Pharm - CH 2: Pharmacodynamics
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
Pharmacodynamics
actions of drug on the body
drugs interact w/ receptors on cell surface/within cell to create an effect
drug receptor complex —> alterations in biochemical/molecular activity
Drug-Receptor Complex
Produce a biological response
Produces a signal transduction —> biological response
Ligand
Refers to s small molecule that binds to receptor protein
can be naturally occuring or a drug
can initiate a series of rxns that result in biological response
Examples: ACH, NE, Epi, Dopamine
Affinity
measure of how tightly a drug bind to the receptor
Intrinsic activity
The ability of the drug-receptor complex to produce maximum functional biologic response
Note: not the same as affinity, which is the ability to bind to the receptor
Agonist
Affinity for receptor = binding to active site
Activates site —> cause intrinsic activity
= affinity + intrinsic activity
Antagonist
Affinity for receptor = binding to active site
Activates site —> no intrinsic activity
= affinity + no intrinsic activity
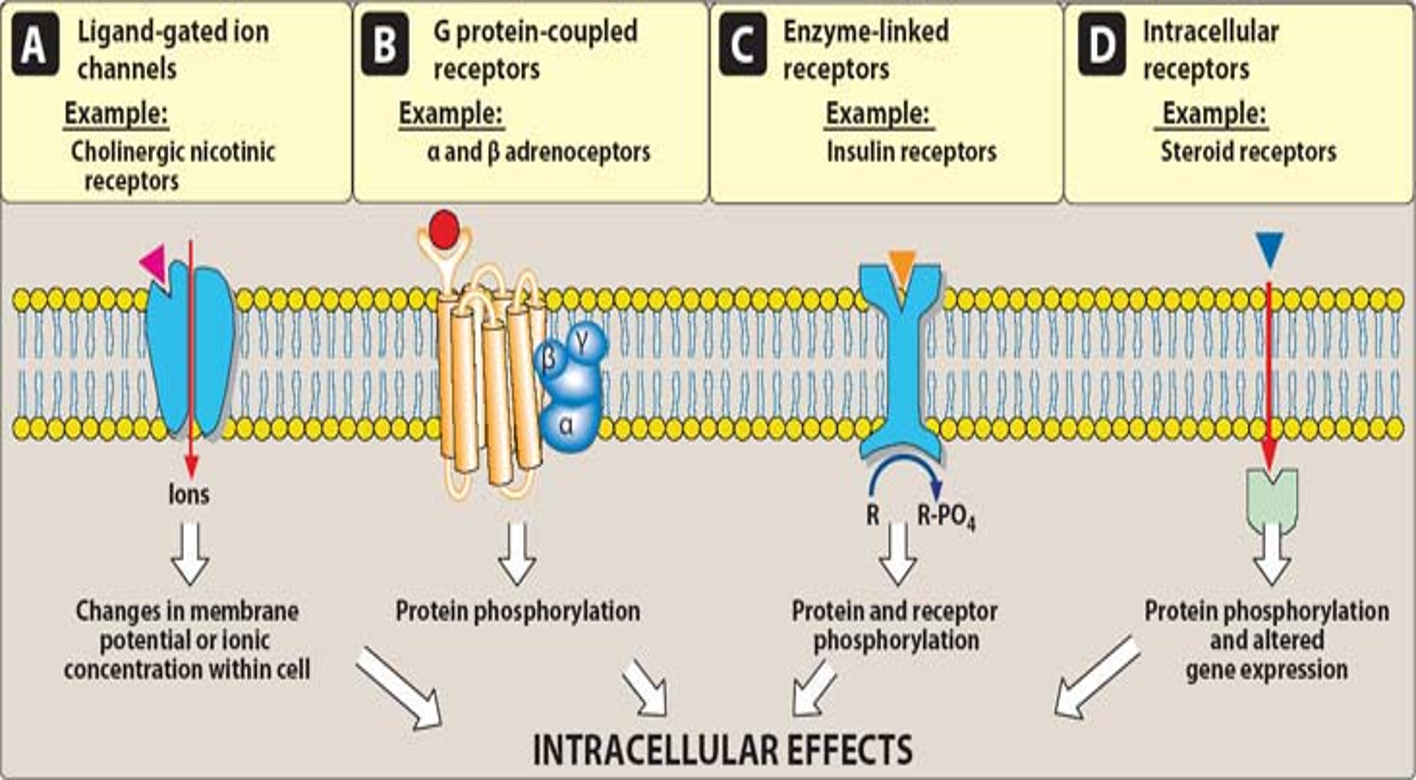
Major Receptor Families in Our Body
Transmembrane Ligand-Gated Ion Channel Receptor
Transmembrane G-Protein Coupled Complex
Enzyme Linked Receptor
Intracellular Receptors
