Brain Circuit (Week 9/10)
1/121
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
122 Terms
Pavlovian conditioning is _____
2 Dimensional
2D categories for Pavlov
Stimulus-action event (Excitatory/inhibitory)
Motivation property event (Appetitive/aversive)
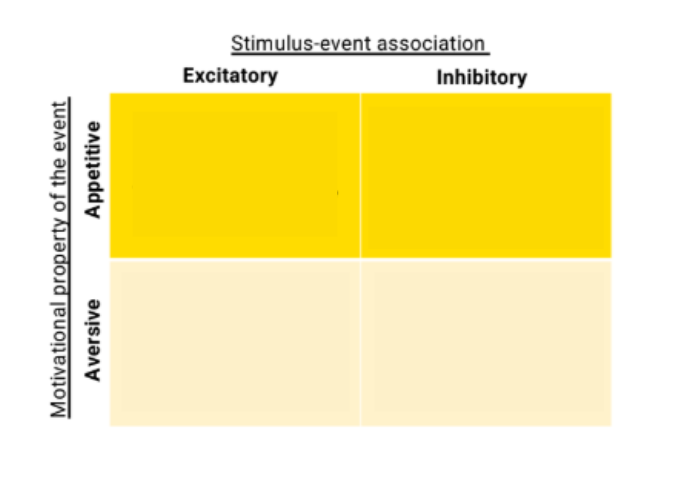
4 types of Pavlov conditioning
Appetitve excitatory = Stimulus present predicts arrival of food
Appetitive inhibitory = stimulus prediction omission of food
Aversive excitatory = Stimulus predicts electric shock
Aversive inhibitory = Stimulus predicts omission of shock
Types of Pavlovian CS
Discrete CS = have start & end —> ie. auditory, tone, light
Context CS = no. imminent start/end —> ie. conditioning chambers
CS that has start & end
Discrete CS
CS w. no end/start
Context US
How to distinguish discrete and context CS
Discrete = Test discrete CS in distinct chamber
Context = test in diff contexts (ABA, ABC)

At what points of time should the brain be manipulated to study acquisition, consolidation & retrieval
Acquisition = Before fear cond/ext
Consolidation = Just after fear cond/ext
Retrieval = Before test

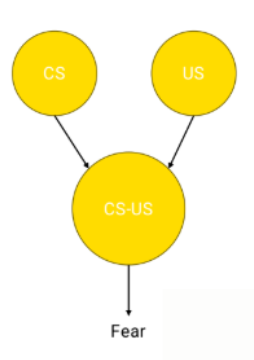
Process to how brain forms association (3 steps)
Process discrete CS individually
Process US
Combine info of CS & US —> form CAUSAL relo —> CS-US forming CR
Brain region for CS modality: auditory CS
Auditory thalamus + auditory cortex
Brain region for CS modality: visual CS
Visual thalamus + visual cortex
Brain region for CS modality: context CS
Hippocampus
Hippocampus related to ____ CS
Context
Auditory/visual thalamus + cortex related to ____ CS
Auditory/visual CS
Difference between thalamus + cortex
Thalamus = process info more rapidly
Cortex = Provides more detailed info
____ processes info more rapidly
Thalamus
y
____ provides more detailed info than ____
Cortex, thalamus
Where is the hippocampus found
Medial temporal lobe
Medial temporal lobe holds _____ (2)
Hippocampus & amygdala
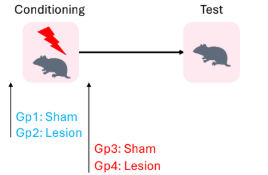
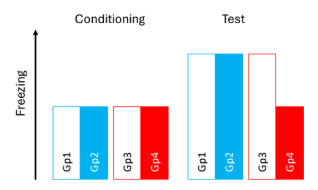
What happens when the hippocampus is silenced (via lesions) pre/post fear conditioning?
