Lange Q&A Registry Review - Image Production
1/377
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
378 Terms
The fixed spatial resolution characteristics of direct digital systems is determined by
A. TFT DEL size
B. Sampling frequency
C. Laser scanner
D. PSP thickness
A. TFT DEL size
In digital imaging, brightness is controlled by
1. IR exposure
2. monitor unctions
3. postprocessing unctions
(A) 1 only
(B) 1 and 2 only
(C) 2 and 3 only
(D) 1, 2, and 3
Image brightness is controlled by
1. IR exposure
2. Monitor functions
3. Postprocessing functions
A. 1 only
B. 1 and 2 only
C. 2 and 3 only
D. 1, 2, and 3
C. 2 and 3 only
As digital image matrix size increases
1. pixel size decreases
2. resolution decreases
3. pixel depth decreases
A. 1 only
B. 2 only
C. 1 and 2 only
D. 2 and 3 only
A. 1 only
An algorithm, as used in x-ray imaging, is a
a. Geometric formula
b. specific exposure factors
c. series of variables instructions
d. predetermined exposure factors
C. Series of variables in instructions
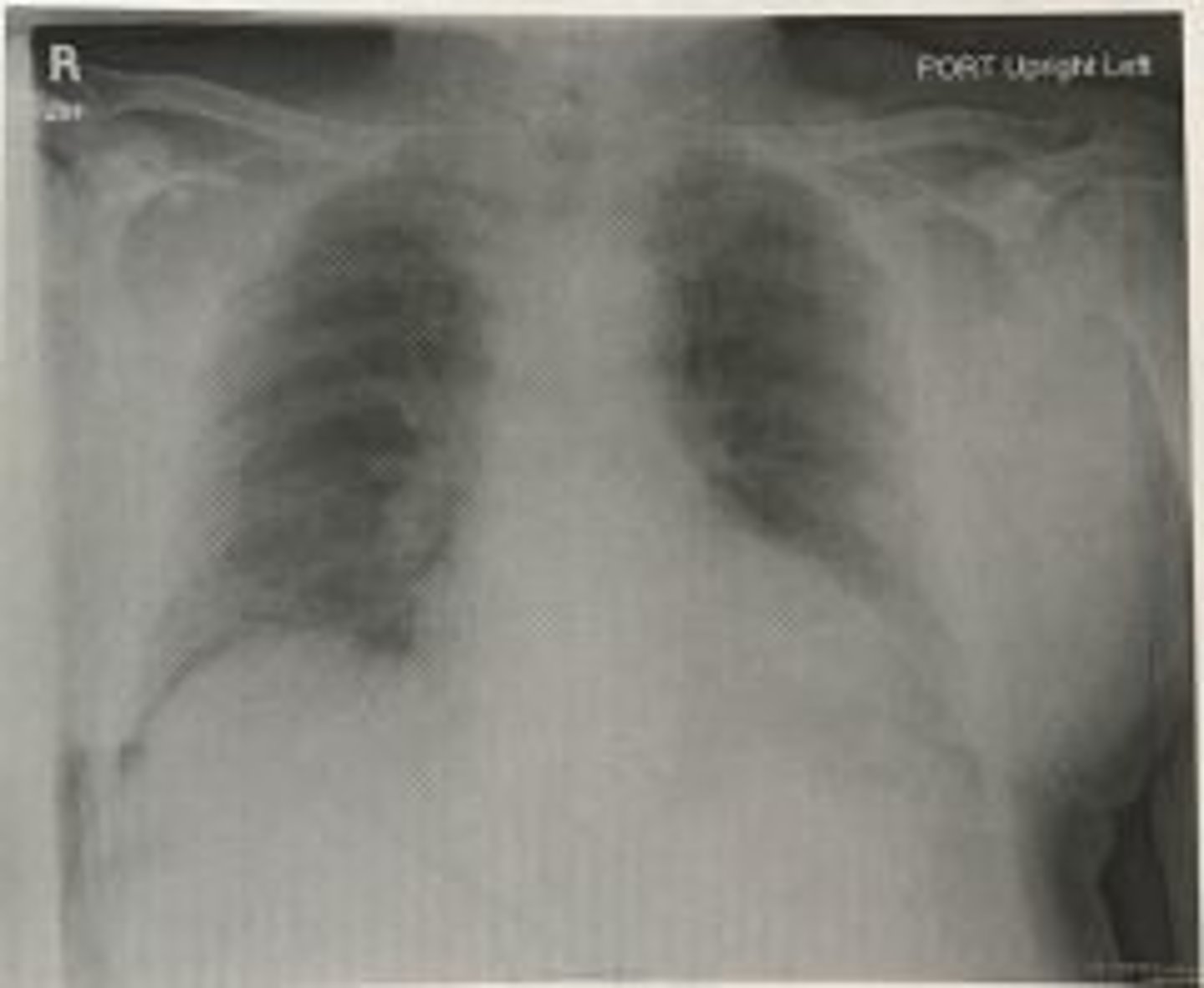
The chest image shown in figure 4-1 demonstrates
a. part motion
b. aliasing artifact
c. double exposure
d. grid cut off
B. Aliasing Artifact
Ionizing radiation intensity decreases as
A. Distance from the source of radiation decrease
B. Distance from the source of radiation increase
C. Frequency increase
D. Wavelength decrease
B. Distance from the source of radiation increase
In which of the following examination should 70 kV not exceeded?
A. Upper GI
B. Barium Enema
C. Intravenous urogram
D. Chest
C. Intravenous Urogram
The reduction in x-ray photon intensity as it passes through material is termed
A. Absorption
B. scattering
C. Attenuation
D. Divergence
C. Attenuation
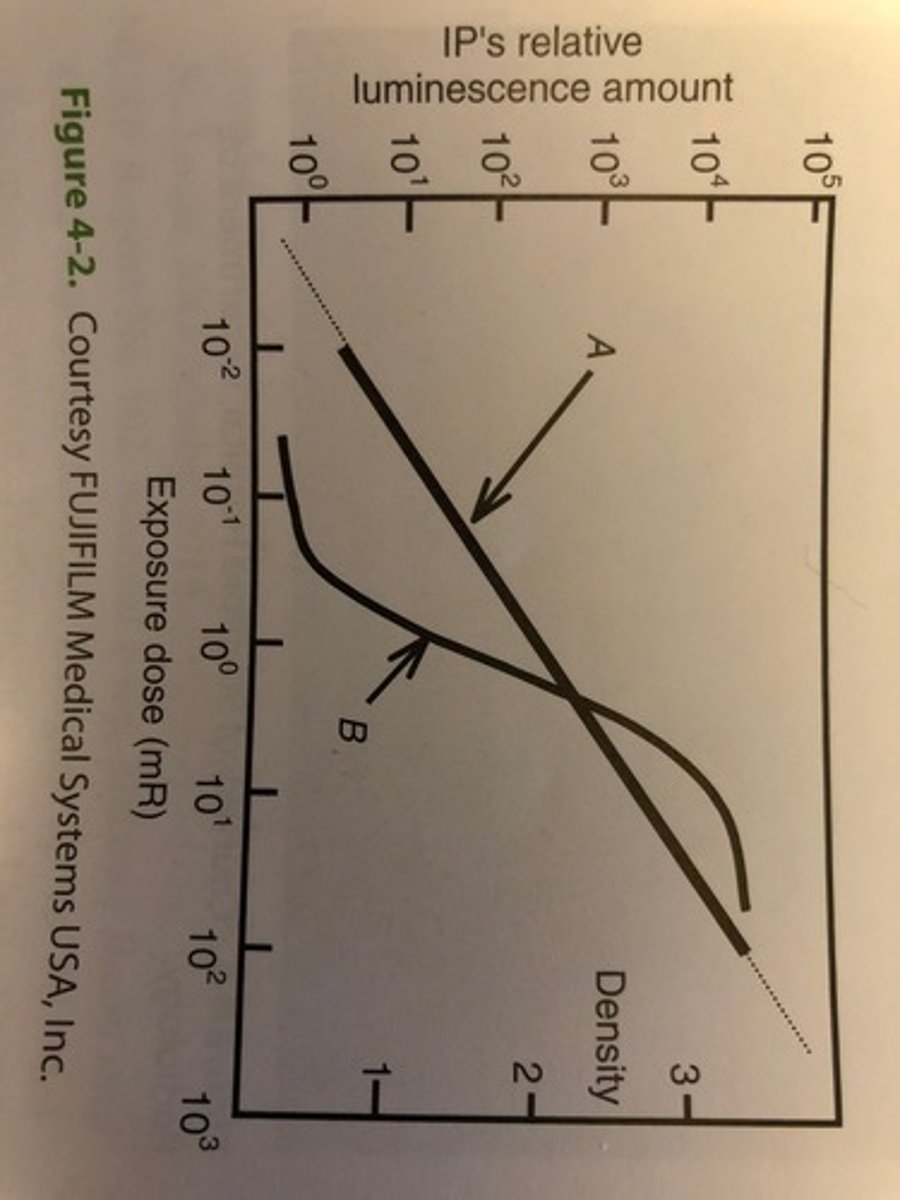
Which of the following lines indicated in figure 4-2 represents the dynamic range offered by computed radiography?
