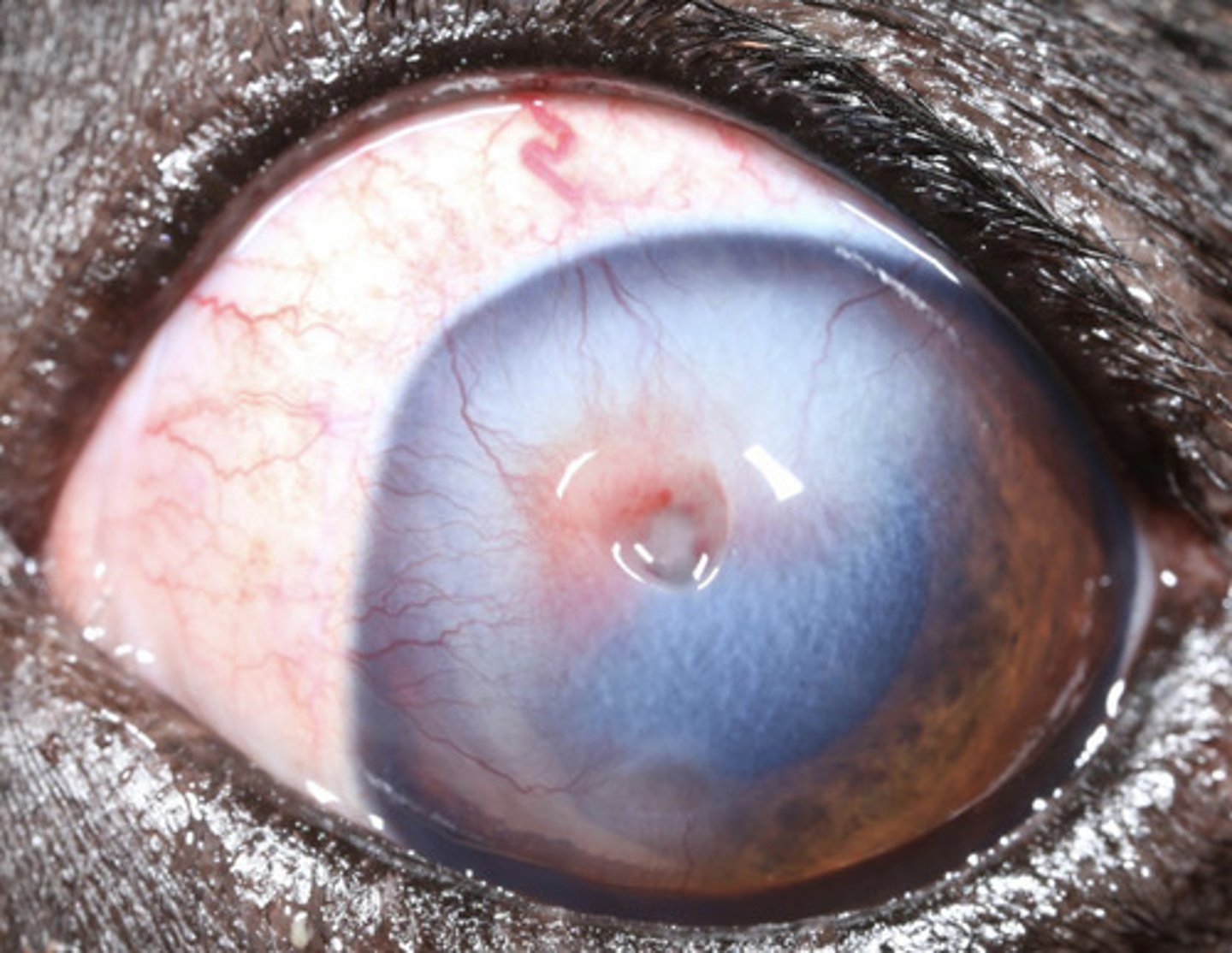
- Ulcerative keratitis* (cornea inflammation)
- Non-ulcerative keratitis
- Keratic precipitates
- Anterior lens luxation
- Glaucoma, uveitis
What are 5 causes of focal corneal edema?
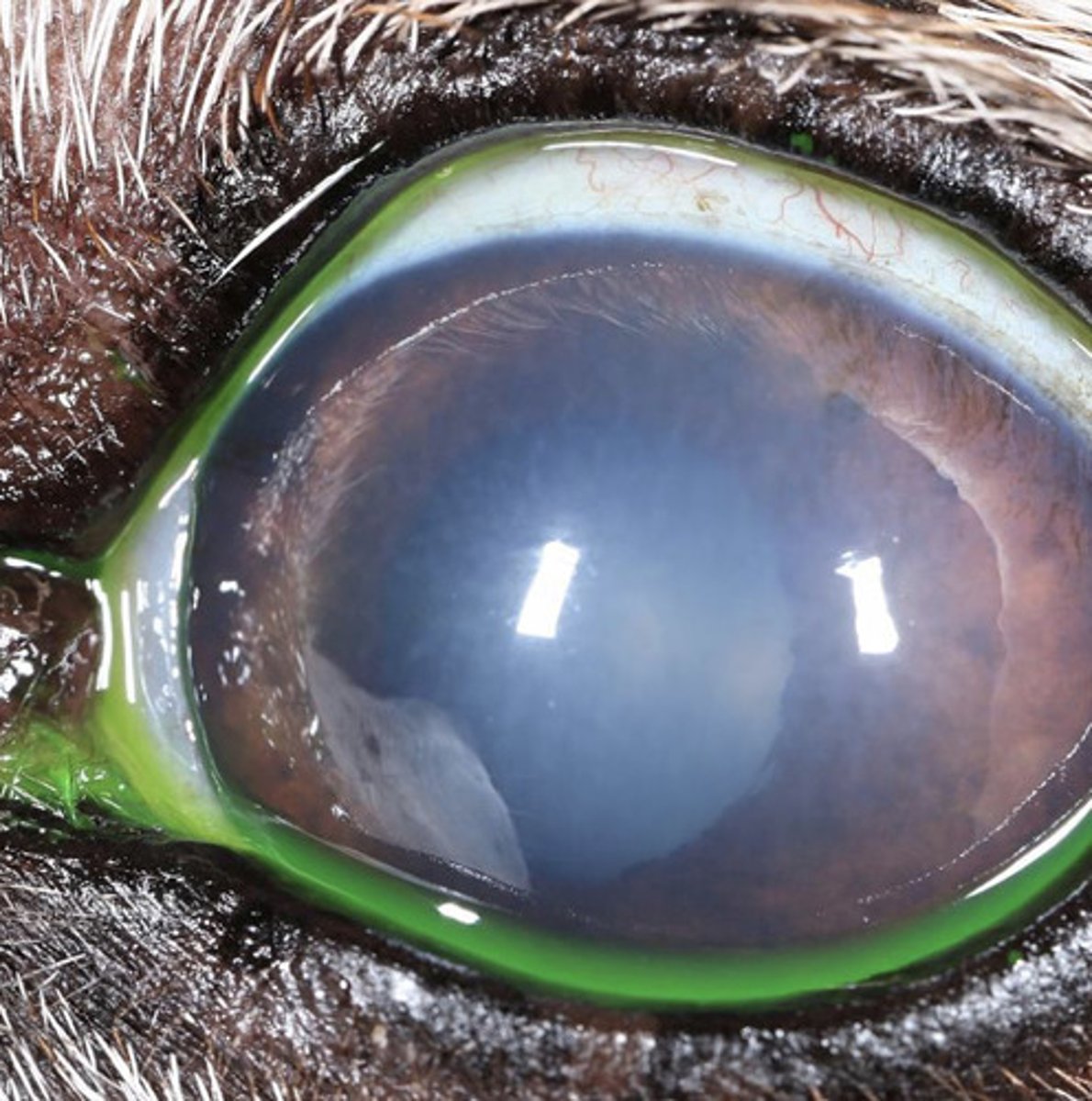
- Glaucoma
- Anterior uveitis
- Endopthalmitis
- Endothelial dystrophy
- Senile endothelial degeneration
- Endothelitis
- Blue eye (CAV-1)
What are 7 causes of diffuse corneal edema?
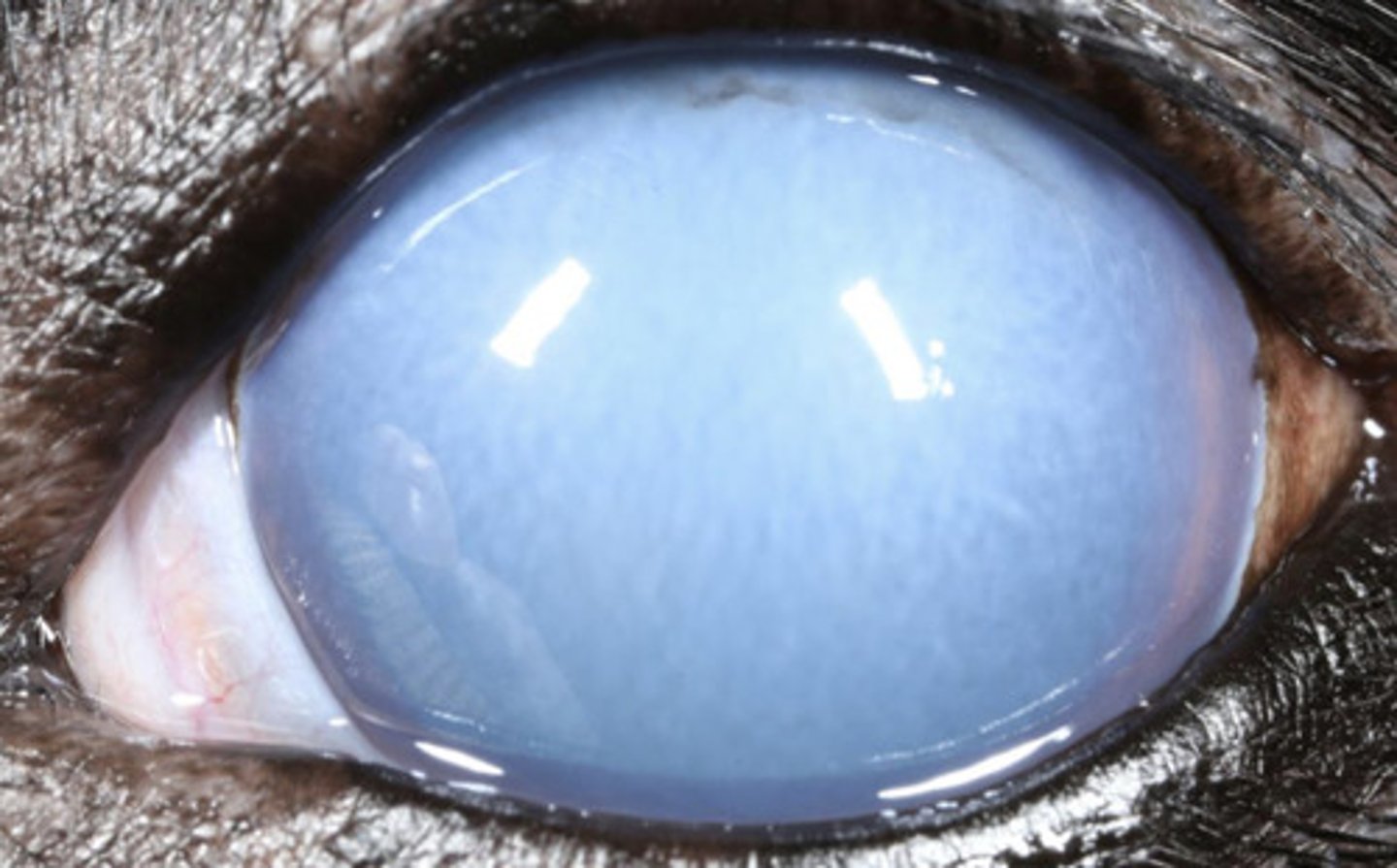
- Boston terrier
- Chihuahua
- Dachshund
- Basset hound
What breeds are more likely to get corneal edema due to endothelial dystrophy? (4)
- Treat primary disease
- Hyperosmotic 5% NaCl ointment
- Thermakeratoplasty (rarely used)
- Keratoleptynsis
- Corneal transplant
- Endothelial transplant - coming soon
What is the treatment for corneal edema?