Pre-cond = No effect
Post-cond = decreased freezing
What conclusion could be made about the hippocampus (fear cond)
Pre-cond = prevent configural representation forming (prefer to use)
Lead to process elements independently —> Thus equiv freezing to controls
Only contextual conditioning
Post-cond = allowed configural representation formation
Post-lesion prevented RETRIEVAL
Thus no fear displayed
Configural rerpresentation
Elements of a context are linked and established as a “configural representation” of the space/context
Advantages fo configural representations (2)
Pattern completion —> enable retrieval all elements of context by perceiving a few
Reduces cog load
Which brain region does the dual-process theory occur
Hippocampus
Dual process theory of the hippocampus 3 assumptions
Context can be processed as separate elemental features in relevant elemental areas (ie. auditory, visual cortex/thalamus)
Context can be processed via configural representation
By default, brain favours configural representations (<cog. load)
Amygdala found in ____
Medial temporal lobe
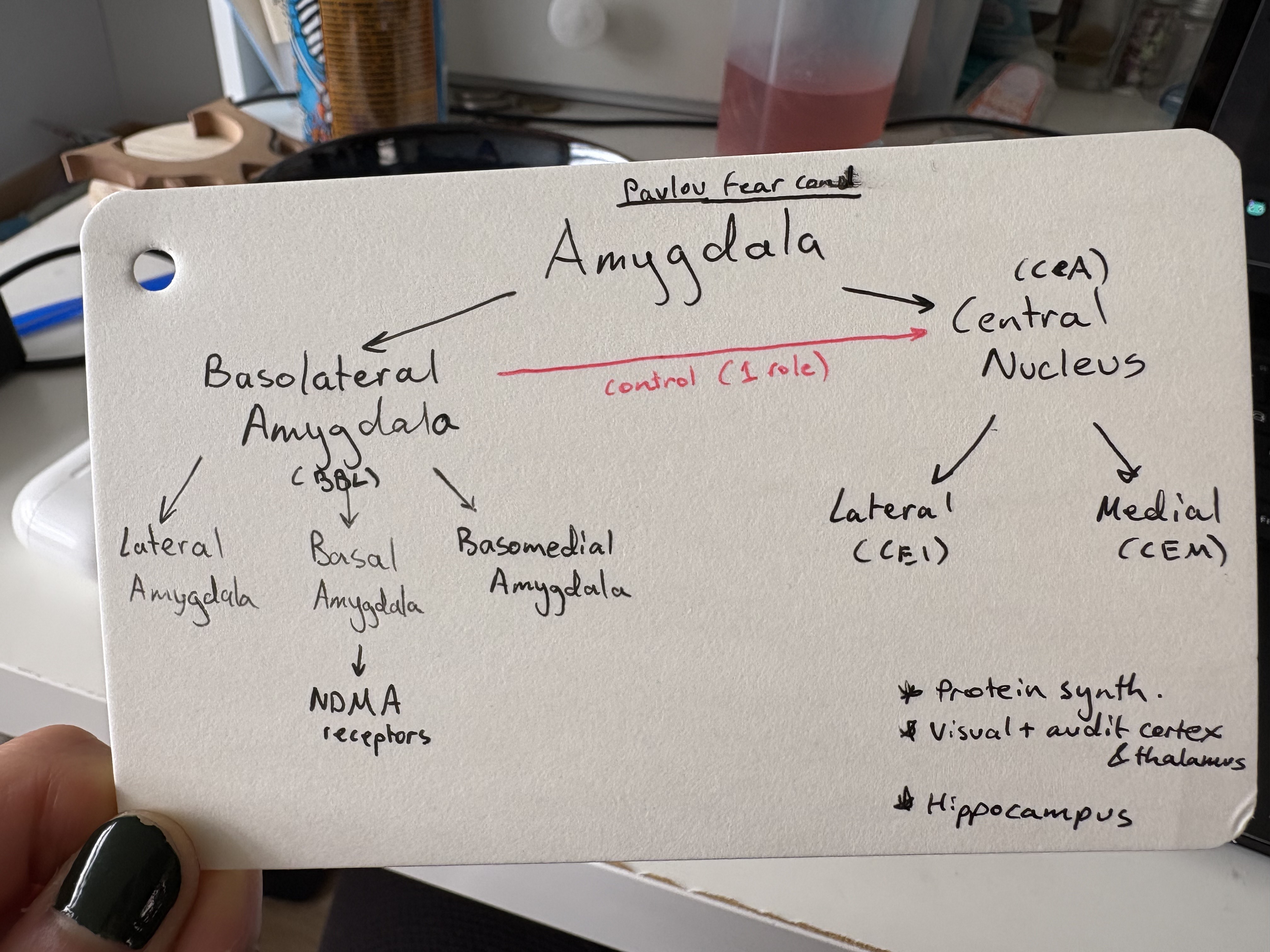
Subnuclei of amygdala (2)
Basolateral Amygdala & Central Nucleus
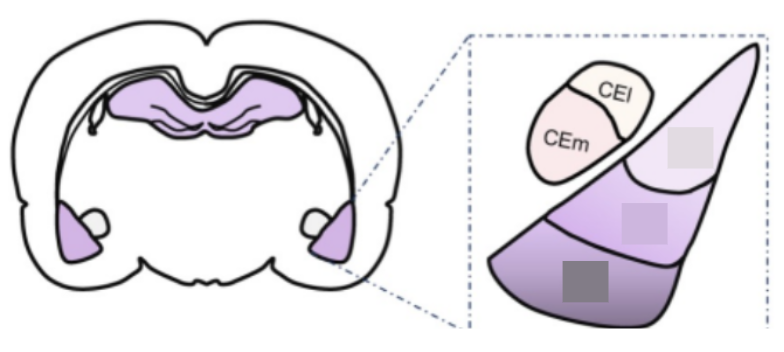
Basolateral Amygdala subnuclei (BBL)
Basolateral Amygdala
Basomedial Amygdala
Lateral Amygdala
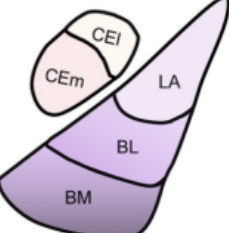
Lateral Amygdala purpose in fear conditioning
Receives discrete cue projections (auditory & visual) for fear cond
_____ receives discrete cue projections (auditory & visual) for fear cond
Lateral Amygdala

Basal Amygdala purpose in fear conditioning
Context fear conditioning —> receive hippocampus projections
____ receive hippocampus projections for fear conditioning
Basal Amygdala
