antibodies and types of immunity
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
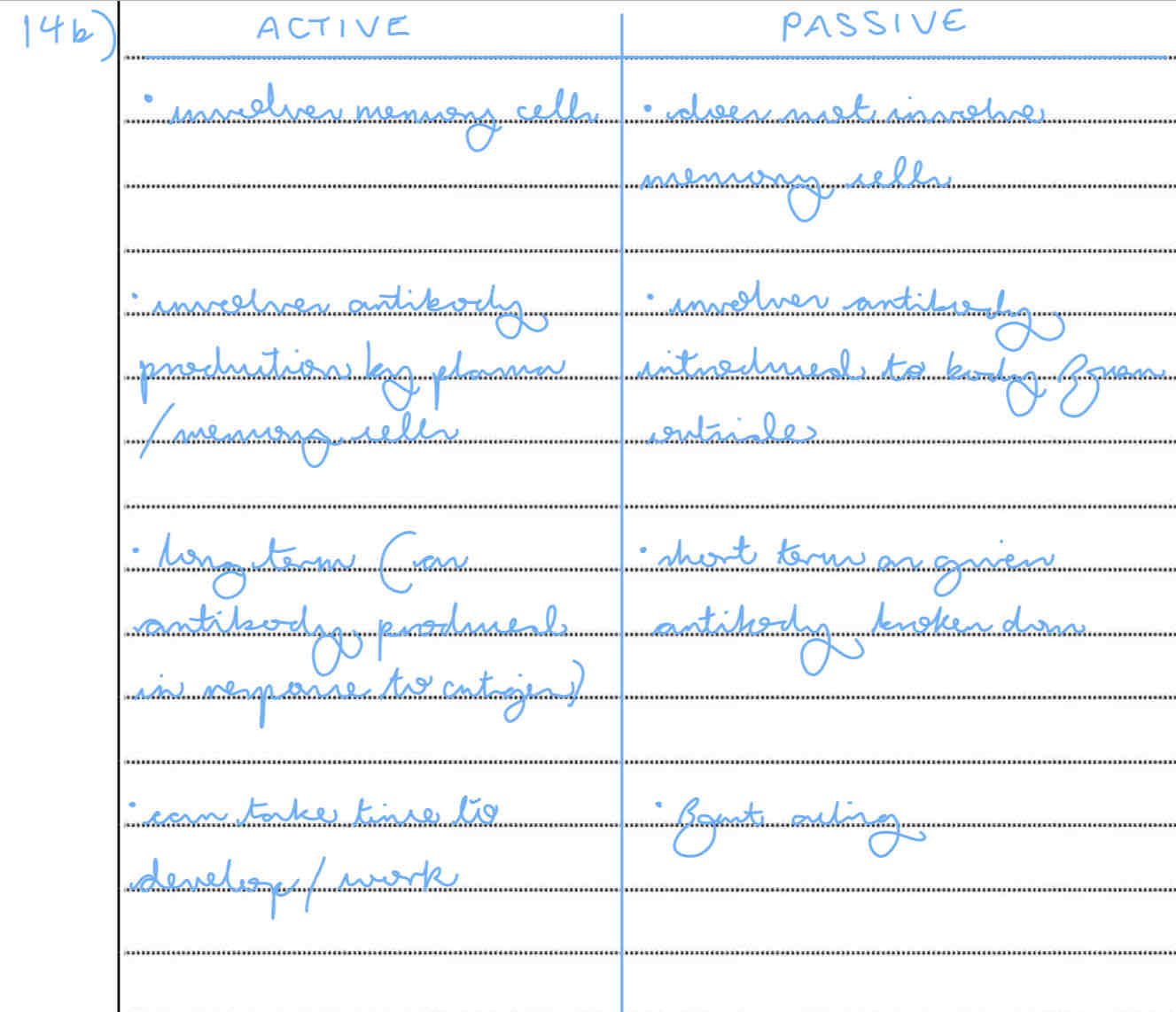
describe the differences between active and passive immunity (5)
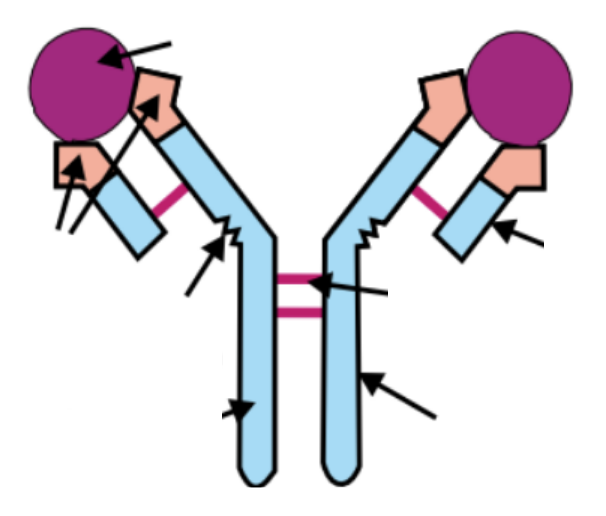
can you label this antibody?