- Vascularization (non-specific for ocular surface or intraocular disease)
- Intrastromal hemorrhage (blood vessels already there)
What are the potential causes of red opacities?
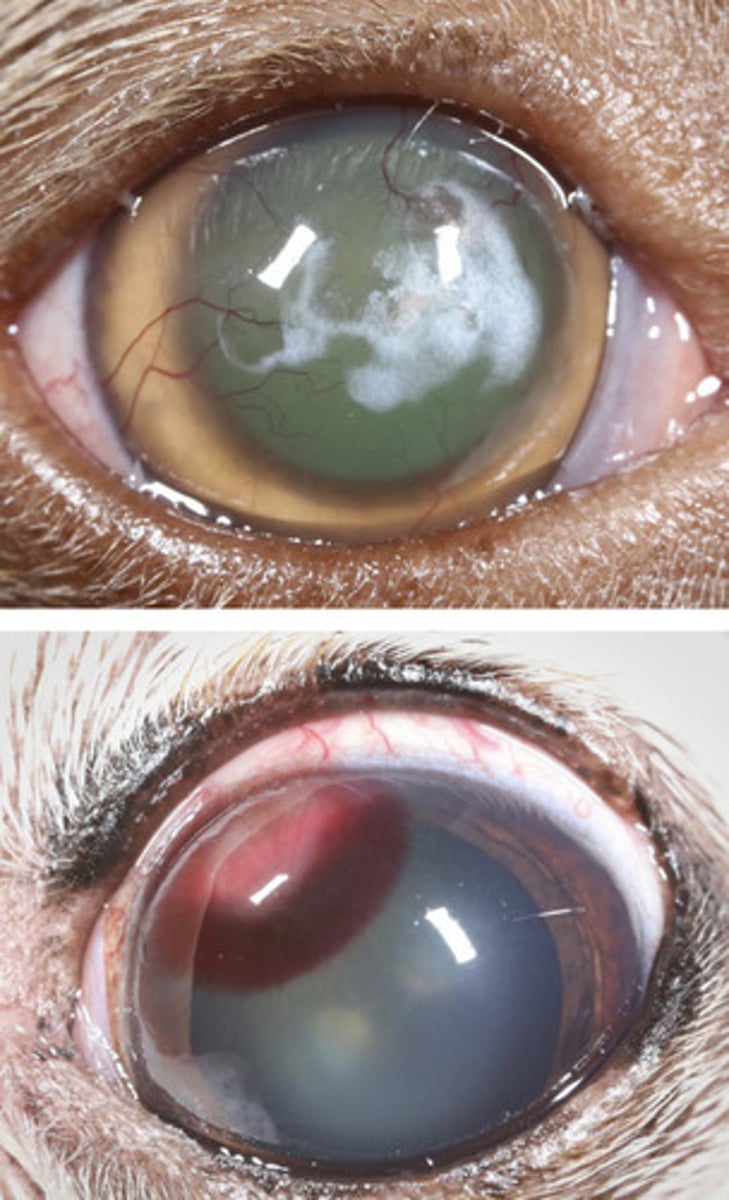
4
1
vascularization takes ___ days to start growing, then grow ___mm per day
Ocular surface disease (KCS, indolent ulcer, etc.)
Superficial red opacities =
Deep stromal , intraocular disease (stromal abscess, uveitis, glaucoma, etc.)
Deep red opacities =
deep vessels (hedgelike)
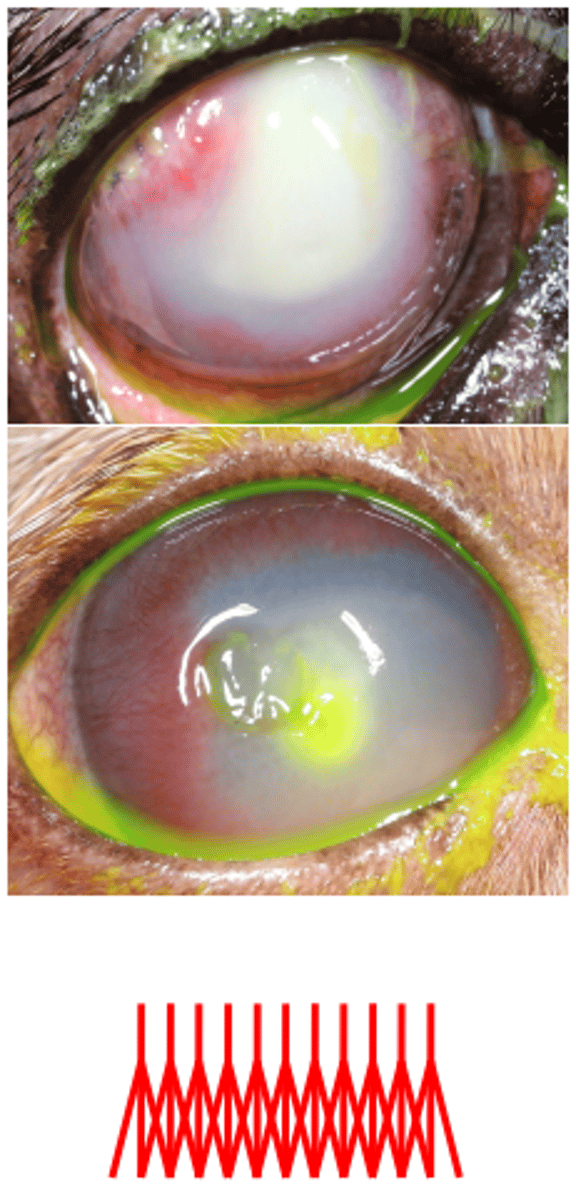
superficial vessels (branching)
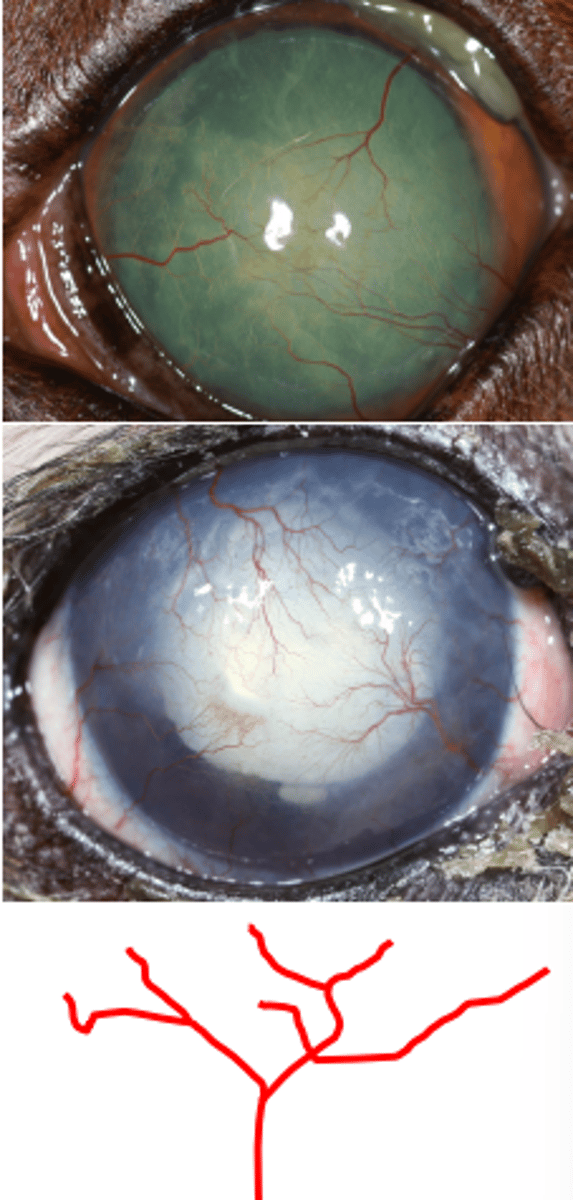
Chronic superficial keratitis (pannus)
What am I describing?
