Everything Thermofluids
1/80
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
81 Terms
What is a level curve in a MVF graph
A curve where a value stays constant
What assumption is made in order to partially differentiate
All the other variables are constants and the variables are independent
What is a partial derivative a measure of
How the function changes when just one variable is changed
What are mixed partial derivatives
2nd order with respect to 2 different variables
What do mixed partial derivatives show
The rate of change in one direction depending on another variable
Does the order you differentiation in for a mixed partial differentiation matter
No if they are continuous
What does a total differentiation tell us
How the function changes when the variables are varied simultaneously
What does differential form express
How something can change when both x and y change
What is an integrating factor
A function that is multiplied by to turn an inexact differential to an exact one
What is a fluid
A substance that flows rather than deforming
What is a shearing force
A force that acts in a direction parallel to the surface, causing one layer of the material to slide past another layer
What is shear stress
The internal force per unit area that resists the shearing force
What is the equation for shear stress
T = F/A
What can shear stress be quantified by
shear strain angle
What is shear strain angle
Shows how much a material shape deforms due to an applied shear stress
What happens to a shear strain angle in a fluid
It increases for as long as the stress is applied, irrespective of the magnitude of the shear stress
What happens to a shear strain angle in a solid
The angle increases up to a maximum value which depends on the magnitude of shear stress and then when it reaches the max it stays constant
What is the continuum hypothesis
The fluid is treated as a continuous substances with no gaps or holes
What does the continuum hypothesis mean for properties
They change smoothly from point to point
What is strain rate
The rate of change in shear strain angle
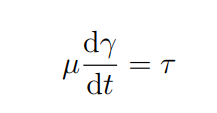
What is gamma in this equation
Shear strain angle
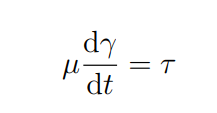
What is T is this equation
Shear strain
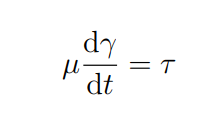
What is mu
Constant of proportionality
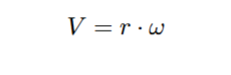
What is r in this
The radius of the circular path
What is Newtons Law of viscosity
The shear stress between fluid layers is directly proportional to the velocity gradient between the layers
What does shear stress induce on a fluid
A velocity gradient
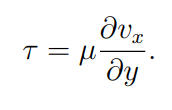
What is Vx
The velocity of the fluid in the x direction
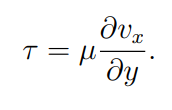
What is y
Vertical Position
What are Newtonian fluids
A fluid whose viscosity stays constant no matter how fast the fluid layers pass each other
What rule do Newtonian fluids obey
Newton’s Law of Viscosity
What is viscosity
The resistance to shear stress
What does the continuum approximation allow
Define fluid properties as if they are continuous variables
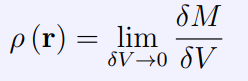
What is the dm referring to
Small amount of mass
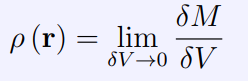
What is dV referring to
Small value of volume
What is often used to compare densities and why
Specific gravity as it has no dimensions
How do you calculate specific gravity
Density of substance/ Density of reference
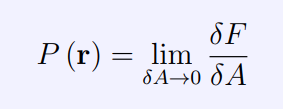
What s dF
Force normal to the area
What is dA
Small area
What is a compressive force
It acts to change the volume of the substances
Is a liquid a compressible fluid and what does this mean for its density
No, its density remains constant
Is a gas a compressible fluid and what does this mean for its density
Yes so its density is a variable
What are the three charateristics of pressure
The force resulting from pressure on a surface acts perpendicular, pressure at a point in a fluid a rest is the same in all directions, the pressure applied to the fluid is transmitted everywhere throughout the fluid
What is Pascel’s Principle
When a change of pressure is applied in an enclosed incompressible fluid, the pressure change is transmitted equally throughout the fluid in all directions
What does the pressure gradient due to gravity refer to
How the pressure changes as you move though the fluid due to the weight of the fluid above
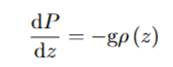
What does p(z) stand for
Density at height z
How does pressure change with depth
It increases with depth
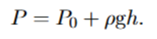
What must the fluid have to use the equation for pressure variation with depth
Constant density
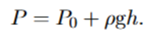
What is Po
Pressure from where the depth is measured
What is gauge pressure
Pressure measured relative to atmospheric pressure
What is the equation for gauge pressure
Absolute pressure - atmospheric pressure
What is absolute pressure
Pressure measured relative to a vacuum
What is a planer surface
A perfectly flat surface
What does moment of a force refer to
The moment

What does P hat refer to
Average pressure
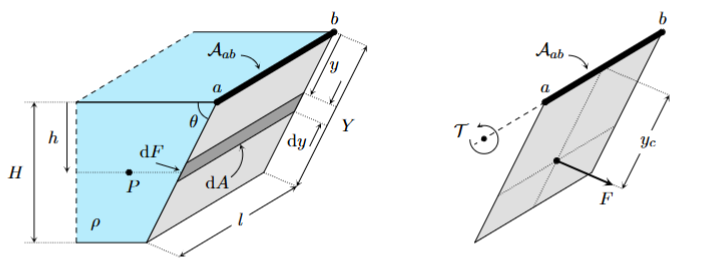
Where does the total force act
Centre of pressure