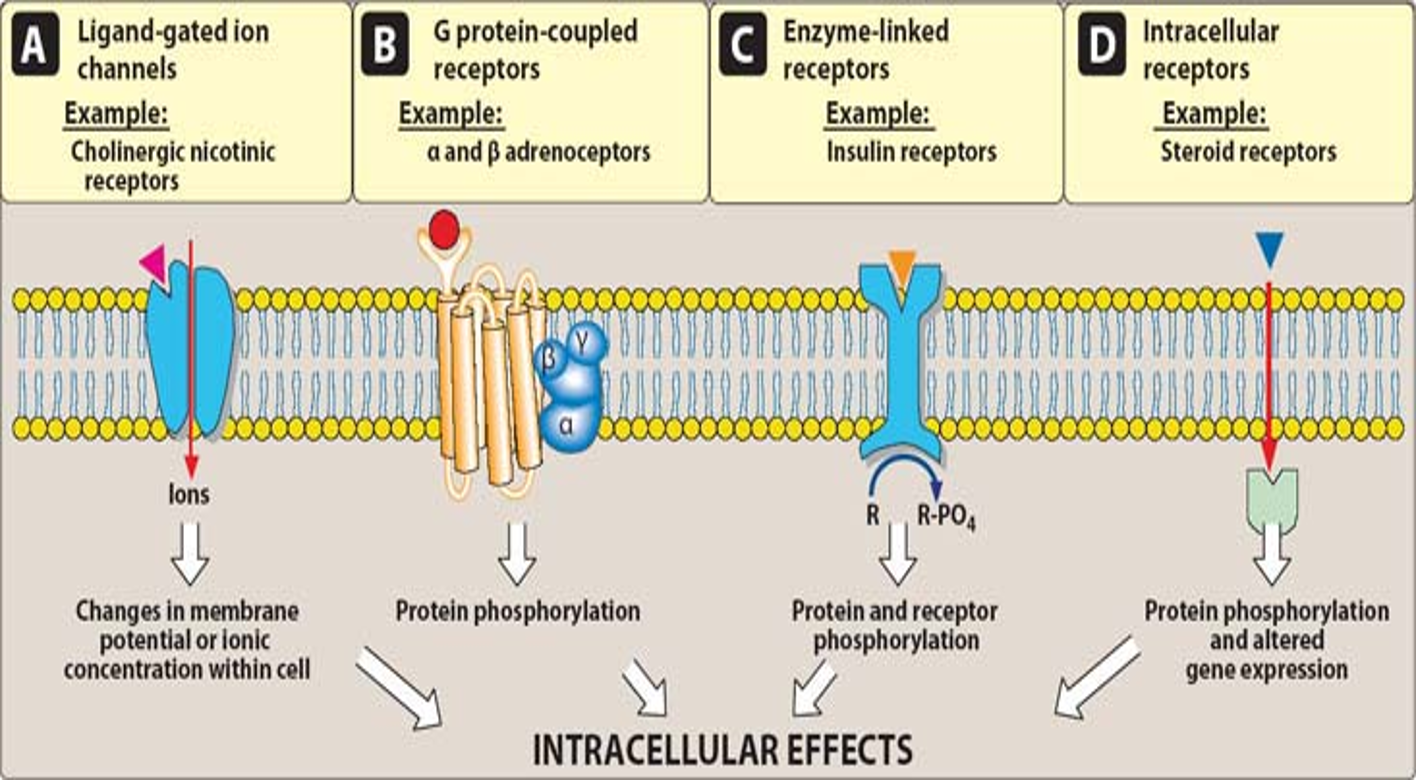
Transmembrane Ligand-Gated Ion Channel Receptor
Regulates ion flow across membrane
changes in membrane or ionic concentration w/n cell (Cl-/Na+)
Ex. nicotinic receptors for neurotransmission, cardiac conduction, muscle contraction
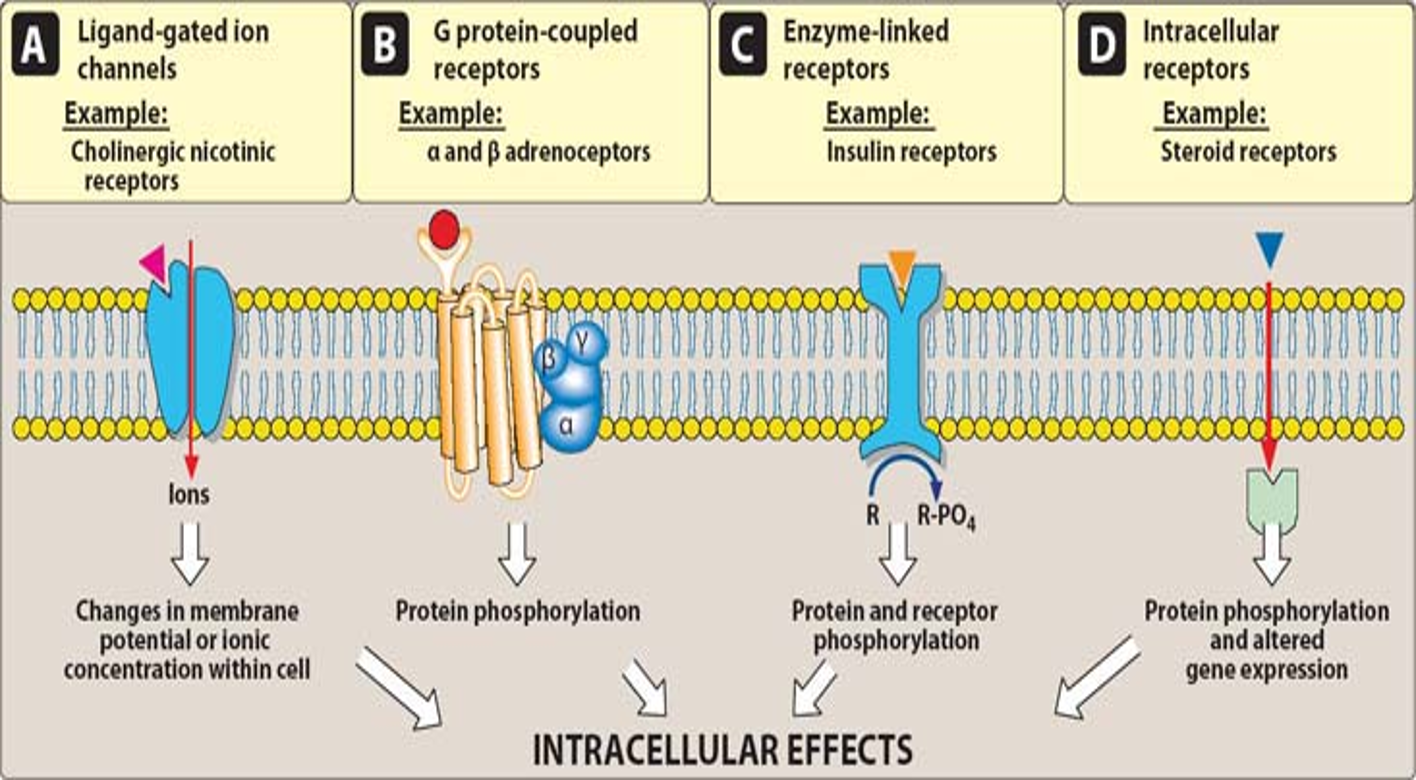
Transmembrane G-Protein Coupled Receptor
Extracellular domain binds to ligand
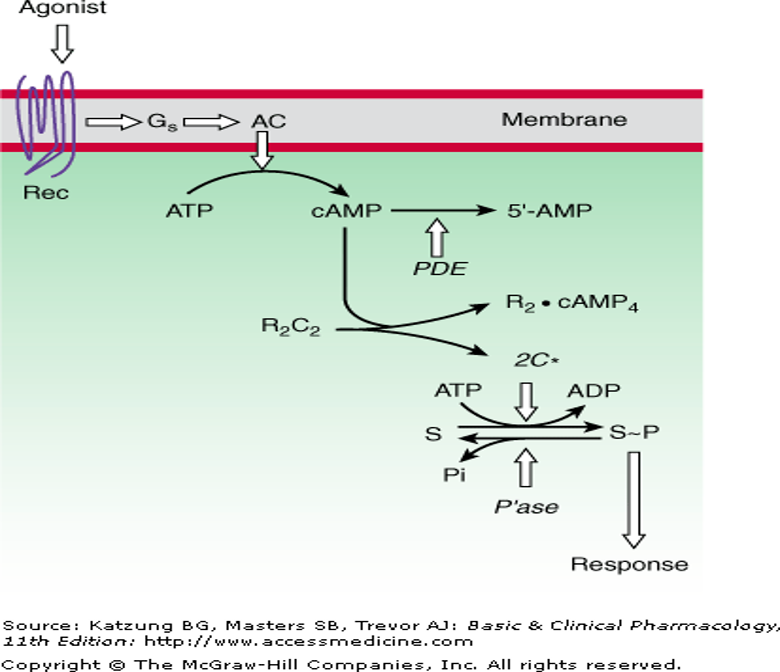
Intracellular domain of receptor linked to G-protein —> activates second messenger
Second messengers = molecules that relay signals from receptors on cell surface to target molecules inside cell, cytoplasm, nucleus
