Gene Transcription and RNA Modification Overview
1/161
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
162 Terms
Transcription
Process of copying DNA into RNA.
Gene
Segment of DNA encoding functional products.
Central Dogma
Flow of genetic information: DNA to RNA to protein.
Template Strand
DNA strand used for RNA synthesis.
Coding Strand
DNA strand identical to RNA transcript, except thymine.
Transcription Factors
Proteins that regulate transcription initiation.
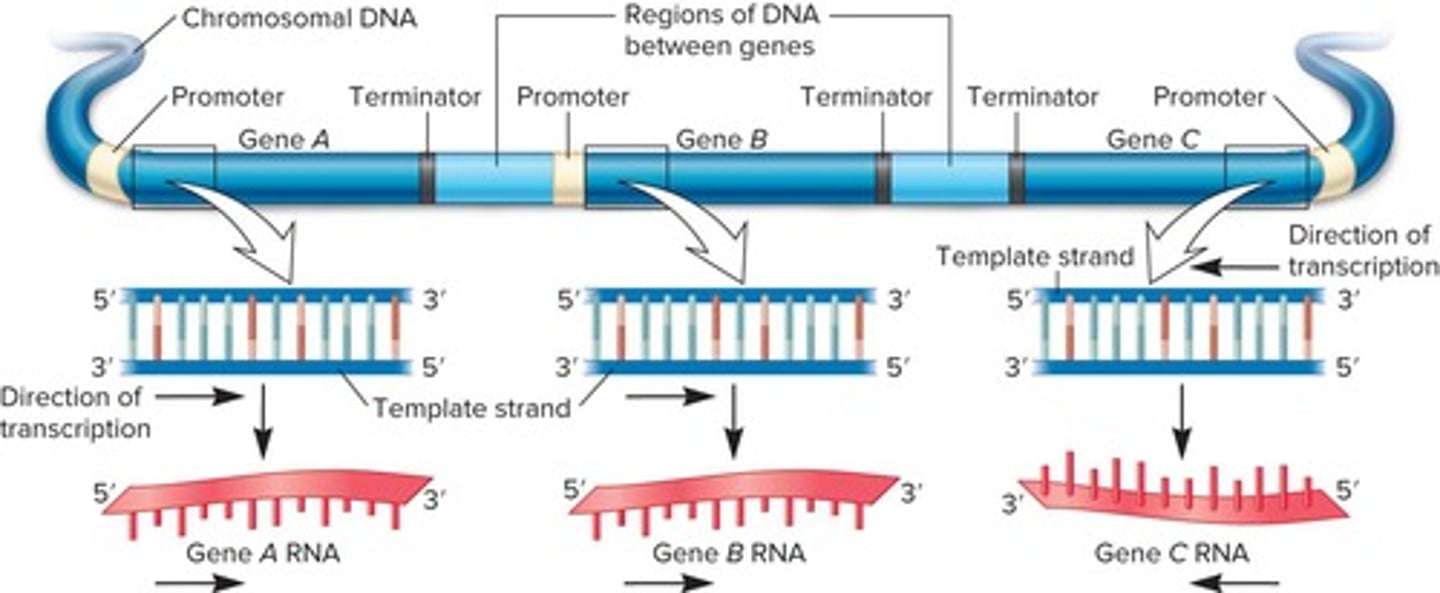
Promoter
DNA sequence that initiates transcription.
Open Complex
Denatured DNA bubble during transcription initiation.
RNA Polymerase
Enzyme synthesizing RNA from DNA template.
Elongation
Synthesis phase of RNA transcript formation.
Termination
Process where RNA synthesis ends and dissociates.
Transcription Start Site (TSS)
Location where transcription begins on DNA.
Consensus Sequence
Most common promoter sequence for high expression.
-35 and -10 Sequences
Specific promoter regions important for transcription.
E. coli
Bacterium used for studying transcription mechanisms.
RNA Transcript
Complementary RNA copy of the DNA template.
Denaturation
Separation of DNA strands during transcription initiation.
Functional Product
Result of gene expression, either RNA or polypeptide.
Gene Expression
Process of using gene information to produce products.
Regulatory Sequences
DNA elements controlling transcription levels.
Bacteriophage
Virus that infects bacteria, used in transcription studies.
RNA Synthesis
Formation of RNA from a DNA template.
RNA polymerase holoenzyme
Complex of core enzyme and sigma factor.
Core enzyme
Composed of five subunits: α2ββ'ω.
Sigma factor
Single subunit that aids in promoter recognition.
Promoter
DNA sequence where RNA polymerase binds to initiate transcription.
Closed complex
Formed when RNA polymerase binds to the promoter.
Open complex
Created when TATAAT box unwinds during transcription.
TATAAT box
Part of the -10 sequence crucial for unwinding.
