Dopamine, fear & amygdala
1/14
Earn XP
Description and Tags
w11how
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
categorising emotions
complex emotions
basic emotions
complex emotions
combinations of basic emotions
may be socially or culturally learned
requires cognitive processing
not automatically expressed
e.g regret
basic emotion
unique characteristics
developed through evolution
fundamental
reflected in facial expressions
relatively automatically generated
e.g fear, sadness
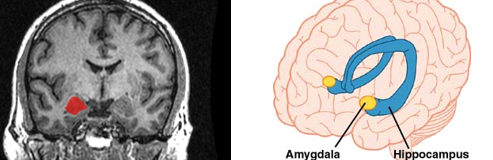
amygdala
plays a key role in fear
rats pre amygdala lesion
runs away to hide
rats post lesion
no fear response
Learning, emotion & amygdala - fear conditioning
what we know about amygdala comes from fear conditioning
first present 2 diff stimuli alone which elicits no response & one that elicits startled response
train mouse to associated tone w/shock
tone therefore elicits startled response as shock & tone is paired/associate with each other
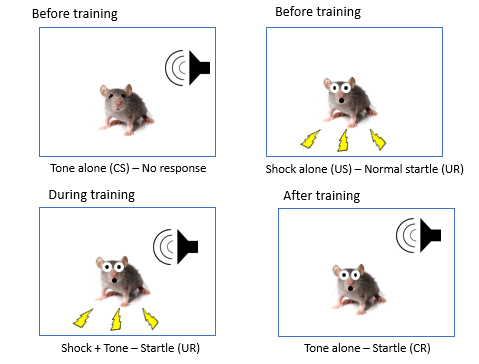
extinction
removing the association of tone w/shock
if tone occurs without shock over and over
unlearns the association
Lateral amygdala cells - patterns of firing during fear conditioning (Quirk et al, 1995)
cells that fire in response to the tone (the conditioned stimulus)
after training they increase their firing especially in the very early phase after tone delivery
The plasticity goes away after extinction
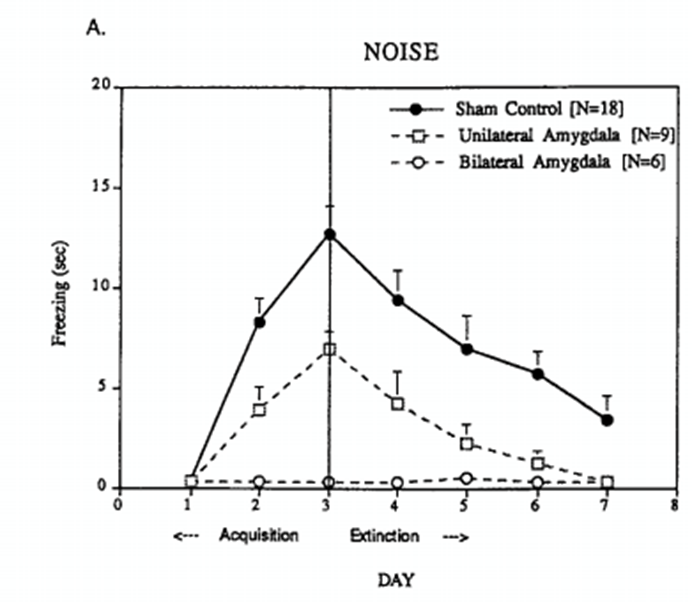
role of amygdala in fear conditioning (LeDoux, 1996)
Amygala lesions block fear learning
Rats w/amygdala lesions do not learn to associate the noise (CS) with the shock (US) to produce a fear response (CR)
unable to be conditioned to fear
role of amygdala in generation of conscious experience of fear
is what is the behavioural response to fear
3 patients with bilateral amygdala lesions due to Urbach-Wiethe disease (Feinstein et al. 2013)
rare disorder in which lesions occur in bilateral (both) amygdala areas
gave p w/bilateral amygala damage co2 inhalation
inhaled CO2 – method of inducing panic
Measured rates of panic attacks & subjective fear/panic
had an elevated panic response
All the amygdala patients had panic attacks, only 25% of healthy controls did
Consistent with earlier suggestions that panic is a false biological alarm, the affective response to CO2 may be part of a protective system triggered by suffocation and acute metabolic distress.