A. Line A is representative of CR
B. Line B is representative of CR
C. Neither lines is representative of CR
D. Both lines are representative of CR
A. Line A is representative of CR
An increase in kilovoltage will have which of the following effects in digital imaging?
1. More scattered radiation will be produced
2. The exposure rate will increase
3. Radiographic contrast will increase
A. 1 only
B. 1 and 2 only
C. 2 and 3 only
D. 1, 2, and 3
B. 1 and 2 only
Factors that can impact image resolution include
1. patient factors
2. focal spots
3. SID
A. 1 only
B. 1 and 2 only
C. 2 and 3 only
D. 1, 2, and 3
D. 1, 2, and 3
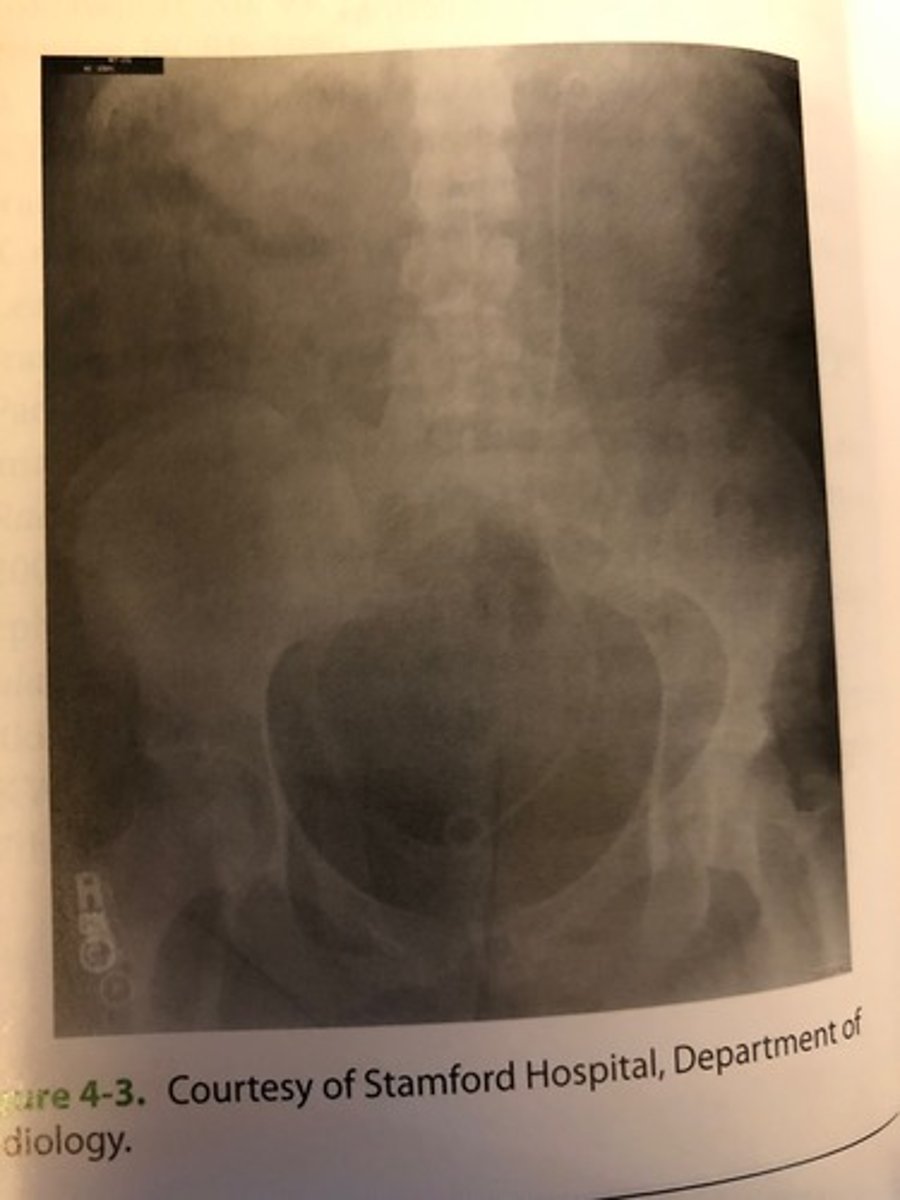
Which is the correct critique of the CR image shown in figure 4-3
A. Double exposure
B. Inverted IP
C. Incomplete erasure
D. Image fading
A. Double exposure
If the lateral projection of an asthenic chest is being performed and the outer photocells are selected, what is likely to outcome?
A. Decreased IR exposure
B. Increase IR exposure
C. Scattered radiation fog
d. Motion blur
A. Decreased IR exposure
Which if the following groups of exposure factors will produce the greatest receptor exposure?
A. 100 mA, 50 ms
B. 200 mA, 40 ms
C. 400 mA, 70 ms
D. 600 mA, 30ms
C. 400 mA, 70 ms
The component of a CR image plate that records the radiologic image is the
A. Emulsion
B. Helium-neon laser
C. Photostimulable phosphor
D. Scanner-reader
C. Photostimulable phosphor
An x-Ray image of the ankle was made at 40 inch SID, 200 mA, 50 ms, 70 KV, 0.6 mm focal spot, and minimal OID. Which of the following modifications would result in the greatest increase in magnification?
A. 1.2 mm focal spot
B. 36 in SID
C. 44 in SID
D. 4 in OID
D. 4 in OID
The radiation dose received by the digital detector for each image is indicated by the
A. mA meter
B. Exposure indicator
C. kV selector
D. Histogram
B. Exposure indicator
HLV is affected by the amount of
1. kVp
2. Beam filtration
3. Tissue density
A. 1 only
B. 1 and 2 only
C. 2 and 3 only
D. 1, 2, and 3
B. 1 and 2 only
The luminescent light emitted by the PSP is transformed into the image seen on the CRT (monitor) by the
A. PSP
B. Scanned reader
C. ADC
D. Helium neon laser
C. ADC
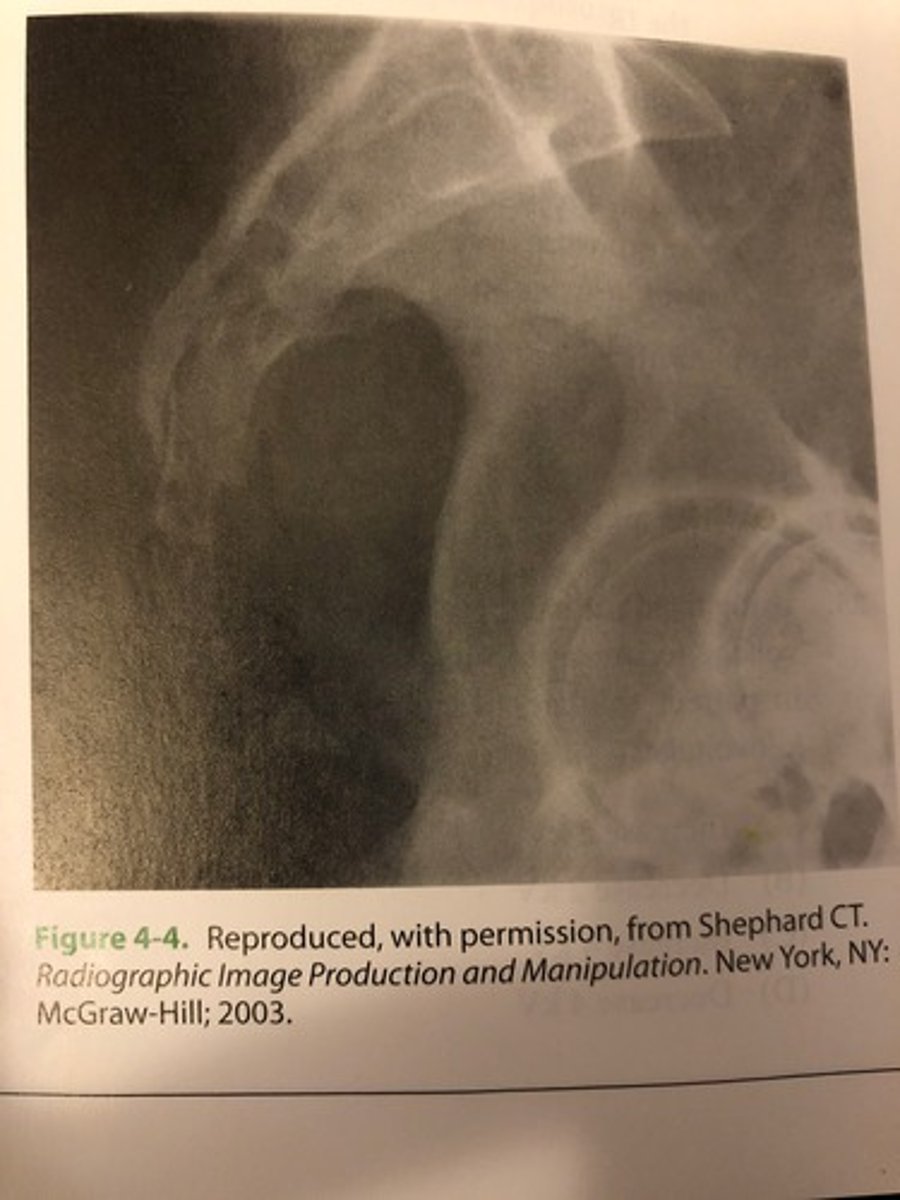
The lateral coccyx image shown in image 4-4 was made using AEC but is overexposed. This is most like the fault of
A. Incorrect selection of the small focal spot
B. Insufficient back up time
C. Selection of the center photocell
D. Incorrect centering of the part
D. Incorrect centering of the part
Which of the following units is/are used to express resolution?
