Biology Keystone 2024: Part 2
1/78
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
79 Terms
Clone
An organism that is genetically identical to the organism from which it was produced.
Gene
A segment of DNA on a chromosome that codes for a specific trait.
Allele
One of a number of different forms of a gene.
Inheritance
The process by which physical and biological characteristics are transmitted from the parent (or parents) to the offspring.
Genotype
The genetic makeup of an organism.
Phenotype
An organism's physical appearance, or visible traits.
Crossing Over
A process in which homologous chromosomes exchange portions of their chromatids during meiosis.
Sister Chromatids
Identical copies of a chromosome; full sets of these are created during the S Phase of interphase.
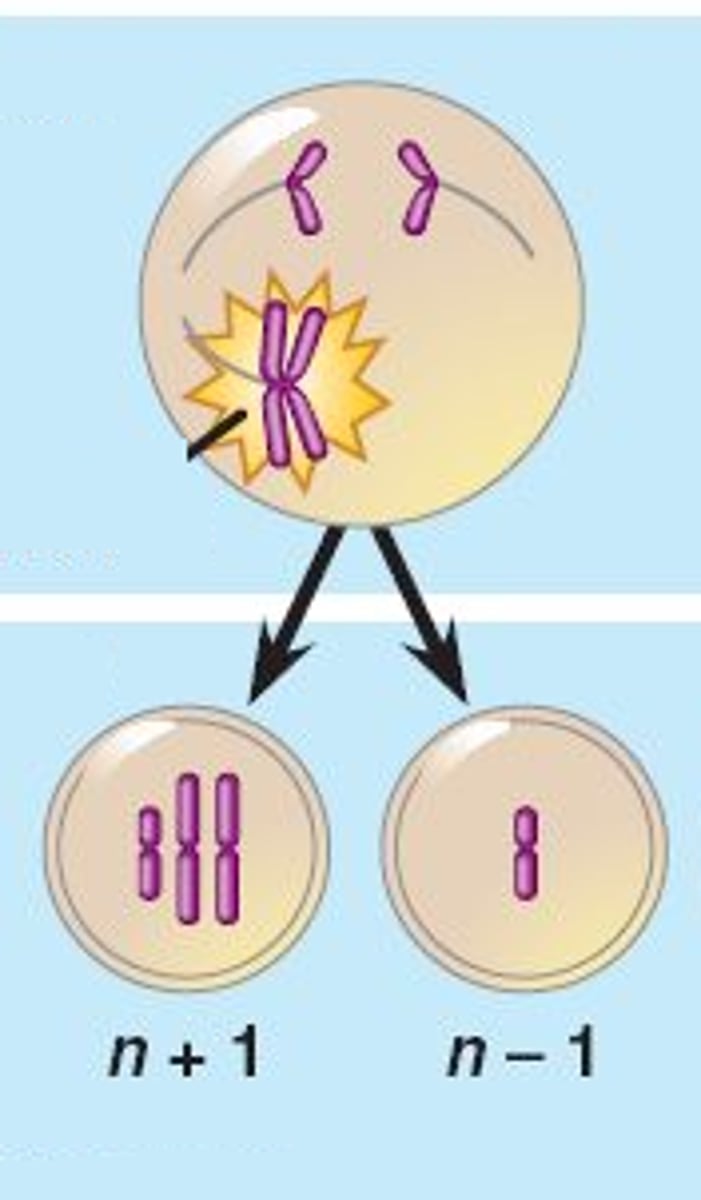
Nondisjunction
An error in meiosis in which homologous chromosomes fail to separate.
Codominance
A condition in which both alleles for a gene are fully expressed. Results in a speckled or spotted phenotype.
Incomplete Dominance
A pattern of inheritance in which two alleles are neither dominant nor recessive. Results in a blended phenotype.
Multiple Alleles
A gene that has more than two alleles. Ex: blood type
Polygenic Inheritance
Occurs when multiple genes determine the phenotype of a trait. Ex: hair color
Sex-Linked Trait
A trait that is determined by a gene found on one of the sex chromosomes.
Biotechnology
A form of technology that uses living organisms, usually genes, to modify products, to make or modify plants and animals, or to develop other microorganisms for specific purposes.