Antisense strand
Template DNA strand for RNA synthesis.
Coding strand
Non-template DNA strand with same sequence as RNA.
RNA transcript
Newly synthesized RNA molecule during transcription.
Elongation phase
Stage where RNA strand lengthens during transcription.
3' to 5' direction
Direction RNA polymerase reads the template strand.
5' to 3' direction
Direction RNA is synthesized using nucleotides.
Nucleoside triphosphates
Building blocks used for RNA synthesis.
Pyrophosphate release
Byproduct of RNA synthesis during elongation.
RNA-DNA hybrid
Temporary structure formed during RNA synthesis.
Termination
End of RNA synthesis, releasing RNA and polymerase.
Rate of RNA synthesis
Approximately 43 nucleotides per second.
Helix-turn-helix structure
Region in sigma factor for tighter DNA binding.
Direction of transcription
Specified by promoter, varies for adjacent genes.
Open complex length
About 17 bases long during transcription.
Rho-dependent termination
Requires rho protein for transcription termination.
Rho-independent termination
Does not require rho protein for termination.
Uracil-rich sequence
Located at the 3' end of RNA.
Stem-loop structure
Forms upstream of uracil-rich sequence.
Eukaryotic transcription complexity
More complex due to larger cells and multicellularity.
RNA polymerase I
Transcribes all rRNA genes except 5S rRNA.
RNA polymerase II
Transcribes protein-encoding genes and some snRNA.
RNA polymerase III
Transcribes tRNA, 5S rRNA, and microRNA genes.
Core promoter
Short DNA sequence influencing transcription start.
TATA box
Common element in core promoters for transcription.
Basal transcription
Low level of transcription from core promoter alone.
Regulatory elements
Short DNA sequences affecting RNA polymerase binding.
Transcription factors
Proteins that influence transcription rate by binding elements.
Enhancers
Regulatory elements that stimulate transcription.
Silencers
Regulatory elements that inhibit transcription.
Cis-acting elements
DNA sequences affecting only specific genes.
Trans-acting factors
Regulatory proteins binding to DNA sequences.
General transcription factors (GTFs)
Proteins required for basal transcription at promoters.
Mediator complex
Mediates interactions between RNA pol II and factors.
Basal transcription apparatus
RNA pol II plus five GTFs for transcription.
Open complex formation
Initial step in transcription involving RNA polymerase.
Transcriptional start site
Location where transcription begins in the core promoter.
Rho-dependent termination
Termination requiring the rho protein for RNA synthesis.
Rho-independent termination
Termination without rho, using RNA sequences.
Uracil-rich sequence
A sequence at RNA's 3' end aiding termination.
Stem-loop structure
RNA structure upstream of uracil-rich sequence.
Core promoter
Short DNA sequence essential for transcription initiation.
TATA box
Common core promoter element for transcription start.
Basal transcription
Low-level transcription from the core promoter alone.
Regulatory elements
DNA sequences influencing RNA polymerase binding.
Transcription factors
Proteins that bind regulatory elements to modulate transcription.
Enhancers
Regulatory elements that stimulate gene transcription.
Silencers
Regulatory elements that inhibit gene transcription.
Cis-acting elements
DNA sequences affecting only nearby genes.
Trans-acting factors
Proteins that bind to cis-acting elements.
General transcription factors (GTFs)
Proteins required for RNA polymerase II transcription.
Mediator complex
Protein complex mediating interactions for transcription regulation.
Open complex formation
Initial step in transcription where DNA unwinds.
Basal transcription apparatus
RNA pol II and GTFs required for transcription.
RNA polymerase II subunits
Composed of 12 subunits for transcription activity.
TFIID
Complex of TBP and TAFs; binds TATA box.
TBP
TATA-binding protein; essential for transcription initiation.
TAFs
TBP-associated factors; assist TBP in promoter recognition.
TFIIB
Binds TFIID; enables RNA polymerase II binding.
TFIIF
Facilitates RNA polymerase II binding to TFIIB.
TFIIE
Maintains open complex; aids TFIIH binding.
TFIIH
Multisubunit protein; helicase and kinase activities.
CTD
Carboxyl terminal domain; phosphorylated during transcription.
Mediator
Multisubunit complex; links regulatory factors to RNA polymerase II.
Open Complex
Formation of unwound DNA for transcription initiation.
Phosphorylation
Addition of phosphate group; regulates protein activity.
Helicases
Enzymes that unwind DNA during transcription.
Core Promoter
Region where transcription factors bind to initiate transcription.
Regulatory Transcription Factors
Proteins that influence gene expression via mediator.
Elongation Phase
Stage where RNA polymerase synthesizes RNA strand.
Subunits
Individual protein components of larger protein complexes.
Cell Type Variability
Different mediator subunits depending on cell conditions.