Animal Behavior Final
1/334
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
335 Terms
Examples of physical features of the environment?
Jungle, ocean, desert, and air
Biologically relevant features for deer?
Identifying the tasty grass from short distance
Biologically relevant features for falcon?
Detecting a mouse from a distance
Biologically relevant features for Kingfisher?
Detecting a fish in the water
What does “turning the sensory system to the biologically relevant stimuli” mean?
Tuning the sensory system to detect stimuli that have biological significance
Typical spider eyes…?
Aim at the web
Jumping spider eyes…?
Promote hunting
What is the Reductionist approach?
Understanding complex systems by breaking them down into their simpler and smaller parts- might try to explain behavior or mental processes by focusing only on genetics or biological components
When you walk in the park you will be able to detect the sound and location or birds, people, cars. Based on the world as a cocktail party, what is the lake, what is the canals, and what is the handkerchiefs?
The park is the lake, your external ears are the canals, and you internal ears are the handkerchiefs
What is sensory neuroethology?
How the nervous system interprets sensory information
Visual system?
Relate the structure and location of eyes to the behavior
Auditory system?
Tuning of hearing to natural stimulus, echolocation
Example of integration of sensory information?
Visual and auditory information in the barn owl
Sensation Perception and Interpretation?
Anything we sense (touch, taste, smell, see, hear) requires billions of nerve cells to flash urgent messages along cross-linked pathways and feedback loops in our brains- performing calculations that we begin to explore
Since sensation perception and interpretation differ across species, this means?
Different animals sense different worlds
Characteristics of an Octopus and giant squids?
Advanced camera type eye, rectangular iris which contracts to a narrow slit- it can focus its eye lens for near and far vision, and a basis of control for all its arms, as well as look for food and watch for predators
Insect that has compound eyes?
Bees
What are compound eyes (ommatidia)?
Many individual units packed together to form the surface of the eye
What way do many insects need to see in while flying at high speed?
Three dimensions
Up to how much frames per second for fast-moving flying insects?
300
What do winged insects have better of than wingless ones?
Better vision
Visual wise, what way are insects better than humans?
Insects see a wider spectrum of colors than humans do
Reasons why insect vision is important?
To find plants for food and protection, and to identify each other
Why is it very unlikely that insects can see stars in the sky?
Because of small eye constraints
Fixed focus eyes must move in close to?
Get a good view
How many facets may bees have?
3,000 to 4,000
The center facets are larger than?
Peripheral sensors
What do bee eyes sense?
Polarization of light in the sky and also UV light
What colors do bees see best?
Blue colors, but they also see ultraviolet colors
Yellow flower may have markings that?
Reflect or absorb light in the UV region
What kind of eyes do dragonflies have?
They have large compound eyes with very wide-angle vision to allow them to see as they fly forward and backward
Describe the type of eyes flounders have?
They have two eyes at the same side
What animal can move its eyes independently?
Frog
Movable eye socket arrangements for?
Looking around to detect predators and food
What can some snakes do without visible lights?
Find warm targets to attack
What makes snakes have the ability to hunt and attack at any time?
Their vision in the infrared (IR) spectral region (thermal energy)- Targets are invisible to human eyes at night
Pit Viper has extended infra-red (IR) vision (well beyond where humans can see) and ?
Color vision
Because Pit vipers have thermal vision, what can they sense ?
Temperature differences of less than 0.03 degrees centigrade
The ability to sense heat waves (infrared radiation) evolved independently in?
Pit vipers, pythons. and boas
Infrared receptors at the pit organ?
TRPA1 channels
What is TRPA1 ?
A heat activated channel
What does “birds need more complex vision systems than many land animals, mean?
Bird rely more heavily on their eye sight than other animals
What do some birds use to navigate?
Sun and even star patterns
What’s an example of a bird having the best vision?
Eagles may see fish from 3,000 or 4,000 meters height (you cant even see the bird from that height)
Birds have the highest density of photoreceptors, what is an example?
The eyes of the hawk have 1 million photoreceptors per square millimeter
Kingfishers can see?
A reflection of a wish in the water
How do we know that Hummingbirds have good focusing ability of near and far objects?