- Red opacities
- Immune-mediated
- Seen in GSDs and sighthounds
- Non-painful, progressive
- Superficial vessels, pigmentation, corneal degeneration, fibrosis
- Starts at the temporal (lateral) limbus
- Can be blinding if no tx
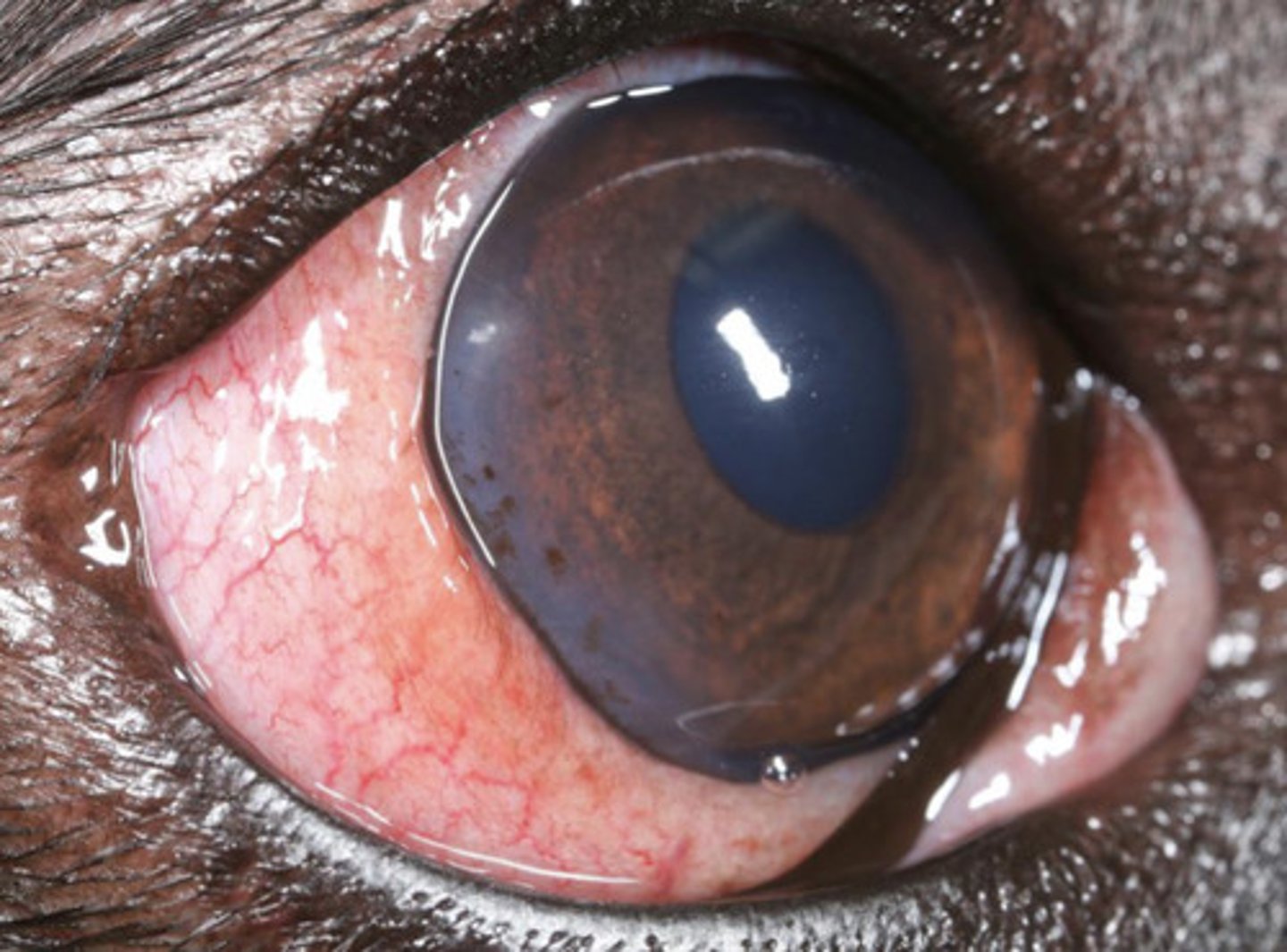
Lifelong immunosuppressant maintenance:
- Topical dexamethasone
- Topical cyclosporine or tacrolimus
What is the treatment for chronic superficial keratitis (pannus)?
Eosinophilic keratitis
What am I describing?
- Red opacities
- Feline, equine, rabbit
- Implications with herpesvirus
- Recurrent, persistent
- Raised pink/white plaques from the limbus with vessels
- Usually unilateral and not ulcerative
- Variable pain
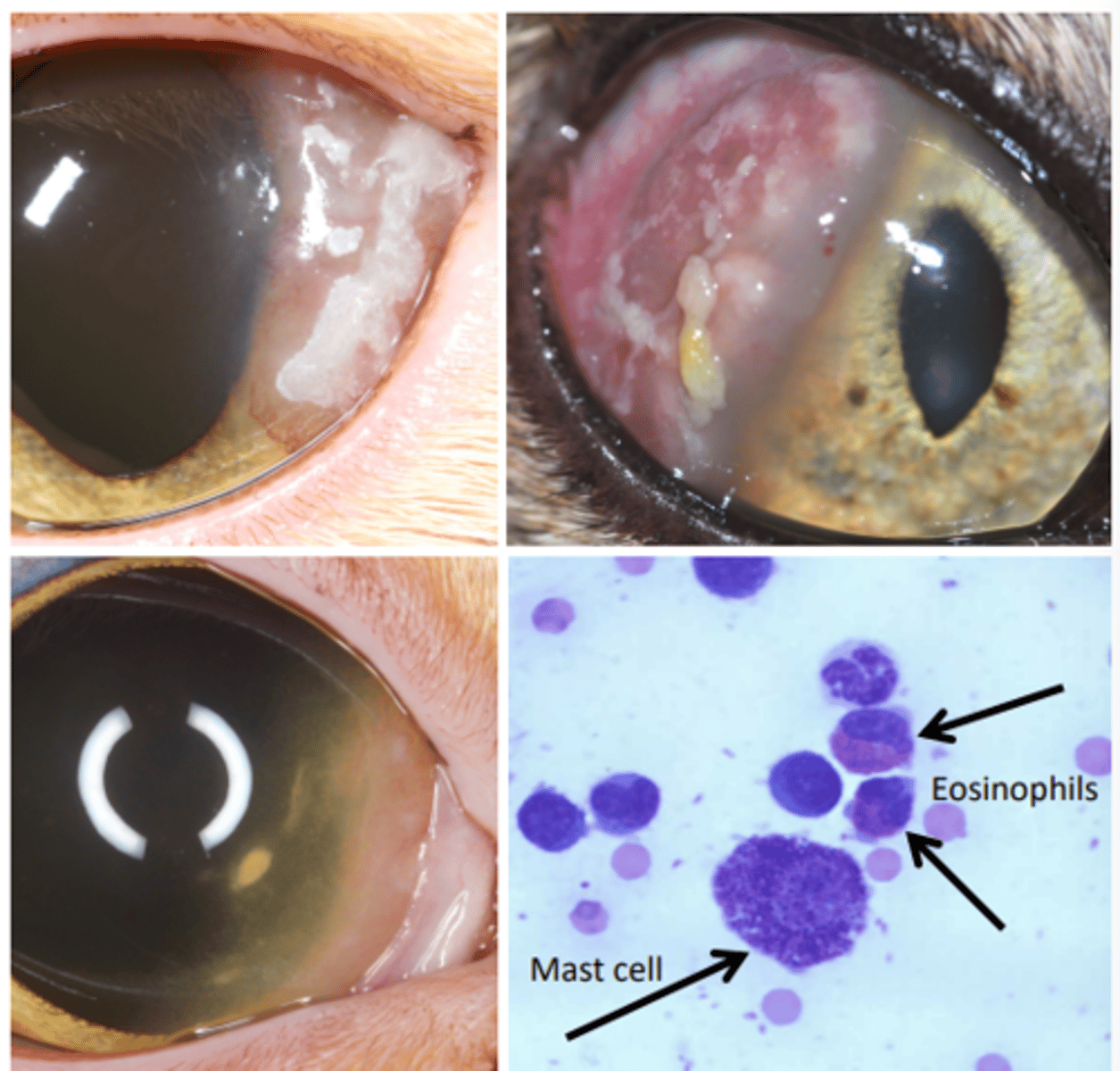
Cytology —> eosinophils, mast cells
How is eosinophilic keratitis diagnosed?
Lifelong immunomodulatory maintenance:
- Topical cyclosporine or tacrolimus
- Topical megestrol
- topical dex (if no ulcer)
What is the treatment for eosinophilic keratitis?
Pigment keratopathy
What am I describing?
- Brown opacities
- Seen in 80% of all pugs
- Hard to remove pigment once it occurs
- Progresses medial to lateral
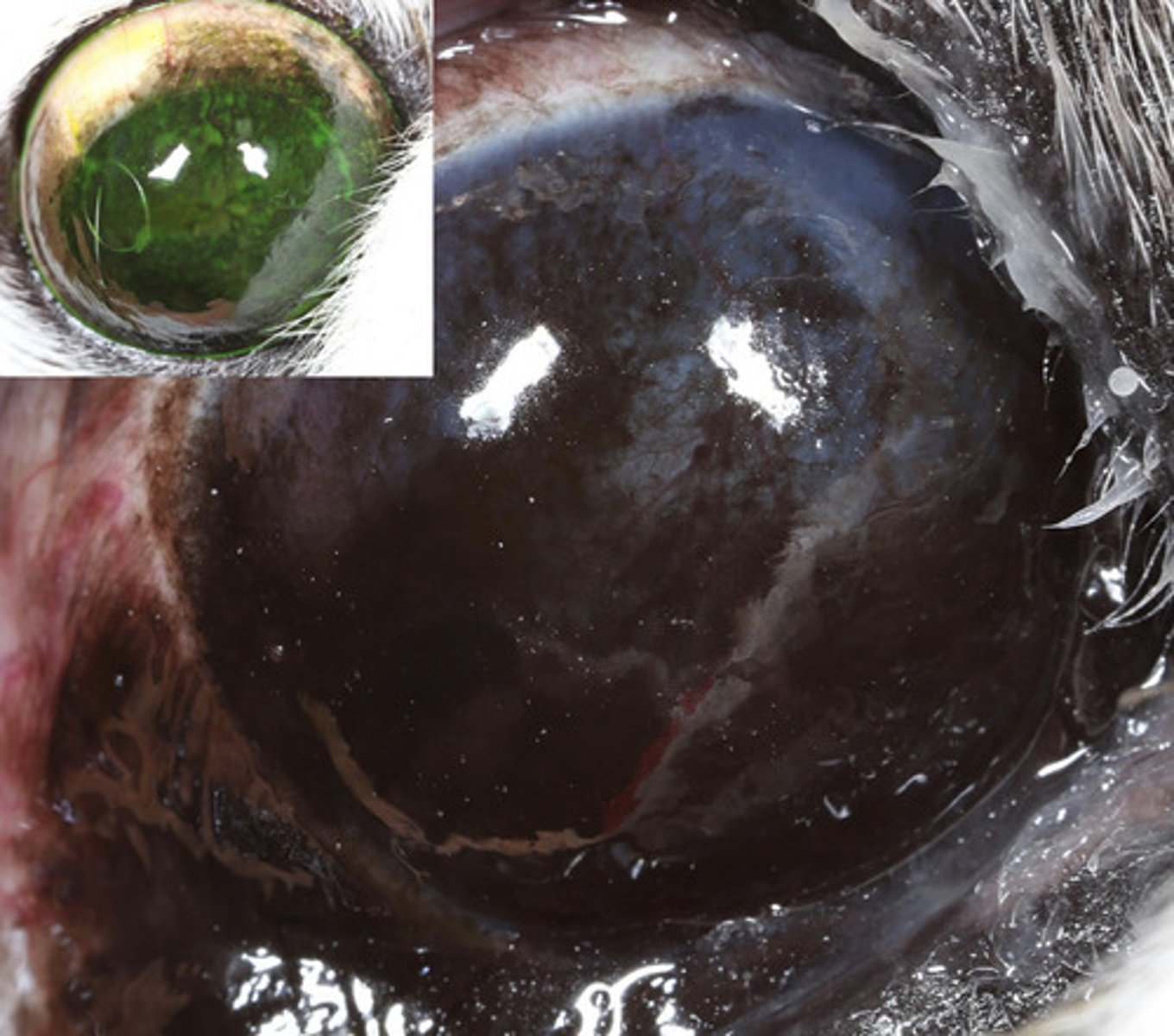
prevent blindness
pigment keratopathy treatment goal?
