Indiana Category 1 Applicator License Studying
1/159
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
160 Terms
Individuals who use or supervise the use of restricted-use pesticides, or any pesticide for-hire, in the production of agricultural crops, or non-crop agricultural lands such as pastures
Who does the Category 1 certification apply to?
5 years
What is the certification term for a Category 1 Applicator's License?
-Option 1: Retesting at the end of their certification term (aka 5 years)
-Option 2: Accrue 20 continuing education hours (CCHs) of Cat-1 related education within the five year term to recertify
How can certified Category 1 applicators renew their certification?
oisc.purdue.edu and click on "Pesticide"
Where can you find the training programs for continuing education hours?
Obtain a commercial pesticide applicator license from OISC
Once you are certified, what is an applicator required to do?
Annually
How often are applicator licenses renewed?
Individuals certified in Cat 1 ay supervise the use of restricted-use pesticides or the for-hire use of any pesticide by a non-certified employee (if rules are followed....see next card)
What is Indiana's Supervision Rule?
1) Non-Certified Applicator: Cat1 applicator must be on-site
2) Registered Technician: if the Cat 1 applicator is either on-site or reachable by phone/voice
What are the qualifications for a Cat-1 applicator to be allowed to supervise 1) a non-certified applicator and 2) a registered technician?
1) provide a category-specific site assessment fact sheet
2) determine the need for any additional site-specific instructions
3) provide copies of product labels
4) make available PPE specified on the label of products being used
5) Assume responsibility of the work of the RT
6) Remain available by phone or other means of voice contact for the RT
When a Cat-1 applicator is not on site but supervising a RT, what are the 6 things the Cat-1 applicator must do/provide?
10 Registered Technicians
What is the max number of Registered Technicians that a Cat-1 applicator can supervise (without written permission from OISC)?
RT's must be able to establish voice contact with their supervisor within 5 minutes during an emergency or within 30 minutes in a non-emergency situation
What is the rule of establishing voice contact if a Cat-1 applicator is supervising an RT?
NO - not if they don't mix or transfer pesticides
If a tender truck driver is not a Registered Technician and acts as a shuttle between the facility and the field, do they need supervision from a Cat-1 applicator?
YES
If a tender truck driver is not a Registered Technician and mixes and loads pesticide, do they need supervision from a Cat-1 applicator?
"a person may not apply a pesticide in a manner that allows it to drift from the target site, in sufficient quantity, to cause harm to a nontarget site"
What is Indiana's Drift Rule?
A nonprofit company/website that helps applicators, specialty crop growers, and stewards of at-risk habitats in IN communicate more effectively to protect sensitive sites from pesticides
What is FieldWatch?
Carry pollen from one plant to another.
Pollinators include bees, butterflies, beetles, and flies.
Define a pollinator
A plan intended to protect pollinator populations from pesticide applications--managed and native--in agricultural and non-ag settings
What is the Indiana Pollinator Protection Plan?
-A website that resulted from the Indiana Pollinator Protection Plan
-A mechanism by which applicators can identify the location of managed hives
What is BeeCheck.org?
2 mile radius of application site
What is the mile radius in which applicators should identify hive locations relative to their application site?
at least 2 years from date of application
How long should Category 1 businesses maintain records of all restricted-use pesticide applications?
1. Applicator's name
2. Applicator's certification number
3. Location of application
4. Type of treatment
5. Pests controlled
6. Application date
7. Acres treated
8. Pesticide brand name & formulation
9. Manufacturer name
10. EPA registration number
What information must be recorded from a restricted-use pesticide application? (Hint: 10 things)
Within 90 days of application
How long after making an application with a RU pesticide must the final record be made?
Restricted-use pesticide dealer registration
What is required of all RU pesticides dealers? (ie. firms that sell RU pesticides)
Sales must be made ONLY to certified applicators (private or commercial)
Who can RU pesticide dealers sell RU pesticides to?
at least 2 years
How long should records of each sale of RU pesticides be kept?