They can see flowers at a distance and very small parts of a flower at close range
Like all cats, lions have retro-reflection characteristics that allow?
The eye to reflect light back to its source
What do lions and tigers need for hunting?
Their large eyes, with long-distance vision
What is an owl’s way of human’s rotating their eyes?
They turn their head at a considerable angel to accomplish the same purpose
What comes with Owl’s eyes being separated by a significant distance?
Good stereo vision and depth perception
What does tapetum lucidum mean?
Mirror in the back of the eyes
What are the two chances to capture a photon?
One the way in, and if not, on the way out
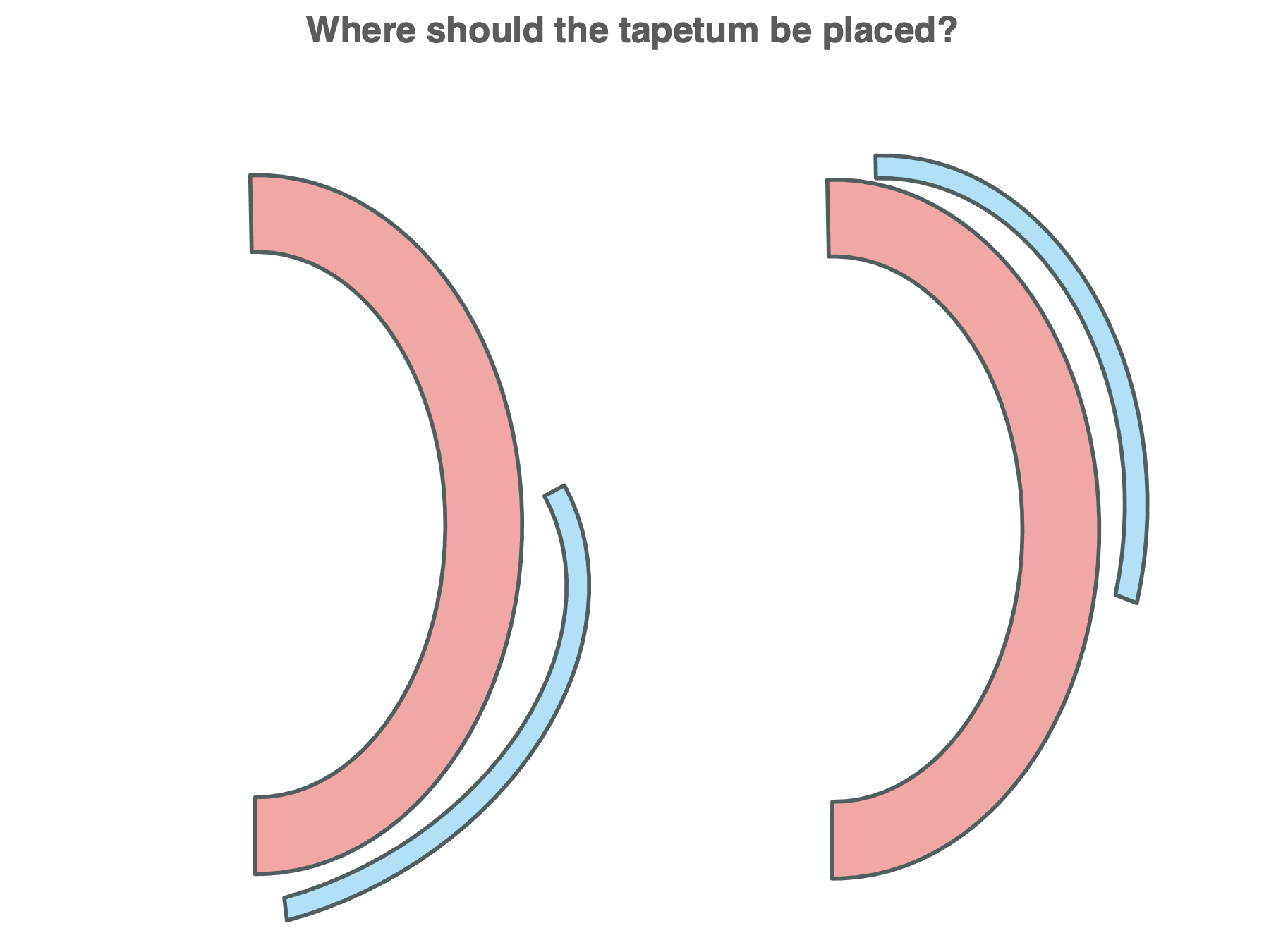
Where should the tapetum be placed?