Muscimol drug
Receptor agonist of GABA
Receptor agonist of GABA
Muscimol drug
GABA
Inhibitor of neuronal activity
Inhibitor of neuronal activity (receptor)
GABA
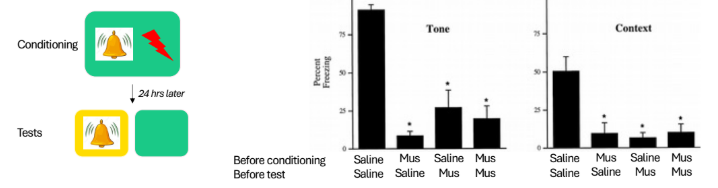
BLA inactivation findings
BLA needed for:
Acquisition of discrete cues + context
Retrieval/expression of fear memory
NDMAr purpose
Triggers memory formation (supports learning)
_____ Triggers memory formation
NDMAr
Ifenprodil drug
Blocks NDMAr —> wthin BLA
____ blocks NDMA
Ifenprodil
NDMA receptor inhibited pre/post conditioning results
Pre-cond = Impaired acquisition
Thus NDMA needed for ACQUISITION
Post-cond = No effect (no retrieval impairments)
What happens during consolidation (post-conditioning)
Protein synthesis to form CS-US pairings
Purpose of protein synthesis
Implementation of structural + physiological changes in neuron supporting a memory
Anisomycin
Blocks protein synthesis
_____ blocks protein synthesis
Animycin
Protein Synthesis Inhibition ___ conditioning results (increasing dosage)
Post —> consolidation = protein synth —> occur post-cond
>impairement of fear w. dosage
Protein synth is needed for CONSOLIDATION
Memory Engram
Phys + biochem changes in brain representing storage of specific memory
______ = Phys + biochem changes in brain representing storage of specific memory
Memory engram
What happens to neurons during memory engrams
Event activates neuronal ensemble (specific pop of neurons) that undergo physiological change
Change enable memory formation + storage
What does retrieval of memory involve (engrams)
Reactivation of specific neuronal ensemble
____ is the reactivation of specific neuronal ensemble
Retrieval
How are neuronal ensembles manipulated?