Cloning
A process in which a cell, cell product, or organism is copied from an original source.
Genetic Engineering
Process of making changes in the DNA code of living organisms.
Genetically Modified Organisms
An organism whose genetic material has been altered through some genetic engineering technology or technique.
Protein Synthesis
The formation of proteins by using information contained in DNA and carried by mRNA.
Transcription
The synthesis of an RNA molecule from a DNA template.
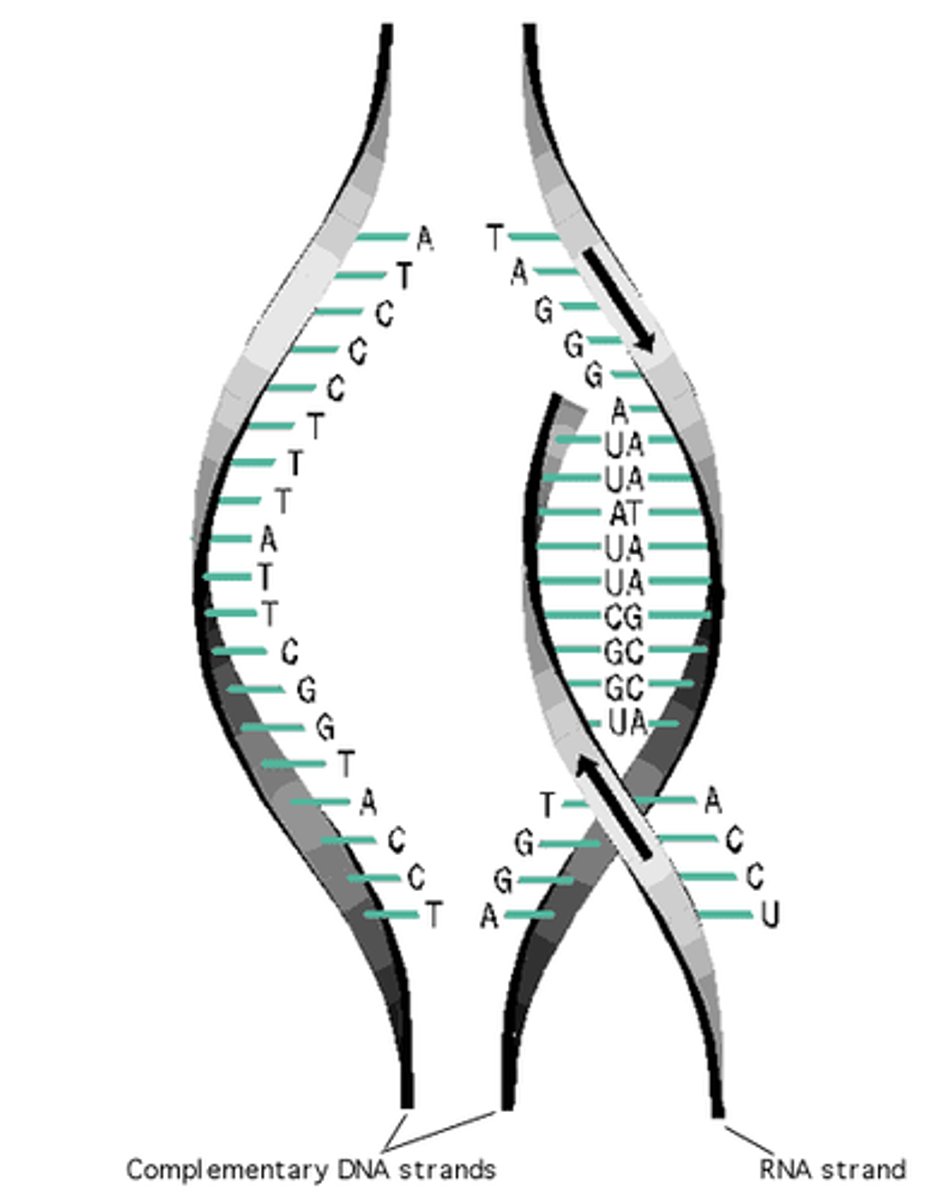
Translation
The process by which mRNA is decoded and a protein is produced.