1. Line-spread function
2. Line pairs per millimeter
3. Line-focus principle
A. 1 only
B. 1 and 2 only
C. 2 and 3 only
D. 1, 2, and 3
B. 1 and 2 only
The term windowing describes the practice of
A. Varying the automatic brightness control
B. Changing the image brightness and/or contrast scale
C. Varying the FOV
D. Increasing resolution
B. changing the image brightness and/or contrast scale
Foreshortening can be caused by
(A) the radiographic object being placed at an angle to the IR
(B) excessive distance between the object and the IR
(C) insufficient distance between the focus and the IR
(D) excessive distance between focus the IR
A. the radiographic object being placed at an angle to the IR
Acceptable method(s) of minimizing motion
unsharpness is (are)
1. suspended respiration
2. short exposure time
3. patient instruction
A. 1 only
B. 1 and 2 only
C. 1 and 3 only
D. 1, 2, and 3
D. 1,2, and 3
Using fixed milliampere seconds and variable kilovoltage technical factors, each centimeter increase in patient thickness requires what adjustment in kilovoltage?
(A) Increase 2 kV
(B) Decrease 2 kV
(C) Increase 4 kV
(D) Decrease 4 kV
A. Increase 2 Kv
In which of the following systems does the radiographer select the anatomic part from the console menu?
(A) AEC
(B) APR
(C) TFT
(D) CCD
B. APR
Potential digital image postprocessing include
1. PACS
2. annotation
3. inversion/reversal
A. 1 only
B. 1 and 2 only
C. 2 and 3 only
D. 1, 2, and 3
(C) 2 and 3 only
Which of the following can impact the signal reaching the digital image receptor?
1. Tissue density
2. Pathology
3. Beam
A. 1 and 2 only
B. 1 and 3 only
C. 2 and 3 only
D. 1, 2, and 3
D. 1,2, and 3
X-ray photon energy is inversely related to
1. photon wavelength
2. applied milliamperes (mA)
3. applied kilovoltage (kV)
A. 1 only
B. 1 and 2 only
C. 1 and 3 only
D. 1, 2 and 3
A. 1 only
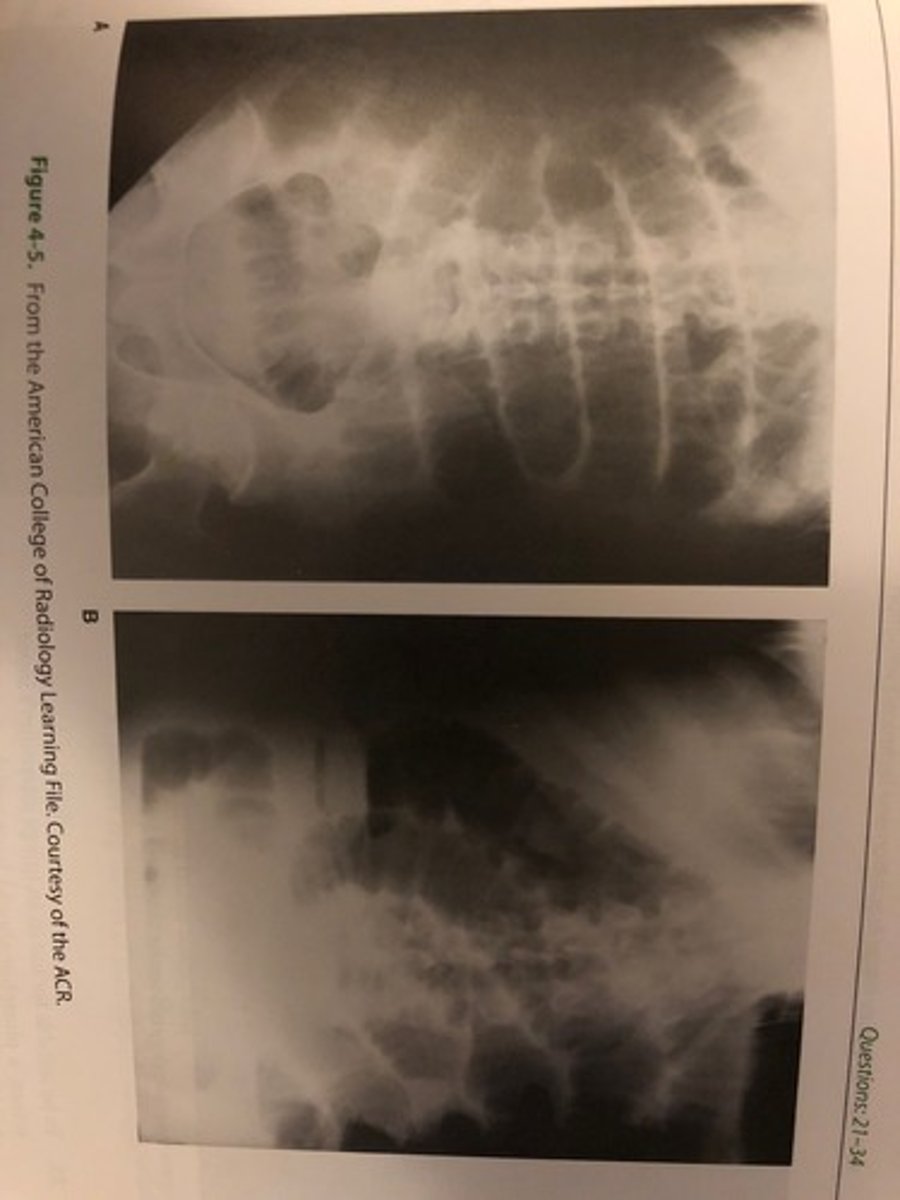
Which of the radiographs shown in 4-5 mostly likely required the greater exposure?
(A) Image A
(B) Image B
(C) No difference in exposure was required
B. Image B
Characteristics of DR imaging include
1. solid-state detector receptor plates
2. a direct-capture imaging system
3. immediate image display
A. 1 only
B. 1 and 3 only
C. 2 and 3 only
D. 1, 2, and 3
D. 1,2, and 3
Compared with a low-ratio grid, a high-ratio grid will
1. allow more centering latitude
2. absorb more scattered radiation
3. absorb more primary radiation
A. 1 only
B. 1 and 2 only
C. 2 and 3 only
D. 1, 2, and 3
C. 2 and 3 only
A decrease in kilovoltage will result in
1. a decrease in image resolution
2. a decrease in photon energy
3. a decrease in receptor exposure
A. 1 only
B. 1 and 2 only
C. 2 and 3 only
D. 1, 2, and 3
C. 2 and 3 only
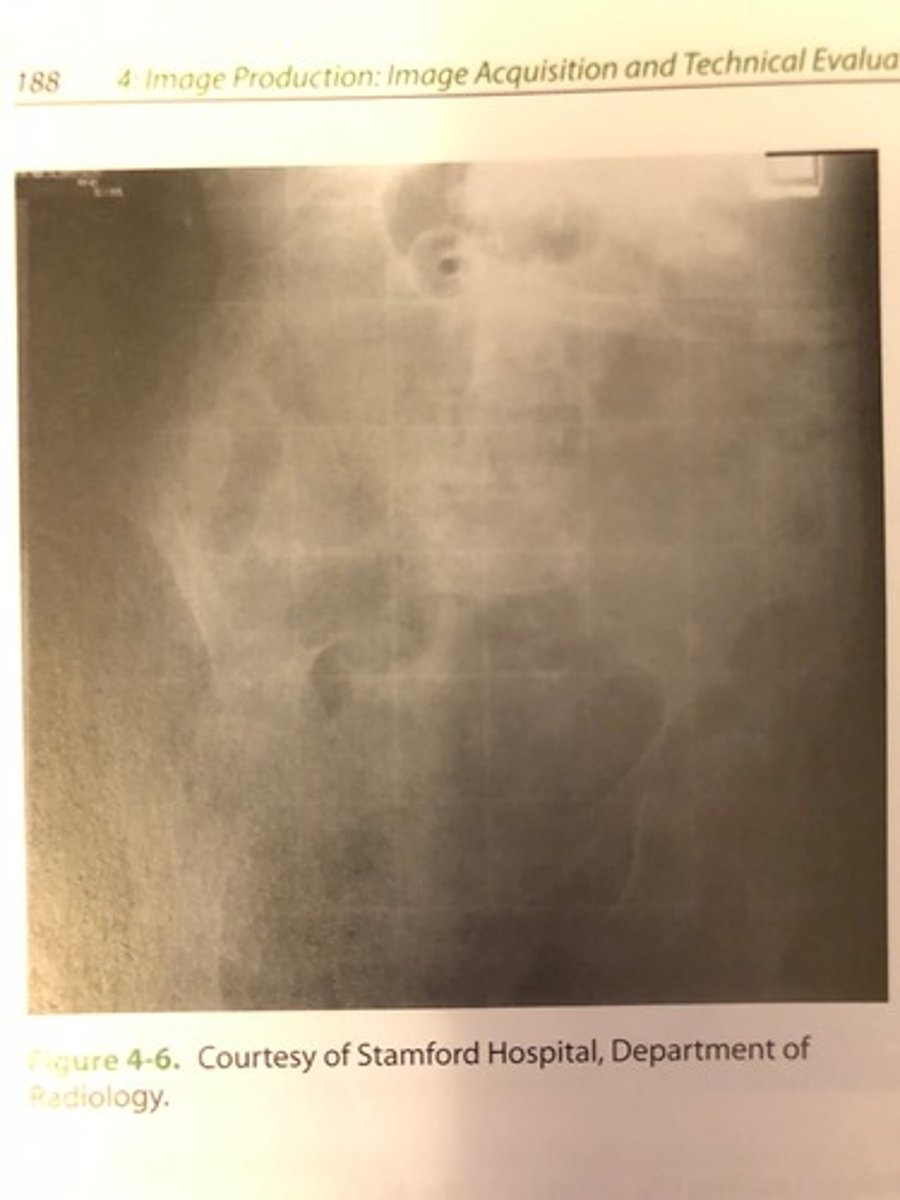
What is the correct critique of the CR image shown in Figure 4-6?