On the basis of storage capacity, not the volume of material actually stores
How does OISC regulate the bulk storage of pesticides and fertilizers? (hint: on what basis?)
more than 55 gallons
How many gallons of liquid pesticide container stored to be considered bulk storage?
more than 100 pounds
How many pounds of dry pesticide in undivided quantities stored to be considered bulk storage?
more than 2,500 gallons
OR
multiple smaller tanks whose combined total is more than 7,500 gallons
How many gallons of liquid fertilizer tank to be considered bulk storage?
more than 12 tons
How many tons of dry fertilizer in undivided quantities to be considered bulk storage?
notify the OISC annually of the bulk containers' location and status
What must facilities that store bulk quantities of fertilizer or pesticide notify the OISC of annually?
secondary containment
What is a "diked area"?
Bulk storage tanks must be stored within a diked area
When are diked areas required?
YES -- unless the tank liquid level is higher than the dike wall
Should bulk storage (primary containment) be anchored?
1) serial number or identification code
2) pesticide name or fertilizer grade
What must each bulk storage tank (primary containment) be marked with? (hint: 2 things)
-Pesticide tanks: NOT ALLOWED
-Fertilizer tanks: yes, but must be locked at all times except when determining liquid level
Are sight gauges on pesticide tanks allowed? Are sight gauges on fertilizer tanks allowed?
Dikes containing storage tanks MUST have a capacity sufficient to hold the volume of the largest tank plus the displacement of everything else stored inside the dike (add an additional 6inches of the height of the dike wall)
What is the required capacity of dikes (secondary containment) containing storage tanks?
NO -- but they can share a common wall
Can fertilizer and pesticides be stored in the same dike containment area?
operational containment for all mixing, loading, minibulk filling, and equipment washing
What are load pads?
-minimum of 10x20 feet
-minimum of 750 gallons
What is the minimum dimensions of load pads? What is the minimum gallon capacity?
1. Have tamper-evident seals or one-way valves on all openings (other than vents)
2. display a unique serial number or identification code
3. Meet DOT packaging requirements
What are the EPAs 3 requirements of minibulk pesticide tanks?
Worker Protection Standards
What does "WPS" stand for?
A federal regulation designed to protect employees on farms from occupational exposure to agricultural pesticides
What are Worker Protection Standards?
1. Inform customers (farmers) about pending pesticide applications
2. Ensure that no one except employees appropriately trained and properly equipped as handlers come into contact with pesticides
3. Provide all handlers with product labels
4. Inspect daily, and maintain all equip. for mixing, loading, transferring, or applying pesticides
