Oral Histology LO 6
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
85%-90%
Major salivary glands provide ——% to ——% of saliva.
25%
The parotid gland provides ——% of the saliva to the mouth.
60%
The submandibular gland provides ——% of the saliva to the mouth.
5%
The sublingual gland provides —% of the saliva to the mouth.
10%
The minor salivary glands provide about ——% of the saliva to the mouth.
Serous
What kind of saliva does the parotid gland produce?
Mixed serous and mucous
What kind of saliva does the submandibular gland produce?
Mucous secretion
What kind of saliva does the sublingual gland produce?
Secretory cells
Epithelial cells that produce saliva are called ——————— cells.
Acinus (or alveolus)
Cluster of mucous/serous/or combination cells that secrete into a terminal collecting duct. Secretory cells are found in a group called an —————. Each ————— is located at the terminal portion of the gland connected to the ductal system. Each ————— consists of a single layer of cuboidal epithelial cells surrounding a lumen.
Zymogen
Serous cells secrete mostly protein and small amounts of carbohydrates secrete ————— granules: precursor to amylase: breakdown of carbohydrate in diet. Water consistency.
Mucigen
For mucous cells, secretion is high in carbohydrate, low in protein. Secretion is viscous, ————— vesicles precursor to mucin. Mucin mixes with oral fluid to become thick and ropey.
Myoepithelial cells
———————— cells facilitate the flow of saliva out of each lumen into connecting ducts. Contractile, squeezing the acinus and forcing the saliva out of the lumen into the connecting duct.
Excretory ducts
The final portion of the salivary gland duct system is the ——————— duct. Pseudostratified columnar to stratified cuboidal to stratified squamous epithelium to blend with surrounding oral mucosal tissues at the ductal opening.
Septum(a)
The ————— divide the inner portion of the salivary glands into larger lobules and smaller lobules.
Remineralization
This is one of the functions of saliva. ————————- and increases enamel hardness in newly erupted teeth: calcium and phosphate ions in saliva.
Amylase
————— breaks down starches to be more easily digestible.
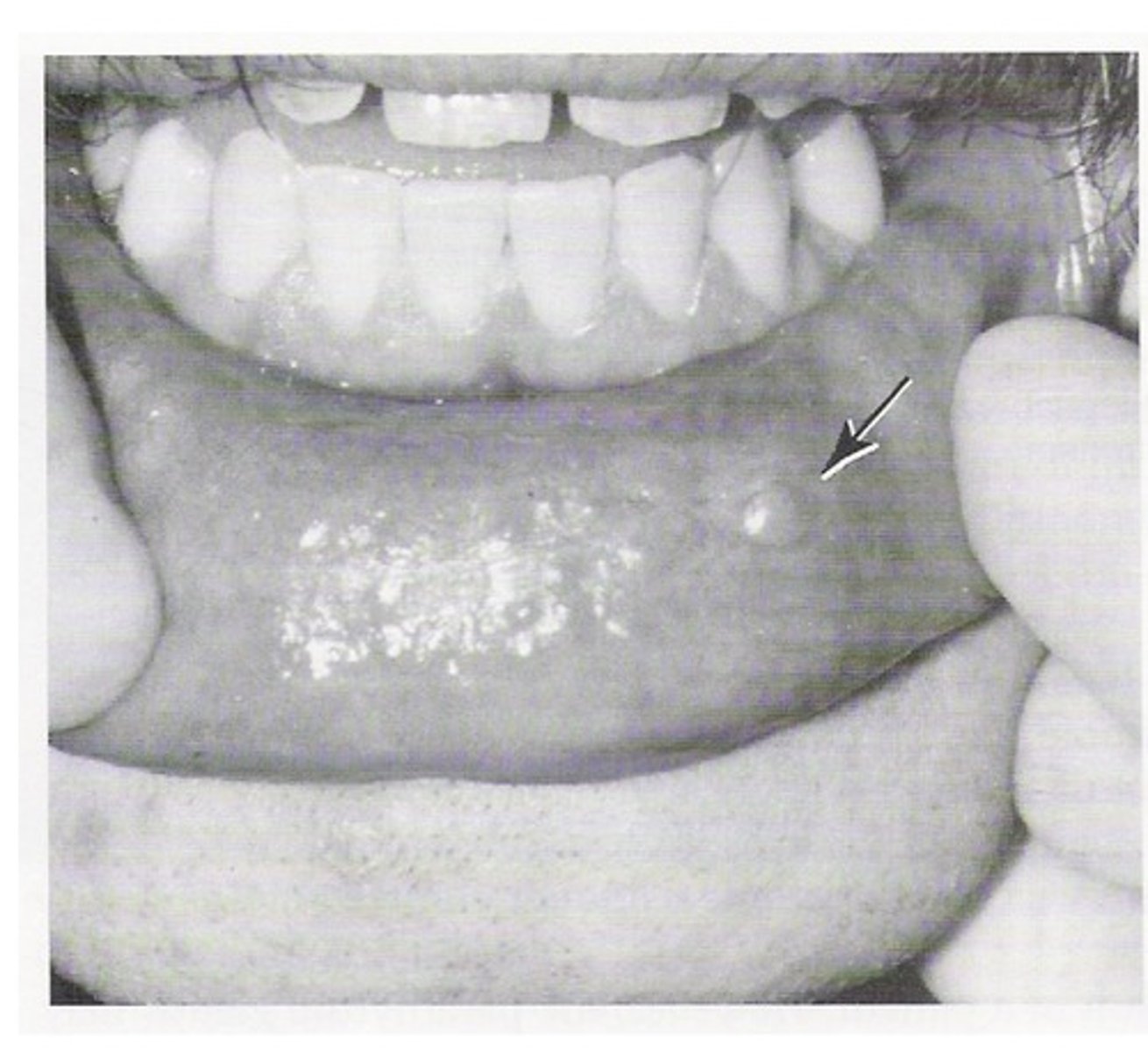
Mucocele
Minor salivary gland duct injured, mucous salivary secretion into adjacent connective tissue, causing swelling in the tissue.