(A) Double exposure
(B) Inverted IP
(C) Incomplete erasure
(D) Image fading
B. Inverted IP
To be suitable for use in an image intensifier's input screen, a phosphor should have which of the following characteristics?
1. High conversion efficiency
2. High x-ray absorption
3. High atomic number
A. 1 only
B. 3 only
C. 1 and 2 only
D. 1, 2 and 3
D. 1, 2, and 3
Resolution in CR increases as
1. laser beam size decreases
2. monitor matrix size decreases
3. PSP crystal size decreases
A. 1 only
B. 1 and 2 only
C. 1 and 3 only
D. 1, 2, and 3
C. 1 and 3 only
What pixel size has a 512 x 512 matrix with a 20-cm field of view (FOV)?
A. 0.07 mm/pixel
B. 0.40 mm/pixel
C. 0.04 mm/pixel
D. 4.0 mm/pixel
B. 0.40 mm/pixel
In radiography of a large abdomen, which of following is/are effective way(s) to minimize amount of scattered radiation reaching the ime receptor (IR)?
1. Use of close collimation
2. Use of low mAs
3. Use of a low-ratio grid
A. 1 only
B. 1 and 2 only
C. 1 and 3 only
D. 1, 2, and 3
A. 1 only
An exposure was made using 300 mA, 40 ms exposure, and 85 kV. Each of the following change will decrease the receptor exposure by one half except a change to
(A) 1/50-s exposure
(B) 72 kV
(C) 10 mAs
(D) 150 mA
C. 10 mAs
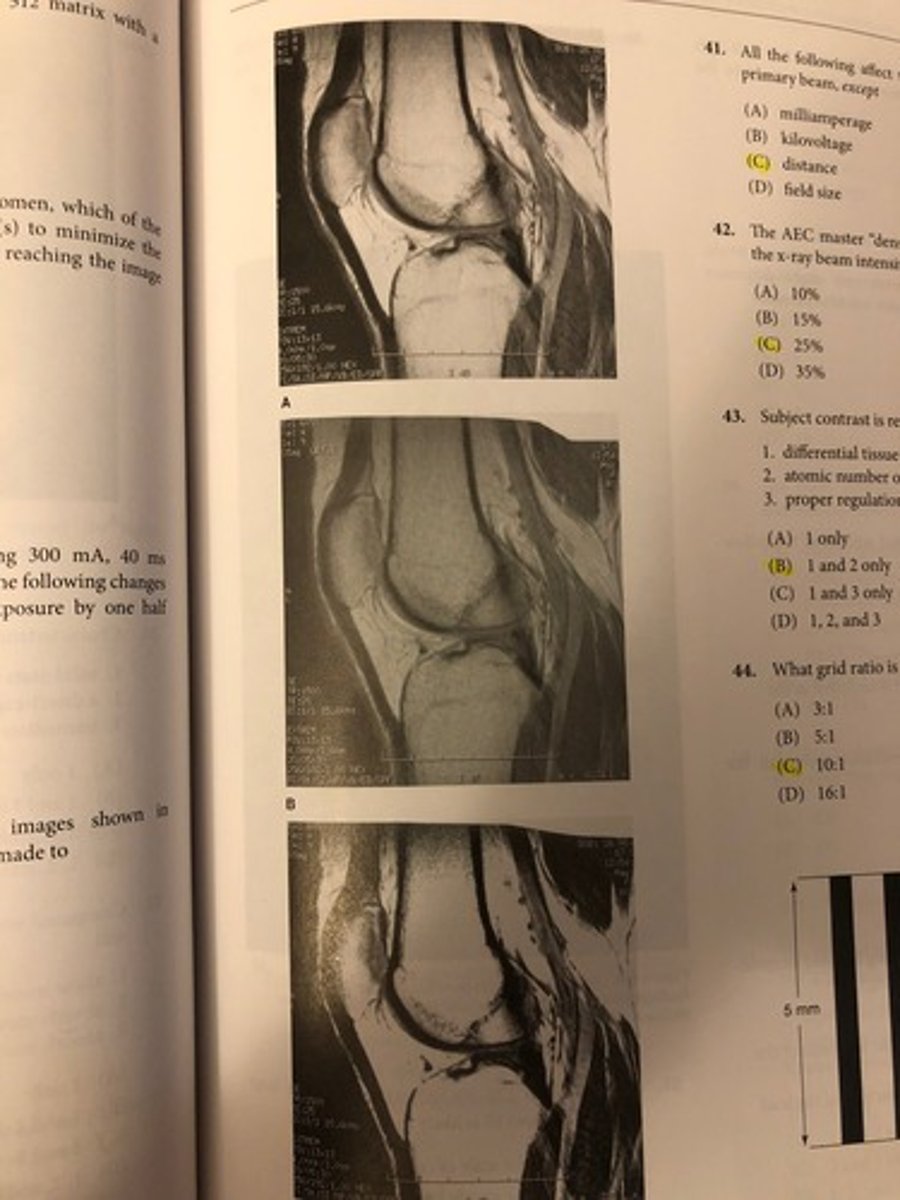
The changes between the images shown in Figure 4-7 represent changes made to
(A) pixel size
(B) matrix size
(C) window width
(D) window level
C. window width
All the following affect the exposure rate of the primary beam, except
(A) milliamperage
(B) kilovoltage
(C) distance
(D) field size
D. Field size
The AEC master "density control" usually adjusts the x-ray beam intensity by what increment?
( A ) 10 %
( B ) 15 %
( C ) 25 %
( D ) 35 %
C. 25 %
Subject contrast is related to
1. differential tissue absorption
2. atomic number of tissue being traversed
3. proper regulation of milliampere seconds
A. 1 only
B. 1 and 2 only
C. 1 and 3 only
D. 1, 2, and 3
(B) 1 and 2 only
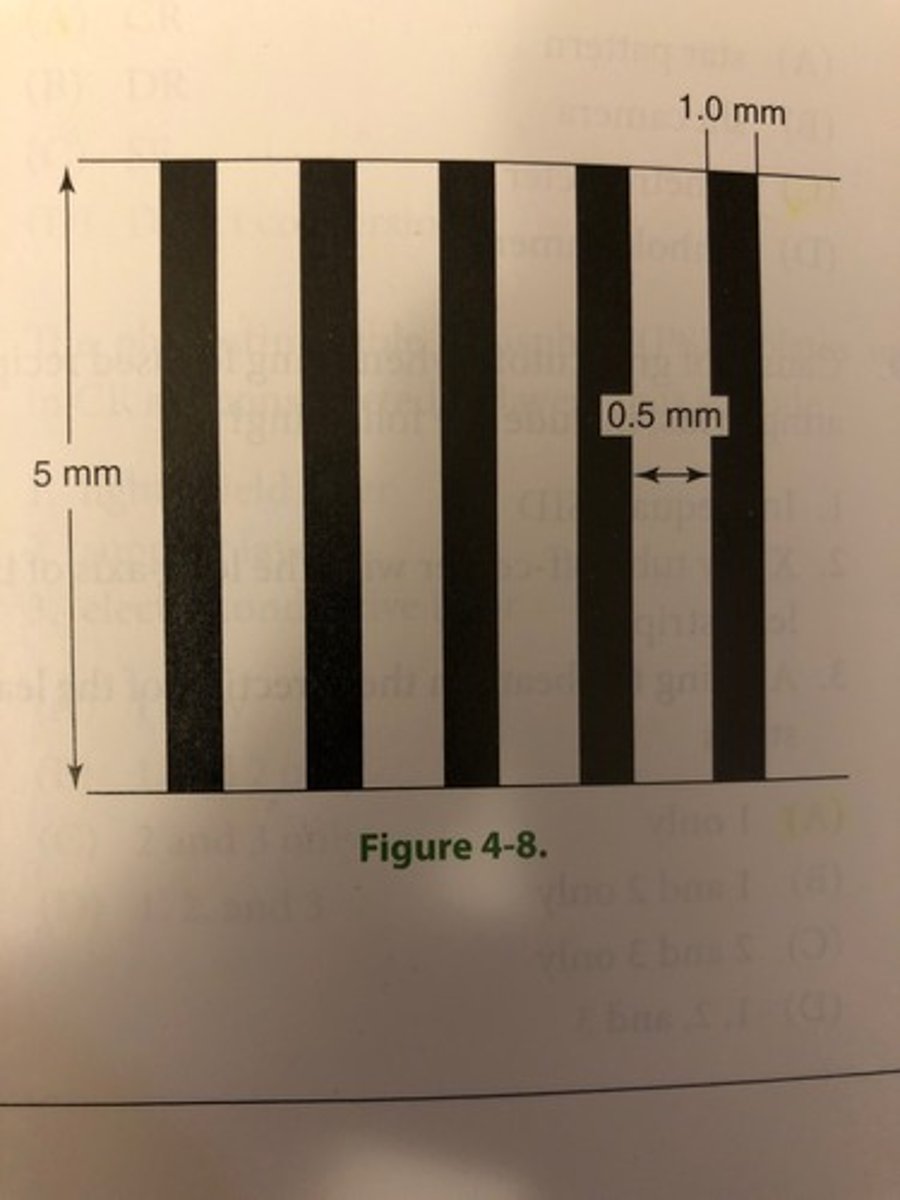
What grid ratio is represented in Figure 4-8
(A) 3:1
(B) 5:1
(C) 10:1
(D) 16:1
(C) 10:1
A 5-inch object to be radiographed at a 44-inch SID lies 6 inches from the IR. What will be the image width?