5. Provide handlers, and ensure the proper use of PPE
6. Provide a respirator if the label explicitly requires it
7. Provide handlers with decontamination supplies (e.g., 3 gallons of water, soap, single-use paper towels, change of clothes)
What are the 7 things that WPS requires Category 1 businesses to do?
1. Regulate spray volume
2. Atomize the spray mix into droplets
3. Disperse the spray in a desired pattern
What are the three functions that nozzles perform?
"calibration begins with nozzle selection"
What does calibration begin with?
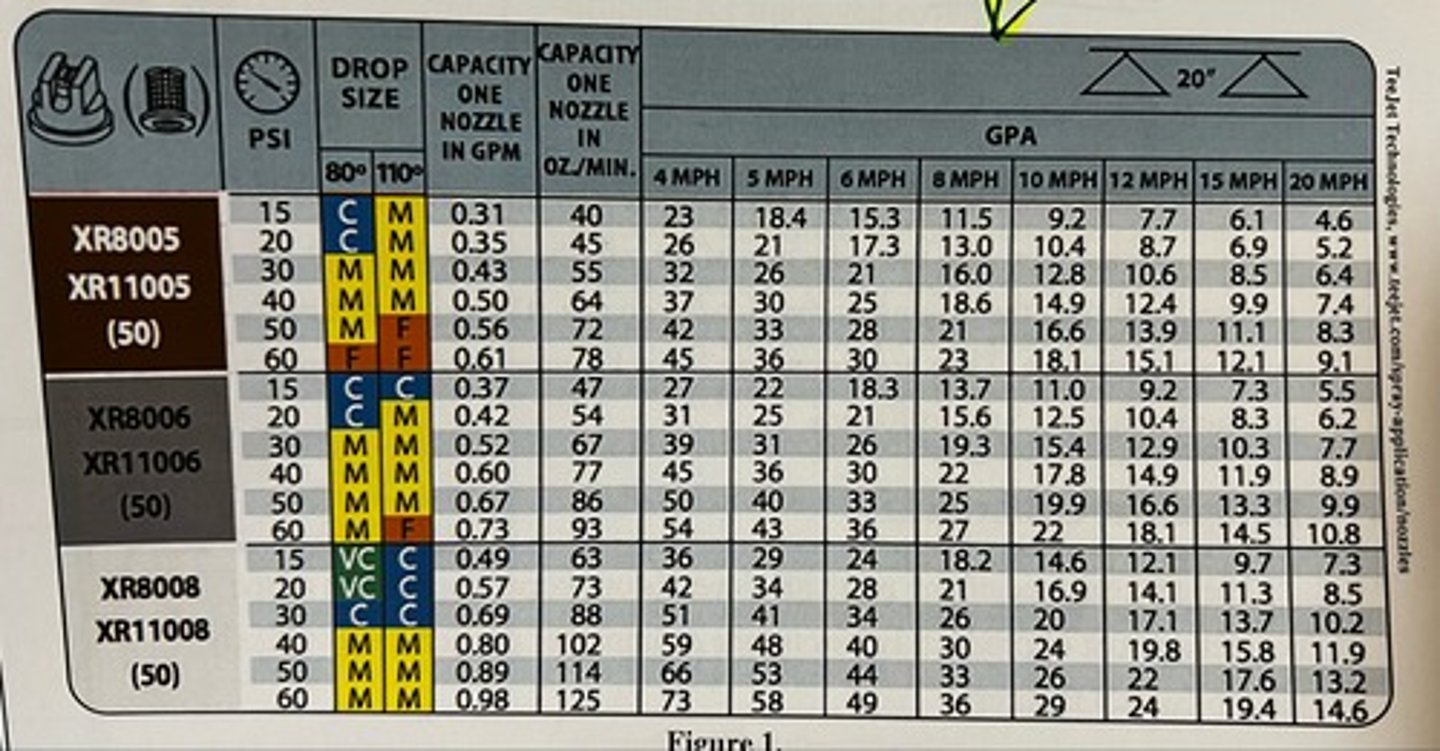
XR11006 gray tip, operated at 40 psi, at a speed of 15 mph.
These nozzles will deliver 11.9 gallons per acre
Product label requirements and site conditions for a given application suggest using extended range (XR) flat-fan nozzles with the following operating parameters: 12 gal/ac spray application rate, 15 MPH spray speed, Medium (M) to coarse (C) droplet size. Which nozzle should the applicator select? (refer to picture of table)
First, determine how many gallons should have been sprayed onto 32 acres: 12 gallons per acre x 32 acres = 384 gallons
Then, subtract the number of gallons sprayed from the number of gallons that were in the spray tank to begin with: 1,000 gallons - 384 gallons = 616 gallons
Any amount left in the tank that differs from 616 gallons indicates either an over- or under-application
Calibration Question: Assume an applicator initially treats a 32 ac field and the sprayer is equipped with a full 1,000 tank. How would you complete a calibration check? (application rate= 12gallons per acre)
1. the label-recommended product rate
2. the calibrated gallon per acre application rate
3. the spray tank capacity
What three factors determine the amount of pesticide product to include in the spray mix?
First, divide the tank capcity by the gallon per acre spray application rate: 1000 gallons / 12 gallons per acres
Then, multiply the product rate by the number of acres that a full tank can treat: 2 quarts per acre x 83.33 acres = 166.67 quarts
166.67 quarts per tank
Tank Mix Math: A weed control recommendation calls for 2 quarts of product per acre. The sprayer is equipped with a 1000 gallon spray tank and calibrated to apply 12 gallons of spray mix per acre. How many quarts of product should you put in the tank?
Refers to t tank mixes where the activity of one or more of the products is reduced (antagonism) or increased (synergism)
What does the term "chemically incompatible" refer to? (hint: antagonism and synergism)
Product mixes changes the characteristics of the spray (may separate, gel, or precipitate solids)
What does the term "physically incompatible" refer to?
1. fill half full with clean water & maintain agitation
2. suspension products
3. water-soluble products
4. emulsifiable products
5. surfactants and drift reduction agents
What is the typical order of tank mixes?