Often activated adenyl cyclase —> cAMP
everything between g-protein receptor and biological response is second messenger
protein phosphorylation
Ex. alpha and beta receptors, muscarinic receptors
Enzyme Linked Receptors
Transmembrane receptor w/ enzyme as integral part as receptor
binding activates/inhibits intracellular enzyme
protein + receptor phosphorylation
Ex. insulin receptor
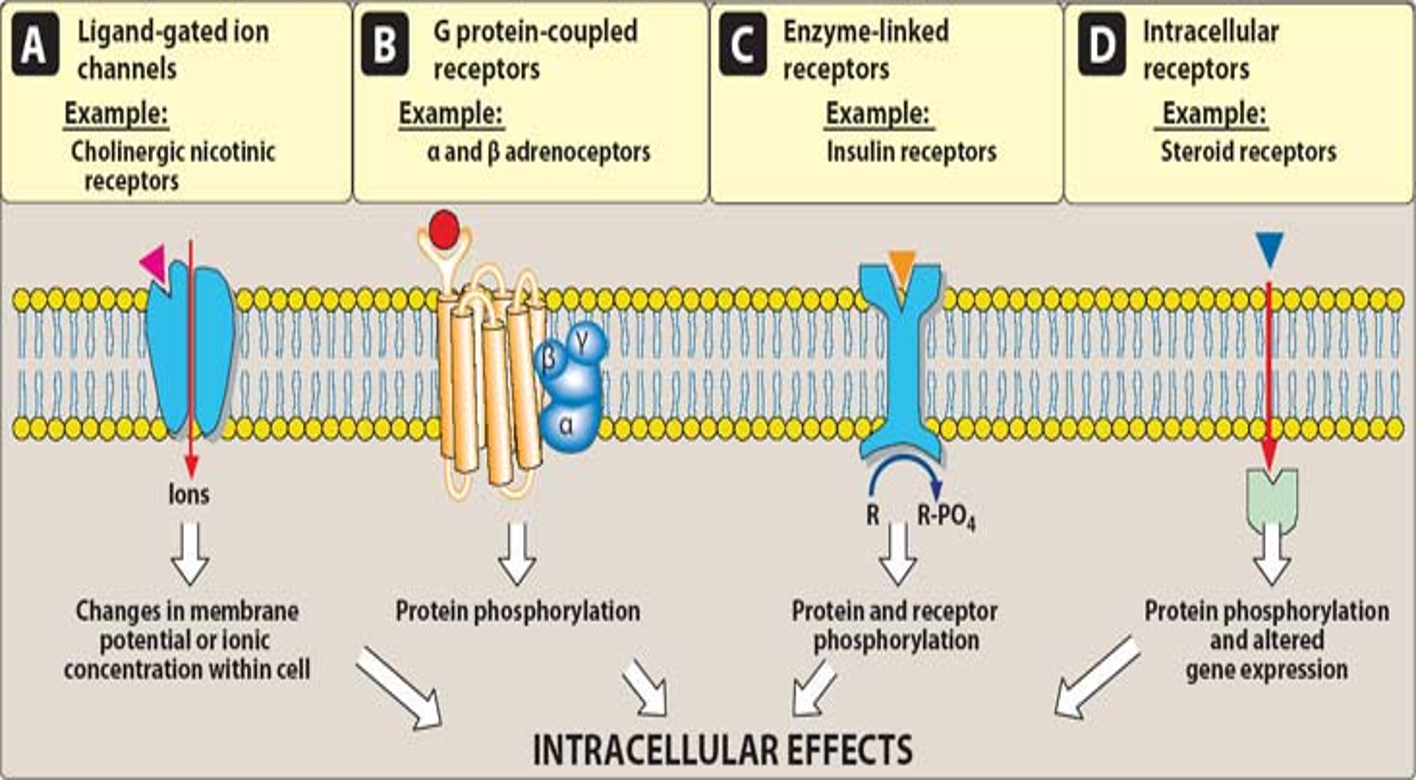
Intracellular Receptor
Receptor entirely intracellular = must diffuse into cell to interact w/ receptor
lipid soluble
protein phosphorylation + altered gene expression
Ex. steroid hormones
Potency
measure of drug necessary to produce an effect