(A) 5.1 inches
(B) 5.7 inches
(C) 6.1 inches
(D) 6.7 inches
(B) 5.7 inches
An image demonstrating many brightness levels, or shades of gray, with only slight difference between the levels/shades is said to possess
1. long-scale contrast
2. low contrast
3. short-scale
A. 1 only
B. 2 only
C. 1 and 2 only
D. 2 and 3 only
(C) 1 and 2 only
The term pixel is associated with all of the following, except
(A) two dimensional
(B) picture element
(C) measured in xy direction
(D) how much of the part is included in the matrix
(D) how much of the part is included in the matrix
Geometric blur can be evaluated using all the following devices, except
(A) star pattern
(B) slit camera
(C) penetrometer
(D) pinhole camera
(C) penetrometer
Causes of grid cutoff, when using focused reciprocating grids, include the following?
1. Inadequate SID
2. X-ray tube off center with the long axis of the lead strips
3. Angling the beam in the direction of the lead strips
A. 1 only
B. 1 and 2 only
C. 2 and 3 only
D. 1, 2, and 3
(A) I only
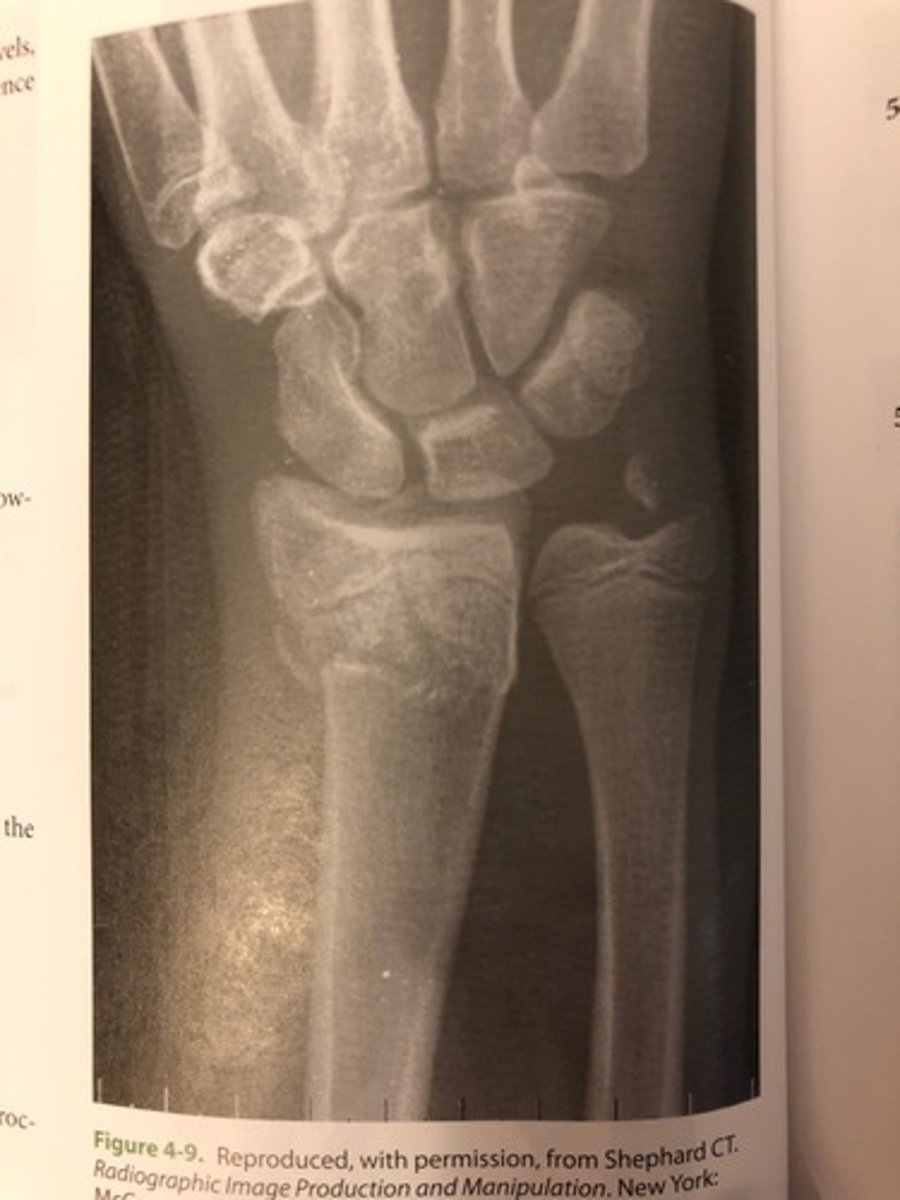
The tiny increased brightness, dropout artifacts, seen in the proximal portion of the CR image of the radius shown in Figure 4.9 are representative of
(A) backscatter
(B) skipped scan lines
(C) dust/dirt on the PSP
(D) image fading
(C) dust/dirt on the PSP
Using a short (25-30 inches) SID with a large ( 14 × 17 inches ) IR is likely to
(A) increase the scale of contrast
(B) increase the anode heel effect
(C) cause malfunction of the AEC
(D) cause premature termination of the exposure
(B) increase the anode heel effect
Special considerations that can require increase from typical technical factors include
1. excessive BMI
2. skeletal sclerosis
3. osteomalacia
A. 1 only
B. 1 and 2 only
C. 2 and 3 only
D. 1, 2, and 3
(B) 1 and 2 only
The distance the center of one pixel to the center an adjacent pixel is termed
(A) picture element
(B) volume element
(C) pixel pitch
(D) bit depth
(C) pixel pitch
Because of the anode heel effect, the intensity of the x-ray beam is greatest along the
(A) path of the central ray
(B) anode end of the beam
(C) cathode end of the beam
(D) transverse axis of the film
(C) cathode end of the beam.
The differences between CR and DR include
1. CR uses IPs
2. CR has higher DQE and lower patient dose
3. CR images are displayed immediately
A. 1 only
B. 1 and 2 only
C. 2 and 3 only
D. 1, 2, and 3
(A) 1 only
The term voxel is associated with all of the following, except
(A) bit depth
(B) volume element
(C)measured in Z direction
(D) field of view
(D) field of view
Using a 48-inch SID, how much OID must be introduced to magnify an object 2 times?
(A) 8-inch OID
(B) 12-inch OID
(C) 16-inch OID
(D) 24-inch OID
(D) 24-inch OID
A particular radiograph was produced using 12 mAs and 85 kV with a 16:1 ratio grid. The radiograph is to be repeated using an 8:1 ratio grid. What should be the new milliampere seconds value?
(A) 3
(B) 6
(C) 8
(D) 10
(C) 8
The main difference between the direct-capture and indirect-capture that
(A) direct capture/conversion has no scintillator
(B) direct capture/conversion uses a photostimulable phosphor
(C) in direct capture/conversion, light is detected by CCDs
(D) in direct capture/conversion, light is detected by TFTs
(A) direct capture/conversion has no scintillator
Analog-to-digital conversion is required in the following imaging system
(A) CR
(B) DR
(C) SF
(D) Direct conversion
(A) CR
The photostimulable phosphor (PSP) plates used in CR are constructed in layers that include
1. light shield layer
2. support layer
3. electroconductive layer
A. 1 only
B. 1 and 2 only
C. 2 and 3 only
D. 1, 2, and 3
(D) 1,2, and 3
For the same FOV, spatial resolution will be improved using
(A) a smaller matrix
(B) a larger matrix
(C) fewer pixels
(D) shorter SID
(B) a larger matrix
Which of the following are methods of limiting the production of scattered radiation?