- Topical cyclosporine or tacrolimus
- Topical dexamethasone
- Lubricant
- Medial canthoplasty
What is the treatment for pigment keratopathy?
Limbal melanocytoma
What am I describing?
- Brown opacities
- Bi-modal age distribution (3-4y, 7-10y) and aggressiveness (rapid in young, slow in old)
- Seen in German shepherds, golden retrievers, and labradors
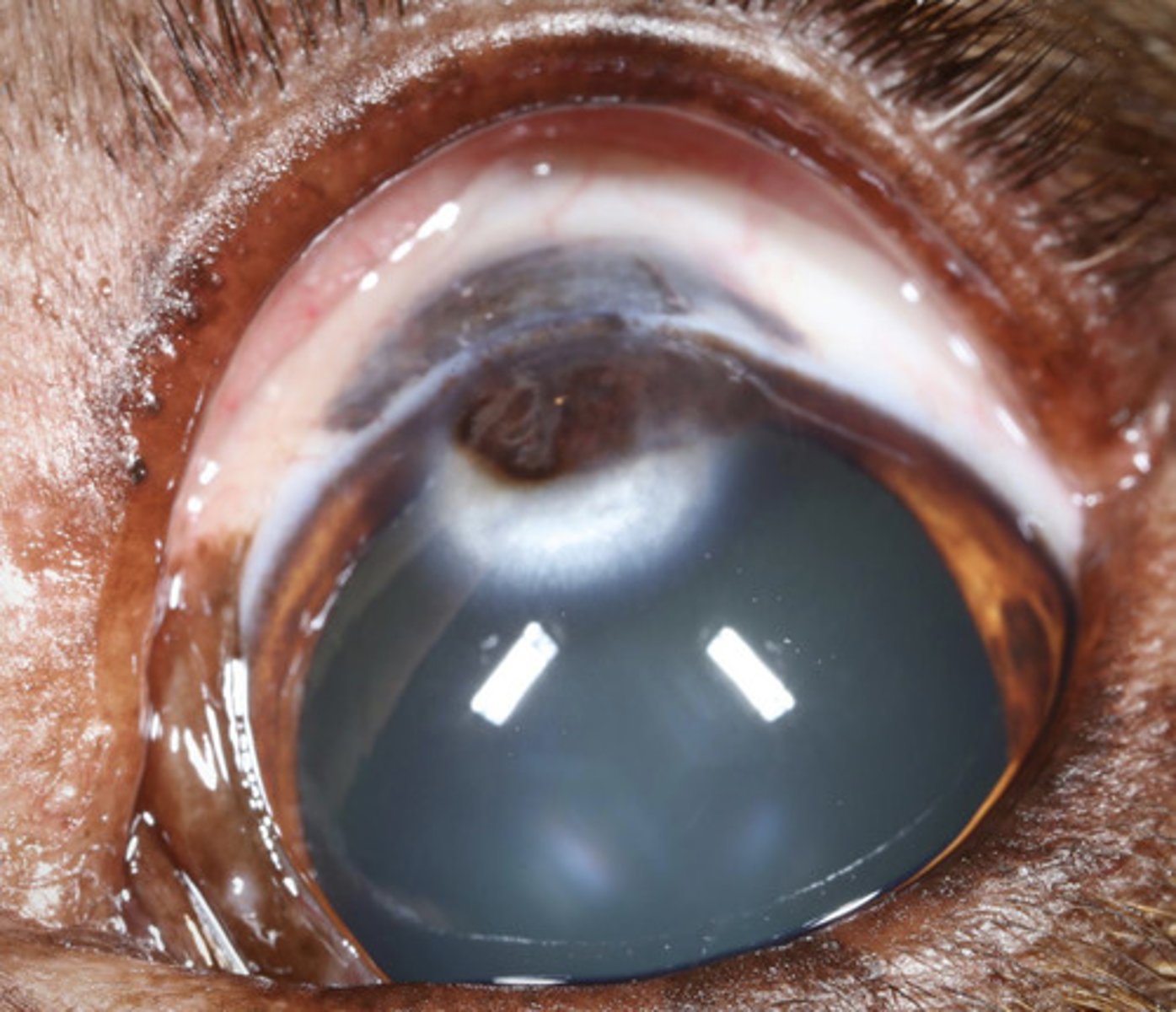
Refer
What is the treatment for limbal melanocytoma?
Feline corneal sequestrum
What am I describing?
- Brown opacities
- Necrotic stroma
- FHV-1 may play a role
- Can vascularize and slough
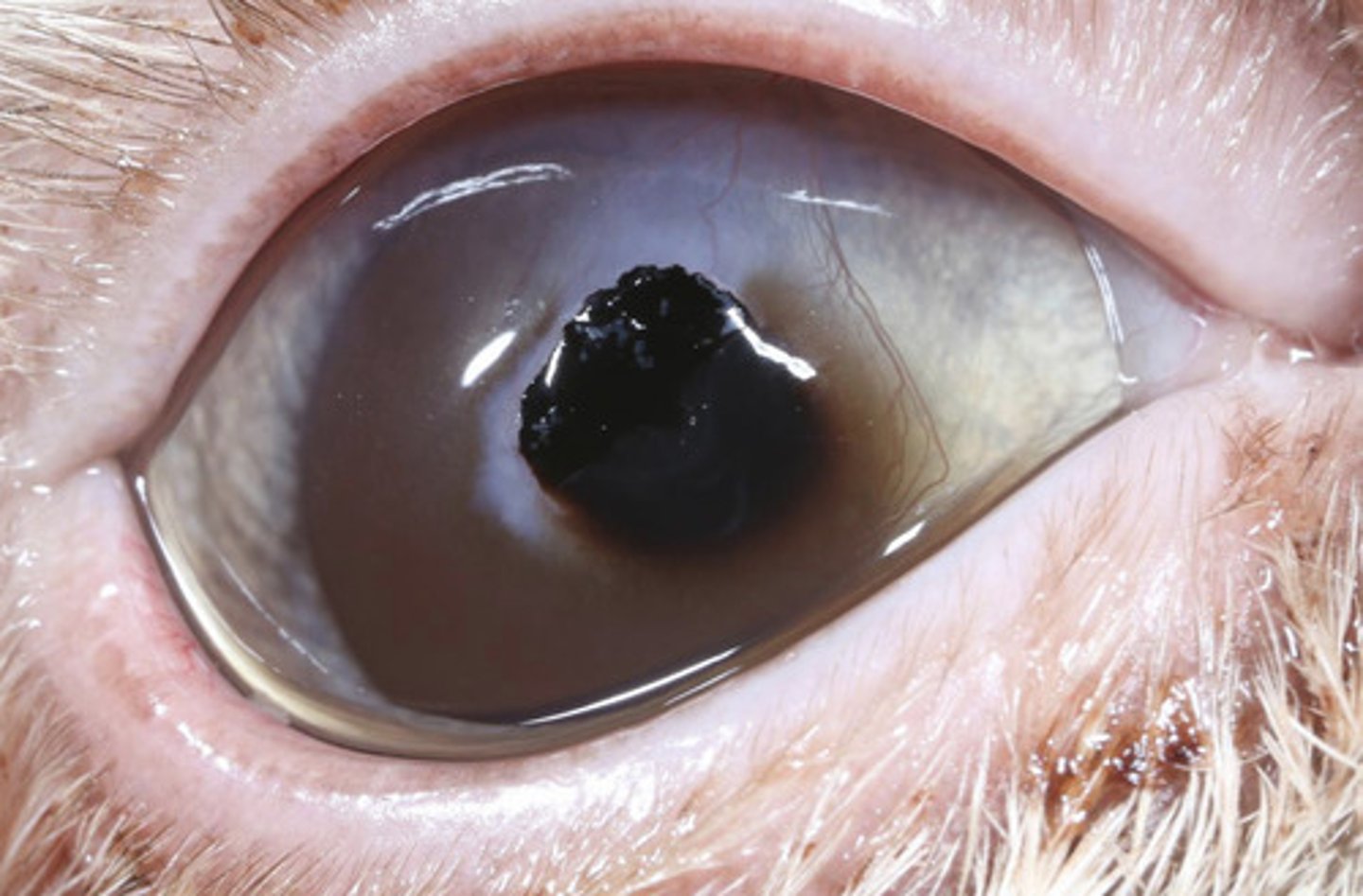
- Topical antibiotics if ulcerated
- Cycloplegia
- Analgesia
- Surgery only definitive tx -- REFER
What is the treatment for feline corneal sequestrum?
Surgery
What is the treatment for dermoids?
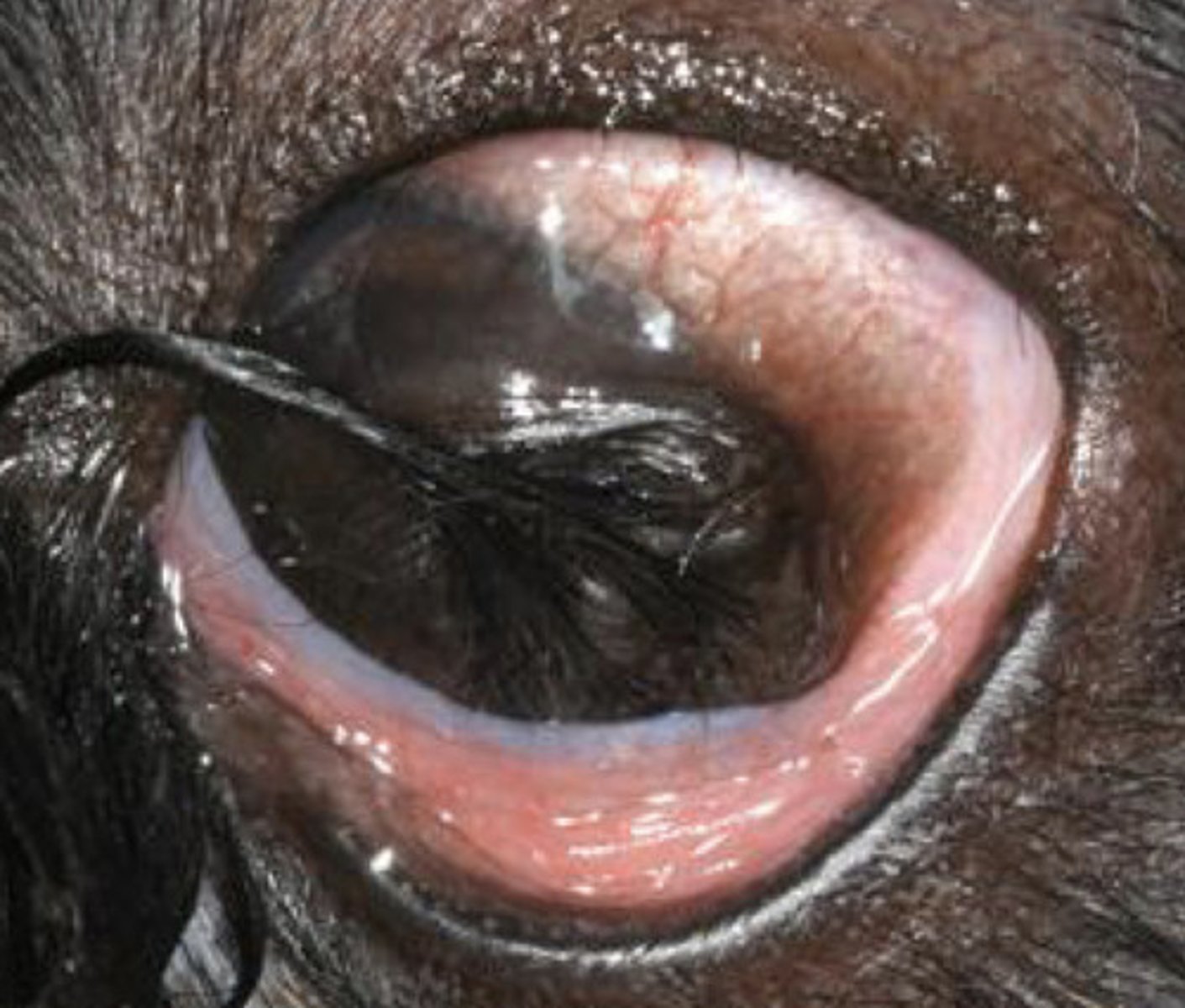
Brown
What color opacity is seen with a dermoid?
