birds (aves)
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
the ancestor of birds was likely a theropod (dinosaur). what are 7 shared characteristics of these two groups?
bipedal, similar feet
carnivorous
4-chambered heart
similar lungs
feathered!
hollow bones
parental care of eggs and juveniles
describe the archaeopteryx
about 150 mya (jurassic)
crow-sized
feathers+wings - bird characters
teeth+bony tail - nonbird characters
what are aves’ characteristics
amniotes
endothermic - thermoregulation
4-chambered heart
feathers
most fly
diverse beaks
diverse feet
specialized respiration and ventilation
whats an amniote
organisms that produce amniotic eggs - which are eggs that can withstand dry environment without suffering from desiccation
name the two types of body heats in vertebrates, provide an example for each
ectothermic: absorb external heat, ex. bees
endothermic: generate their own internal heat throguh metabolic processes, ex. bears
name the two types of thermoregulation in vertebrates, provide an example for each
homeothermy: ability to maintain a constant temperature, ex. mouse
heterothermy: variable temperature, ex. lizards
list three types of thermoregulation mechanisms
behavioural
physiological
physical
describe behavioural thermoregulation, provide examples
orientation relative to heat source
basking, huddling and varying contact with heat surface
moving locations throughout the day
ex. lizards maintain body temp between upper and lower limits by moving between hot and cold microhabitats
ex. penguins huddling together for body heat
describe physiological thermoregulation
too hot: increase blood flow to periphery, sweating (evaporative cooling), panting
too cold: decrease blood flow to periphery, shiver (metabolic heat)
in hypothalamus: negative feedback system
describe physical thermoregulation, provide examples
insulation (fur, feathers, fat)
surface area<volume
colour
ex. jack rabbits vs arctic hares
countercurrent heat exchangers
ex. whale tongue, mammal foot, brown adipose tissues
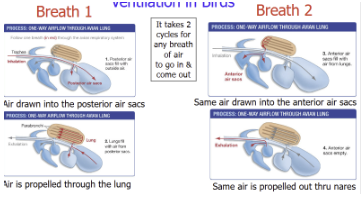
describe avian respiration
flying and endothermy demand high amount of oxygen
system much more complex and efficient than mammals
system:
numerous air sacs (8-9): anterior and posterior
unidirectional flow of air through lungs (vs. us that have tidal air flow: in and out)
takes 2 cycles for any breath of air to go in and out
breath 1: air drawn into posterior air sacs, air propelled through the lung
breath 2: same air drawn into anterior air sacs
same air is propelled out through nares
how many times has flight evolved, name each group that evolved
4 times
insects
pterosaurs
birds
bats
Note: flying is different than gliding
what is convergent evolution? provide an example
independant evolution from different lineages, all end up evolving the same trait due to the selection/environment
ex. wings are evolved across many lineages, but evolved independantly
list 3 adaptations “for” flight
hollow bones
sternum enlarged and keeled: increases SA for attachment of flight muscles (large pectoral muscles)
feathers
what are feathers’ functions?
insulation
flight
sensory structures
lining nests
what are feathers derived from? what are they made of?
evolved from scales (reptiles!)
composed of beta-”keratin”
most birds have reptile-like scaled skin on their legs
what were the two hypotheses of how flight evolved from the ground? which is more likely, why?
tree-down: jump from trees, flap their arms and survived better
ground-up: hatchlings run from danger, often steep inclines, flapping their wings, angle of wing flapping created traction rather than lift
likely ground-up, based on species’ ancestors of those that can fly now