PSYC Exam 2
1/221
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
222 Terms
change blindness
we are bad at detecting changes if we don’t know where to look or where to direct our attention
Selective attention
selecting which stimuli to attend to and to ignore
Ex: talking to one person at a party - ignoring everyone else and paying attention/focuses on the conversation with that person
Door study
One person would ask a stranger for directions
A door/painting interrupts the conversation and as it goes past, that person switches out with another
the stranger still answers as if its the same person
they didn’t notice the change
Attention
involves multiple mechanisms (mainly frontal lobe)
will direct additional blood flow to relevant areas —> leading to higher activity in these areas to accommodate additional processing
RCBF and aging
in aging individuals (as early as 30) PET scans show rCBF significantly decreases to frontal cortices —> this leads to decrease in memory capability, attention, bodily function control
blood flow to frontal cortex decreases as we age
first few years of age experience a spike of blood flow to these areas —> to compensate for demand for attention, learning, metabolism (“as children, we are a sponge”)
“if we can’t pay attention properly, we cannot comprehend properly”
ADHD and blood flow
less blood flow to frontal lobe
reduced frontal lobe and temporal cortices size
medications like Guanfacine (treats high BP by lowering HR) can be used to allow better blood flow
other medications increase NE and DA transmission
cocktail party effect
while in a noisy environment, we can still attend to one conversation
t/f we are very good at selectively attending to only the information that is currently relevant
true
we can miss extremely salient events that happen right in front of our eyes
t/f the same processing is used to information that is attended and unattended
false
different processing happens for attended information than unattended
inattentional blindness
if we attend to one thing we often miss others especially if unexpected
people’s intuition is very wrong - we believe we see everything especially unexpected (opposite of what’s true)
inattentional blindness - radiologists
24/25 radiologists did not find the hidden gorilla embedded in xray scans
expertise does not overcome inattentional blindness in most cases
you may miss things that are actually there (type II error)
dividing attention
blood flow direction is a fixed amount, when doing multiple tasks/divide attention = less blood flow directed to each task
the more we try to multi-task, the less effective we are at doing that task
not all tasks are equal/as complex
tasks differ in amount of attention needed
as we practice and get more efficient, the less attention and blood flow we will need
t/f the more you divide you attention the longer it takes to process any of your attention modalities
true
as you drive and talk on the phone you have a longer reaction time
why would have a physical passenger make you a better drive
the passenger is also exposed to the same stimuli and can help reaction
social pressure may make you feel more responsible or pay more attention
limits of attention
tracking speed: how fast are the attended objects moving or how fast your eyes can keep up (faster = more difficult to process)