they can experience panic
Amygdala patients and controls who did have panic attacks had similar levels of subjective panic → capable to experience fear
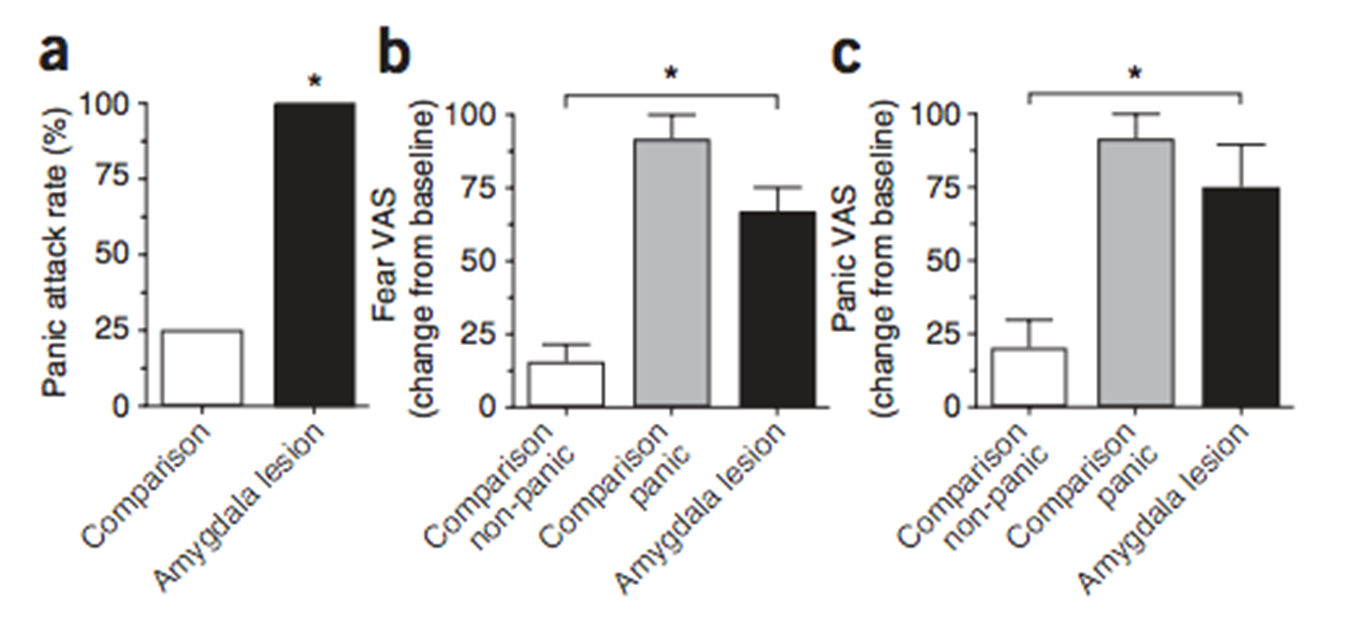
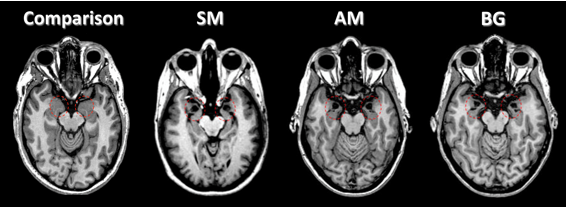
amygdala plays a role in the translation of external threats into a fearful response
Intact fearful response to carbon dioxide inhalation in patients missing both amygdalae suggests such patients can experience fear
Suggests amygdala is not necessary for the conscious experience of fear
perhaps amygdala plays role in translation of external threats into fearful response
conscious or unconscious learning in the amygdala (Bechara et al. 1995)
studied 3 p – 1 w/amygdala lesion, 1 w/hippocampal lesion, 1 w/damage to both
Conditioned Stimulus (CS): coloured slide/tone
Unconditioned Stimulus (US): Boat horn
Measured Skin Conductance Response (SCR)
asked P to report explicit knowledge of which CS predicted the US → conscious knowledge
Measured SCR to loud noises paired with a visual or auditory conditioned stimulus
double dissociation of conditioning & declarative knowledge relative to amygdala & hippocampus
P w/amygdala damage showed impaired SCR to the conditioned stimulus but intact factual learning
little skin conductance response
can consciously identify
P w/hippocampus damage showed normal SCR to the conditioned stimulus but impaired factual learning
normal SCR
P w/both amygdala & hippocampus damage showed impaired SCR to conditioned stimulus and impaired factual learning
Amygdala is necessary for implicit learning of threat
hippocampus is involved in declaritive learning
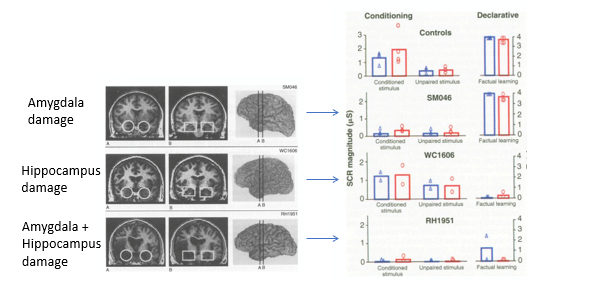
Role of amygdala in fear summary
Amygdala necessary for generation of fear response
Amygdala involved in the translation of threatening stimuli into a behavioural response not in the conscious experience of fear per se
These data have been influential in the generation of the 2 emotion systems hypothesis
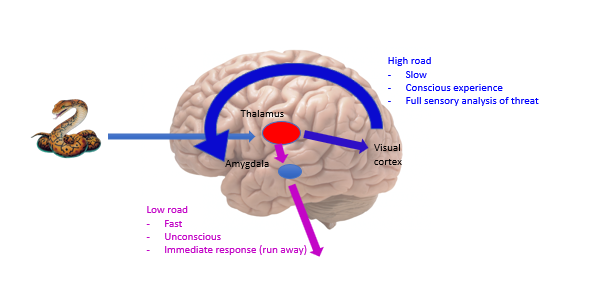
Low road: Fast, automatic, immediate responses (amygdala)
High road: Slow, conscious experience of emotion (cortex)
LeDoux → 2 emotion systems
Information about a threatening stimulus reaches the amygdala via two pathways – the high road and low road.
information takes about 15ms to go down the low road and is fairly crude
nformation takes about 300 ms to travel down the high road and has a much higher level of detail – the sensory properties of the stimulus are analysed in the visual cortex before travelling to the amygdala
intelligent, goal directed behaviour
executive function
working memory
emotion
object recognition
attention
all contribute to result in goal directed behaviour
where they are mapped/whether they build on each other