B8 - Exchange and Transport in Animals
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
relationship between sa:v and size of organism
as organism gets bigger, sa:v decreases
why do smaller animals not need transport systems
they have small sa:v ratio and are able to diffuse in any neccessary gas
relationship between organism size and diffusion distance
as organism size increases, so does diffusion distance
alveoli
in lungs exchange o2and co2
villi
in small intestine, absorb nutrients
root hair cells
absorb water and minerals
leaves
absorb co2
how does a large sa:v help exchange surfaces
more molecules are able to diffuse at once, so rate of diffusion is faster
how does thin exchange surfaces assist exchange surfaces
smaller diffusion distance
how does a blood supply assist a specialised exchange surface
maintains a concentration gradient
how does a good supply of external medium assist specialised exchange surfaces
maintains a concentration gradient
What happens within the lungs
when blood arrives, it is deoxygenated, so o2 diffuses into haemoglobin, and co2 is diffused from blood stream into alveoli
how are the lungs adapted for gas exchange
air travels into lungs from trachea into bronchi, into alveoli, which have very short diffusion distsanecs between capillaries and membranes, as well as large sa:v and moist walls
root of oxygenated blood in heart
pulmonary vein → left atrium → left ventricle → aorta → body
root of deoxygenated blood in heart
vena cava → right atrium → right ventricle → pulmonary artery → lungs
capillaries
exchange nutrients and oxygen; one cell thick; permeable (allowing for easy diffusion); small lumen, however total cross sectional area very large so low pressure
veins
carry blood to heart; large lumens and thin walls so low pressure; valves prevent blood flowing backwards
arteries
carry blood away from heart; blood is high pressure; walls are thick and small lumen; walls made of elastic and muscle tissue
platelets
fragments of cell which clot blood when cut, and prevent microogranisms entering, and blood exiting
plasma
straw colored liquid makes blood flow, carries: amino acids, nutrients, glucose
white blood cells
immune system, includes lymphocytes, phagocytes and antitoxins
red blood cells
carry oxygen in haemoglobin. biconcave disk so large surface area, no nucleus so more space for oxygen
aerobic respiration reaction
glucose + oxygen → CO2 + water
when and where does aerobic respiration take place
in mitochondria, continuously
anaerobic respiration reaction
glucose → lactic acid
when and where does anaerobic respiration take place
takes place in cytoplasm, when there is an insufficient supply of oxygen e.g. when exercising
why is anerobic respiration less good than aerobic
it is inefficient as incomplete breakdown of glucose. also lactic acid is very damaging to bodily tissues, so must be removed quickly
why must humans respire
release energy used for:
building larger organisms
muscle contraction
maintains body temp
part of metabolism
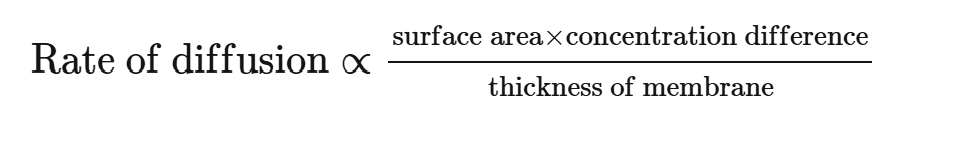
ficks law