1. Using moderate ratio grids
2. Using the prone position for abdominal
3. Restricting the field size to the smallest practical size
A. 1 and 2 only
B. 1 and 3 only
C. 2 and 3 only
D. 1, 2, and 3
(C) 2 and 3 only
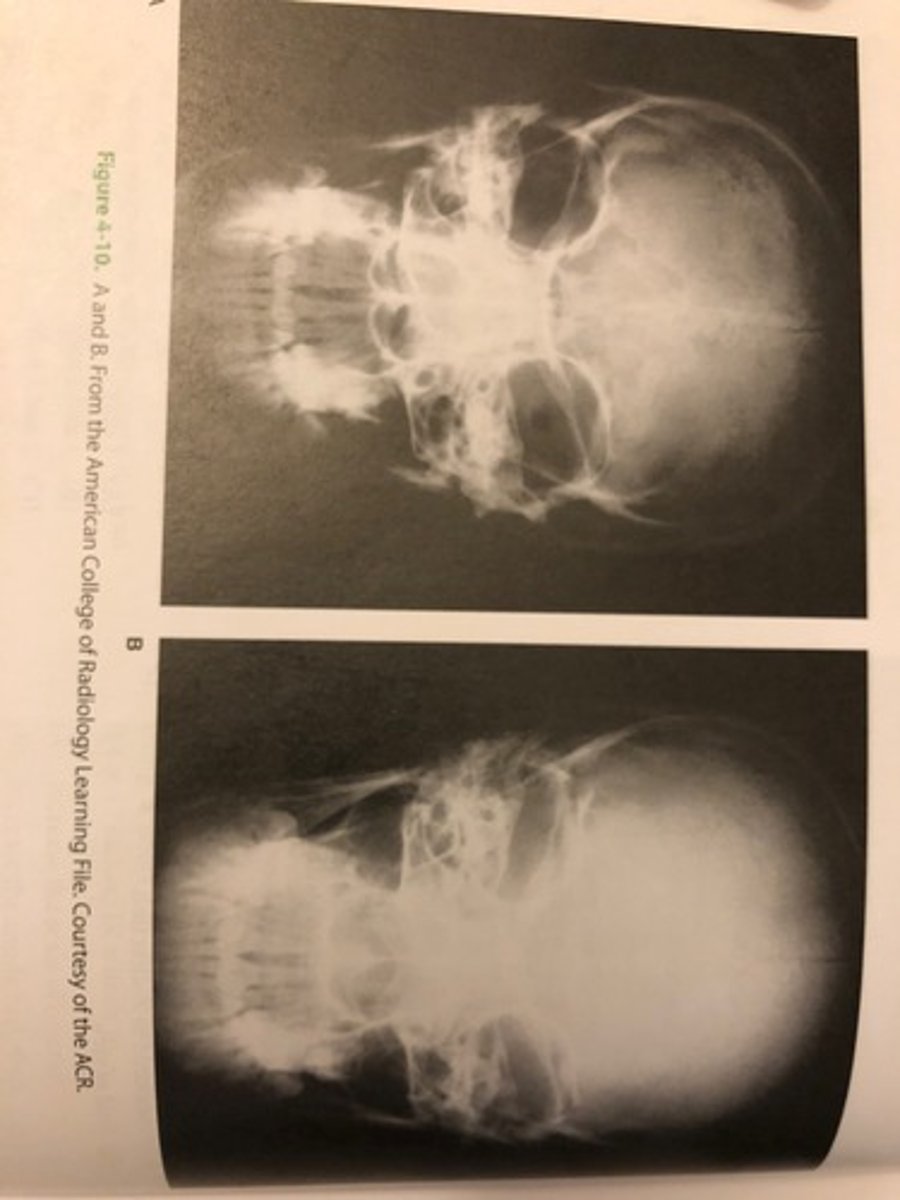
Two images of the skull are shown in Figure 4-10. Which of the two images of the following best describes their different appearance?
(A) Image B was made using grid
(B) Image A demonstrates higher contrast
(C) Image A demonstrates motion
(D) Image B demonstrates shape distortion
(B) Image A demonstrates higher contrast
Exposure factors of 90 kV and 3 mAs are used for a particular nongrid exposure. What should be the new milliampere seconds (mAs) value if a 12:1 grid added?
(A) 86
(B) 9
(C) 12
(D) 15
(D) 15
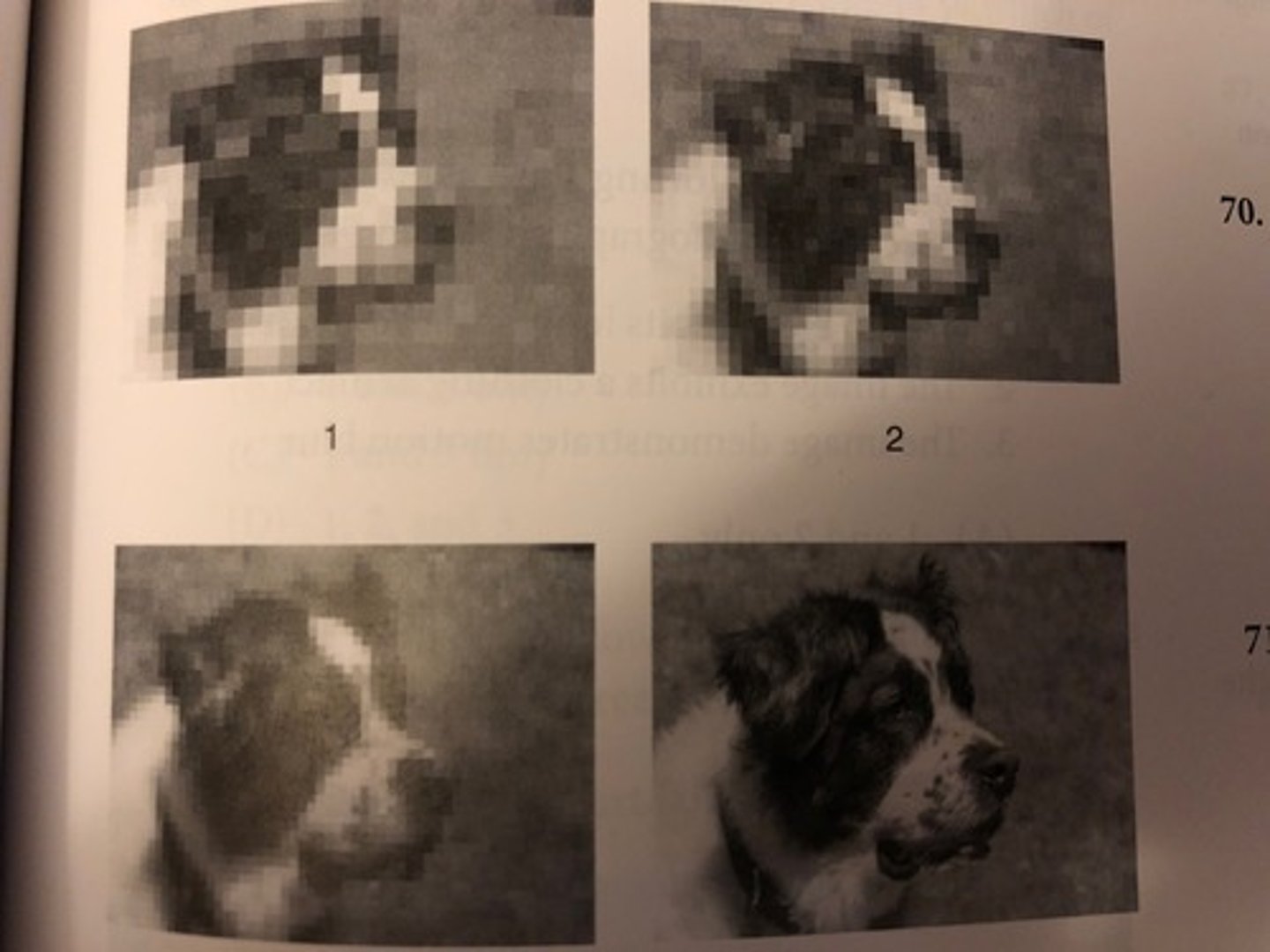
Which of the images in figure 4-11 has the smallest matrix size?
(A) Image #1
(B) Image #2
(C) Image #3
(D) Image #4
(A) Image #1
Types of shape distortion include
1. magnification
2. elongation
3. foreshortening
A. 1 only
B. 1 and 2 only
C. 2 and 3 only
D. 1, 2, and 3
(C) 2 and 3 only
For the same FOV, as the matrix size increases
1. spatial resolution increases
2. image quality increases
3. pixel size decreases
A. 1 only
B. 1 and 2 only
C. 2 and 3 only
D. 1, 2, and 3
(D) 1, 2, and 3
In digital imaging as the size of the image matrix increases,
1. FOV increases
2. pixel decreases
3. spatial resolution increases
A. 1 only
B. 1 and 2 only
C. 2 and 3 only
D. 1, 2, and 3
(C) 2 and 3 only
All the following are related to spatial resolution, except
(A) milliamperage
(B) focal spot size
(C) SID
(D) OID
(A) milliamperage
A satisfactory radiograph was made using 36-inch SID, 12 mAs, and a 12:1 grid. If the be repeated at a distance of 42 inches and using a 5:1 grid, what the new milliampere seconds value to maintain the original receptor exposure?