Efficacy
ability of drug to elicit a respons
Dose Response Relationships
graded dose response relationship
quantal dose-response curve (ED50/TI)
Graded Dose Response Relationship (EC50)
Determines EC50
Effective Conc. 50 = drug dose that shows 50% of max response in an individual
Used to determine potency
smalled EC50 = more potent
constructed for one patient
conc. of drug increases —> magnitude of pharmacologic effect
dose and effect vary BUT SUBJECT IS CONSTANT (1)
since dose and effect varies
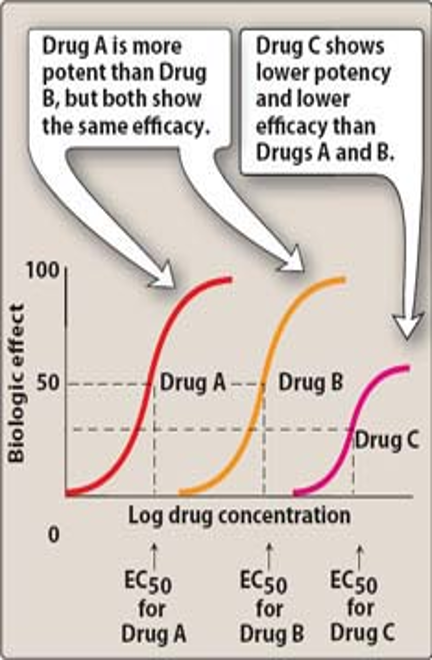
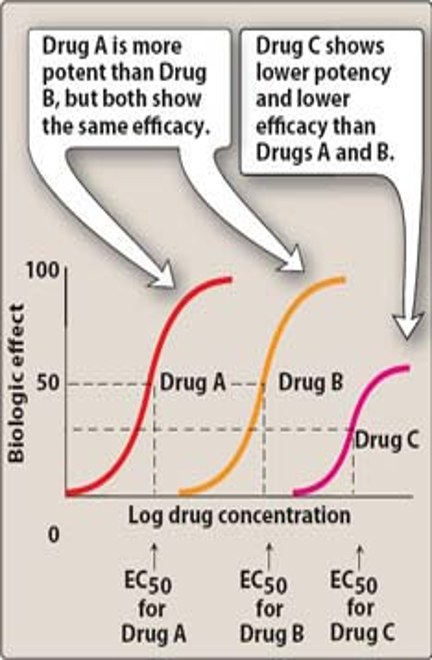
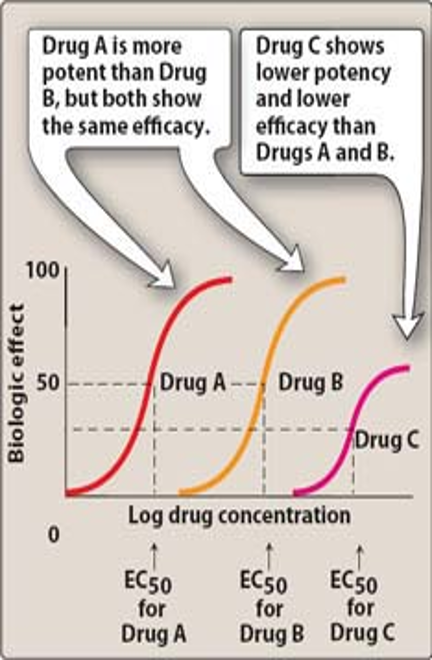
Which drug is more potent?