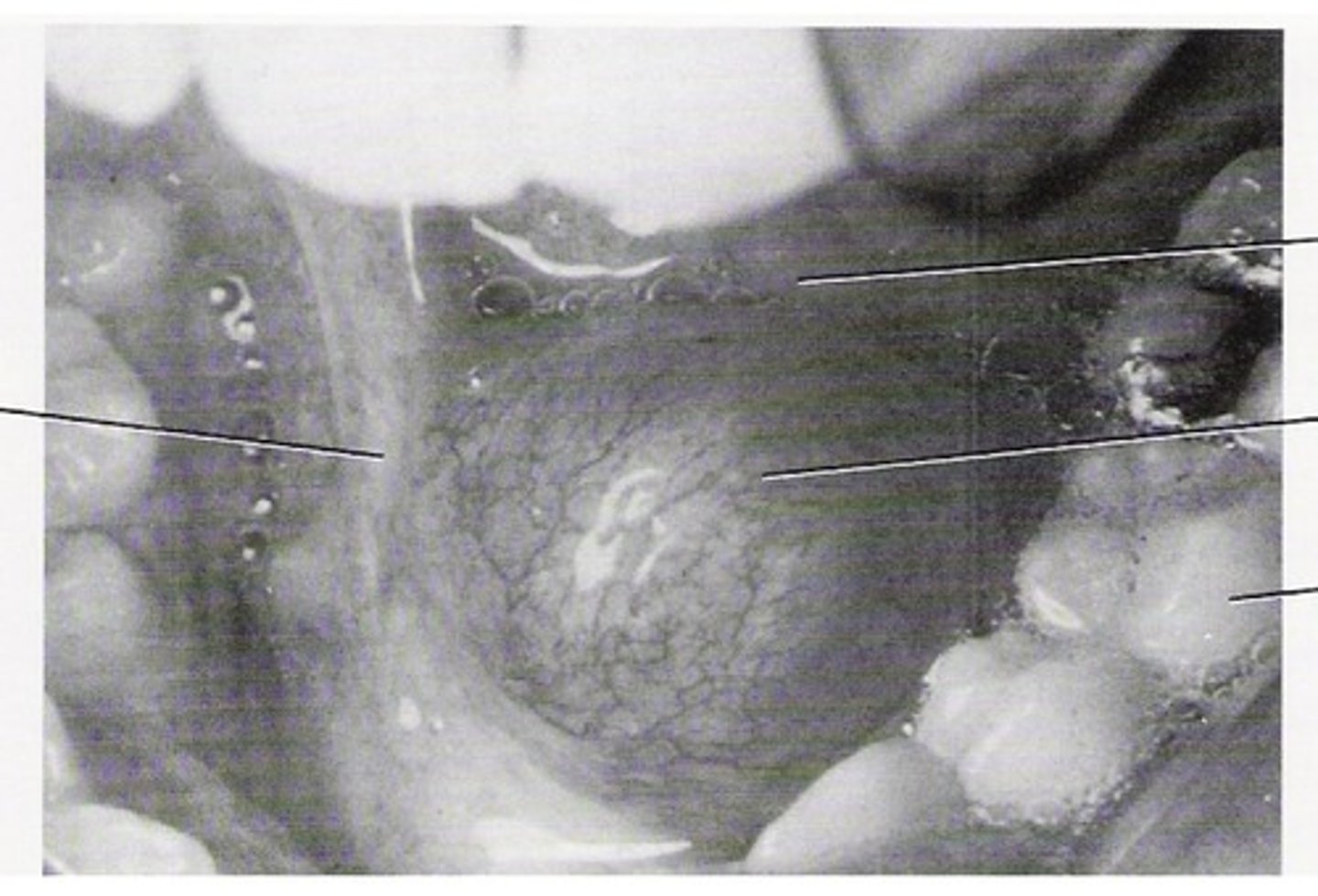
Ranula
Obstruction or injury to the submandibular or sublingual duct causing unilateral swelling on the floor of the mouth.
Waldeyer's ring
Tonsillary tissue surrounds the oropharynx in a ring called:
Adenoids
The pharyngeal tonsil is sometimes called the —————. It's in the midline of the oropharynx. Made of pseaudostratified epithelium, part of the nasopharynx.
Palatine tonsils
These tonsils are located bilaterally posterior to the molars. Made of stratified squamous epithelium. These are the largest tonsils divided into lobules with crypts. Infection: deep crypts becomes plugged with lymphocyte discharge and desquamated epithelial cells. Seromucous glands assist flushing only the surface of the crypts.
Lingual tonsils
These tonsils located on the surface of the posterior 1/3 of the tongue. Wide mouth crypts mucous glands, skeletal muscle, adipose tissue, cleansed easily with saliva.