(A) 5.6
(B) 6.5
(C) 9.7
(D) 13
(B) 6.5
Of the following groups of exposure factors, which will produce the most receptor exposure?
(A) 400 mA, 30 ms, 72-inch SID
(B) 200 mA, 30 ms, 36-inch
(C) 200 mA, 60 ms, 36-inch SIE
(D) 400 mA, 60 ms, 72-inch SID
(C) 200 mA, 60 ms, 36-inch SID
Image resolution improves as
1. scintillation increases
2. DEL size decreases
3. fill factor increases
A. 1 only
B. 1 and 2 only
C. 2 and 3 only
D. 1, 2, and 3
(C) 2 and 3 only
All of the following statements regarding digital imaging are true, except
(A) window level adjustments are associated with image brightness
(B) brightness is related to IR exposure
(C) image visibility is a function of IR exposure able terms
(D) brightness and density are not interchange
(B) brightness is related to IR exposure
In digital imaging, kV selection has an effect on
1. photon energy
2. penetration
3. image contrast
A. 1 only
B. 1 and 2 only
C. 2 and 3 only
D. 1, 2, and 3
(B) 1 and 2 only
Which of the following influence(s) the production of scattered radiation?
1. Kilovoltage level
2. Tissue density
3. Size of field
A. 1 only
B. 1 and 2 only
C. 2 and 3 only
D. 1, 2, and 3
(D) 1, 2, and 3
Exposure factors of 2 mAs and 75 kV were used for a particular part. Which of the following changes would result in twice the exposure to the image receptor?
(A) 1 mAs
(B) 4 mAs
(C) 76 kV
(D) 64 kV
(B) 4 mAs
Factors impacting spatial resolution include
1. focal spot size
2. subject motion
3. SOD
A. 1 and 2 only
B. 1 and 3 only
C. 2 and 3 only
D. 1, 2, and 3
(D) 1, 2, and 3
A grid usually is used in which of following circumstances?
1. When radiographing a large or dense body part
2. When using high kilovoltage
3. When a lower patient dose is required
A. 1 only
B. 3 only
C. 1 and 2 only
D. 1, 2, and 3
(C) 1 and 2 only
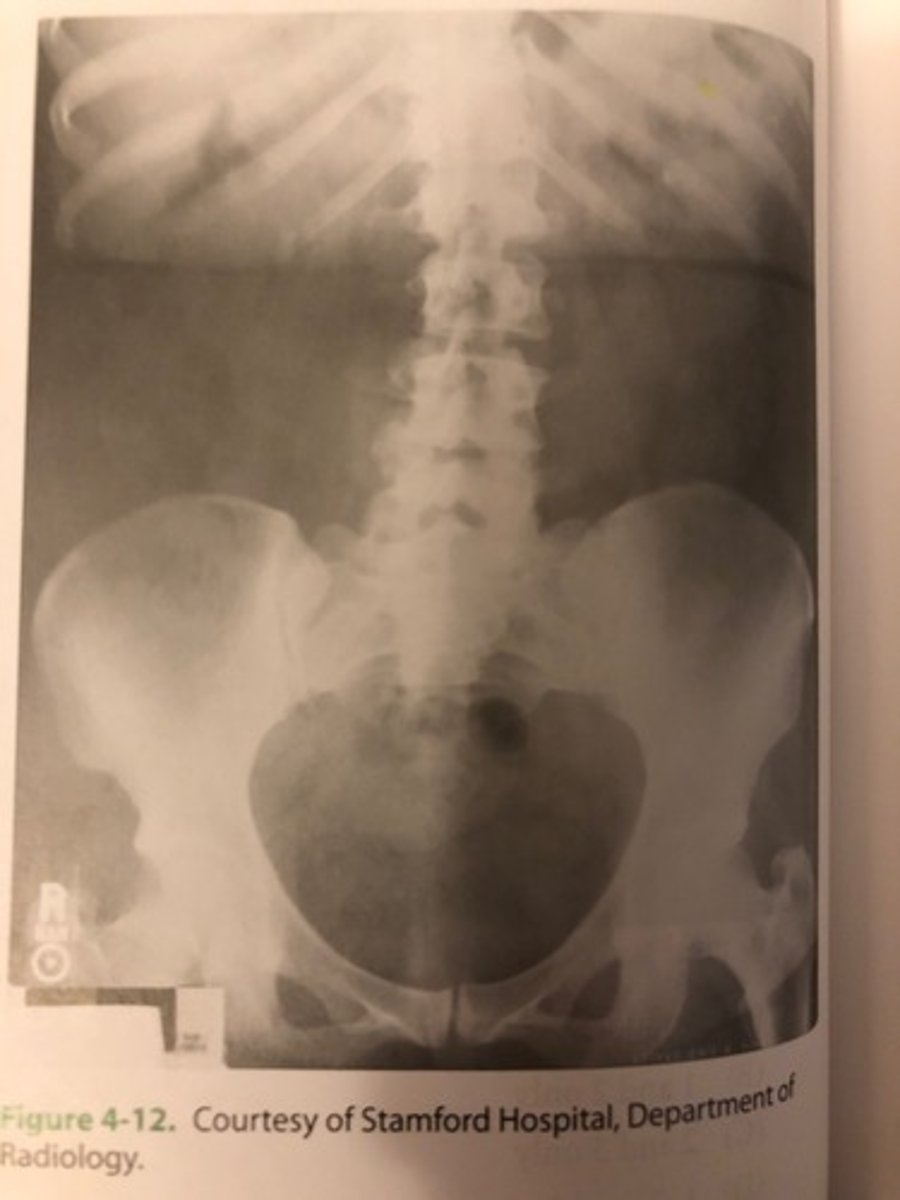
Which of the following statements is/are true with respect to the radiograph shown in Figure 4.12?
1. The image exhibits long-scale contrast
2. The image exhibits a clothing artifact
3. The image demonstrates motion blur
A. 1 and 2 only
B. 1 and 3 only
C. 2 and 3 only
D. 1, 2, and 3
(D) 1, 2, and 3
How are mAs and patient dose related?
(A) mAs and patient proportional dose are inversely
(B) mAs and patient dose are directly proportional
(C) mAs and patient dose are unrelated
(D) mAs and patient dose are inversely related plate
(B) mAs and patient dose directly proportional
Image plate front material can be made of which of the following?
1. Carbon fiber
2. Magnesium
3. Lead
A. 1 only
B. 1 and 2 only
C. 1 and 3 only
D. 1, 2, and 3
(B) 1 and 2 only
Which of the following pathologic conditions would require a decrease in exposure factors?
(A) Congestive heart failure
(B) Pneumonia
(C) Emphysema
(D) Pleural effusion
(C) Emphysema
An exposure was made at a 36-inch SID using 300 mA, a 30-ms exposure, and 80 kV and an 8:1 grid. It is desired to repeat the radiograph using a 40-inch SID and 70 kV. With all other factors remaining constant, what new exposure time will be required?