capacity: number of objects you can process at the same time
crowding: the closer objects are to one another, the harder it is to identify them (how dense is the information)
relationship between blood flow and measuring attention
positive correlation
as blood flow increases, attention increases
reaction time
time it takes to react
SHORT reaction time = GOOD
relation between reaction time and task complexity
positive correlation
the more complex the task, the longer the reaction time
Information in sensory memory last __ seconds
3
Information in short term memory last __ seconds
15-20 if not rehearsed
Information in long term memory lasts
virtually unlimited, if we don’t forget it
Memory flow chart
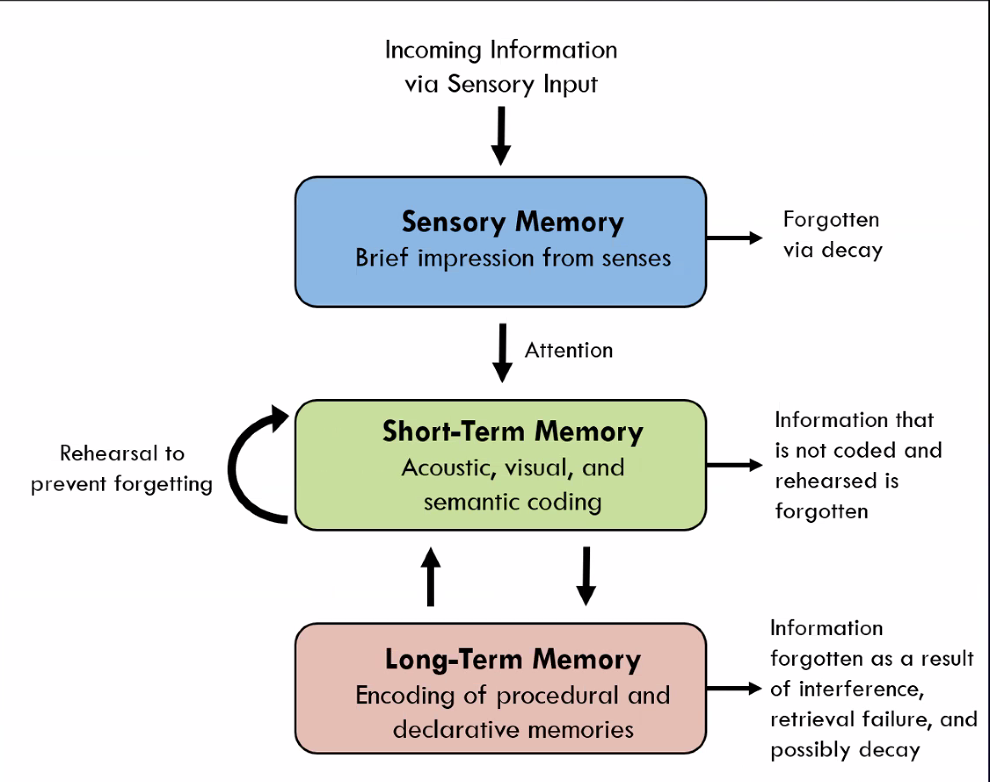
Sensory memory
brief impression from senses
unless attention is devoted to an aspect of the scene, the sensory memory will decay
short term memory
acoustic, visual, and semantic coding (temporary storage)
disappears after 15-20 seconds if not rehearsed or coded
can be passed/coded into long term memory
long term memory
encoding of procedural and declarative memories
more important memories are encoded more quickly
Explicit/conscious memory —> episodic (experiences) vs semantic (facts, concepts) memory
Implicit/unconscious memory —> procedural memory (skills, tasks)
active manipulation
often referred to as working memory
components of short term memory
actively engaging short term memory
Ex: remembering numbers
constantly saying the number to remember them is active manipulation
baddeley’s theory of working memory
emphasizes how attention and conscious processing mediate the memory encoding
working memory can involve active manipulation of multiple sensory modalities simultaneously
components: central executive, visuospatial sketchpad, episodic buff, phonological loop, long term memory
Ex: we can read while listening to music
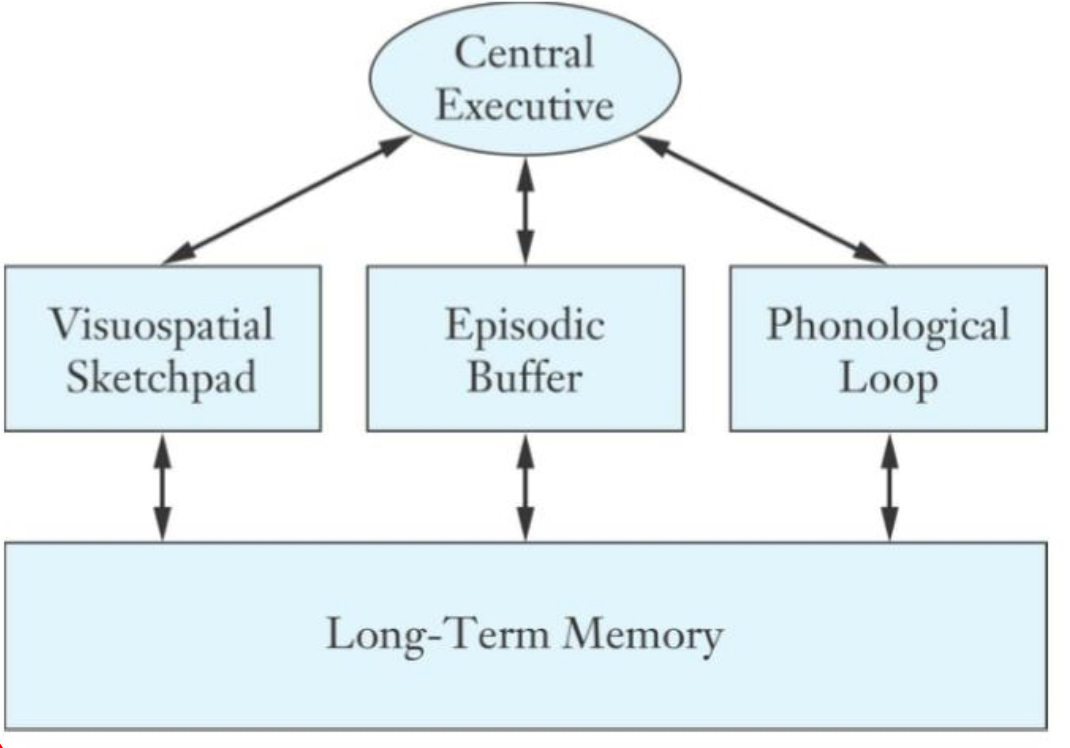
Central executive - Baddeley’s theory of working memory
directs our attention while ALSO coordinating the subsidiary systems
visuospatial sketchad - Baddeley’s theory of working memory
being able to imagine/visualize things at different angles or recall color
“mental screenshot”
visualizing important stuff and ignoring everything else that’s in your visual field
episodic buffer - Baddeley’s theory of working memory
connecting information current experience to past memories
connecting phonological and visual elements into a single cohesive memory
Phonological loop - Baddeley’s theory of working memory
utilizes rehearsal to maintain things into short term memory
Memory capacity compare to non humans - chimpanzees
they have a better working memory
important for them to process multiple things at once in a short amount of time
Relationship between accessing memories and long term memory
The more you access a memory = the more they restructure = the more likely they’ll encode into long term memory
implicit memory
memories are accessed and utilized unconsciously
long term memory
procedural memory: how to execute procedures to carry out tasks automatically
can occur together with explicit memory
explicit memory
conscious recollection
semantic memory: general facts and knowledge about our world
episodic memory: memory for specific events that have happened to us
episodic and semantic memory