Adjuvants can enhance spray mix characteristics in a variety of ways that include...
1) modifying spray water quality
2) improving spray droplet retention on target surfaces
3) increase pesticide adsorption and uptake by the pest
4. reduce off-target movement
What can spray adjuvants do?
lower the surface tension of spray droplets
allows droplets to spread over a larger surface areas of the target--improving coverage
What do surfactants do?
help spray droplets better stick to the target surface
What can sticker adjuvants do?
help pesticides penetrate the waxy cuticle that covers leaf surfaces
What do oil concentrate adjuvants do?
bone with dissolved minerals in hard water -- prevents pesticides that are sensitive to hard water from bonding with those same dissolved minerals
What do water conditioning agents do?
Can significantly increase crop uptake and translocation of certain pesticides
What do nitrogen fertilizer solution adjuvants do?
help incompatible products work together
What do compatibility agents do?
modify the spray mix's pH
What do pH adjusters do?
minimize problems associated with foam formation during mixing and application
-Antifoaming agents = added IN ANTICIPATION of foam formation
-Defoamers = added AFTER foaming occurs
What do defoamer and antifoaming agents do?
First, convert 1/2% to decimal equivalent: .5%=.005
Then, multiply .005 by the tank capacity: .005 x 800 gallons = 4 gallons
This application requires the addition of 4 gallons of surfactant to 800 gallons of spray mix
Adjuvant Math Q: Given a spray tank capacity of 800 gallons, how much surfactant is needed to mix a full tank when the surfactant label calls for 1/2% concentration by volume?
First, divide the tank capacity by 100 gallons: 1,200 gallons / 100 gallons = 12
Then, multiply the result above by the recommended amount of adjuvant: 12x 4 liquid oz = 48 liquid oz
This application requires the addition of 48 ounces of surfactant to 1,200 gallons of spray mix.
Adjuvant Math Q: Given a spray tank capacity of 1,200 gallons, how much surfactant is needed to mix a full tank when the surfactant label calls for 4 liquid ounces of surfactant per 100 gallons of spray mix?
Check the label for product-specific cleaning requirements
Where should you always look first before cleaning spray equipment?
1. Spray out booms at the end of the day
2. Perform the first rinse in the field (away from ditches and water sources)
3. Remove and clean all screens
4. Remove and clean boom end caps
5. Perform a second rinse with water
6. Add tank cleaner
7. Perform final rinse & flush with water
What are the 7 steps for cleaning sprayers?
When wind blows spray droplets away from the target site during application
When does spray drift occur?
1. select appropriate nozzles
2. use lowest nozzle-recommended spray pressure consistent with appropriate coverage
3. Lower the boom height
4. add a drift reduction agent
5. spray when winds speeds are low
What are the 5 basic concepts of drift management?
1. droplet size
2. operating pressure
3. spray angle
4. boom height
5. equipment speed
What 5 things does nozzle type dictate?
SIZE OF SPRAY DROPLETS
What is one of the most important factors determined by nozzles??
small droplets provide better coverage... but are more prone to drift
large droplets are less likely to drip, but can compromise coverage
What size of droplets--small or large--provide better coverage?
spray pressure influences the formation of spray droplets as it forces spray liquid through the nozzle
What does spray pressure influence?
HIGHER PRESSURES CAUSE SMALLER DROPLETS
Does higher or lower pressure cause smaller droplets?
the interior angel between the outer edges of the spray pattern from a single nozzle
What is the spray angle?
WIDER SPRAY ANGLES PRODUCE THINNER SHEETS, AND SMALLER DROPLETS
Do nozzles with a wider or narrower spray angle produce smaller droplets?
3 to 5 MPH directional breeze
What are the ideal wind conditions to spray? (hint: mph)
A temperature inversion is a condition where air temp increased with increasing height above the ground)
Inversion tend to develop when warm afternoons are followed by calm, cool nights (typically start before sunset and reach maximum intensity shortly after sunrise)
What is a temperature inversion? When are these most likely?
WAY more likely
Is drift more or less likely in a temperature inversion?
Vapor drift occurs when a liquid pesticide volatilizes (changes from liquid to gas) after application to a target area
More likely when temps are higher (e.g., above 85 degrees F)
What is vapor drift? When is vapor drift more likely?