benign, congenital growth of skin-like tissue (choristoma) in an abnormal location, often containing hair, sebaceous glands, and connective tissue.
what even is a dermatoid????
Brown
What color opacity is seen with an iris prolapse?
- Surgery
- Treats as an infected rupture
What is the treatment for iris prolapse?
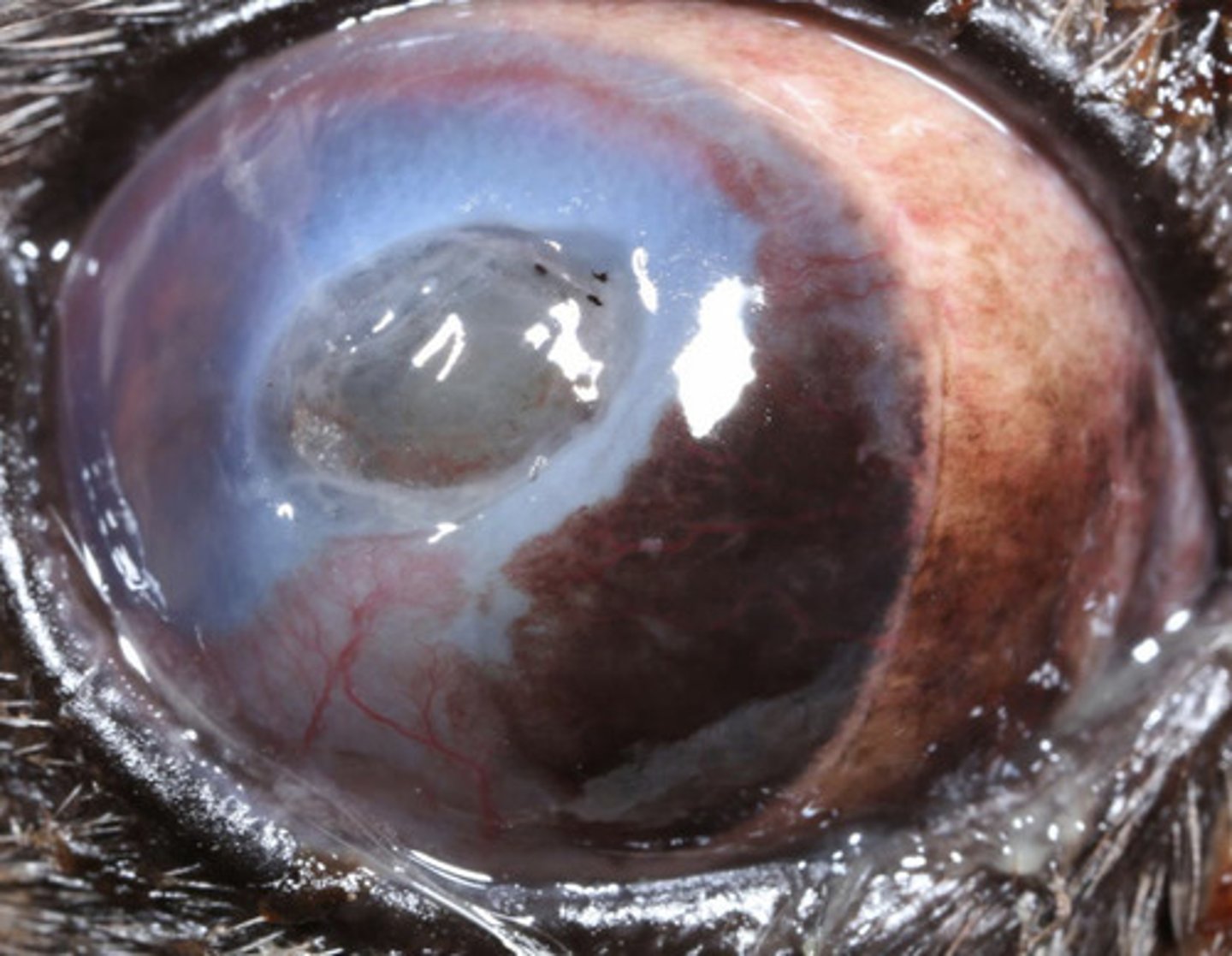
- Hydropulsion
- Treat as a superficial ulcer
What is the treatment for superficial foreign bodies?
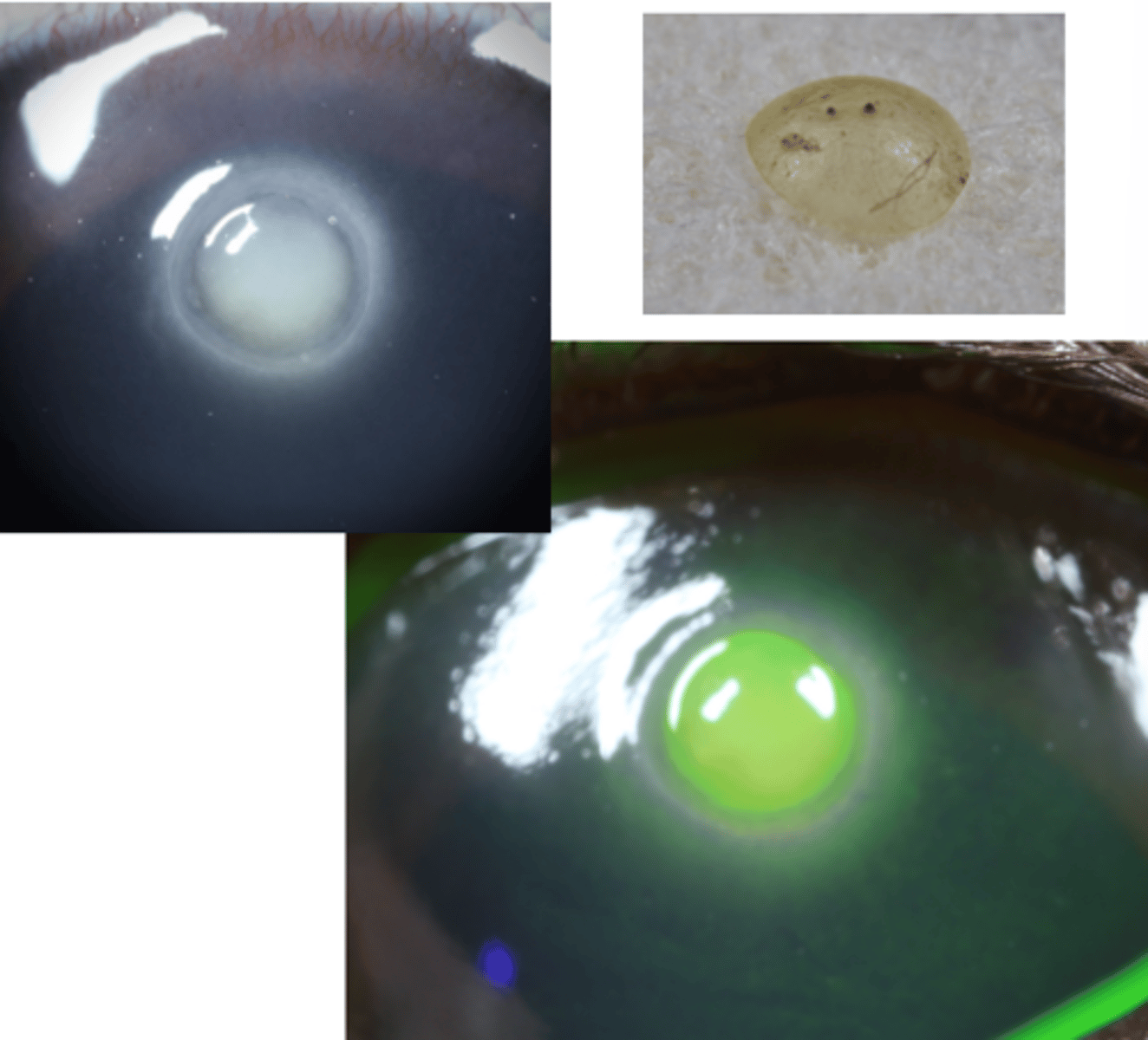
Surgery
What is the treatment for stromal, intraocular foreign bodies?
Lens capsule damage
What is an important prognostic indicator for stromal/intraocular foreign bodies?
As an infected stromal ulcer
How is corneal cellular infiltrate treated?