Behind the retina so the light passes through the retina, hits the tapetum, reflects back, and gives the retina a second chance to detect it- the diagram on the right
Different ear structure means?
Different frequency ranges
Up to what frequency can most people hear?
Up to 20kHz
Bats hear and produce high frequency sounds for?
Echolocation
Low frequency sounds are made by?
Large animals that also travel long distance
Approximate Range (Hz) for human?
64-23,000
Approximate Range (Hz) for dog?
67-45,000
Approximate Range (Hz) for cat?
45-64,000
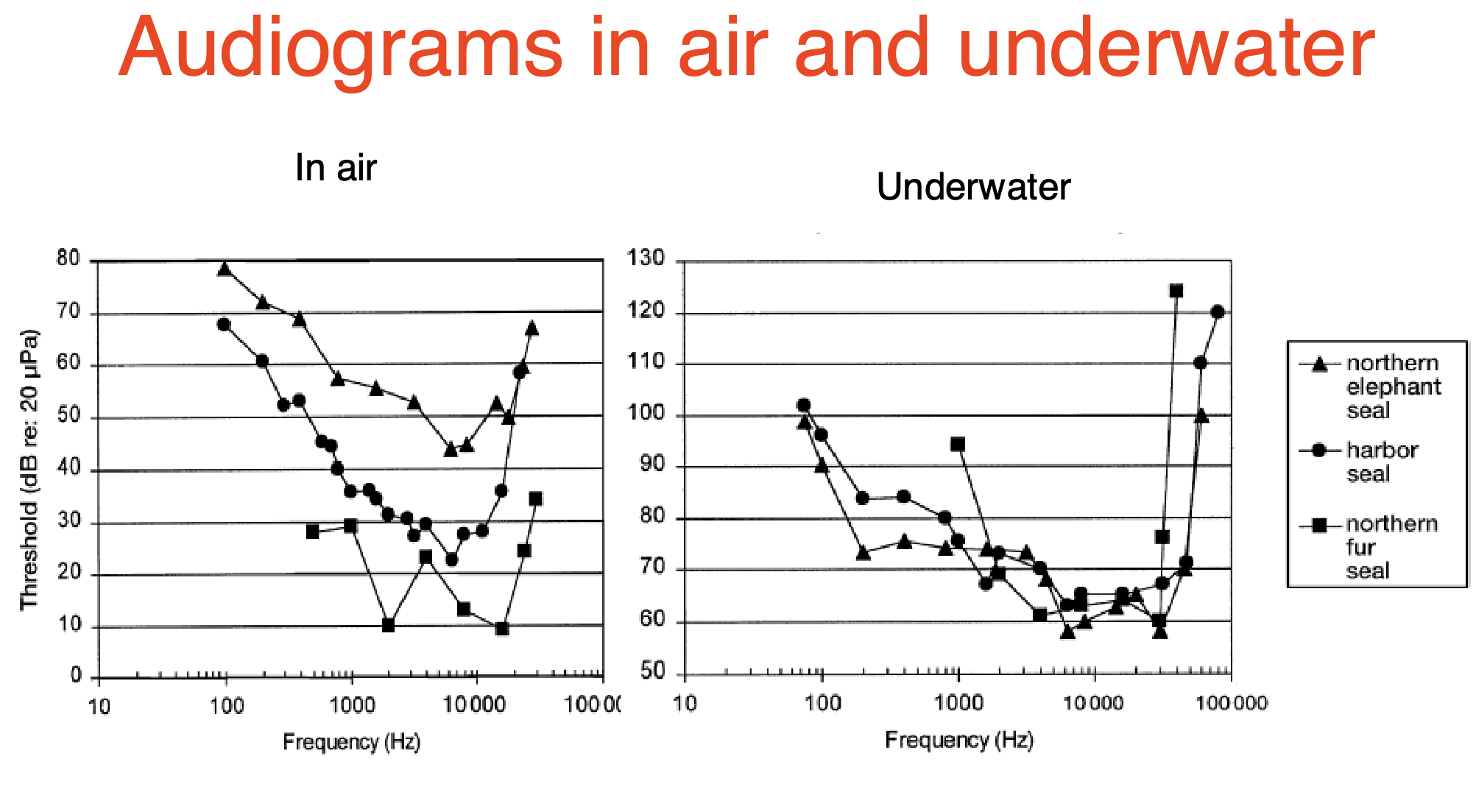
What does this graph show?