can shift from episodic to semantic over time (development of phobias due to traumatic incident)
Ex: petting a cat then getting mauled (episodic) —> over time lead to phobia of cats (semantic)
Mechanisms of memory
long term potentiation: long lasting increase in synaptic efficacy following repeated and frequent activation between neurons
neurons that fire together, wire together
repeated simultaneous activation = postsynaptic cell to become more sensitive, and make synapse stronger and more likely to be activated ion in the future
synaptic plasticity change can
neurotransmitter released
number of postsynaptic receptors available
results in synaptic strength
Neuronal ensembles
group of neurons correlated with spontaneous and evoked activity
memory encoding and retrieval activate these
t/f: experiences and memories change the connection between neurons, altering the ensembles over time
true
dementia
decline in mental ability severe enough to interfere with daily life
alzheimer’s is a type of dementia
Alzheimer’s
plaques deposit on brain and tangled proteins cause affected neurons
sleep may play into development of plaques and tangles (lack of sleep = bad)
affects hippocampus first before speading
spreading = neuronal cell death —> leads to memory loss, disorientation, emotional instability
Priming
facilitation of responding that occurs as a result of the presentation of a semantically or phonologically related word
Ex: saying nurse will lead to doctor
absent mindedness - forgetting
inability to properly encode the information we wish to remember
divided attention = cannot rehearse information = decay
blocking - forgetting
inability to properly retrieve information that is still stores in brain
can be encumbered by all the associations we have and are left with partial recall
relates to crowding in attention
transience
details of memories deterioriate over time
can recall last night’s dinner in detail but sunday may not have as much detail
trace decay theory
explains WHY memories fade over time
“use it or lose it”
all memories are slowly fading
Intrusion error - memory error
brain will recreate words that associated with the group even if it was not in the group
Ex: “bed, rest, awake, tired, dream, snooze” —> sleep is NOT included but people may include it
type 1 error: signal not there but response is that it is
source monitoring - memory error
ability to link a given memory to its origin
limited to ability to remember context of the memory and to what extent
error = source misattribution: incorrectly attributes the source of a memory to a specific experience
interference - memory error
proactive: inability to recall newly- learned information due to previously learned information and newly-learned information
a friend having the same number for years, then changes it —> unable to learn new number due to only remembering old one
Retroactive: inability to recall old information due to interference with newly-learned information
go to a website you haven’t been to in years —> try recent passwords but can’t remember old passwords
flashbulb memories
memory for circumstances surrounding shocking, highly charged important events
do flashbulb memories decay at the same rate as regular memories
yes
you believe you remember exactly where you were and what happened for flashbulb memories because confidence in recall STAYS constant