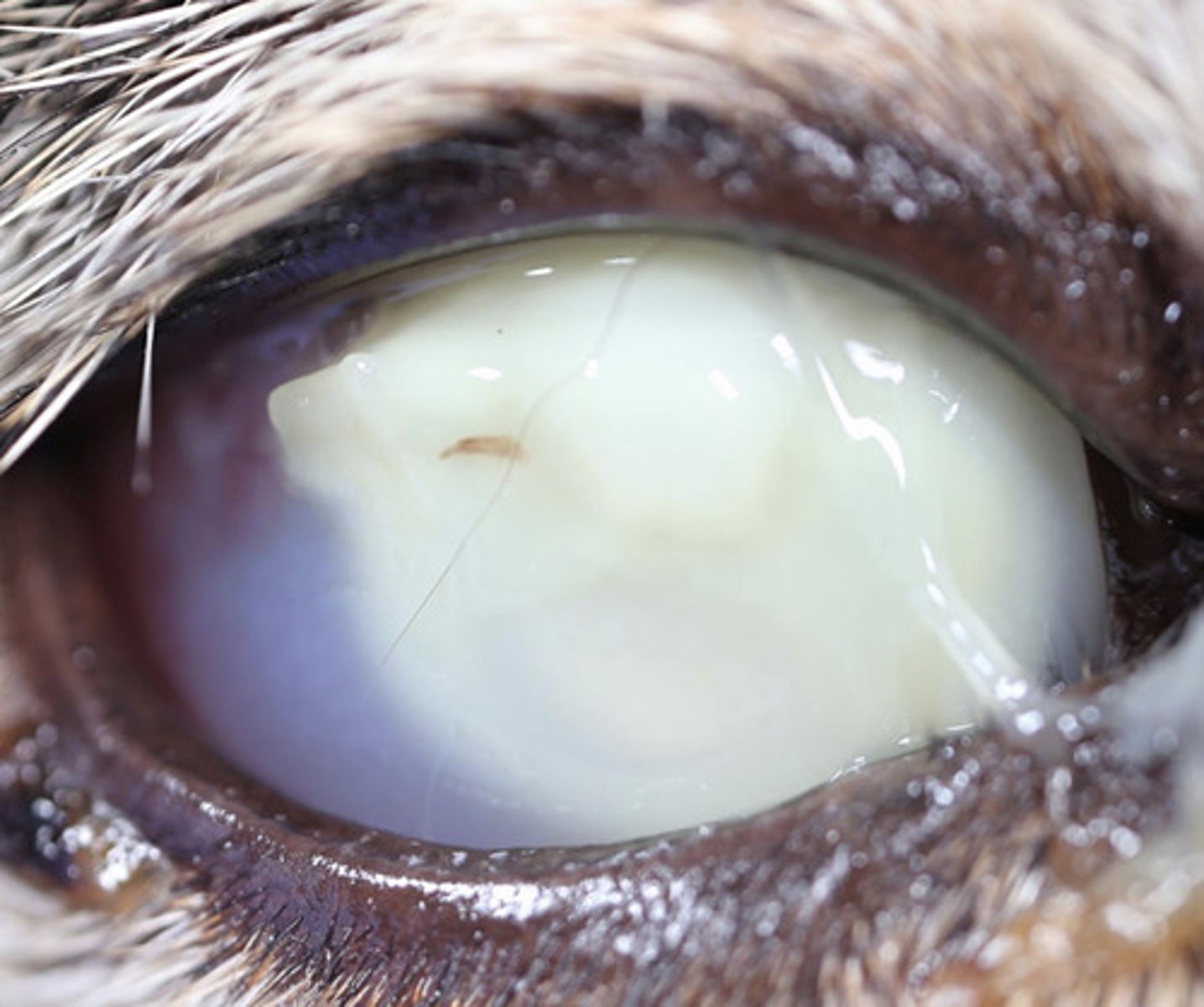
Fluorescein staining:
- Epithelium = no uptake
- Stroma = uptake
- Descemet's membrane = no uptake
How is corneal ulceration diagnosed?
loss of protective epithelium
Corneal Ulceration
- Superficial
- Not infected -- no infiltrate, organisms, or melting
- Heal in appropriate time (less than a week + minimal scarring)
- No complicating factors
Describe simple corneal ulceration.
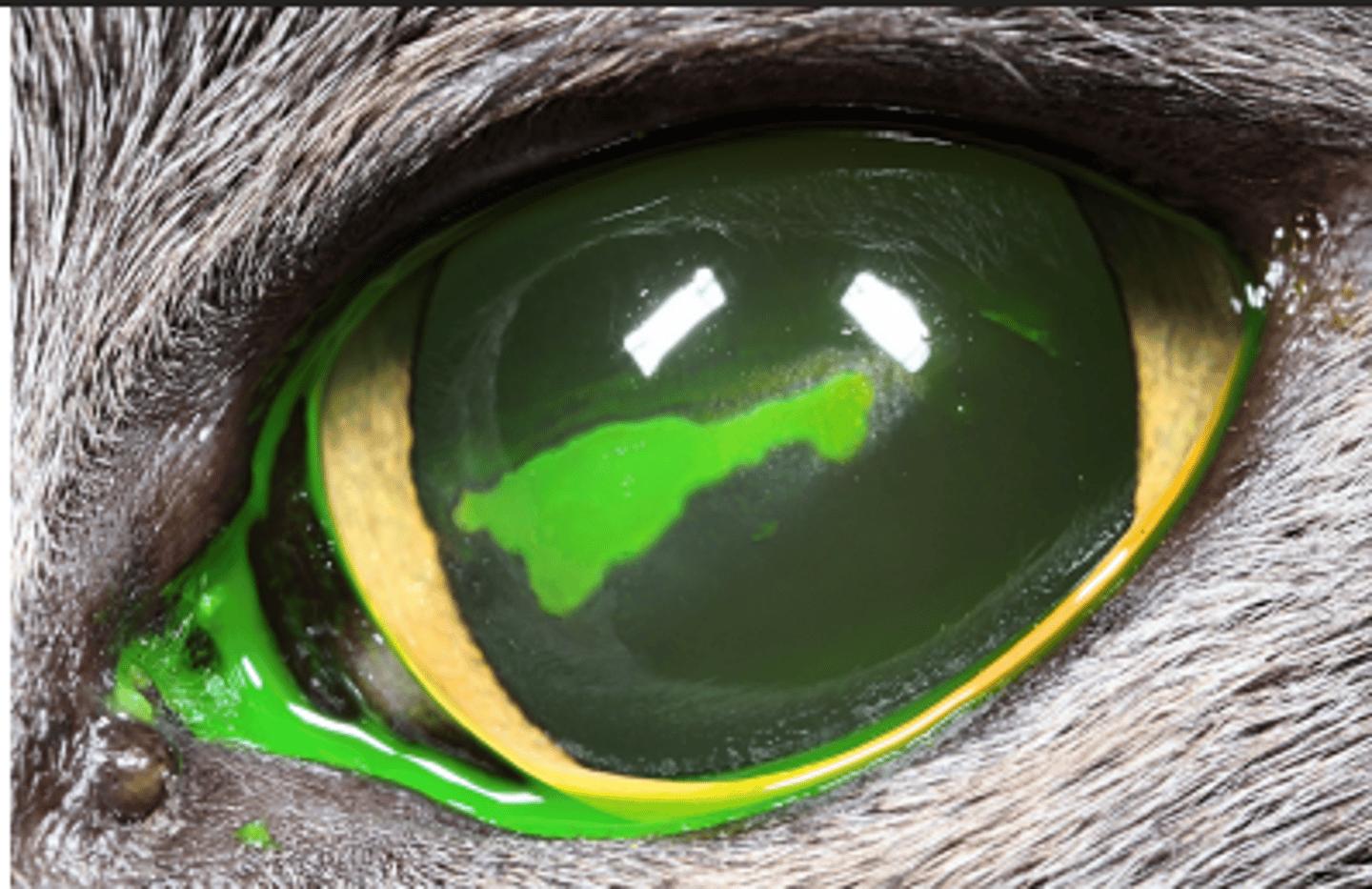

- Broad-spectrum topical antibiotics TID
- Atropine (cycloplegic)
- Analgesic / anti-inflammatory
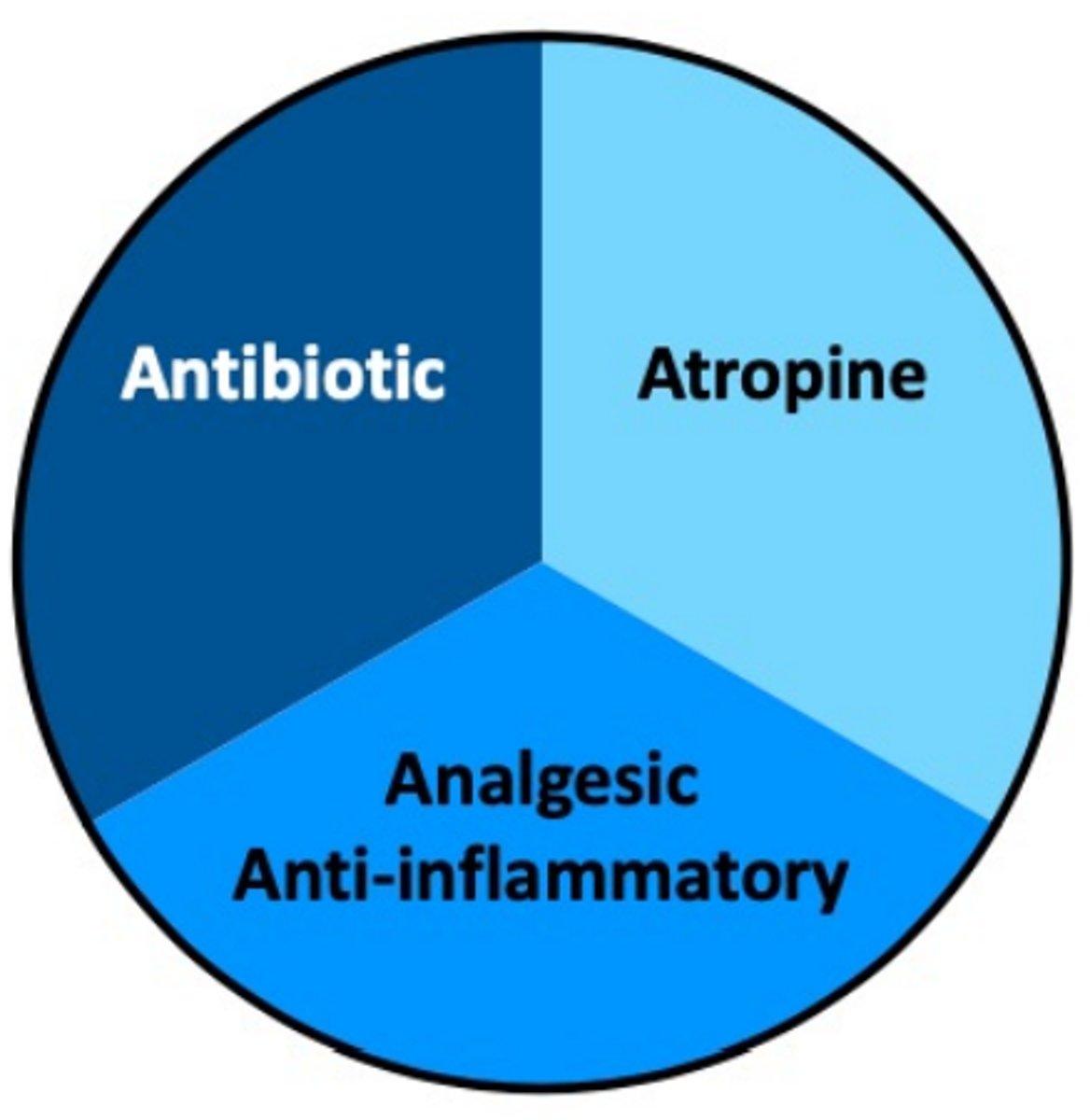
Goal - Prevent worsening while it heals on its own!