Condition in context A —> see which neuronal ensemble is activated
Tag activated neuronal ensemble w. OPSINS
Place in context A (test) —> should see neuronal ensemble light up
Place in context B —> Able to manipulate via optogenetics
Able to see fear in context A in B —> usually won’t happen
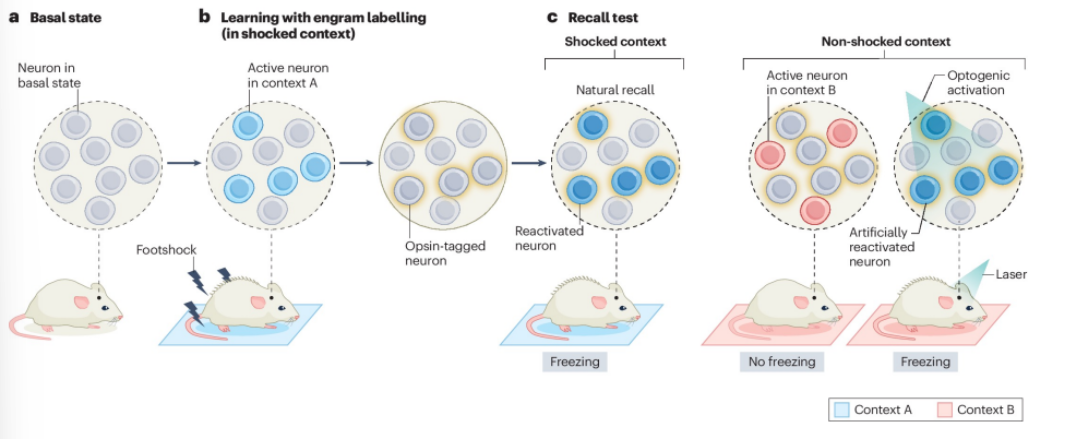
What genetic tool was used for neuronal ensemble manipulation
Optogenetics
What did fear engrams (tagging) support the BLA subnuclei’s indiv purposes?
Basal amyg = lit up during context fear
Ie. freeze more in high fear context
Amygdala = lit up during discrete fear
Freeze more from auditory cues
What did fear engram tagging suggest overall
Fear memory engrams are present within BLA
Involved in acquisition, consolidation & retrieval of memories
Muscimol drug used to inhibit GABA in:
BLA & CeA (Central nucleus Amygdala) & Interlimbic Cortex
Ifenprodil used to inhibit
NDMA receptors in BLA
Anisomycin used to inhibit
Protein synthesis
CeA inhibition findings pre cond/testing:
Pre-cond = Little fear
Couldn’t form memory
Pre-testing = little fear
Couldn’t retrieve/express memory
CeA needed for ACQUISITION + RETRIEVAL
CeA roles
Controlled by BLA + contribute to acquisition & retrieval of fear memories
Amygdala lesion but intact hippocampi?
Can process contextual, not discrete CS
Ie. don’t learn to fear auditory or visual, can process factual info
Whst brain region is hyperactive for anxiety disorders? Why?
Amygdala
Pavlovian fear cond increases amyg activity
CeA subnucleis
Lateral & medial
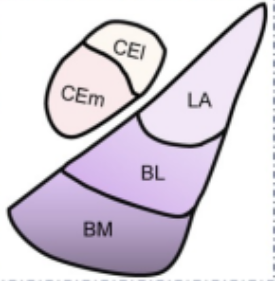
What are all the brain parts related to Pavlovian Fear Conditioning
Bonus: Purposes of each if can remember
Amygdala (2 subs, 3 and 2 extra sub respectively)
NDMA receptors
Protein synth
Cortex + thalamus (discrete)
Hippocampus (context)
Goal directed behaviour
Action based on its consequences & have goal
Help learn + update new skills
Cognitively demanding
Habitual behaviour
Little thinking/automatic behav
Little cog oversight
Help refine skills —> esp motor (ie. playing piano)
Can we look at performance to distinguish goal & habitual behav - why?
No, both forms promote actions & responses
Causality & value —> difference between goal & habitual
Goal
Have causal relo w. outcome
Deem outcome w. VALUE
Thus sensitve to change in causality/value
Habitual
Insensitive to change —> no cause or value
Can obtain via overtraining

Schedules of reinforcement difference between goal & habitual
Ratio = no. action correlate w. no. delivered outcomes —> goal-directed
Interval = time interval dictates outcome delivery —> habitual
What is contingency degradation used for?