What is T
Total Moment

What is yc
Centre of pressure
What assumption can we make about the center of pressure
It acts at the centroid
Where is the centroid for a square, circle and rectangular
The centre
Where is the centroid in a triangle
2/3 from the short side

When do you use these equations
For an unsubmerged gate at an angle
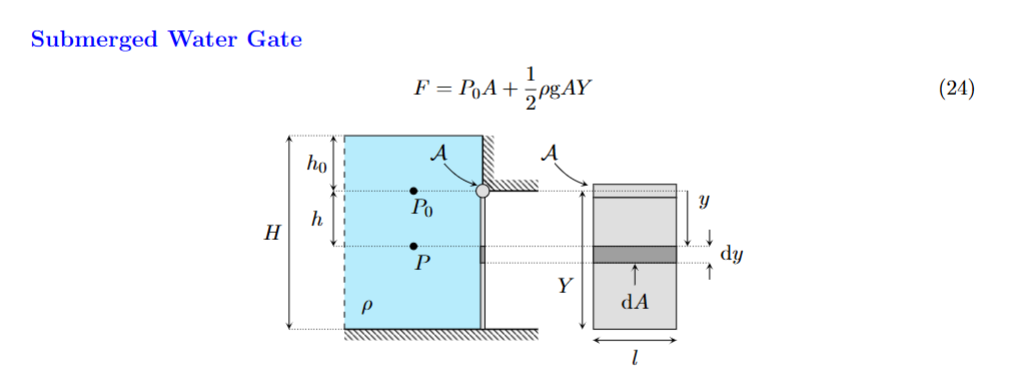
When do you use these equations
For a submerged water gate not at an angle
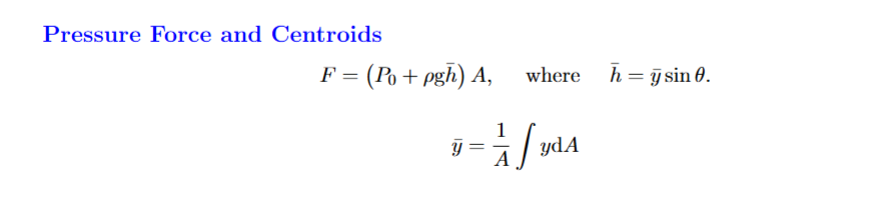
When do you use these equations
For a submerged gate at an angle
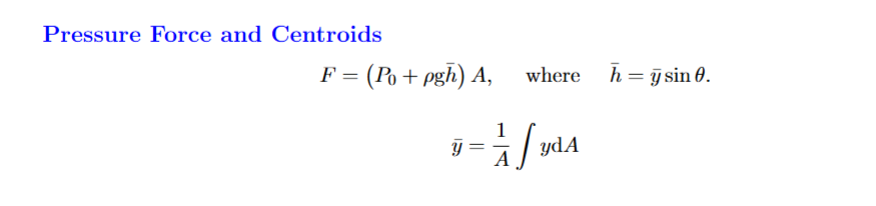
What is H bar
The average vertical depth of the centroid
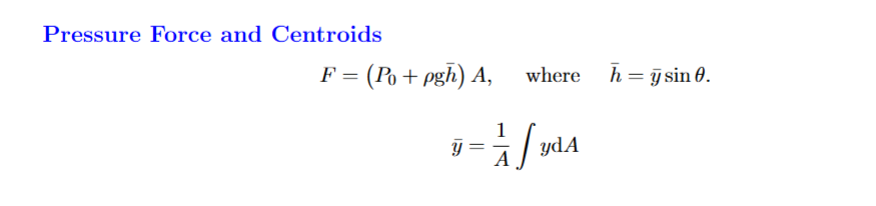
What is Y bar
Centroid
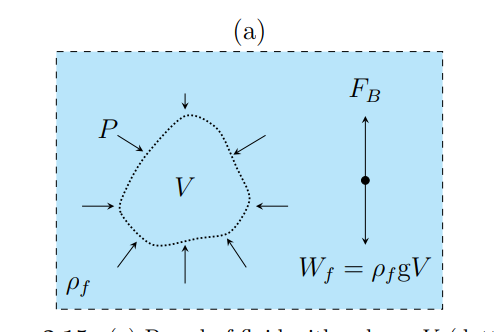
What is the weight of v
Density times volume times gravity
What causes a buoyancy force
The pressure gradient
What is buoyancy force equal to
The weight of the fluid displaced by the body
In which direction does buoyancy force act
Upwards
What is another name for Archimedes’ Principle
Law of buoyancy
What does Archimedes’ Principle state
Any object that is wholly or partially submerged in a fluid experiences an upward buoyancy force equal to the weight of the fluid displaced
What are the 3 approaches to visualising fluid flow
Path line, Velocity fields and stream lines
What does a fluid path line follow
The path of a particle moving with the fluid
What does the particle tracing the path line have in common with the fluid surrounding it
Same direction and speed
What is the velocity in a velocity field a function of
Time and position
What do the arrows show on a velocity field graph
Magnitude and direction
What is a streamline
A curve though the fluid tangent to the local velocity at each point
How can the equation for a streamline be found
Solving the differential equation
What is a steady flow
A flow where the flow velocity at a point does not change with time
What is transient flow
A flow that changes for a short period before becoming steady
When are path lines and streamlines identical