E COLLAR
What is the basic 3-pronged treatment for simple corneal ulceration?
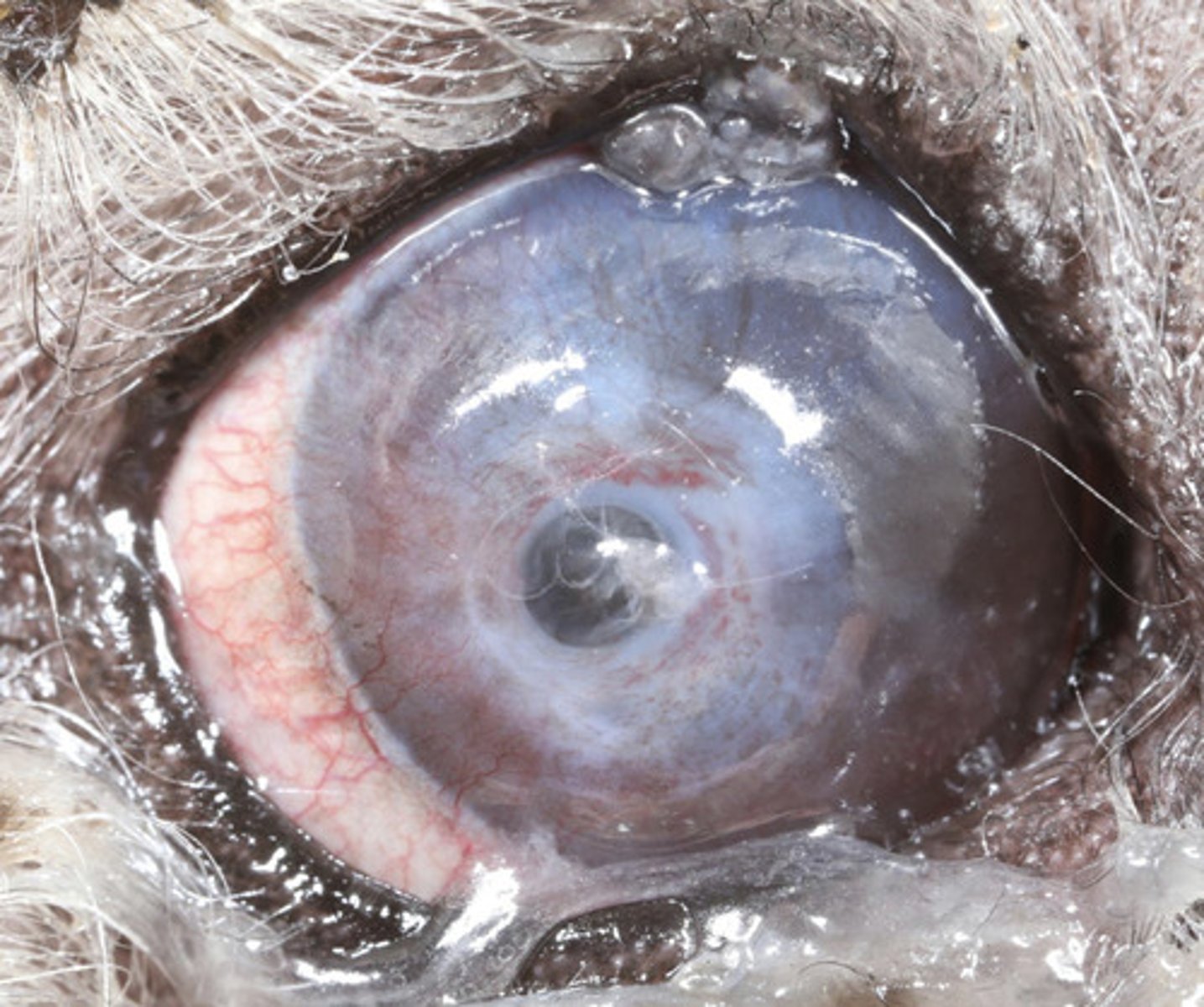
- Loss of stroma
- Infected / melting -- infiltrate, organisms
- Slow to heal >1w
- Complicating factors (Ectropion, KCS, eyelid tumors, distichiasis, ectopic cilia, neuro, Diabetes)
Describe complicated corneal ulceration.
Is the dog visual? (PLR)
- If not —> enucleate
- If VISUAL, and no option for referral - nothing wrong with giving it a chance (especially in young, cats, no other ocular problems)
What is the first decision to make when treating complicated corneal ulceration?
Refer or not refer?
- If >50% depth, consider referral for surgical grafting
- LEAKAGE: If Seidel positive, immediate referral
What is the second decision to make when treating complicated corneal ulceration?
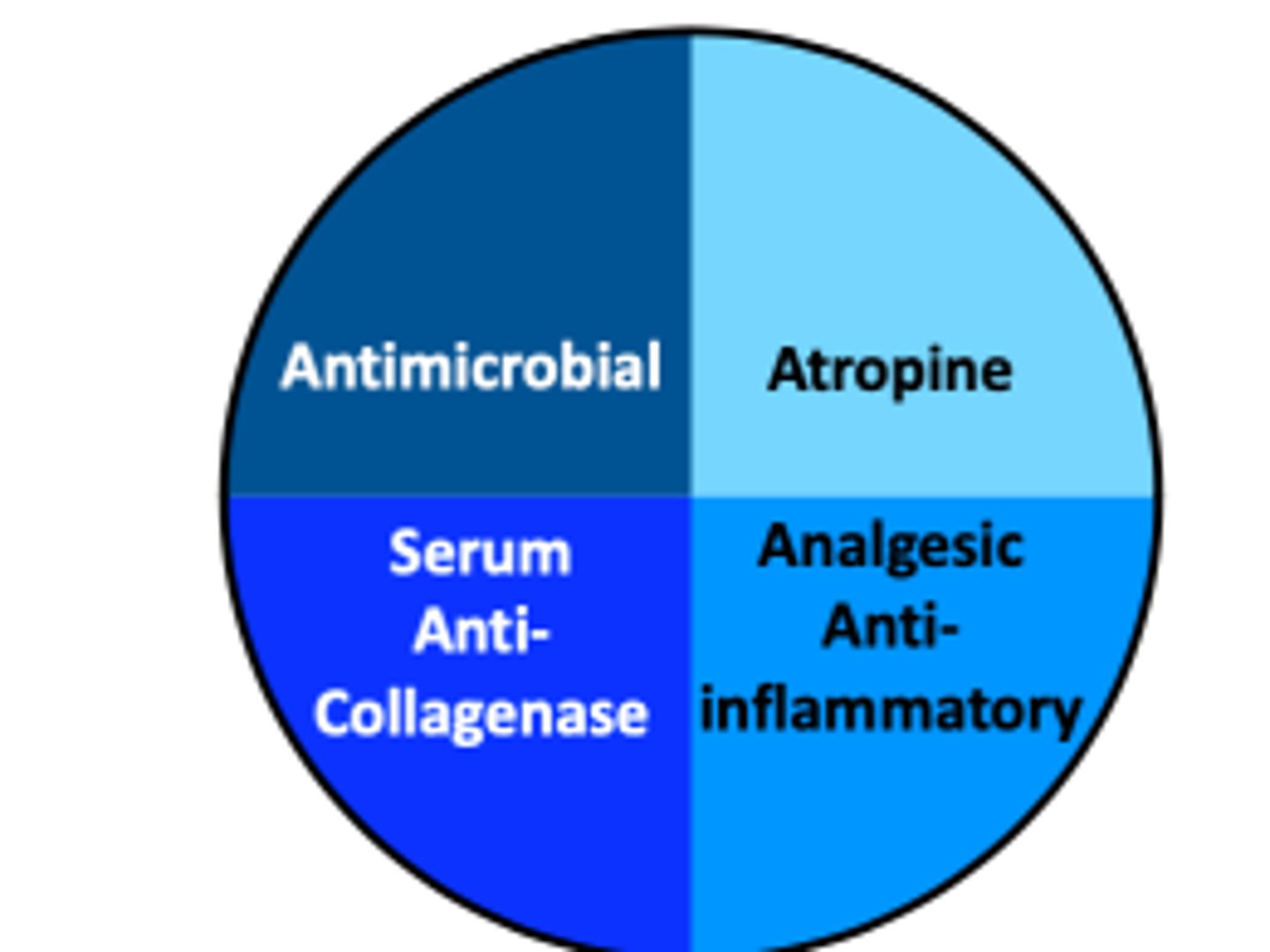
- Antimicrobials
- Atropine
- Analgesic / anti-inflammatory
- Serum anti-collagenase
(NO OINTMENTS)
What is the basic 4-pronged treatment for complicated corneal ulceration?
Indolent ulcers
What am I describing?