Drug A b/c less amt is needed to produce an effect
However, A and B have equal efficacy (biological effect)
The lower the EC50., the less conc. needed to produce 50% of max effect and higher potency
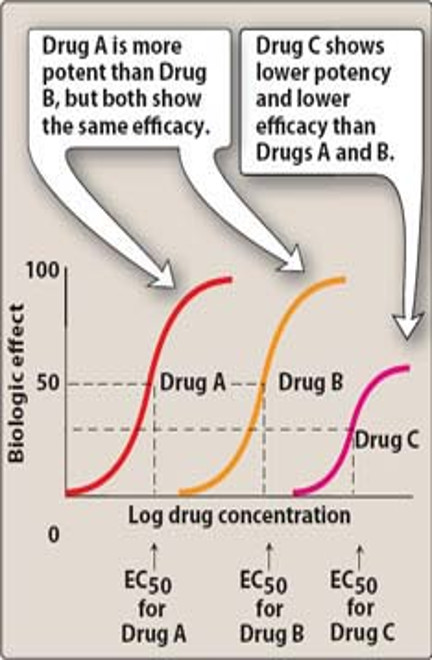
Which drug has the least efficacy?
Drug C = lower biological effect
Which is therapeutically more beneficial, a drug that is more potent, or a drug that has greater efficacy?
Drug w/ greater efficacy
A more potent drug requires a smaller dose to reach 50% of its maximum response (lower EC₅₀), but that doesn’t mean it can produce a stronger or better therapeutic outcome.
In contrast, a drug with greater efficacy can produce a higher maximal response regardless of how much drug is needed to get there.
Therefore, from a clinical standpoint, efficacy determines the therapeutic usefulness of a drug, because it reflects the maximum effect that can be achieved in the body, not just the dose required to achieve it
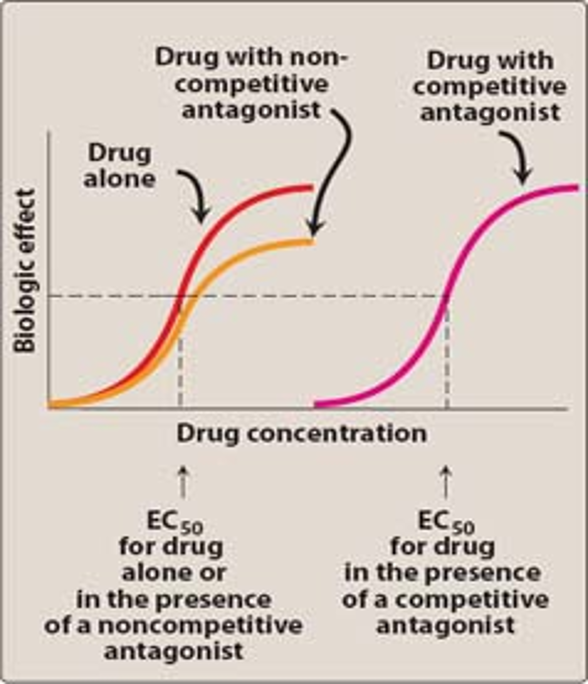
Competitive (reversible) Antagonists
The dose response curve is shifted to the right
antagonist and agonist bind and compete for the same site
Antagonism - w/ competitive antagonist, is reversible
can be overcome by adding more agonist drug to the equation
capacity to reach maximal response still exists
The EC50 of the agonist increases and shifts to the right in the presence of competitive antagonists
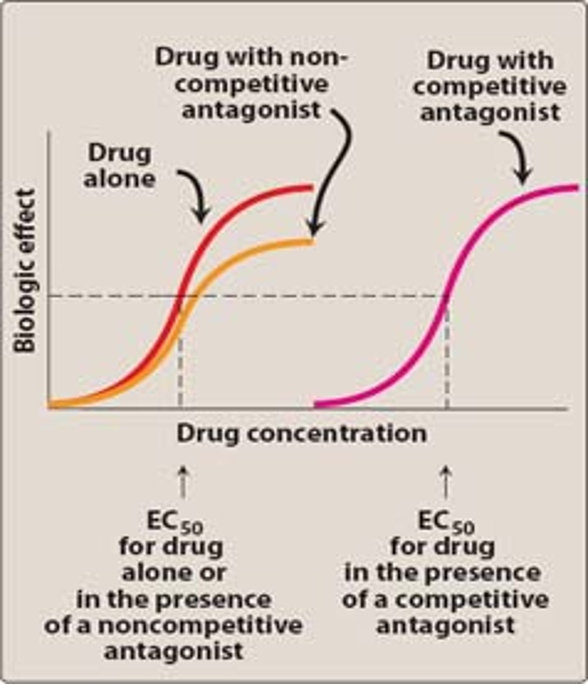
Non-Competitive (irreversible) Antagonist
Addition of non-competitive antagonist causes a downward shift of the maximum biological effect seen by the agonist
no shift of curve on dose of EC50
irreversible antagonists cannot be overcome (or competed w/) by adding more agonist to the equation
