Biology - Transport in Plants
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
What does the transport system in plants consist of?
a network of very fine tubes made up of specialized tissues called xylems and phloems
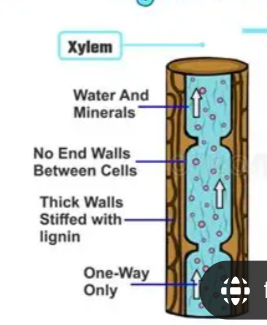
What does the xylem do?
transport water and mineral salts from the roots to the leaves
What does the phloem do?
transport glucose from the leaves to the entire plants
Through what process does the xylem take water and mineral salts up by the roots?
osmosis and active transport, respectively
What is a network of vessels for circulation called?
vascular system
What is a vascular bundle?
A long continuous strands of closely grouped xylem and phloem tissue. It extends from the roots up the stem and to the leaves of the plants.
Which vessel is made of lignin?
Xylem
What is lignin
dead cells that form a thickened woody material to strengthen the cell walls and keep the xylem water-proof
What are the three ways water moves through a flowering plant?
Root pressure, transpiration, capillarity
What is transpiration?
The evaporation of water from the leaves of of plants to the air
The movement of water through the _____ depends on transpiration
xylem
As water is lost from the leaves, more water is pulled ______ through the _____
upwards, xylem

How does water enter a plant
root hairs via osmosis
How does water move after it’s entered the plant
across the root cortex —→ passes into the xylem vessel —→ forms an unbroken column from the roots through the stem & into the leaves
How does water evaporate from the leaves
mainly through the stomata by transpiration
What is the transpiration stream?
the constant upward flow of water through a plant.
What is transpiration pull?
the suction force generated by the process of transpiration, which draws water and minerals from the roots to the reast of the plant
How are xylem vessels well suited to their function
they are very narrow and they acts as capillaries for the water
What is capillarity?
forces of cohesion between water molecules and the adhesive force between water and the cell walls that help water move upward
What is root pressure?
Pressure created in the roots when minerals are actively absorbed, causing water to enter by osmosis and push water upward through the xylem, mainly at night or when transpiration is low.

Where is the stomata found?
on the underside of leaves
When do the stomata open and close?
open: when the gaurd cells are turgid
close: when the gaurd cells are flacid
How doe the guard cells of the stomata become turgid?
by taking in water by osmosis
When do stomata become flacid?
when they lose water by osmosis
what’ll happen if water supply in the soil is low, why does it happen?
plant cells become flaccid so stomata closes to reduce water lost by transpiration.
what’ll happen to a plant if it loses more water than it’s roots take up?
It will wilt
What are the factors affecting transpiration?
temperature, humidity, wind velocity, light intensity, water content of the soil, water availability
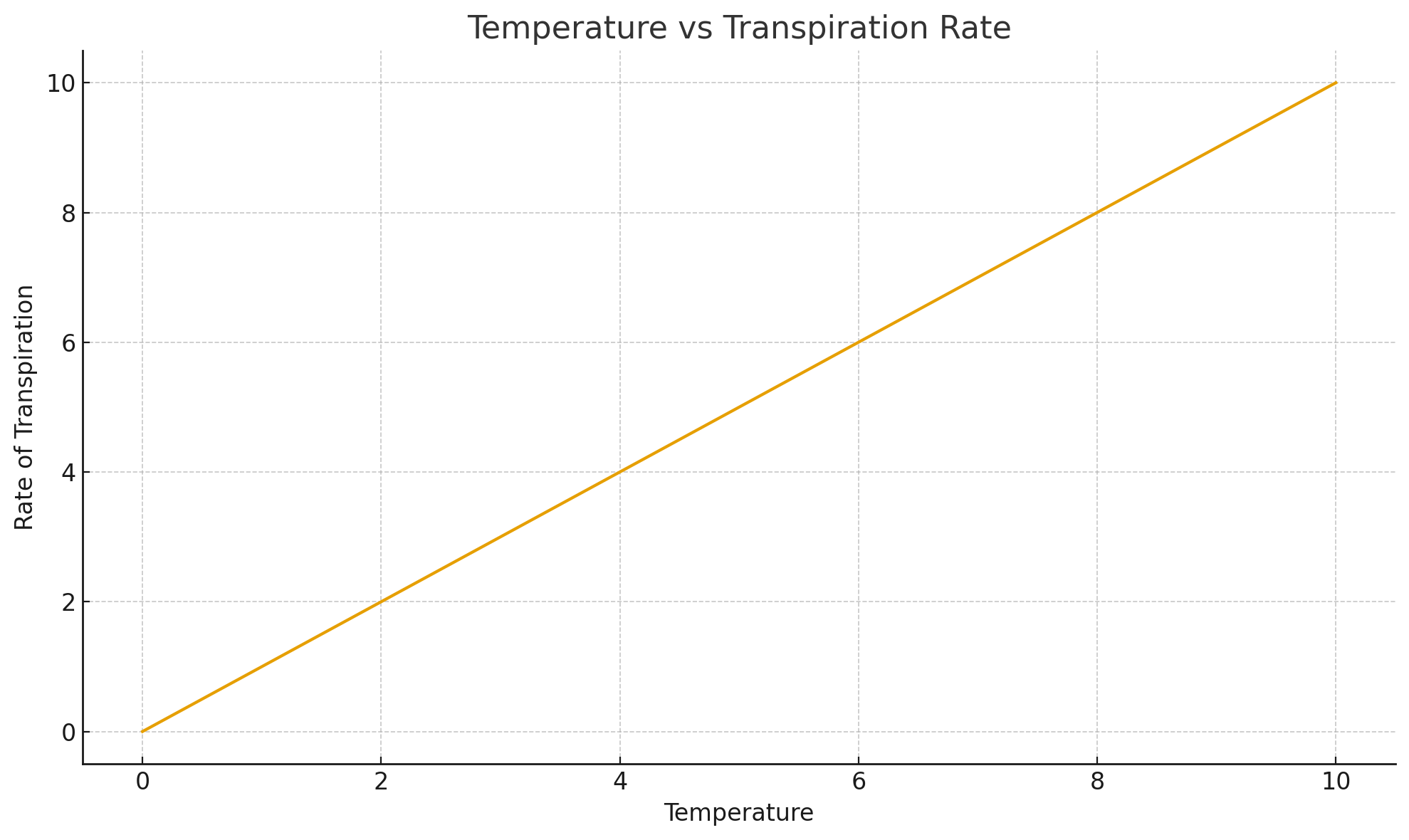
How does temperature effect transpiration?