(A) 0.03 s
(B) 0.07 s
(C) 0.14 s
(D) 0.36s
(B) 0.07 s
Practice(s) that enable the radiographer to reduce the exposure time required for a particular image includes
1. Use of a higher milliamperage
2. Use of a higher kilovoltage
3. Use of higher radio grid
A. 1 only
B. 1 and 2 only
C. 2 and 3 only
D. 1, 2, and 3
(B) 1 and 2 only
All of the following statements regarding kV correct, except
(A) increased kV produces increases beam intensity
(B) receptor exposure can be doubled or halved by using the 15 % rule
(C) increased kV can decrease absorbed dose
(D) kV and wavelength are directly proportional
(D) kV and wavelength are directly proportional
Factors impacting spatial resolution in indirect digital/CR imaging include
1. pixel pitch
2. sampling frequency
3. DEL size of the TFT
A. 1 only
B. 1 and 2 only
C. 2 and 3 only
D. 1, 2, and 3
(B) 1 and 2 only
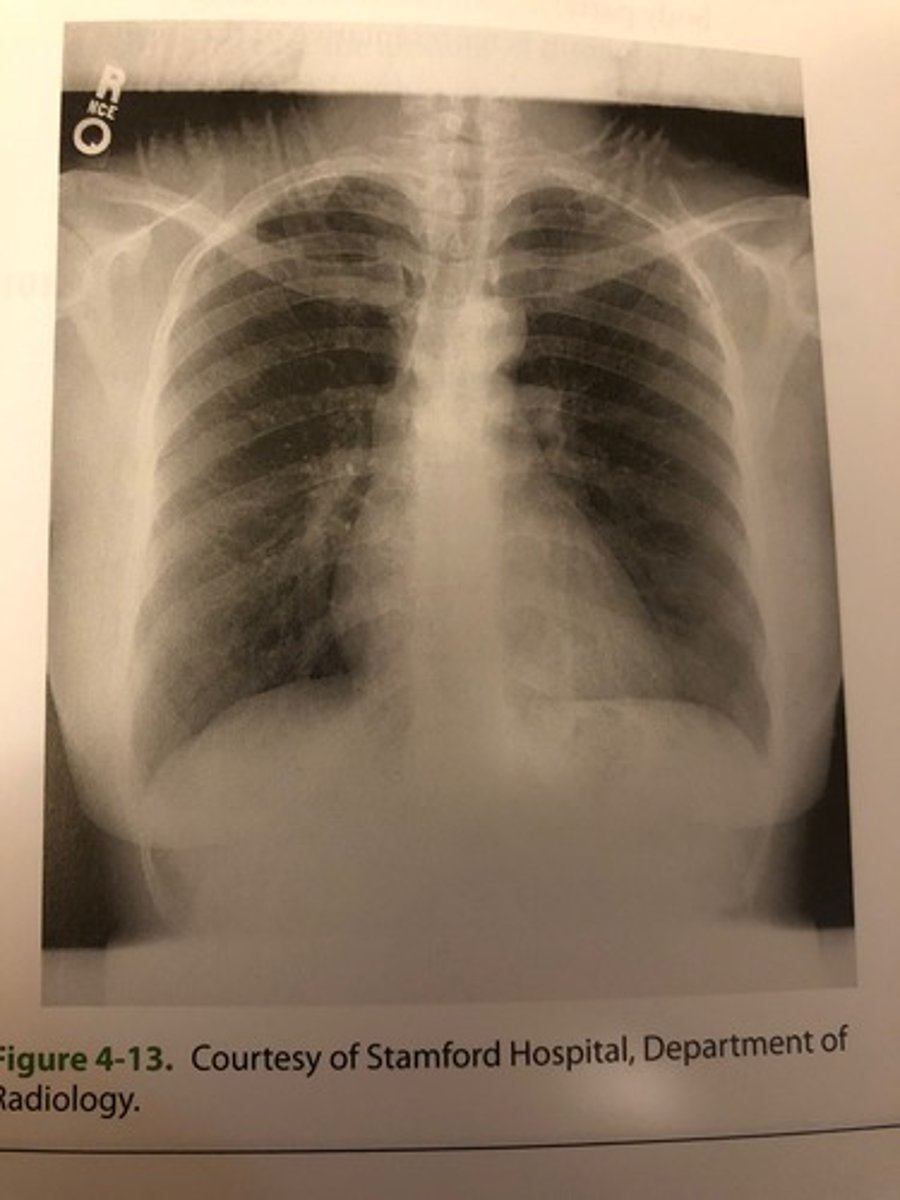
The radiograph shown in Figure 4-13 demonstrates an example of
(A) motion blur
(B) underexposure
(C) scanner/reader artifact
(D) exposure artifact
(D) exposure artifact
Exposure-type artifacts include
1. double exposure
2. motion
3. image fading
A. 1 only
B. 1 and 2 only
C. 2 and 3 only
D. 1, 2, and 3
(B) I and 2 only
An increase in the kilovoltage applied to the x-ray increases the
1. x-ray wavelength
2. exposure rate
3. patient absorption
A. 1 only
B. 2 only
C. 2 and 3 only
D. 1, 2, and 3
(B) 2 only
Which of the following statements about histograms is/are true?
1. A histogram illustrates pixel value distribution
2. There is default histogram for each/different body parts
3. A histogram is representative of the image grayscale
A. 1 only
B. 1 and 2 only
C. 2 and 3 only
D. 1, 2, and 3
(D) 1, 2, and 3
Misalignment of the tube-part-IR relationship results in
(A) shape distortion
(B) size distortion
(C) magnification
(D) blur
(A) shape distortion
If the radiographer is unable to achieve a short OID because of the structure of the body part or patient condition, which of the following adjustments can be made to minimize magnification distortion?
(A) A smaller focal spot size should be used
(B) A longer SID should be used
(C) A shorter SID should be used
(D) A lower ratio grid should be used
(B) A longer SID should be used
The exposure factors used for a particular nongrid x-ray image were 300 mA, 4 ms, and 90 kV. Another image, using an 8:1 grid, is requested. Which following groups of factors is most appropriate?
(A) 400 mA, 3 ms, 110 kV
(B) 400 mA, 12 ms, 90 kV
(C) 300 mA, ms, 100 kv
(D) 200 mA, 240 ms, 90 kv
(B) 400 mA, 12 ms, 90 kV
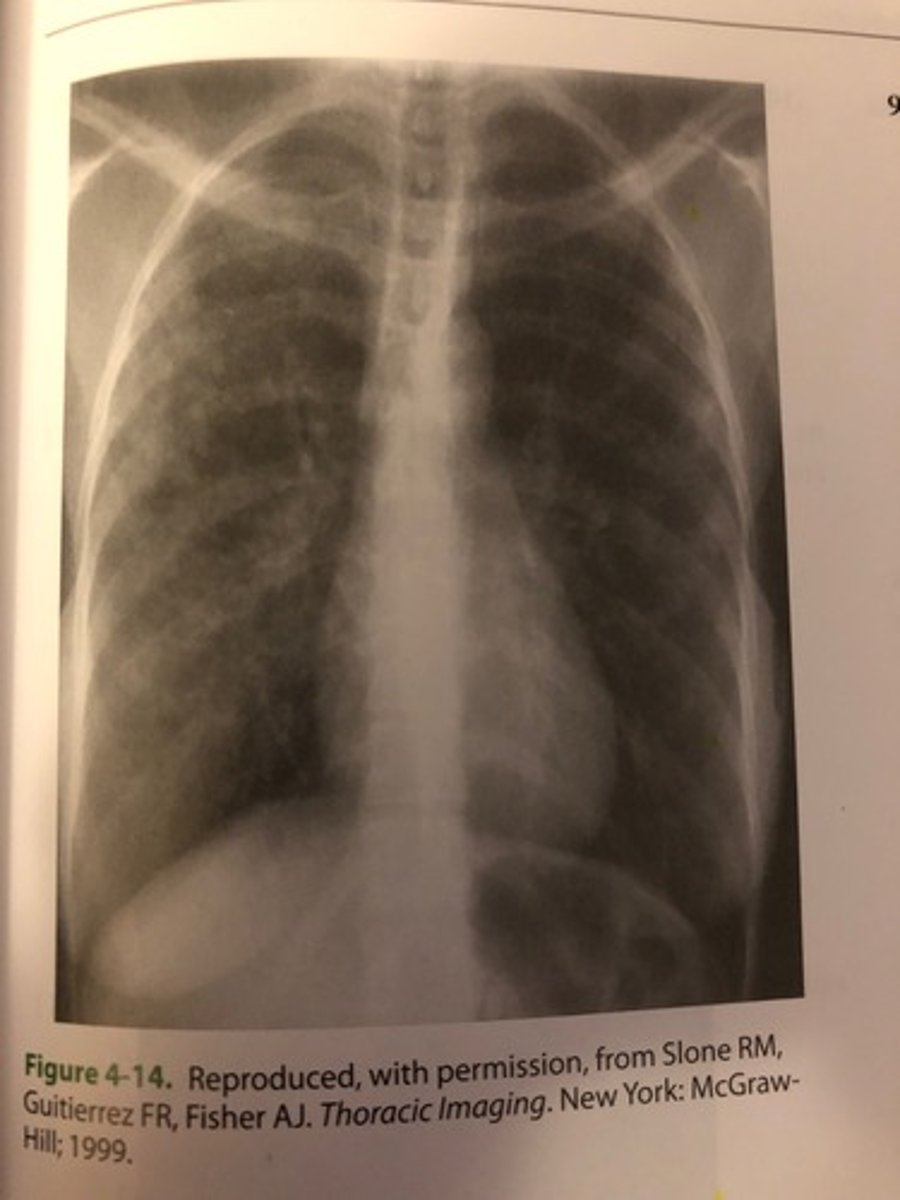
The PA chest image shown in Figure 4-14 exhibits which of the following qualities?
1. Adequate penetration of the heart
2. Long-scale contrast
3. Adequate inspiration
A. 1 only
B. 1 and 2 only
C. 2 and 3 only
D. 1, 2, and 3
(D) 1, 2, and 3
Exposure rate will decrease with an increase in
1. SID
2. kilovoltage
3. focal spot size
A. 1 only
B. 1 and 2 only
C. 2 and 3 only
D. 1, 2, and 3
(A) 1 only
Which of the following pathologic conditions probably will require a decrease in exposure factors?
(A) Osteomyelitis
(B) Osteoporosis
(C) Osteosclerosis
(D) Osteochondritis
(B) Osteoporosis
Distortion can be caused by
1. tube angle
2. the position of the organ or structure within the body
3. the radiographic positioning of the part
A. 1 only
B. 1 and 2 only
C. 2 and 3 only
D. 1, 2, and 3
(D) 1,2, and 3
Reducing the number of repeat images is an important way to decrease patient exposure and can be can be accomplished by
1. using AEC
2. good patient communication
3. accurate positioning skills
A. 1 only
B. 1 and 2 only
C. 2 and 3 only
D. 1, 2, and 3
(D) 1, 2, and 3