What growth regulator herbicide is especially prone to vapor dift?
Ester (oil-based) formulations
Runoff is the movement of pesticide across the soil surface in flowing water
What is runoff?
1. compacted soils or soils prone to erosion
2. wet soils or heavy, clay soils that pesticide cannot easily infiltrate
3. moderate to steep slopes
What are the 3 site-related conditions that increase the potential for runoff? (hint: soil conditions)
Leaching refers to the movement of pesticide down through the soil profile
More likely to occur on sandy soils or where groundwater is near the soil surface
What is leaching? When is leaching more likely? (hint: soil conditions)
-Monocots: emerge with single leaf or cotyledon (grasses and sedges)
-Dicots: emerge with two seed leaves or cotyledons (also called broadleaves)
What is the difference between monocots and dicots?
The growing point on monocots remain below, or close to, ground level (protected from mowing, grazing or other types of above ground injury)
Where is the growing point on monocots?
The growing point on dicots remains at the top of the plant (making dicots more vulnerable to above-ground physical damage)
Where is the growing point on dicots?
1. seedling
2. vegetative
3. reproductive
4. maturing/dormancy
What are the four growth stages of a weed?
-Emerge = fall
-Vegetative = fall & early spring
-Reproductive = late spring
-Maturity = early summer
When do winter annuals complete their emergence, vegetative, reproductive, and maturity stages?
-Emerge = spring
-Vegetative = summer
-Reproductive = late summer
-Maturity = fall
When do summer annuals complete their emergence, vegetative, reproductive, and maturity stages?
during their seedling stage
When are annual weeds the most vulnerable?
over a two year period
How long does it take for a biennial weed to complete the 4 stages of development?
During their first year, before they are able to establish a large taproot
When are biennials most susceptible to chemical control?
over multiple years
When do perennials complete their 4 stages of development?
1. Seeds
2. Rhimzones (underground vegetative stems)
3. Stolons (above ground vegetative stems)
What are the 3 ways perennials can reproduce?
the hairy or membranous structure that occurs at the base of the leaf where it attaches to the stem
What is a ligule?
the stem-like structure that connects the leaf blade to the stem (may be absent on some plants)
What is a petiole?
Giant foxtail
What weed is this?

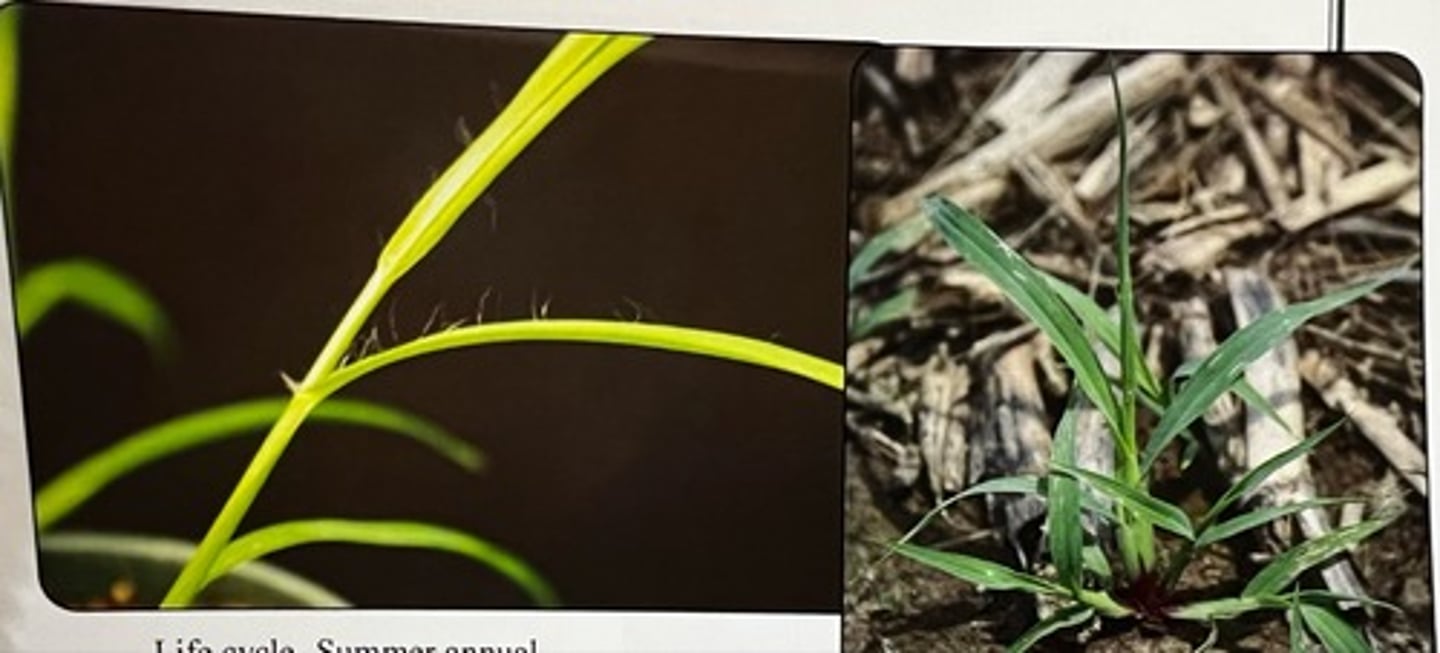
Fall panicum
What weed is this?

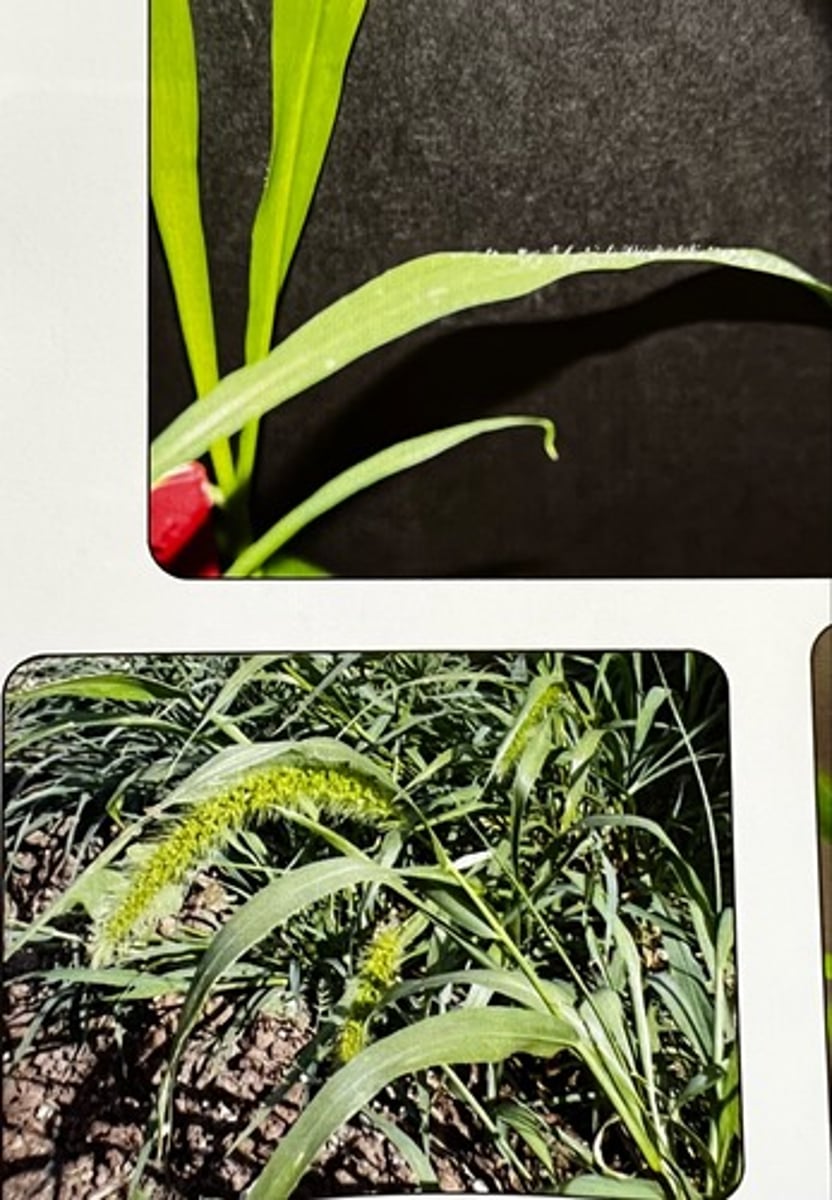
Yellow foxtail
What weed is this?