Higher temperature → increases transpiration because evaporation of water from leaf surfaces becomes faster.
Lower temperature → decreases transpiration because evaporation slows down.
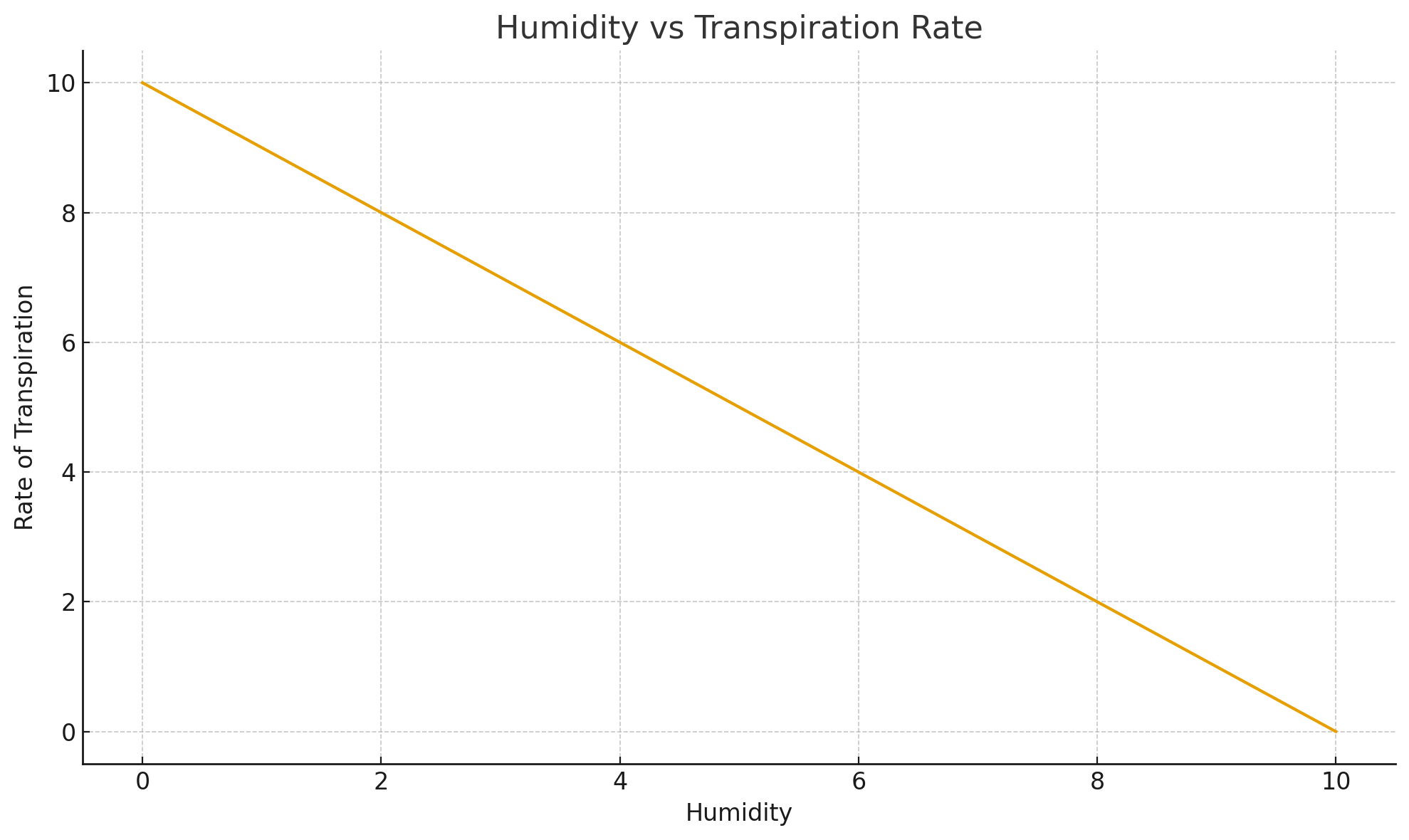
How does humidity effect transpiration?