Used to test causality in instrumental cond
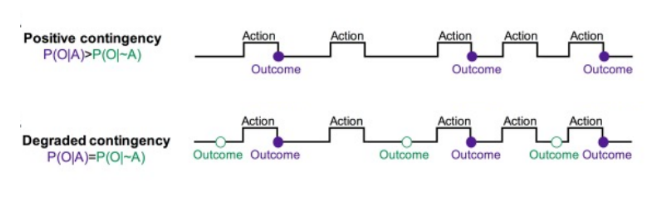
What is contingency degradation & probabilities
Tests for causality
Initially learn 2 positive contingencies (lever = outcome)
Prob. higher for CS-US than CS-noUS when press lever
Then freely deliver outcome sometimes during instrumental conditioning
Equal prob. in CS-US & CS-noUS
Lead to causality loss
What is the probability of CS-US & CS-noUS in positive contingency learning
CS-US higher than CS-noUS
What is the probability of CS-US & CS-noUS in positive contingency degradation
Equal chance of both
Contingency degradation effect
Perform non-degraded action more than degraded action
Larger for goal-directed indiv (loss of causality)
Smaller for habituation
Is the contingency degradation effection larger for goal or habituation & why
Goal —> loss of causality
Habituation doesn’t need any causality to begin with
Outcome devaluation purpose
Test whether goal directed behav. is influenced by value
Cause one lever to be more “valued”
Types of outcome devaluation
Sensory-specific satiety & conditioned taste aversion
Sensory-specific satiety
Gives hungry animal free access to one food for brief time period
Gorge themselves w. outcome (devaluing)
_____ gives hungry animal free access to one food for brief time perio
Sensory-specific satiety
Conditioned Taste-Aversion
Outcome given freely too
But injected w. LITHIUM CHLORIDE —> make mildly sick
Repeated process (associate food w. sickness)
Takes away food appeal
_____ gives outcome freely, then makes mildly sick using ____
Conditioned taste aversion, lithium chloride
Lithium chloride use:
Outcome devaluation
Make sick & devalue an outcome
Tests for instrumental conditioning are extinction tests because:
Reflect animal’s knowledge of what was encoded during training
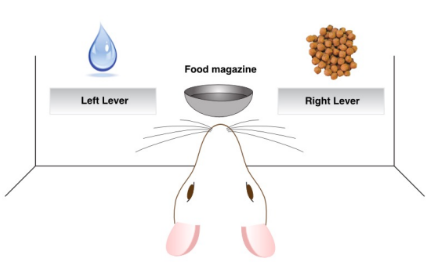
Specific satiety testing between 2,5 & 20 days results & type of behav
2-5 days show devaluations effect
More response to “valued” than devalued
GOAL-DIRECTED
20 days showed no devaluation effect
Equiv response between both lever outcomes
HABITUATION
Which brain sections are related to goal-directed behaviour:
Amygdala & prelimbic cortex’s: medial prefrontal + dorsal striatum
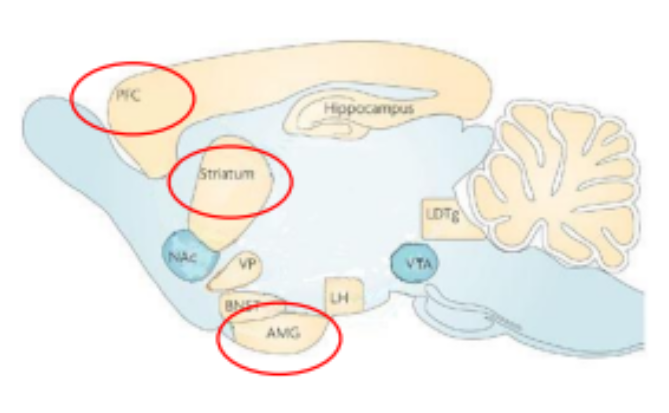
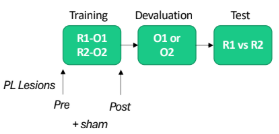
Prelimbic cortex & specific satiety test & pre/post lesions
Pre-cond w. lesions = show habituation
Therefore show prelimbic cortex necessary for ACQUISITION of value