yes
how do antibodies help to destroy pathogens?
bind and neutralise toxins
agglutination
what is agglutination? why is it significant?
antibodies are flexible, which cause pathogens to clump together
→ this makes the pathogens easier to locate and destroy by phagocytes
draw the shape of the primary/secondary immune response graph:
explain the shape of the primary/secondary immune response graph:
primary immune response:
takes time for clonal selection and expansion of specific T and B cells
antibodies do not begin to appear in the blood for several days after the foreign antigen enters the body (this is when symptoms occur)
some B cells differentiate during clonal expansion into plasma cells and memory cells but plasma cells are short lived :(
secondary immune response:
B memory cells recognise antigen and quickly / and differentiate into plasma cells and more memory cells
very quick response → pathogens killed before symptoms develop
what is active immunity?
immunity developed after immune system makes its own antibodies
what is natural active immunity?
immunity developed after immune system makes its own antibodies following infection
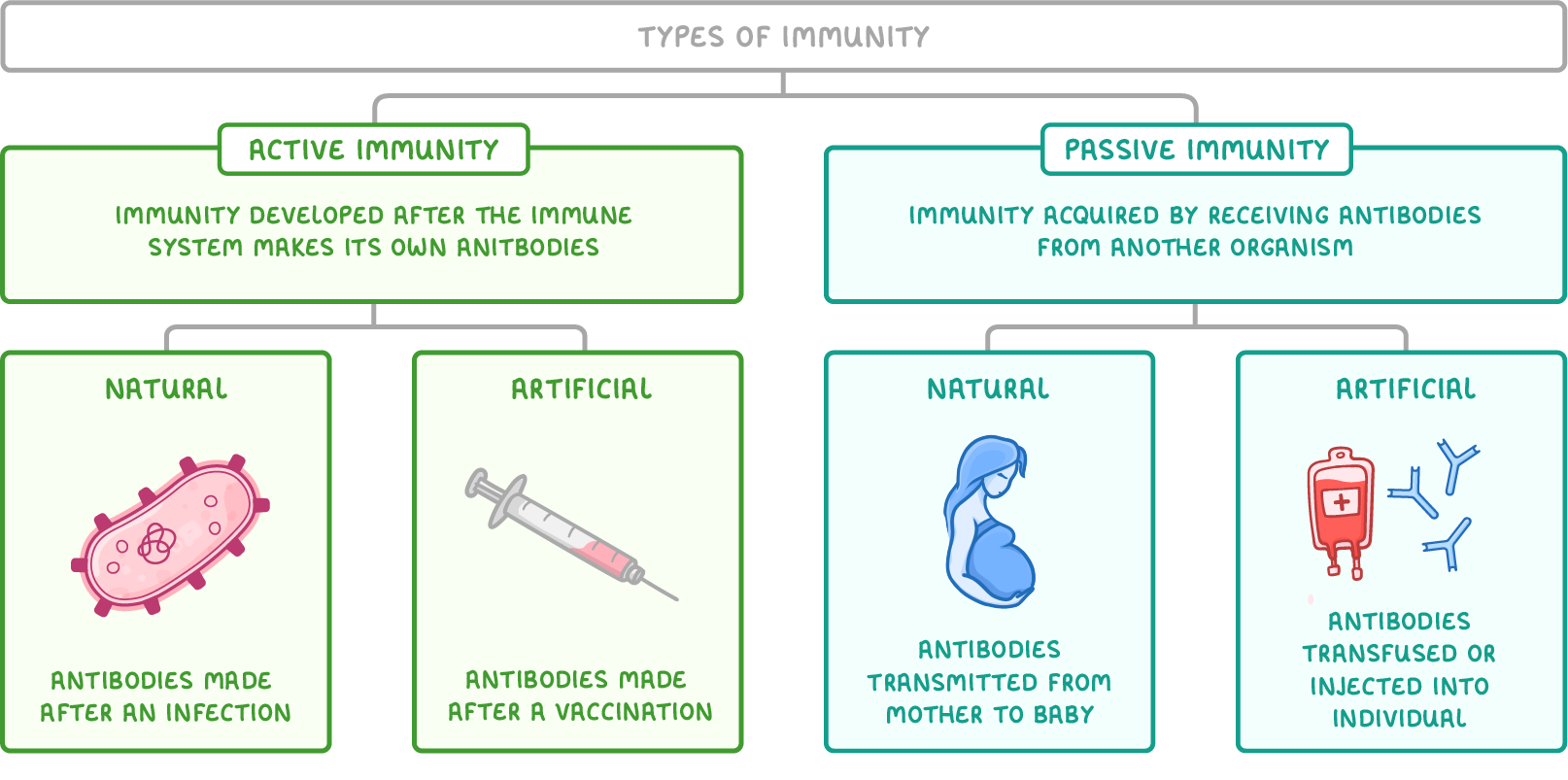
what is artificial active immunity?
immunity developed after immune system makes its own antibodies following vaccination
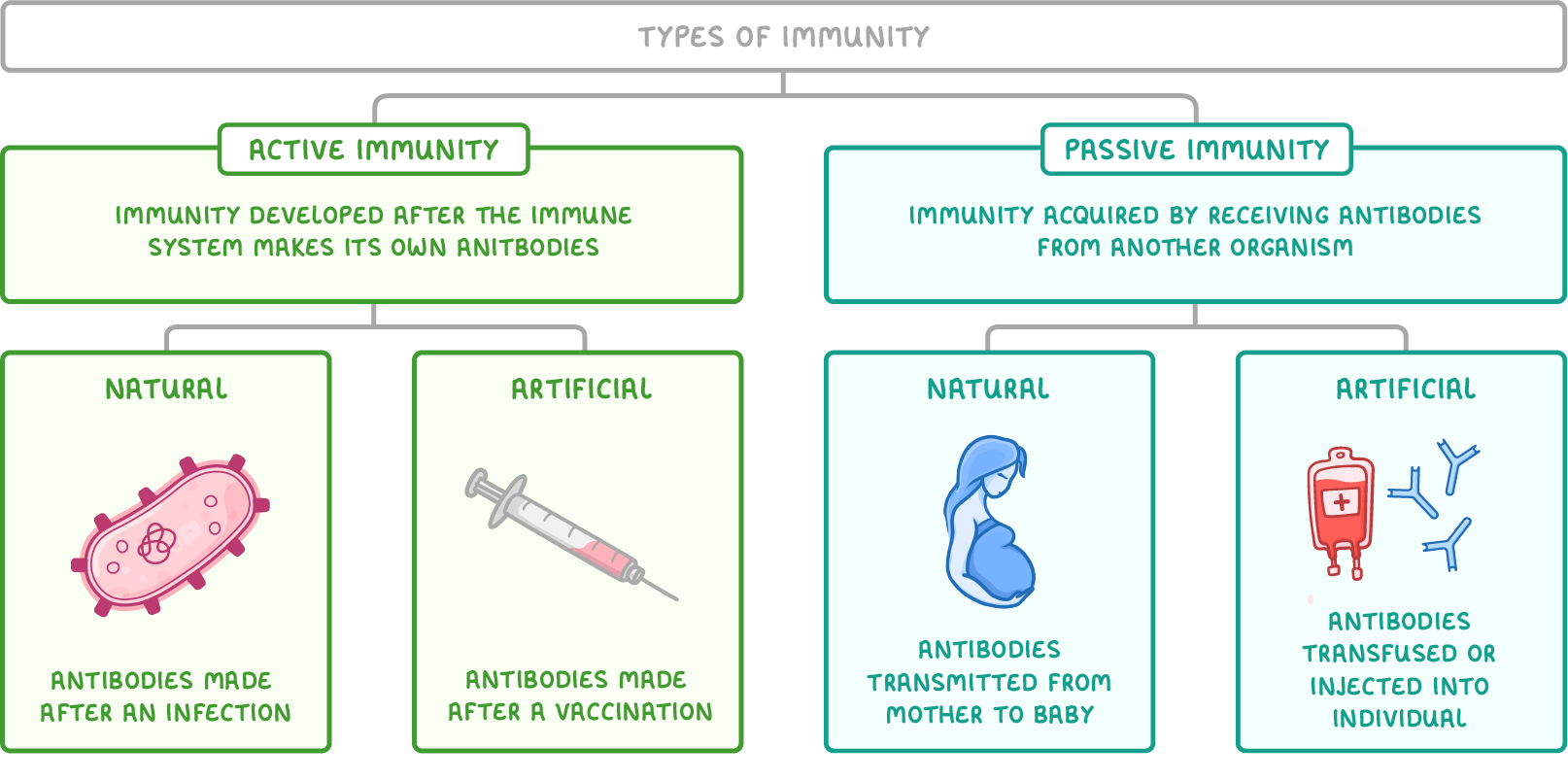
what is passive immunity?
immunity acquired by receiving antibodies from another organism
what is natural passive immunity?
immunity acquired by transmission of antibodies from mother to baby
what is artificial passive immunity?
antibodies transfused/injected into an individual
what is vaccination?
injection of a(n) antigen/proteins/dead/weakened microorganism/pathogen/virus
stimulates production of antibodies/plasma cells/memory cells