no increase in EC50
In the presence of a noncompetitive antagonist, the maximum effect is unattainable. increasing the dose of the agonist
Ex. Q-drug for opioid OD
Quantal Dose-Response Curve (ED50)
plots fraction of the pop. that responds to a given dose of a drug
not one person
describes conc. of a drug that produces a given effect in a pop.
dose and pop. vary BUT EFFECT IS CONSTANT
compared to the graded dose response curve where dose and effect vary but subject was constant
ED50
effective dose 50 = dose of drug required to produce therapeutic effect in 50% of a certain pop.
Useful for determining drug dose to which MOST of the pop. responds to
also used to calc. therapuetic index
Therapeutic Index (TI)
Measure of drug’s safety
determined by measuring the frequency of the desired response + toxic response at various doses of the drug
larger value = wider margin b/n dosed that are effective + toxic
TI = TD50/ED50
doses that produce therapeutic effect and toxic effect in 50% of the pop:
ED50 = dose that produces therapeutic effect in 50% of the pop.
TD50 = dose that produces toxic and undesirable effect in 50% of the pop.
unwanted adverse effect
TD50: drug dose that produces toxic efcet on ½ pop.
ED50: drug dose that produces therapeutic/desired response in ½ pop.
measure of toxic dose (TD50)/therapeutic effect dose (ED50)
ratio that produces toxixity of the dose that produces a clincically desire of effective response in pop. of indivduals
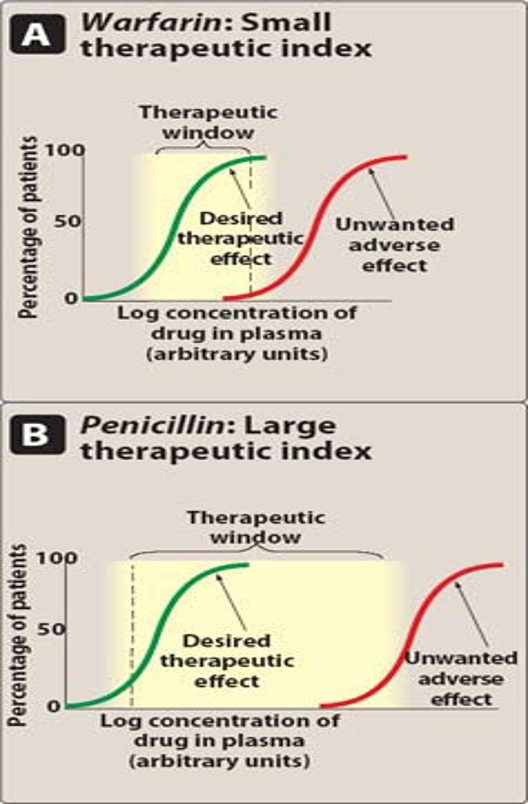
Therapeutic Index =TD50/ED50
Drug Example # 1: 1000mg/10mg= TI of 100
Drug Example # 2: 100mg/10mg= TI of 10
Q- Which drug is more safe?
Example 1, the higher the TI ratio, the safer the drug……!!!!!!!