psych/soc meow 3
1/32
Earn XP
Description and Tags
notes, questions, concerns.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
social capital vs. cultural capital
social:
“who you know” aka social circles. e.g. wealthy people have access to wealthy people
cultural:
knowledge that doesn’t have a direct payoff in doing job, but knowledge that helps you in social world (e.g. golf)
the thomas theorem
individual beliefs have real consequences
How would a structural functionalist interpret the efficacy of yoga as part of a smoking cessation therapy?
A. Yoga provides an alternate understanding of healthful practices that enables the individual to better understand his or her personal needs and motives.
B. Yoga provides an inexpensive therapy option for those lacking the financial resources necessary for more expensive medical interventions.
C. The utility of yoga as an effective smoking cessation therapy stems from the transformation of the individual’s self-concept as a nonsmoker.
D. The utility of yoga as an effective smoking cessation therapy is an unintended, though beneficial, outcome of a yoga practice.
D:
Functionalism makes a distinction between manifest, or intended, and latent, or unintended, functions of social practices which sustain social stability. The option describes a latent, or unintended, function. Because the expected function of yoga is not specifically smoking cessation, its utility as a cessation therapy is a latent function of the social activity.
A: This option offers an explanation at an individual level which is not consistent with a functionalist approach.
B: This option refers to social inequalities. Functionalism does not focus on social inequalities.
C: This option describes dynamics at an individual level which is not consistent with a functionalist perspective.
cbt therapy addresses:
maladaptive behaviors through behavior therapy to systematically modify a person’s behavior. This is followed by sessions designed to foster cognitive change through self-assessments.
psychodynamic therapy can…
examine personal history
aversion therapy can…
associate negative states w unwanted behaviour
Although the study examines a specific bias in group decision-making, similar biases can influence individual decision-making. Which of the following individual-level effect is most similar to groupthink?
A.Self-serving bias
B.Confirmation bias
C.Hindsight bias
D.Response bias
B:
Confirmation bias is the tendency to put more weight on information that confirms one’s pre-existing attitudes. As with a group affected by groupthink, an individual’s confirmation bias causes the person to seek, and attend to, only information that confirms their existing point of view and to ignore disconfirming evidence.
alzheimer’s disease is associated with
increased amyloid B and NFT proteins
groupthinkg is the process of….
conformity and failure to critically evaluate alternatives n options
social loafing means that people are more productive….
ALONE than in a group.
less critical n creative in groups
Which type of psychoactive drug has the lowest risk of dependence?
A.Stimulants
B.Hallucinogens
C.Alcohol
D.Sedatives
B: hallucinogens
fundamental attribution error
justify someone’s behaviour based on DISPOSITIONAL factors n ignore situational factors when judging others’ behaviour
16
absolute poverty
an economic condition in which individuals cannot meet their basic needs
marginal poverty
stems from unstable employment conditions for an individual in which they cannot achieve minimum standards of living
relative poverty
social disadvantage by income or wealth as compared to the social advantages linked to income or wealth in a society
structural poverty
a lack of economic opportunities for individuals to leave poverty
latent learning takes place
in the absence of reinforcement or punishment
dissociative amnesia
cannot recall important autobiographical info, usually related to trauma or stressor
retrograde amnesia
loss of memory of previous info due to injury or neurological disease
schizoprenia
symptoms like delusions, hallucination, disorganized or diminished speech or behaviour
conversion disorder
impairments to voluntary motor or sensory function, NOT due to a recognized neuro/medical condition
cbt vs. psychoanalytic therapy vs. humanistic therapy
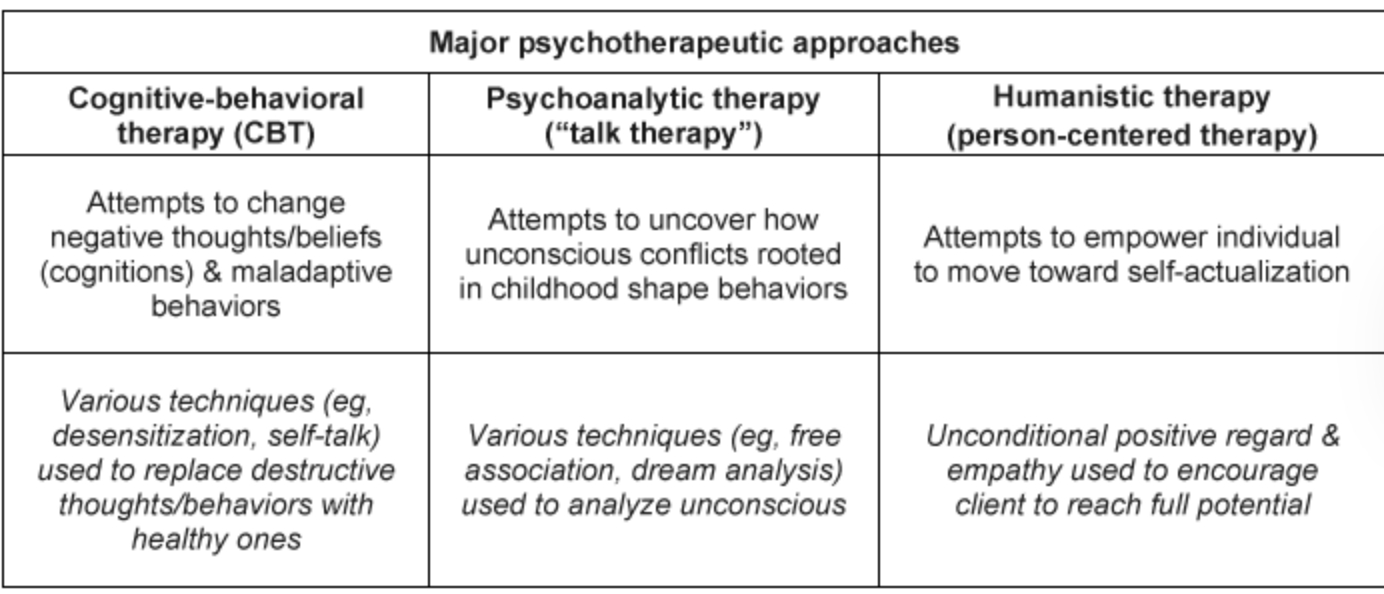
sensory adaptation occurs in the…
PNS
2 ways of long term potentiation
INC. number of receptors at postsynaptic neuron
INC. number of NT released by presynaptic neuron
= INC. firing rate
abbalation of hippocampus leads to
ANTEROGRADE amnesia aka inability to form NEW memories
explicit vs. implicit memory
EXPLICIT (declarative) SE
semantic: facts, concepts
episodic: experiences, events
IMPLICIT PE
procedural: skills, tasks
emotional/reflexive
self serving vs. actor-observer bias vs. FAE
SELF SERVING: success/failure
SUCCESS OWN = internal
FAILURE OWN = external
ACTOR-OBSERVER: attribute behaviour
OWN = external
OTHERS = internal
FAE: only OTHERS’ behaviour
OTHERS = personal > situational
2 types of memory that are STABLE w aging
SP
semantic (facts, concepts) n procedural (skills, tasks)
avoidance vs. escape learning
AVOIDANCE: want to PREVENT it from happening
ESCAPE: it’s already happening and you want to TERMINATE this aversive stimuli
BOTH = negative reinforcement aka REMOVE aversive stimuli to INCREASE behaviour
linguistic relativity hypothesis
language —> thoughts/cognition
if no word for green in your language, then you cannot identify green as a distinct colour
cognitive behavioural therapy CBT
systematically change one’s behaviour + foster cognitive changes via self-assessments