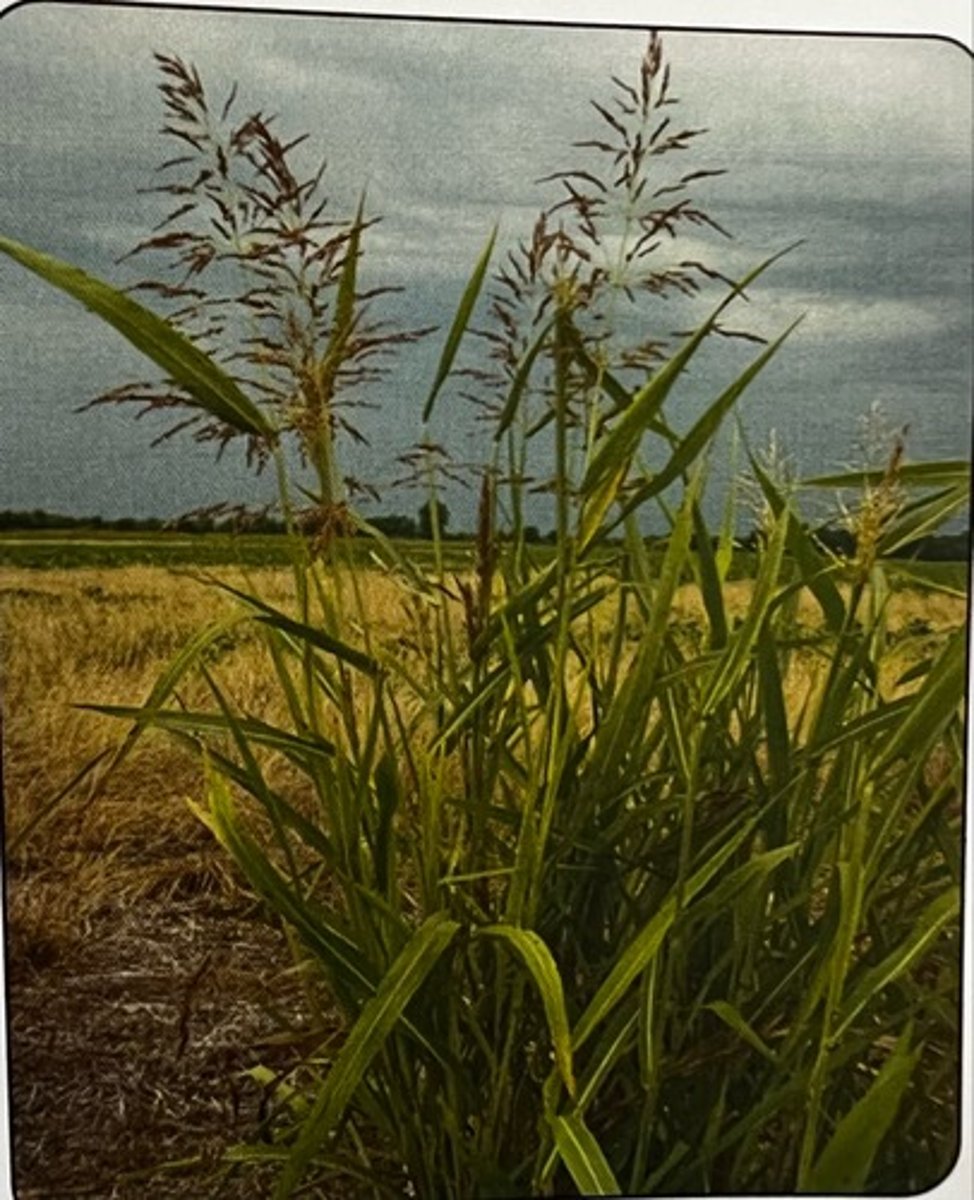
Johnsongrass
What weed is this?