Gene Expression
The process by which information encoded in DNA directs the synthesis of proteins.
Mutation
A change in the genetic material of a cell.
Chromosomal Mutation
A change in the structure of a chromosome.
Point Mutation
A gene mutation in which a single base pair in DNA has been changed.
Frame-Shift Mutation
A mutation that shifts the "reading" frame of the genetic message by inserting or deleting a nucleotide.
RNA
Ribonucleic Acid. A nucleic acid that plays an important role in the production of proteins.
Messenger RNA
A type of RNA that carries copies of instructions for the assembly of proteins to the ribosomes.
Genetic Code
A collection of codons of mRNA, each of which directs the incorporation of a particular amino acid into a protein during protein synthesis.
Limiting Factor
Any biotic or abiotic factor that restricts the existence, numbers, reproduction, or distribution of organisms.
Extinction
A term that typically describes a species that no longer has any known living individuals.
Nonnative Species
Species that migrate into an ecosystem or are deliberately or accidentally introduced into an ecosystem by humans.
Succession
A series of predictable and orderly changes within an ecosystem over time.
Biogeochemical Cycle
A process in which elements, chemical compounds, and other forms of matter are passed from one organism to another and from one part of the biosphere to another.
Consumer
An organism that obtains energy by feeding on other organisms.
Producer
An organism that can make its own food.
Decomposer
An organism that breaks down wastes and dead organisms.
Competition
The struggle between organisms to survive in a habitat with limited resources.
Endemic Species
Species that are native to and found only within a limited area.
Symbiotic Relationship
The relationship between two species that live in close association with each other.
Predation
An interaction in which one organism kills another for food.
Parasitism
A relationship between two organisms of different species where one benefits and the other is harmed.
Mutualism
A relationship between two species in which both species benefit.
Commensalism
A relationship between two organisms in which one organism benefits and the other is unaffected.
Predator
An animal that hunts other animals for food.
Niche
An organism's particular role in an ecosystem, or how it makes its living.
Prey
An organism that is killed and eaten by another organism.
Herbivore
A consumer that eats only plants.
Carnivore
A consumer that eats only animals.
Omnivore
An animal that eats both plants and animals.
Abiotic
Non-living things. Ex: water, soil, air.
Biotic
Living things. Ex: plants, animals.
Biome
A group of ecosystems that share similar climates and typical organisms.
Habitat
The natural home or environment of an animal, plant, or other organism.
Terrestrial
Relating to the land.
Biosphere
Consists of all life on Earth and all parts of the Earth in which life exists, including land, water, and the atmosphere.
Community
All the different populations that live together in an area.
Ecology
The scientific study of interactions among organisms and between organisms and their environment.
Ecosystem
A biological community of interacting organisms and their physical environment.
Environment
The surroundings or conditions in which an organism operates.
Population
A group of individuals that belong to the same species and live in the same area.
Theory
A hypothesis that has been tested with a significant amount of data.
Inference
A conclusion reached on the basis of evidence and reasoning.
Observation
Information obtained through the senses.
Hypothesis
A testable prediction.
Analogous Structure
Body part that is similar in function as a body part of another organism but is structurally different.
Embryology
The study of embryos and their development.
Fossils
The preserved remains of once-living organisms.
Homologous Structures
Similar structures that related species have inherited from a common ancestor.
Selective Breeding
The process of selecting a few organisms with desired traits to serve as parents of the next generation.
Vestigial Structures
A remnant of a structure that may have had an important function in a species' ancestors, but has no clear function in the modern species. Ex: appendix
Founder Effect
A change in allele frequencies as a result of the migration of a small subgroup of a population.
Gradualism
The theory that evolution occurs slowly but steadily.
Migration
The movement from one region to another.
Punctuated Equilibrium
Pattern of evolution in which long stable periods are interrupted by brief periods of more rapid change.
Isolating mechanism
Any factor that acts to reduce or block the flow of genes between two populations.
Speciation
The formation of new and distinct species in the course of evolution.
Evolution
A change in a kind of organism over time; process by which modern organisms have descended from ancient organisms.
Natural Selection
A process in which individuals that have certain inherited traits tend to survive and reproduce at higher rates than other individuals because of those traits.