over time details can be lacking like regular memory
other memories will have a decreasing recall confidence
Memory improvement
recitation
taking breaks
mnemonics
self-referencing: relate it to yourself
context when learning - recall example
state of mind matters during priming memories
people are better at recall when they’re sober if they learned it sober
people are better at recall when they’re drunk if they learned it drunk
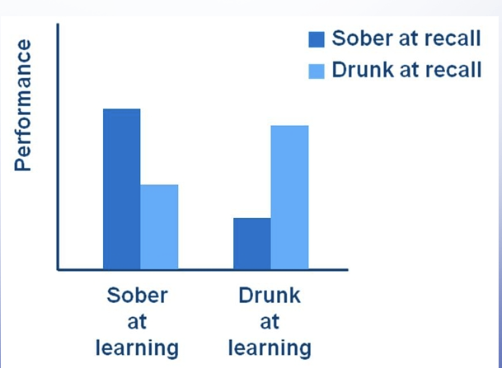
Importance of context when learning graph
cognition
ability to process knowledge, understand concepts, and solve problems
involves ability to plan for future/talk about past, imagine abstract concepts, assimilate new information, and communicate with others
ability to talk about time besides the present effectively and imagine abstract images makes human cognition unqiue
where is logic and reasoning activated in the brain
frontal lobe
as the brain develops so does logic and reasoning ability
schizophrenia
improper development of the frontal lobe (one of the reasons)
breakdown in thought, emtoion, and behavior relationship
leads to faulty perception, inappropriate feelings and actions, withdrawal from reality, personal relationships into fantasy and delusion
Human problem-solving
we emply different tactics based on the type and complexity of the problem
common tactics:
algorithmns
heuristics
trial and error
insight
algorithms
step by step procedure that guides individuals through complex situations ensuring a logical and consistent approach to decsion making
tend to memorize algorithm
may not be efficient, in cases like CPR it IS ultilized to optimize success but may not work for EVERY patient
heurisitic
mental shortcut that allow people to quickly make judgement and solve problems
ex: middle aged patient comes to the er with chest pain
chest pain = symptom of heart attack
assess demographics and may suspect a heart attack took place
trial and error
trying a number of different solutions and ruling out that those don’t work
good if you have a limited number of options available
can be frustrating due to how time consuming it is
Ex: taking different medications for pain and trying to find one that works
insight
refers to common human experience of suddenly understanding a previously incomprehensible problem or concept
2 step process: don’t know —> aha moment
brief superior temporal gyrus activation before connection is made —> this structure is vital for making connections
bias and hueristics
heurisitics uses top down processing to process sensory input/infer since we cannot process it all
leads to potential bias —> if it happened to me it must happen to everyone else
can lead to errors in judgement or thinking due to personal experience
confirmation bias
propensity to favor evidence that confirms our ideas while disregarding evidence that doesn’t
belief perservance
tendency to continue to believe things even after out reasons to believe them have been undermined
means of protecting out egos
Psychological reactance
When we are told what to do or think, we perceive that as having some of our freedoms or rights taken away —> react by doing the opposite
Hindsight bias
Propensity to perceive outcomes AFTER the fact
when reflecting, details consistent with the outcome become apparent/more important