- Superficial ulcer
- No stromal loss
- Not infected
- Loose, non-adherent epithelium
- A stromal issue (failure to allow epithelial adherence
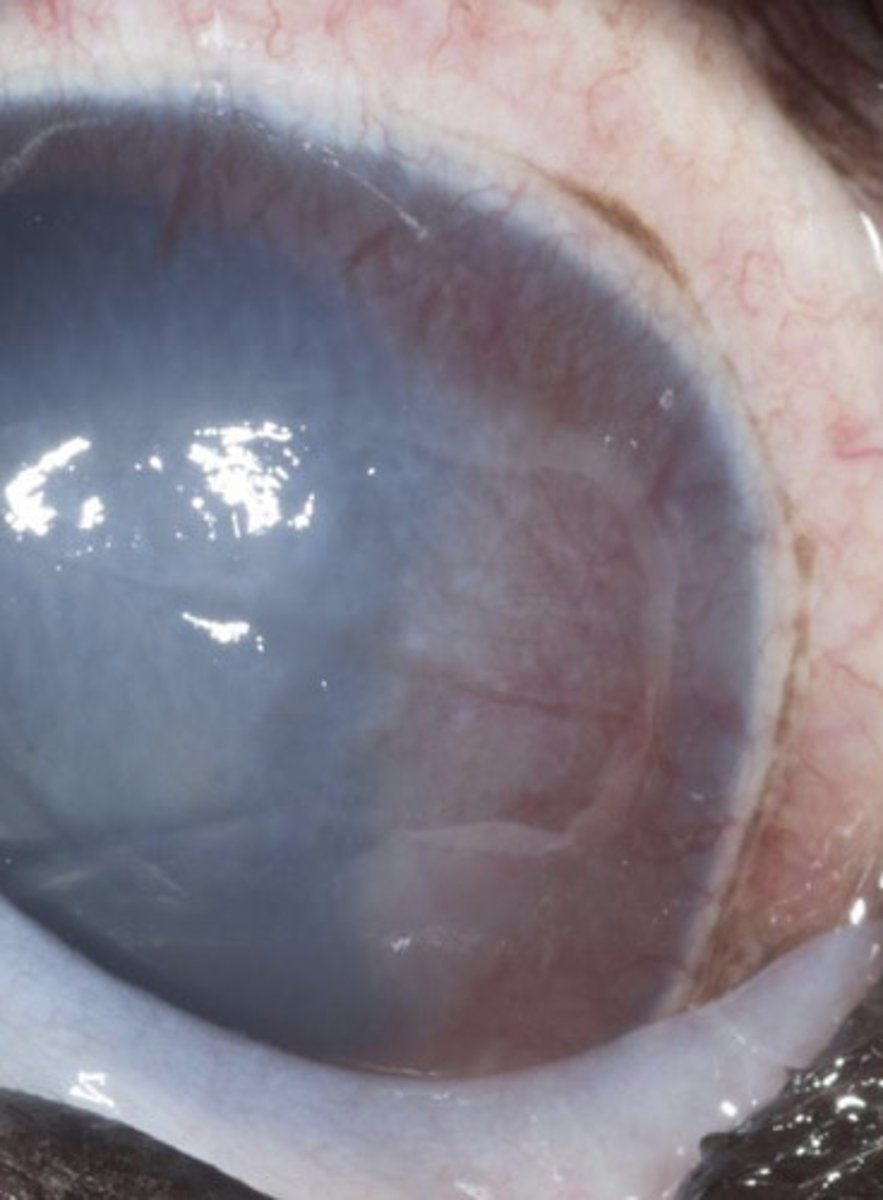
Boxers
What breed is predisposed to indolent ulcers?
- Topical analgesia
- Dilute betadine solution
- Debridement (cotton-tip debridement; diamond burr; grid keratotomy)
- Post-procedure management (e-collar, atropine, tetracycline, oral NSAIDs)
What is the treatment for an indolent ulcer?
FHV-1 keratitis
What is the most common cause of indolent ulceration in cats?
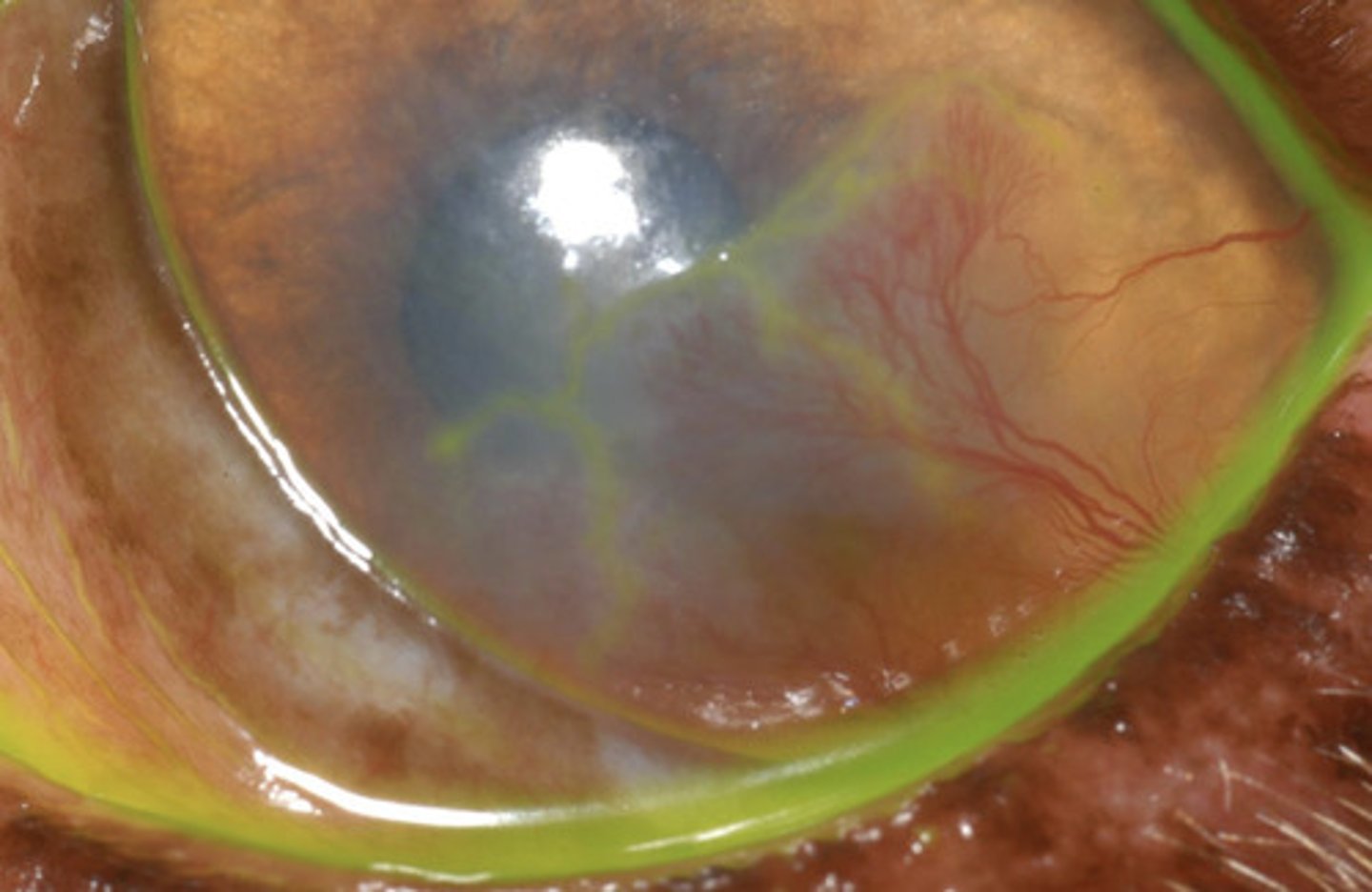
- Same as superficial ulcer (broad-spectrum topical antibiotics; atropine; analgesia) +
- Anti-viral therapy (Cidofovir)
- L-lysine
- Minimize stress
How are corneal ulcers due to FHV-1 keratitis treated?
Immune-mediated (poorly understood)
What is the etiology of episcleokeratitis?
- Cocker spaniels
- Collies
- Mixed breed dogs
What dog breeds are predisposed to episclerokeratitis?
- Parasitic granuloma (Onchocerca)
- Neoplasia
- Foreign body
What are 3 differential diagnoses for episclerokeratitis?
Episclerokeratitis
What am I describing?
- Immune-mediated
- Raised episcleral masses +/- vascular infiltrate in the perilimbal cornea
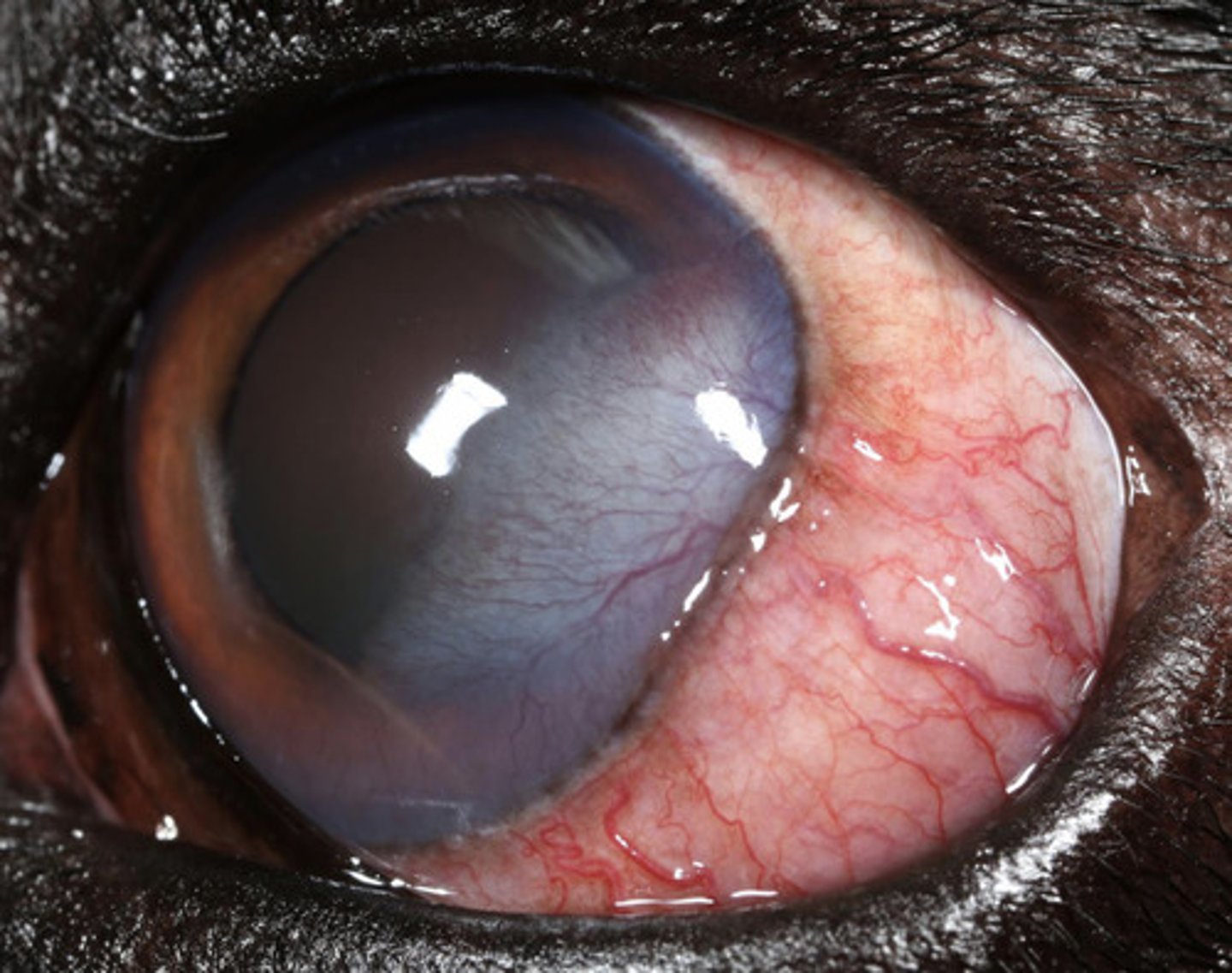
Immunomodulatory:
- Topical dexamethasone TID
- Topical cyclosporine or tacrolimus TID
- If poor response to topicals, can do oral or subconjuntival of cryotherapy
What is the treatment for episclerokeratitis?