which type of immunity does a vaccine provide?
artificial active immunity
as body is stimulated to produce an immune response, producing its own antibodies
what may be injected in a vaccination?
dead/inactivated pathogens
attenuated (weakened) pathogen strains
harmless version of a toxin
isolated antigens from a pathogen
genetically engineered antigens
what is herd immunity?
where those not vaccinated are protected as a large proportion of the population is vaccinated
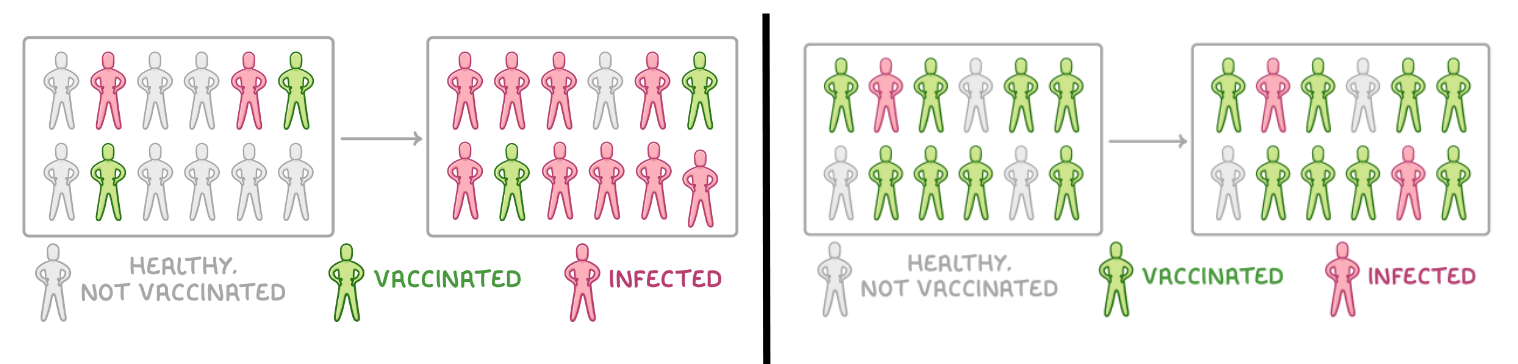
how does herd immunity work?
large proportion of pop vaccinated and immune
→ reduces change of non vaccinated individuals coming into contact w/ pathogen
fewer individuals infected
why may vaccines not eliminate disease?
immunity failure
pre immunity infection
antigenic variability
pathogen variants
pathogen ‘hiding’
personal/religious/ethical/medical objections