Hindsight bias and overconfidence
Our bias becomes overconfident which is a mis-judgement of our aptitude at a certain task
when we think back to a prior issue, our hindsight bias makes us think we er more accurate in predicting the outcome of the issue
Influence of language on cognition
Structure of language affects its speakers worldview or cognition and thus people’s perception are relative to their spoken language
Sapir-whorf hypothesis
cultures have different names for specific colors, they should perceive it differently than others
abandoned due to lack of experimental evidence
lead to development of cognitive behavioral therapy
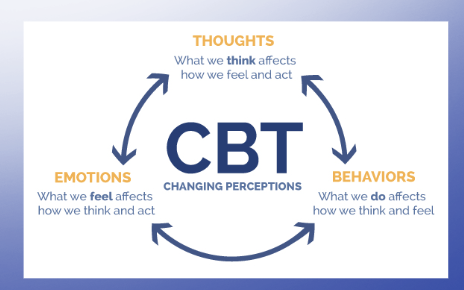
cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT)
empathizes interaction between thoughts, feelings, and behaviors
relies on ability to utilize our internal monologue to correct maladaptive behaviors and feelings
Language development theories - nativist Chomsky
Humans are born with language acquisition device
all language have the same structural elements
Only operates during critical period of development (birth-12)
Language development theories - learning theory skinner
Linguistic ability is not innate but rather language is acquired through enforcement
can’t fully account for the ability of children to produce words or sound combinations they’ve never heard before
Ex: child learns to say the word mama because it begins with sounds like “m-“ or “ma-“
Language develop theory - interactionist theory vgotsky
Biological and social factors interact to motivate children to learn a language
combines that we do have biological predisposition for language acquisition and that it can be mediated by social factory
Draws upon child’s desire to communicate, motivated to learn language so they can communicate
If a child is not properly socialized they will not develop language fully
Gene Wiley
unfortunately trapped in her house and was not talked to or taught how to speak
When rescued at 13, could only make infant like sounds
Learned word, BUT could NOT communicate and articulate words (grammar)
supports critical period hypothesis of language acquisition
Bella devyantknia
Bella’s mother was a language tutor decided to socialize Bella and expose her to a variety of languages
By 4, she could speak 7 languages
By 6, she could read in all these languages
wernicke’s aphasia
say words, but no real meaning, difficulty reading
**fluent speech pattern but impaired comprehension of language
broca’s area aphasia
unable to form words properly, difficulty writing
arcuate fasciculus
connects broca and wernicke’s area (conduction pathway)
damage can result in conduction aphasia = fluent speech but paraphasic speech (not tested on)
Ex: 1, 2, 3, moose, boy, 6, 7
dsylexia can be explained by issues with arcuate fasciculus
Dsylexia
learning disability that affects the ability to read or interpret words, letters, and other symbols
many types
posterior brain are not being activated
abnormalities in arcuate fasciulus
Intelligence
ill-defined = many different theories
Neal’s defintion: ability to formulate a number and certain quality level of inferences based on a given input
Spearman’s G
G = general intelligence
intelligence can be reduced to a single number (IQ)
higher G score on one task —> same high score on another