High humidity → decreases transpiration because the air already has a lot of water vapour, so diffusion is slower.
Low humidity → increases transpiration because dry air pulls water vapour out of the leaf quickly.
How does wind velocity effect transpiration?
High wind → increases transpiration because wind removes moist air around the leaf, keeping the diffusion gradient steep. (difference in concentration big)
Little/no wind → decreases transpiration because moist air builds up and reduces the gradient.
How does light intensity effect transpiration?
High light → increases transpiration because stomata open wider for photosynthesis, letting more water escape.
Low light/dark → decreases transpiration because stomata close.
How does water content effect transpiration?
High soil water → increases transpiration because the plant has enough water to replace what is lost.
Low soil water → decreases transpiration because guard cells lose turgor, become flaccid, and stomata close.
Why is transpiration important?
> Draws water up to the leaves for photosynthesis
> Supplies plant cells with water to keep them turgid
> Evaporation of water from the surface cools the plants
How did plants adapt to conserve water?
> Deep roots that extend to great depth
> Extensive shallow roots that cover wide area
> Thick, waxy, cuticles over the stems and leaves
> Thick leaves and/or stems to store water
Concentration is normally ______ in root tissue than in soil
higher
where is the energy for active transport made?
mitochondria in the cells of the root hair
Why do the roots take up mineral ions against their concentration gradients in the reverse direction to normal diffusion?
so cells can build up stores of substances that’d otherwise be spread out by diffusion.
What happens to mineral ions when they are in the root cells
they are dissolved H2O for transportation tot eh rest of the plant through the xylem
In what form does the phloem transport food materials?
as sugars
are phloem cells dead or living ?
living
what is the structure of sieve cells?
cylindrical and joined at their end walls to form strands of tissue called sieve tubes
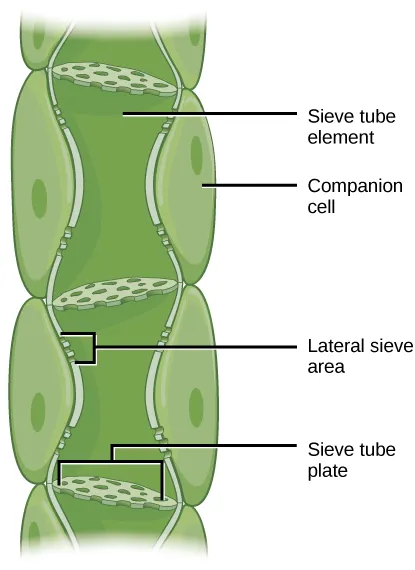
Mature sieve cells are alive. They contain _________ but no _______
cytoplasm, nucleus
what is a sieve plate?
the end wall of each sieve cell (it’s pierced with holes)
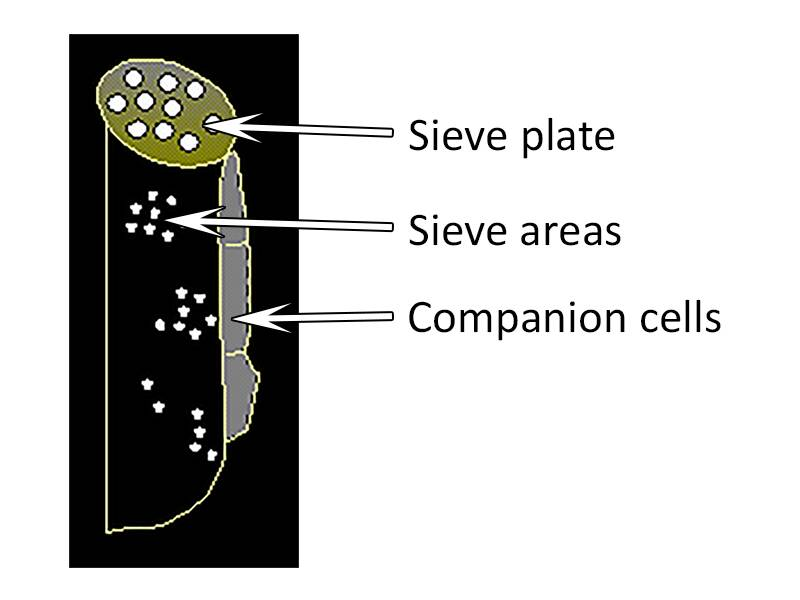
There is a _________ cell next to each sieve plate.
companion
what is translocation?
the process that moves sugars from where they are made (usually leaves “source”) to where they are needed for growth or storage ("sinks")
the translocation of _____ depends on the ___________ in sugar _____________ in different parts of the plant
sugar, differences, concentration
Sugar is converted to what and stored in the roots?
starch