In Air, the northern fur seal hears best in air- since it has the lowest thresholds and high frequency, Underwater all three seals hear much better underwater than air, their thresholds are lower and more sensitive to higher frequencies
When do males become attracted to female buzzing?
24 after maturity
For humans, who has more acute hearing?
Woman than men of a similar age
For females when is auditory threshold lower?
Lower around the time of ovulation
What else is lower around ovulation?
Olfactory threshold
How does estrogen help humans and animals?
improve their memory
What is the most primitive sense in evolution?
Smell
When do humans get the ability to detect smell?
It is an innate ability- so when first born
What is the first smell babies encounter?
Their mother’s smell
What animals are very sensitive to the smell of fear in humans?
Dogs and Horses
Women can discriminate between armpit swabs taken from people who?
Were watching “happy” and “sad” films
What makes a person more attractive to a mosquito than other people?
Higher levels of carboxylic acids on their skin
Memory is often associated with smell so this means?
Smell and memory are intimately linked
How many smells can humans distinguish?
Around 10,000 different smells
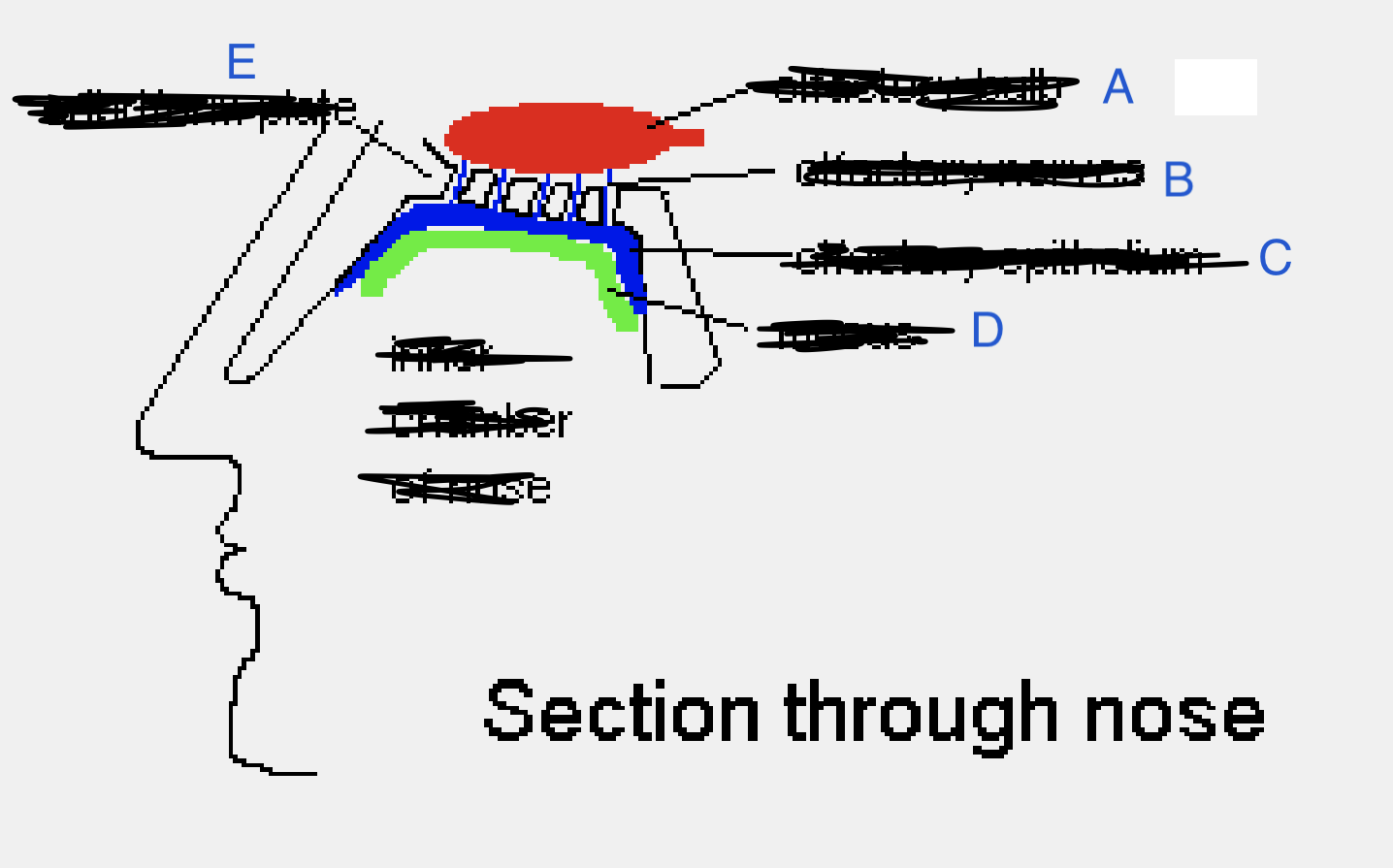
Name the parts in order
A. Olfactory bulb B. Olfactory nerves C. Olfactory epithelium D. Mucus E. Cribriform plate
What is ontop of the olfactory bulb?
Limbic area
Although there are hundreds of odorant receptors, how many are expressed in each olfactory receptor neuron?
Only one or at most a few
How many intact olfactory receptors (OR) are in a human?
About 400
What is the Olfactory epithelium?
Its a patch of cells that lie deep within the nasal cavity where neurons that sense odor molecules go
Each olfactory neuron in the epithelium is topped by ?
At least 10 hair-like cilia that protrude into a thin bath of mucus at the cell surface
What is the outcome of receptor proteins that recognize and bind odorant molecules?