Post-cond w. lesions = show outcome devaluation
Not necessary for consolidation
Is the prelimbic cortex related to goal directed/habitual behaviour
Goal-dirercted
Prelimbic cortex relevance in goal-directed behaviour
Acquisition of value
Striatum relevance to humans
Represents instrumental conditioning in humans via CAUDATE
posterior vs anterior lesions & specific satiety
Lesions for either posterior or anterior were presented pre-cond
pDMS showed indifference between levers
pDMS needed for acquisition of goal-oriented actions
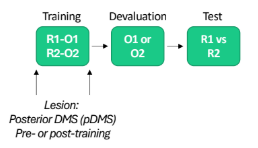
Further looking into pDMS (pt2) pre & post-cond lesion for specific satiety
Pre-training = shows insensitive to devaluation (equal pressing)
Post-training = shows insensitive to devaluation (equal pressing)
Therefore important for RETRIEVAL OF GOAL-DRECTED ACTIONS
BLA (basolateral amygdala) pre-cond lesions results for specific satiety
Insensitive to specific satiety
Relevant for ACQUISITION
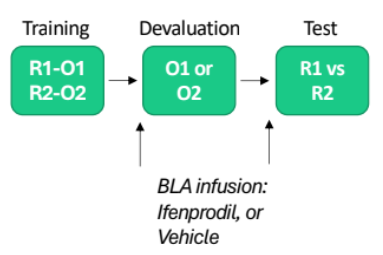
BLA (pt2) specific satiety (pre & post devaluation)
Pre-devaluation = showed insensitive to devaluation
Post-devaluation = showed sensitive to devaluation
Results higher than vehicle’s valued lever
Overall imply that BLA is important for processing changes in assignment of value
Not really involved in encoding contingencies
Which brain network involved in habitual actions
Corticostriatal network (Infralimbic cortex, dorsalateral striatum & central amygdala)
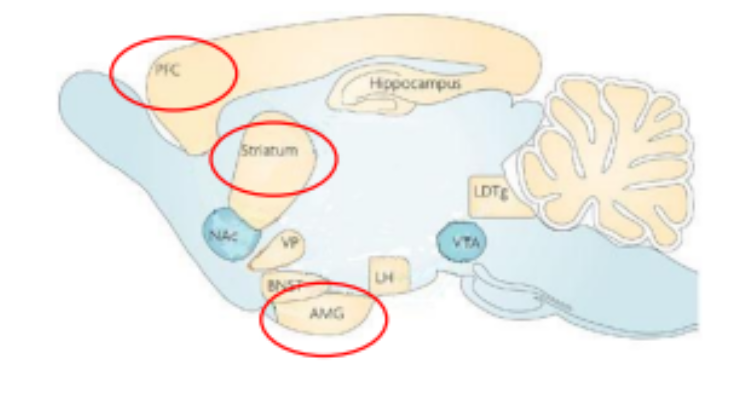
Brain parts involved in habitual actions (ICDS)
Infralimbic cortex
Dorsalateral striatum
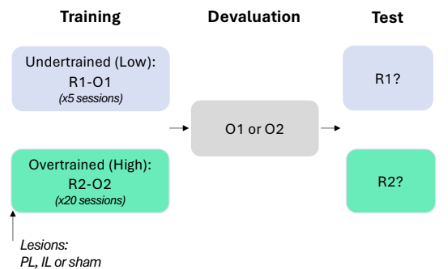
Infralimbic Cortex (IL) vs Prelimbic Cortex (PL) in outcome devaluation
Pre-training lesions
2 diff contexts trained in (overtrained and undertrained w. diff outcomes)
Undertrained
IL = show devaluation effect
PL = equal responding (insensitive)
PL have role in ACQUISITION OF GOAL DIRECTED ACTIONS
Overtrained
IL = equal responding (insensitive)
IL have role in ACQUISITION OF HABITUAL ACTIONS
PL = devaluation effect
Interlimbic Cortex’s role in instrumental conditioning
Needed for acquisition & retrieval of habitual actions
Prelimbic cortex’s role in instrumental conditioning
Needed for acquisition of goal directed action
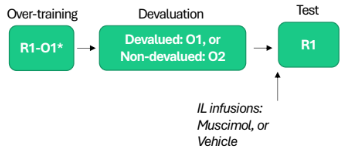
Interlimbic cortex study (devaluation)
Post-devaluation (muscimol infusion) of overtrained rats
Sensitive to outcome devaluation (despite overtraining)
IL needed for retrieval of habitual actions