belief how you do on one cognitive task correlates to how you do on other cognitive tasks
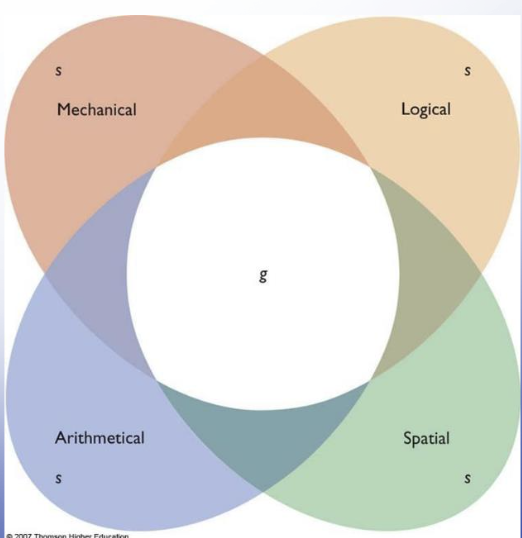
G underlying factors
symbol of an individual’s working memory capabilities, neural processing speed, and myelination
processing speed
attention and attentional filtering
working memory capacity
cognitive control
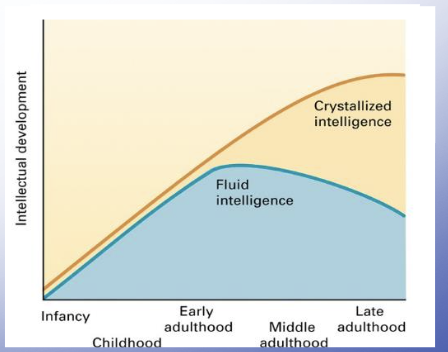
Fluid intelligence
fluid reasoning
ability to deal with new and unusual problems, identifying patterns, and problem solving
“Fluid = creativity”
Crystallized intelligence
acquired knowledge (life experience)
includes verbal knowledge and expertise
“Crystal is hard, crystallized intelligence is hard facts”
Fluid and crystallized intelligence over age
Fluid peaks at early adulthood
crystallized increases over time (likely due to more experiences and expertise)
Robert Sternberg’s triarchic theory
Analytic intelligence: mental steps used to solve problems
Creative intelligence: use of experience to insight
practical intelligence: read and adapt everyday contents
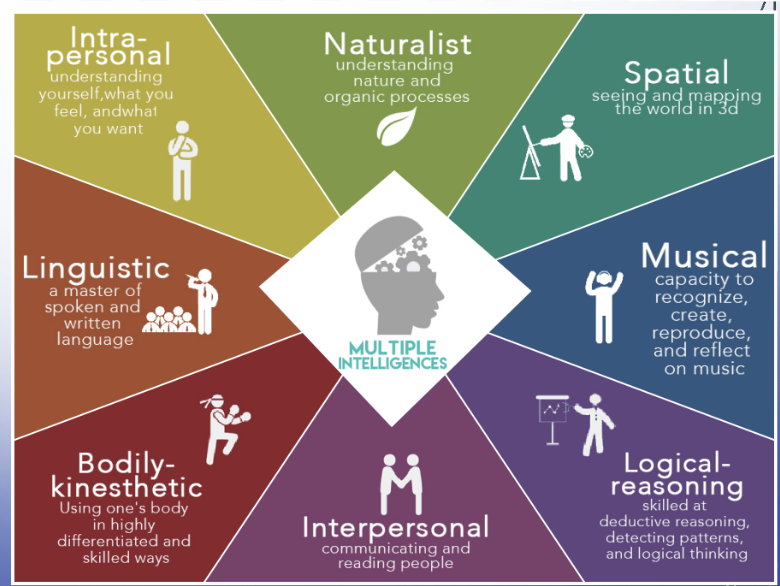
Gardner’s theory
we have multiple TYPES of intelligence
Beginning of measuring intelligence
France 1904, universal elementary education - Alfred Binet
designed first intelligence tests
IQ Distribution
standardized - average IQ = 100
how you compare to the average individual in your society of the same age
Why are our IQ levels higher than our grandparents - Ted Talk
we like in a world that goes beyond concrete fact
historically average IQ levels were about 70
due to different needs at the time, no specific need for problem solving, complex thought, etc
humans began to perform problem solving/other higher ways of thinking - higher intelligence is not due to innate ability
classification, logic, and taking hypothetical seriously
Ex: he asked his racist grandparents how would you feel if one day you were black —> responded no one wakes up black spontaneously —> could not think past the hypothetical
IQ Nowadays
wechsler adult intelligence scale
measures a mix of fluid and crystallized intellience
focuses heavily on fluid
Root of intelligence
genetic similarity
Heritability of intelligence
as genetic similarity drops, similarity intelligence drops
HOWEVER, intelligence is not relatively fixed —> environment can also lead to increases in IQ
especially if you started in terrible conditions
Consciousness
awareness of external events, awareness to internal sensations, and awareness of your own thoughts and emotions
continuum
frontal lobe and limbic system involved
executive control allows us to make decision that will be advantageous to us in the moment and future
limbic system and consciousness
regulation of bodily states
consciousness of our bodily states allows us to plan and seek sustenance
access to memory allows us to efficiently forage for food
Why have consciousness
unconscious processes like breathing, blood flow, would be too much
awareness is important when its important to be aware to stimuli —> when unconscious processes become aware to us (ex: breathing while swimming)
Limbic system
conscious awareness of our bodily states allow us to plan
amygdala - emotion
thalamus - sensory processing
hypothalamus - hunger/thirst/sleep
hippocampus - memory
Pseudocoma
patients appear to be in coma but are conscious
locked in syndrome