Stimulate the cell to send signals to the brain
What does the olfactory cortex directly connects to?
The hypothalamus, which controls sexual and maternal behavior
How long does it take for the sensation of the olfactory cells in the nose reach the olfactory area of the cotext?
After only a single relay in the olfactory bulb
What is the olfactory epithelium region in humans?
5cm²
What is the olfactory region in a cat?
25cm²
What is meant my there being money in smell?
Around $24 billion is spent on scented products per annum in the US alone
There are at least 6 types of touch receptors in the skin, which are?
For hot, for cold, for pain, for pressure, for touch, and for fine touch
On level of pain tolerance there is a high variance between animals, what are some exampels?
Horse has low tolerance, while a cow has high tolerance
What kind of animal did pain emerge in?
Early vertebrates
The conditions for pain were first fulfilled in?
Cambrian explosion
What are the two types of axons, pain perception is carried by?
Delta fibers and C fibers
What are delta Fibers?
Small myelinated fibers that carry the sensation of sharp pricking pain - the sensors are confined to the skin and mucous membranes
What are C fibers?
Small unmyelinated fibers that transmit signals more slowly- they come from polymodal nociceptors that respond to mechanical, thermal or chemical stimuli and cause the sensation of long-lasting burning pain
In the spinal cord, why do C fibers release Substance P?
To transmit the pain signal to axons projecting to the thalamus
An enkephalin interneuron acting on the C fiber terminal will?
Inhibit Substance P release, causing analgesia [endorphins, enkephalins']
The enkephalin interneuron is itself controlled by?
Serotonergic fibers descending from the medulla of the brain stem
In the Pleasure-Pain axis what is associated with pain and what is associated with pleasure?
Central gray matter of midbrain is pain, and the Septal area is pleasure
What does the Limbic system include?
The thalamus, hypothalamus and other structures